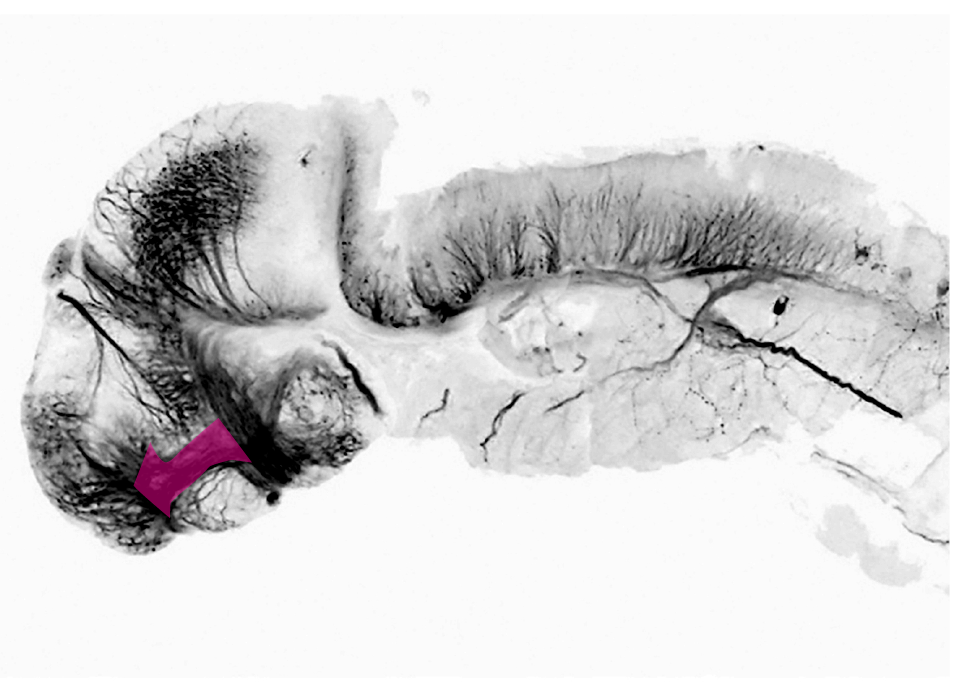
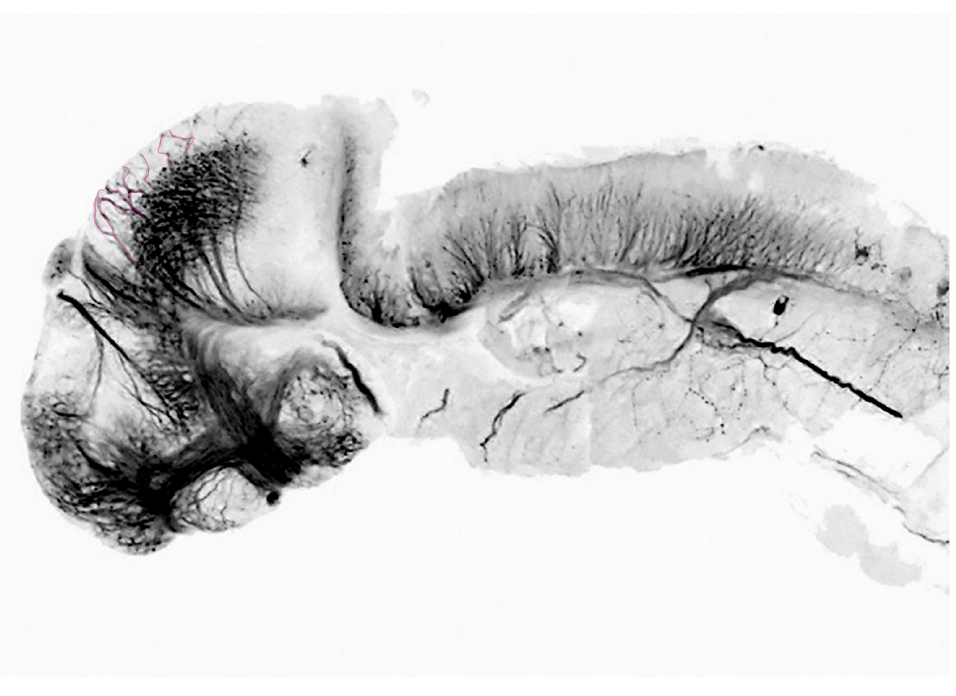
A visual guide to some of the main tracts and commissures in the larval zebrafish brain. Tracts and commissures have been grouped into forebrain, midbrain and hindbrain white matter.
forebrain white matter
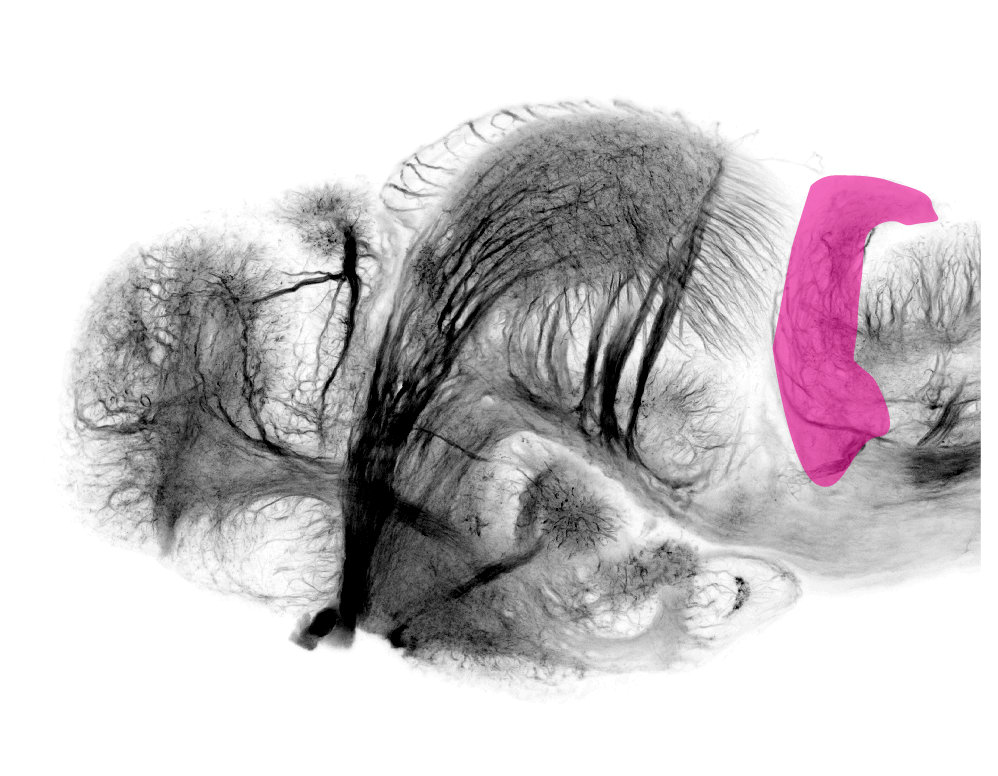
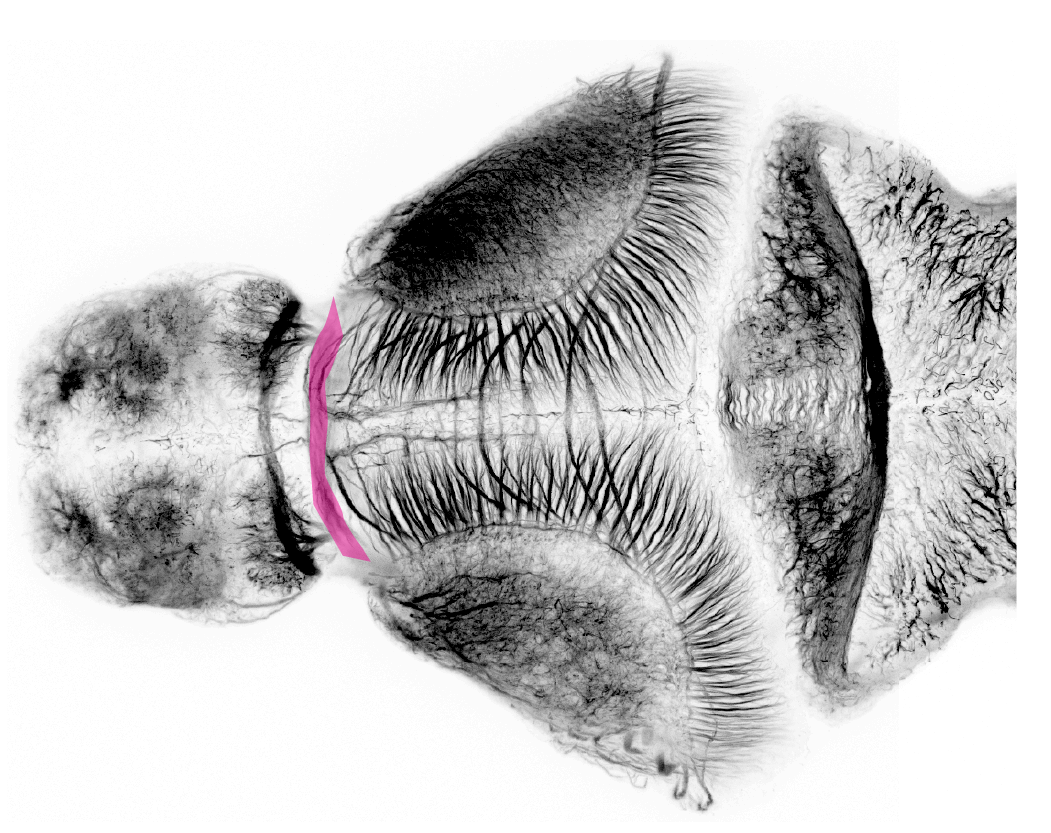
4dpf ventral view. Tract of the anterior commissure leading to anterior commissure shown as semi opaque.
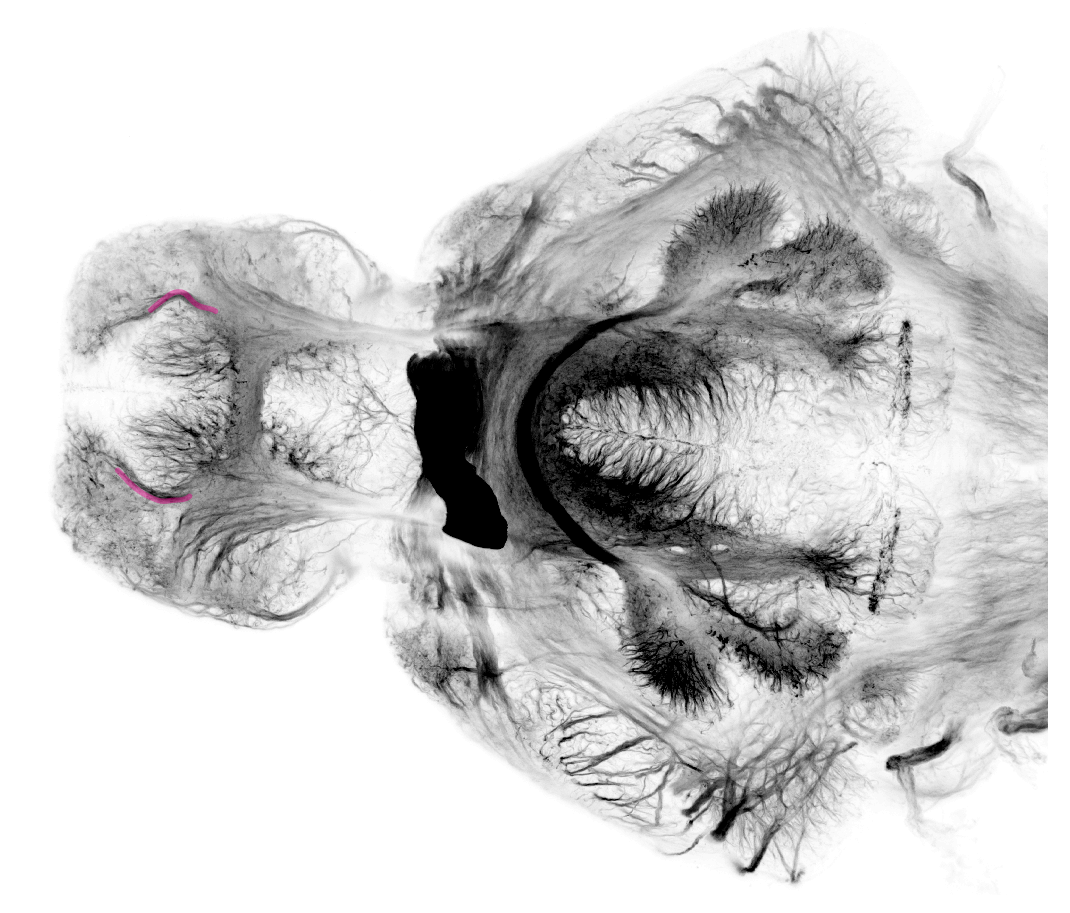
4dpf dorsal view. Posterior commissure is where the tract of the posterior commissure crosses the midline.
synonyms: caudal commissure
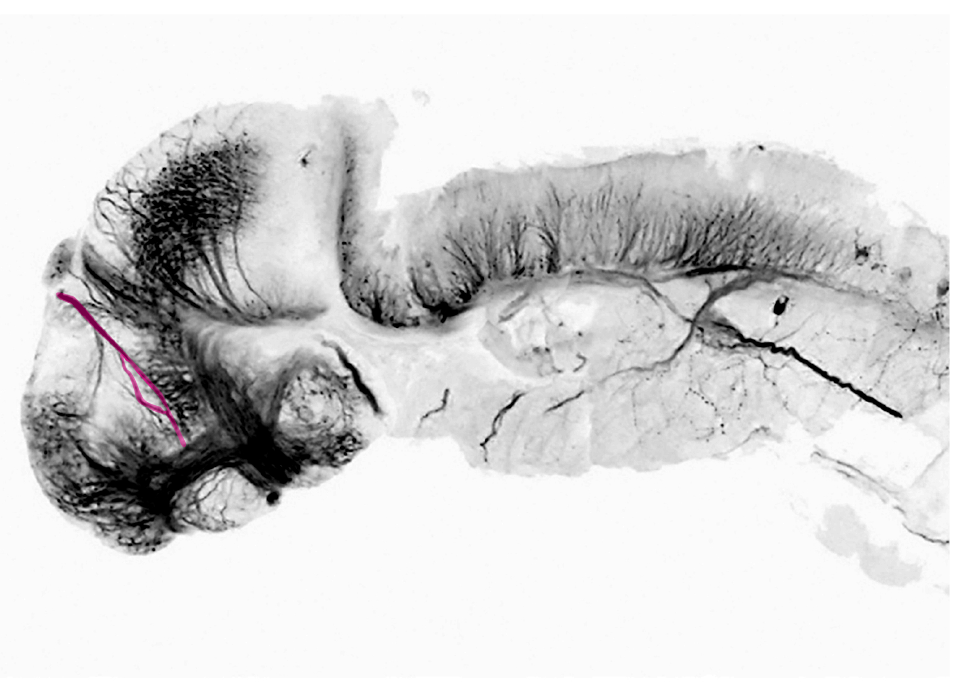
4dpf lateral view. The posterior commissure is where the tract of the posterior commissure crosses the midline.
synonyms: caudal commissure
48hpf lateral view. The posterior commissure is where the tract of the posterior commissure crosses the midline.
synonyms: caudal commissure
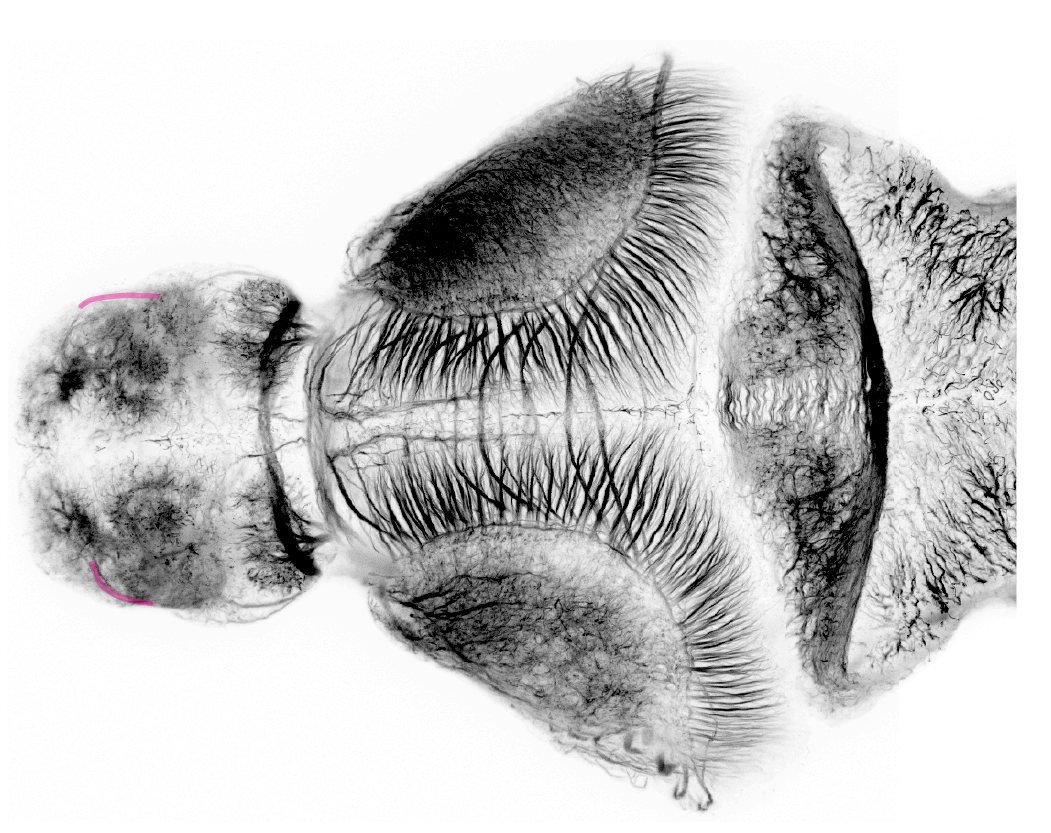
4dpf dorsal view. This tract originstas from the epiphysis and connects with the tract of the postoptic commissure in the ventral diencephalon.
48hpf lateral view. This tract originates from the epiphysis/pineal organ and connects with the tract of the postoptic commissure in the ventral diencephalon.
Transverse section of brain and eyes of a zebrafish embryo 3 days post fertilization. The retinal ganglion cell layer of the retina and the optical neurons projecting to the optic tectum, the visual processing centre of the brain, are seen in green. Nuclei are counterstained with DAPI (magenta).
Transverse section of brain and eyes of a zebrafish embryo 3 days post fertilization. The retinal ganglion cell layer of the retina and the optical neurons projecting to the optic tectum, the visual processing centre of the brain, are seen in green. Nuclei are counterstained with DAPI (magenta).
Transverse section of brain and eyes of a zebrafish embryo 3 days post fertilization. The retinal ganglion cell layer of the retina and the optical neurons projecting to the optic tectum, the visual processing centre of the brain, are seen in green. Nuclei are counterstained with DAPI (magenta).
4dpf lateral view of tg(foxd3:GFP) brain labelled with anti-GFP(FIRE) and anti-tubulin(grey).