Description
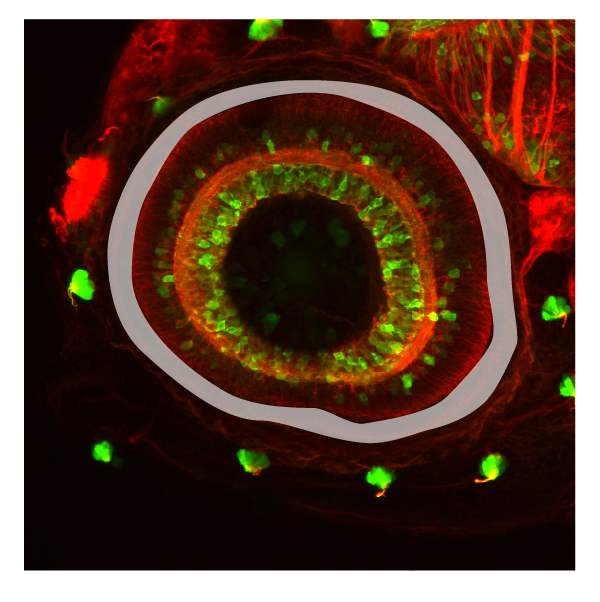
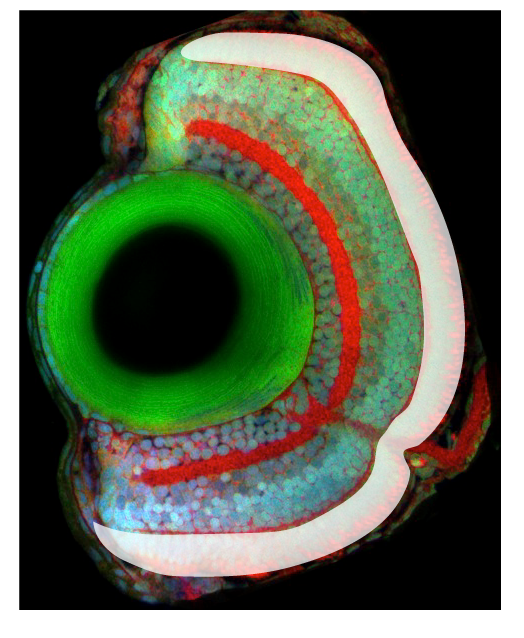
Layer of the neural retina that contains the photoreceptor cells. Photoreceptor cells span the outer nuclear layer as well as the outer and inner segment layers. These light sensing cells of the retina, the cone and rod photoreceptors, are located in the apical-most layer of the retina, and display a stereotypical subcellular organization with their nuclei basal to the inner segment (cell body or soma) and outer segment, which abuts the retinal pigmented epithelium (RPE) and is full of membrane invaginations packed with light-sensitive cell-specific opsins. All photoreceptors have opsin-containing outersegments, which are replaced on a daily basis. The older membrane and protein debris is shed from the distal tip of the outersegment and phagocytosed by the adjacent RPE cells. Because zebrafish are diurnal, their retinae contains a large number of bright-light sensitive cone subtypes in addition to dim-light sensitive rod photoreceptors, all of which are organized into regular mosaic patterns that can best be visualized in tangential sections. Below is more detailed information about the distinct types of photoreceptors found in zebrafish.
retinal cell types found in the outer nuclear layer
Ontology
is part of: neural retina
has parts: photoreceptor cell
Transgenic Lines/Antibodies that label this brain region
Key Publications