In the somatosensory system, chemical, mechanical and thermal stimuli to the head are sensed by different trigeminal sensory neuron subtypes that have varied morphologies and distinct axonal connections to second-order neurons.(Pan et al., 2012).
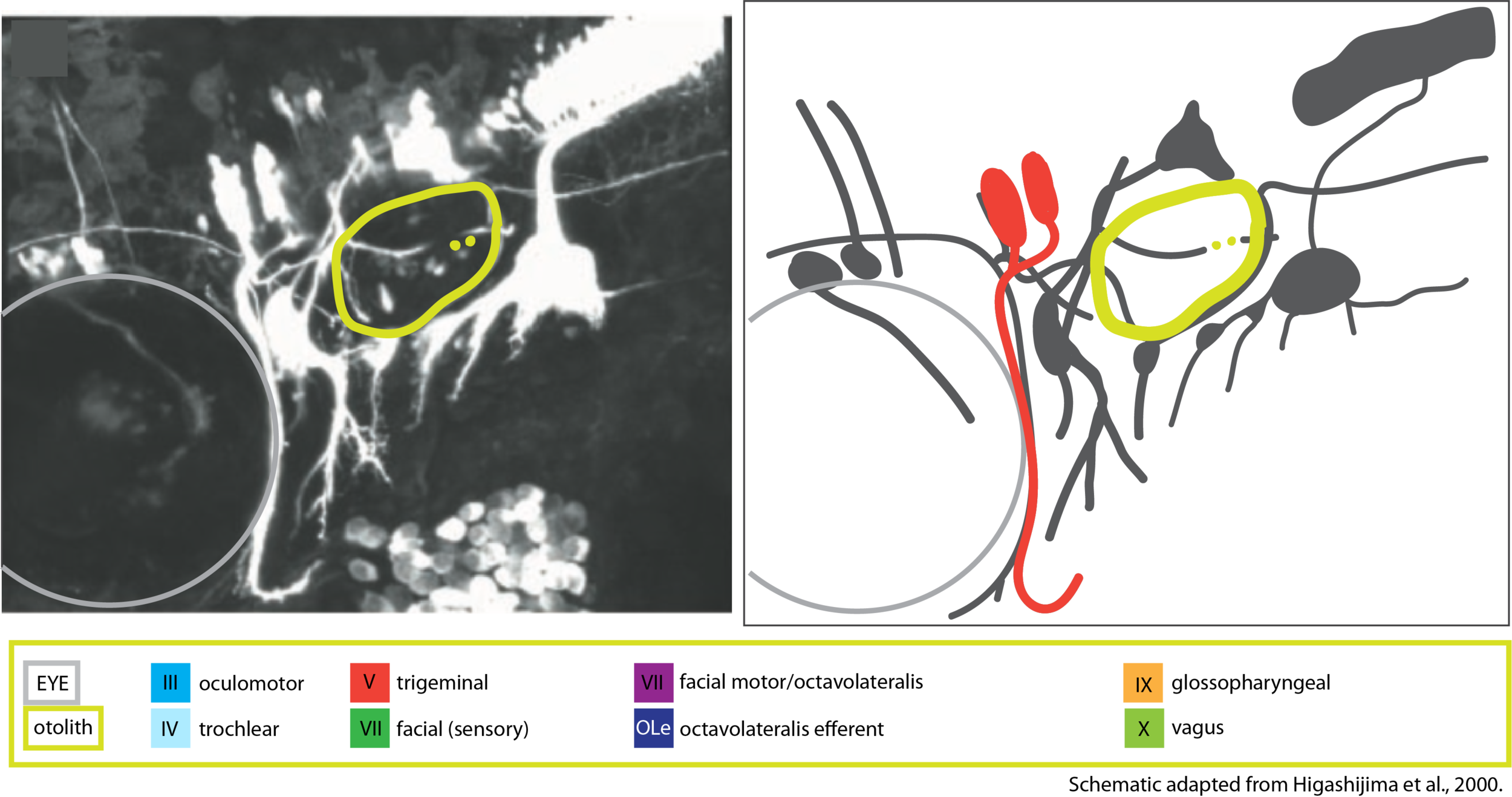
Motor efferents of the trigeminal nerve innervate the follwing muscles of the mandibular arch: Intermandibularis anterior, Intermandibularis posterior, abductor mandibulae, levator arcus palatini, dilator operculi (Higashima et al., 2000).
Both the dorsal and ventral divisions of the trigeminal motor nucleus are positive for choline acetyltransferase (ChAT) the acetylcholine synthesising enzyme indicating that this nucleus forms part of the cholinergic system in zebrafish (Mueller et al., 2004).
Key Publications
Shin-ichi Higashijima, Yoshiki Hotta, and Hitoshi Okamoto
Visualization of Cranial Motor Neurons in Live Transgenic Zebrafish Expressing Green Fluorescent Protein Under the Control of the Islet-1 Promoter/Enhancer.
The Journal of Neuroscience, January 1, 2000, 20(1):206–218
Pan YA, Choy M, Prober DA, Schier AF
Robo2 determines subtype-specific axonal projections of trigeminal sensory neurons.
Development. 2012 Feb;139(3):591-600. doi: 10.1242/dev.076588. Epub 2011 Dec 21.
Koide T, Yabuki Y, Yoshihara Y.
Terminal Nerve GnRH3 Neurons Mediate Slow Avoidance of Carbon Dioxide in Larval Zebrafish.
Cell Rep. 2018 Jan 30;22(5):1115-1123. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.01.019.
Jane A. Cox, Angela LaMora, Stephen L. Johnson, Mark M. Voigt
Diverse mechanisms for assembly of branchiomeric nerves.
Developmental Biology 357 (2011) 305–317
Thomas Mueller, Philippe Vernier, Mario F. Wullimann
The adult central nervous cholinergic system of a neurogenetic model animal, the zebrafish Danio rerio
Brain Research 1011 (2004) 156–169