About
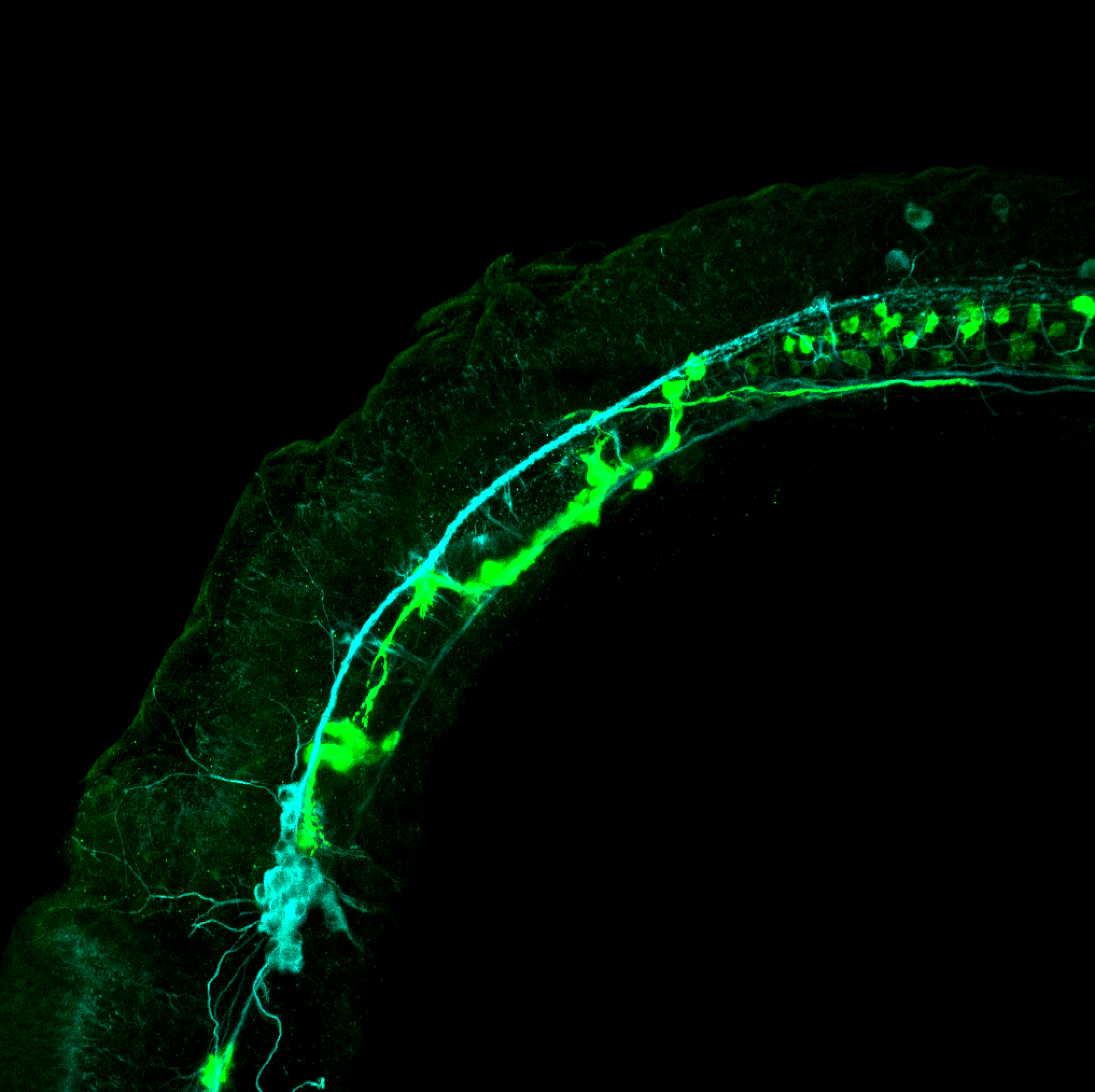
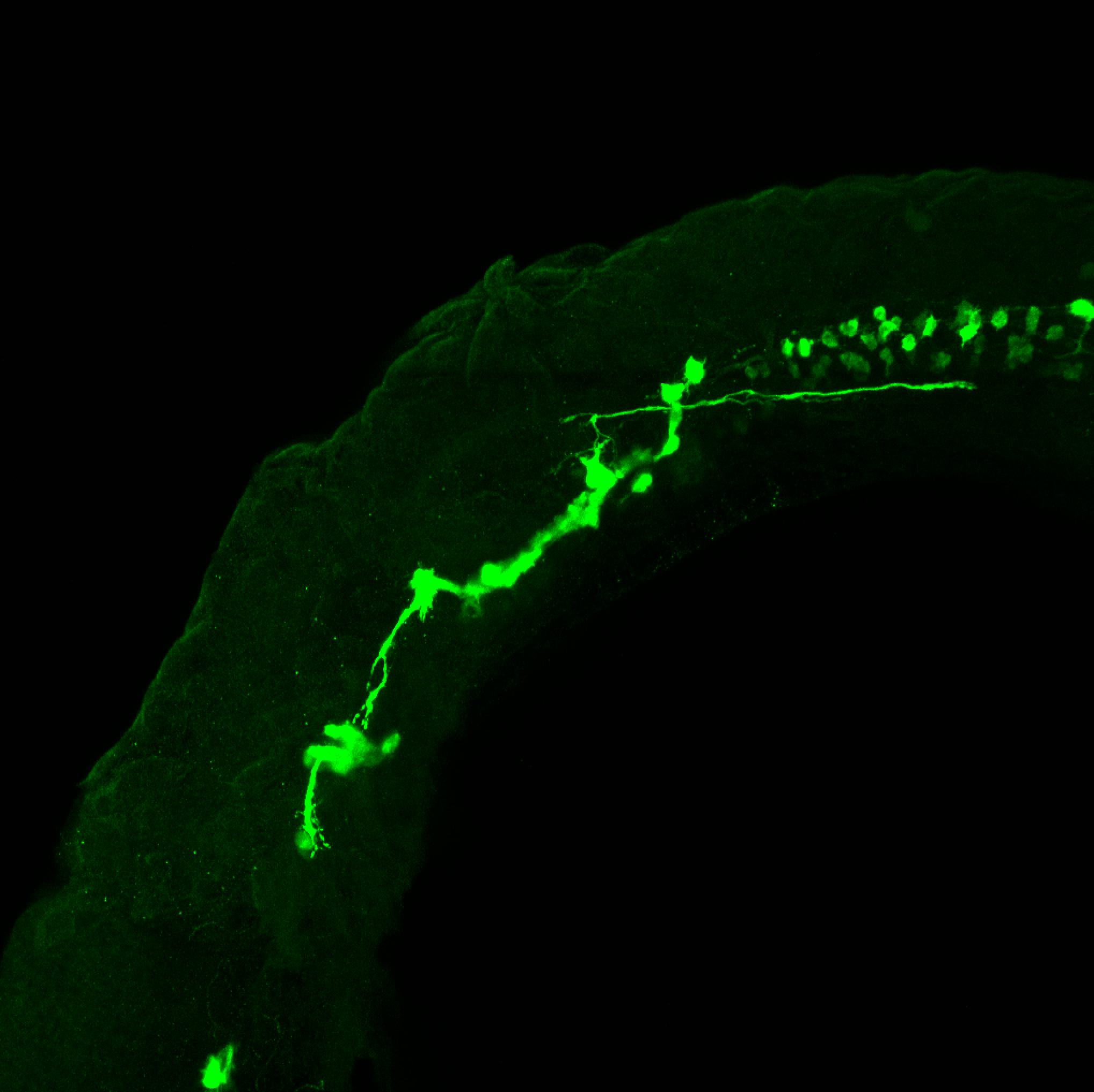
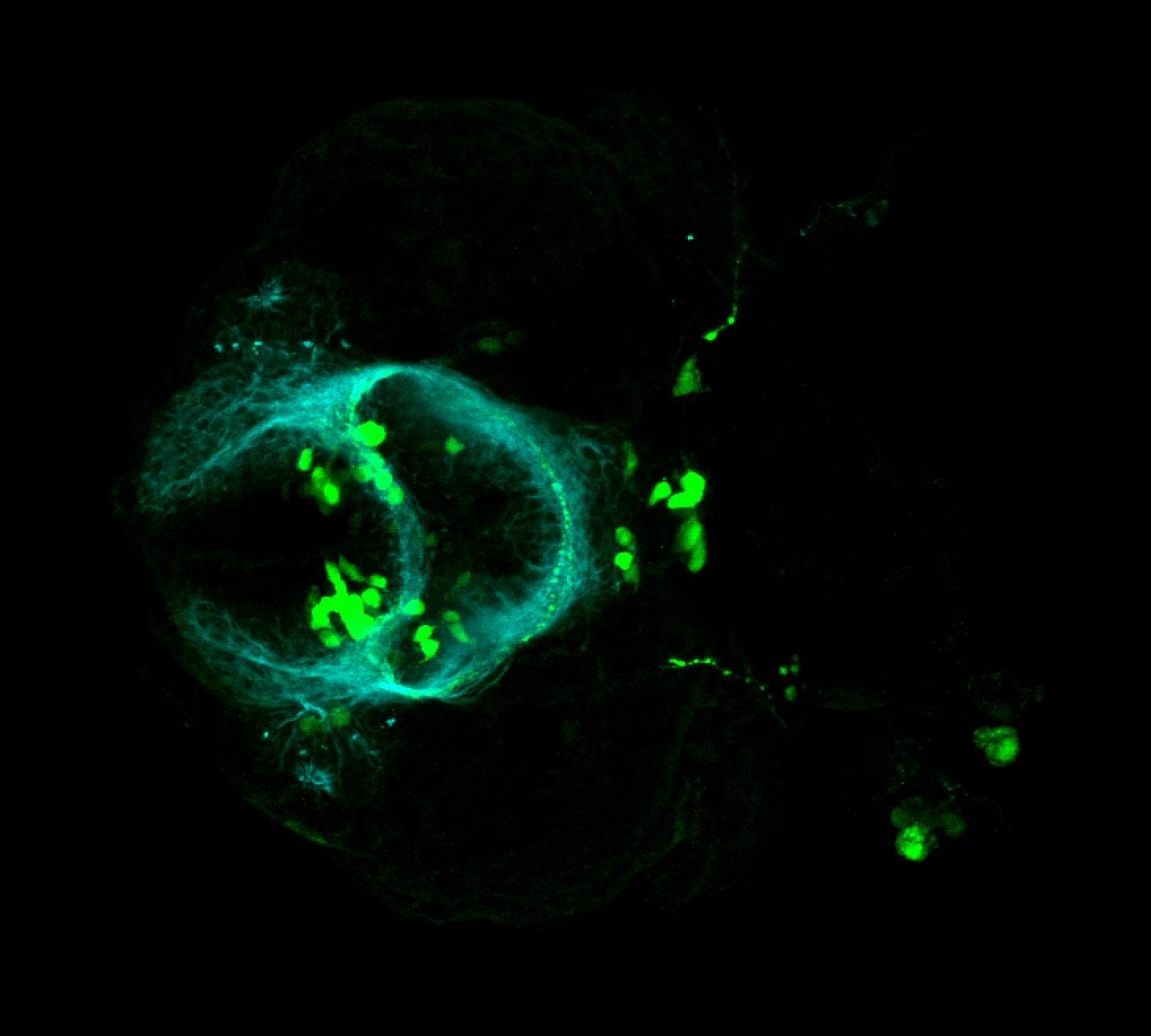
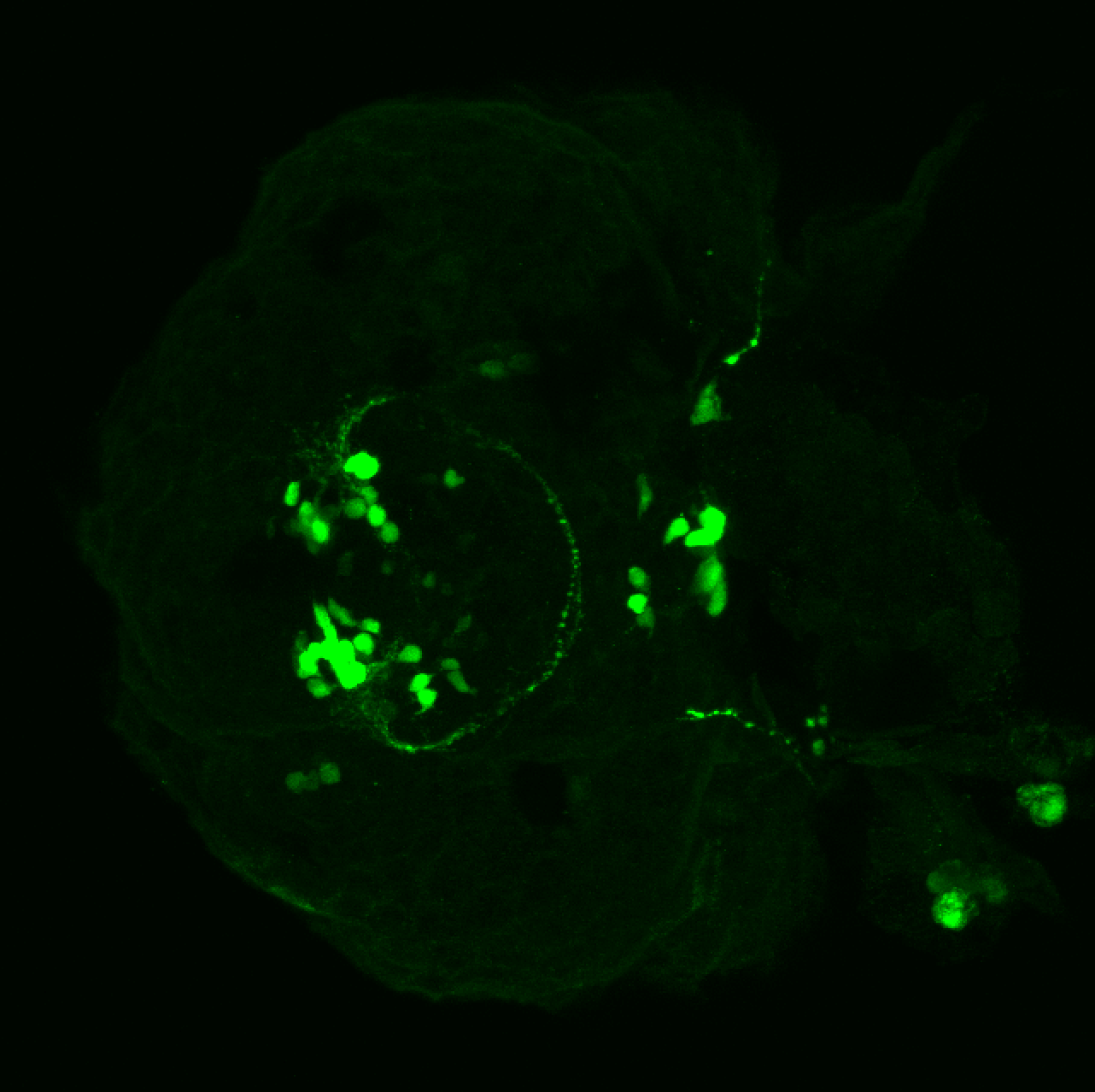
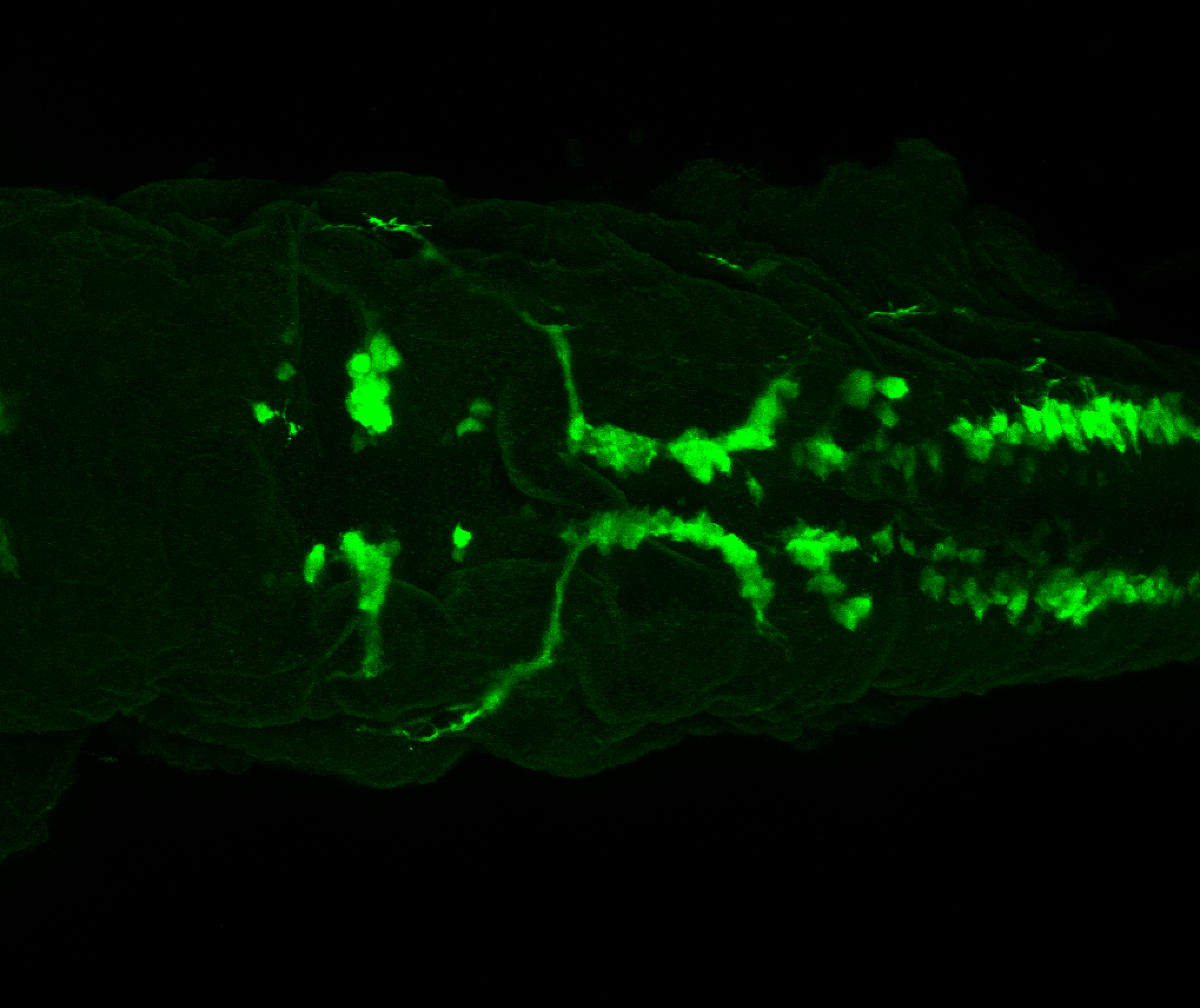
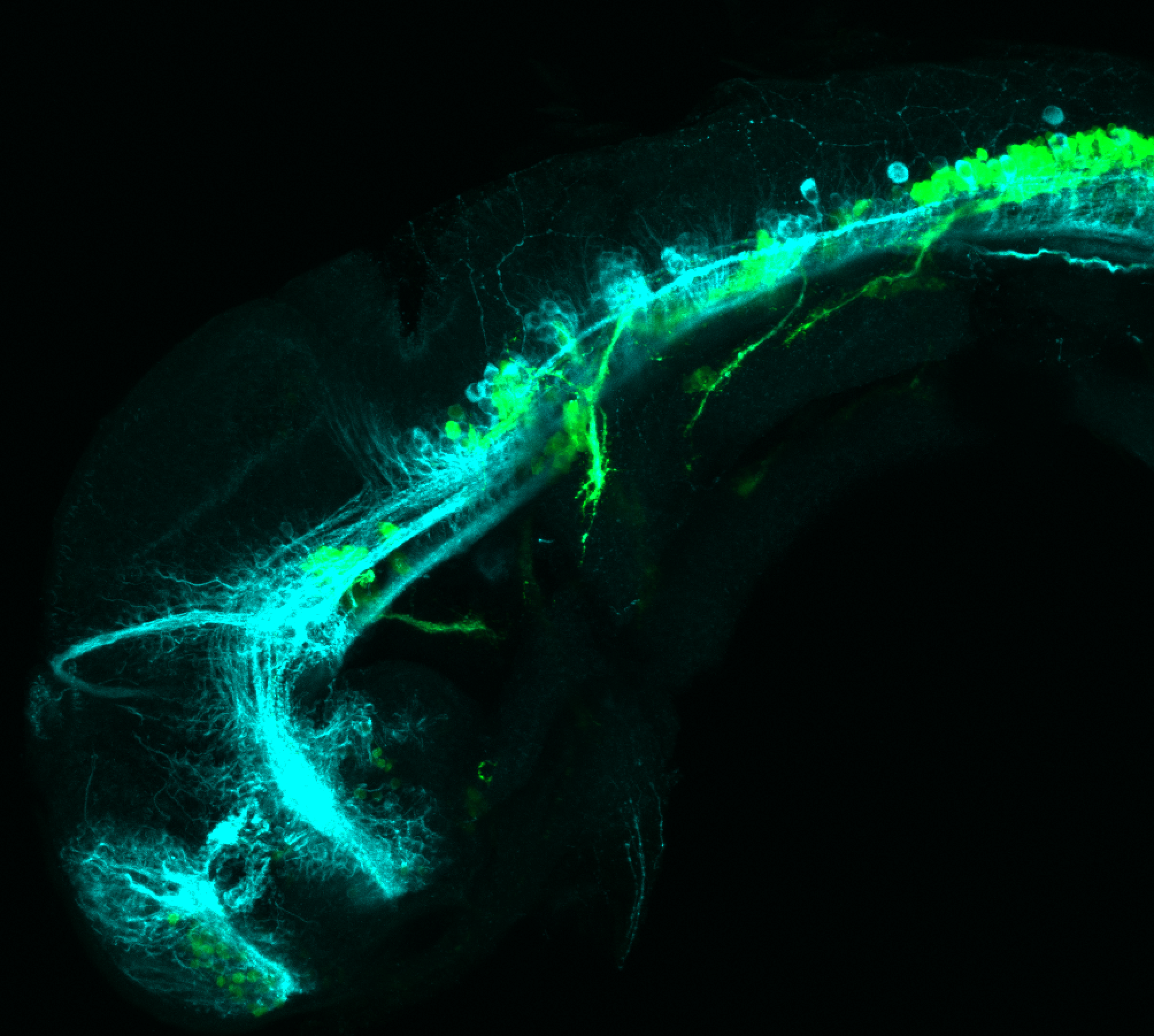
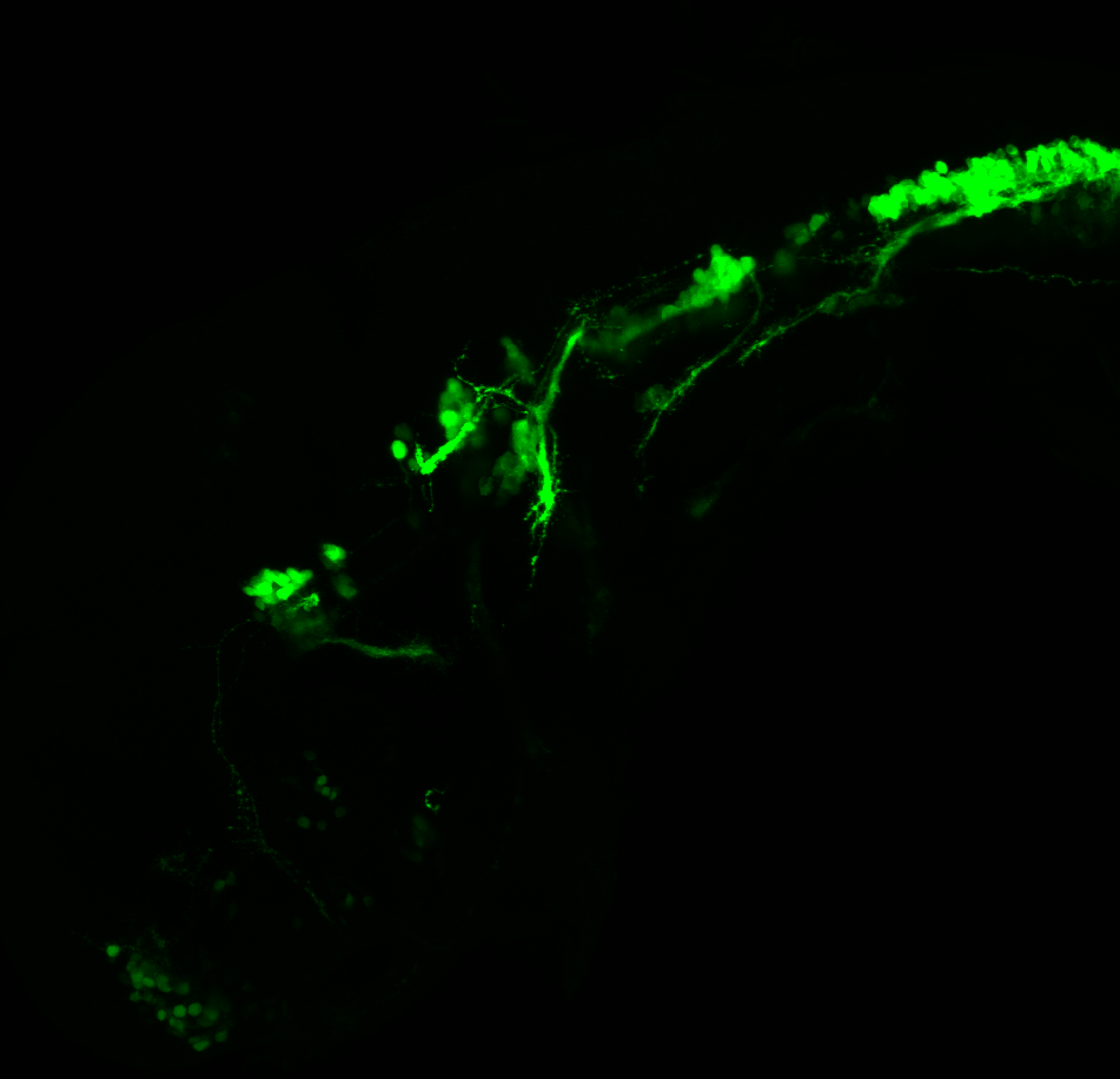
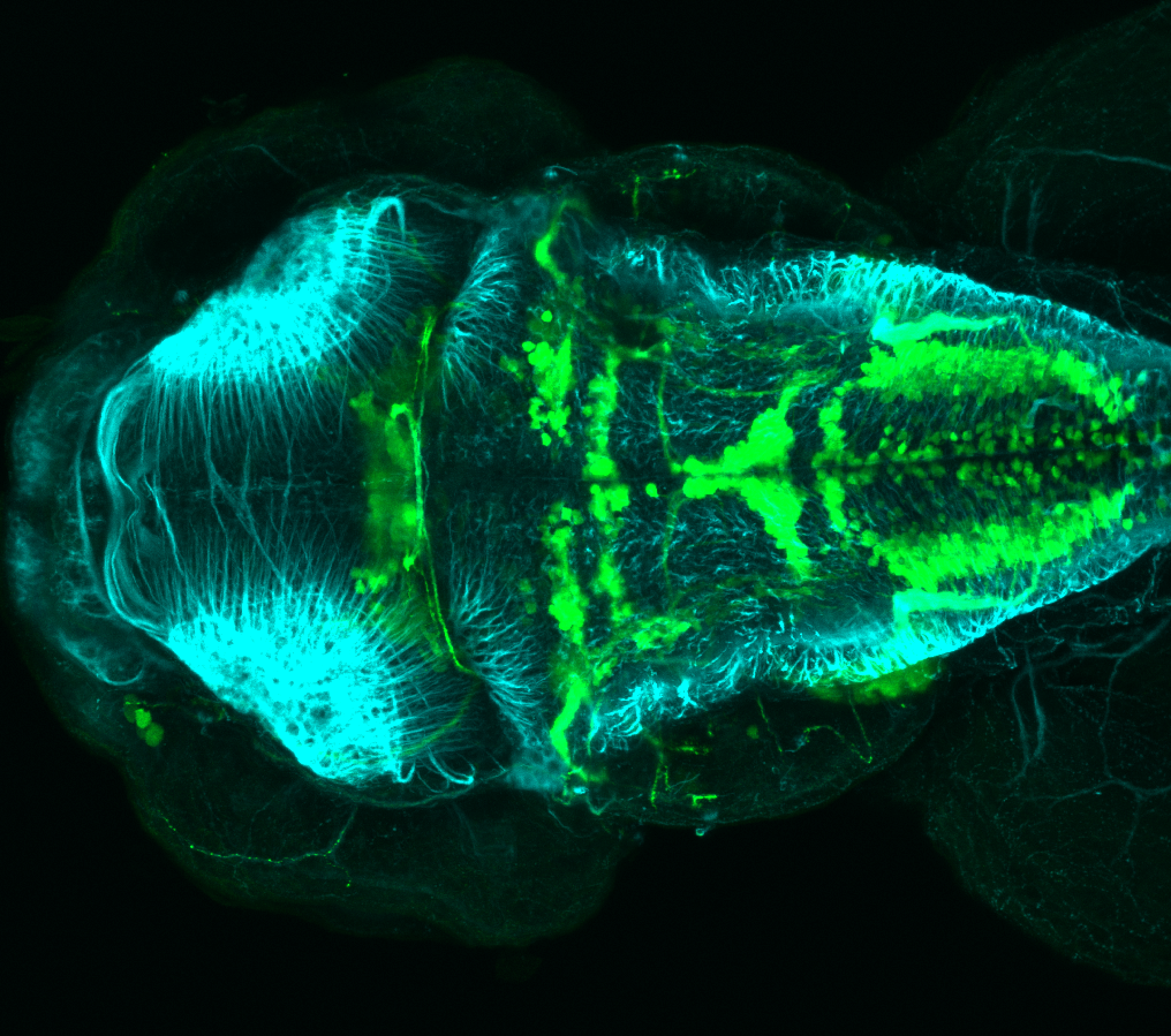
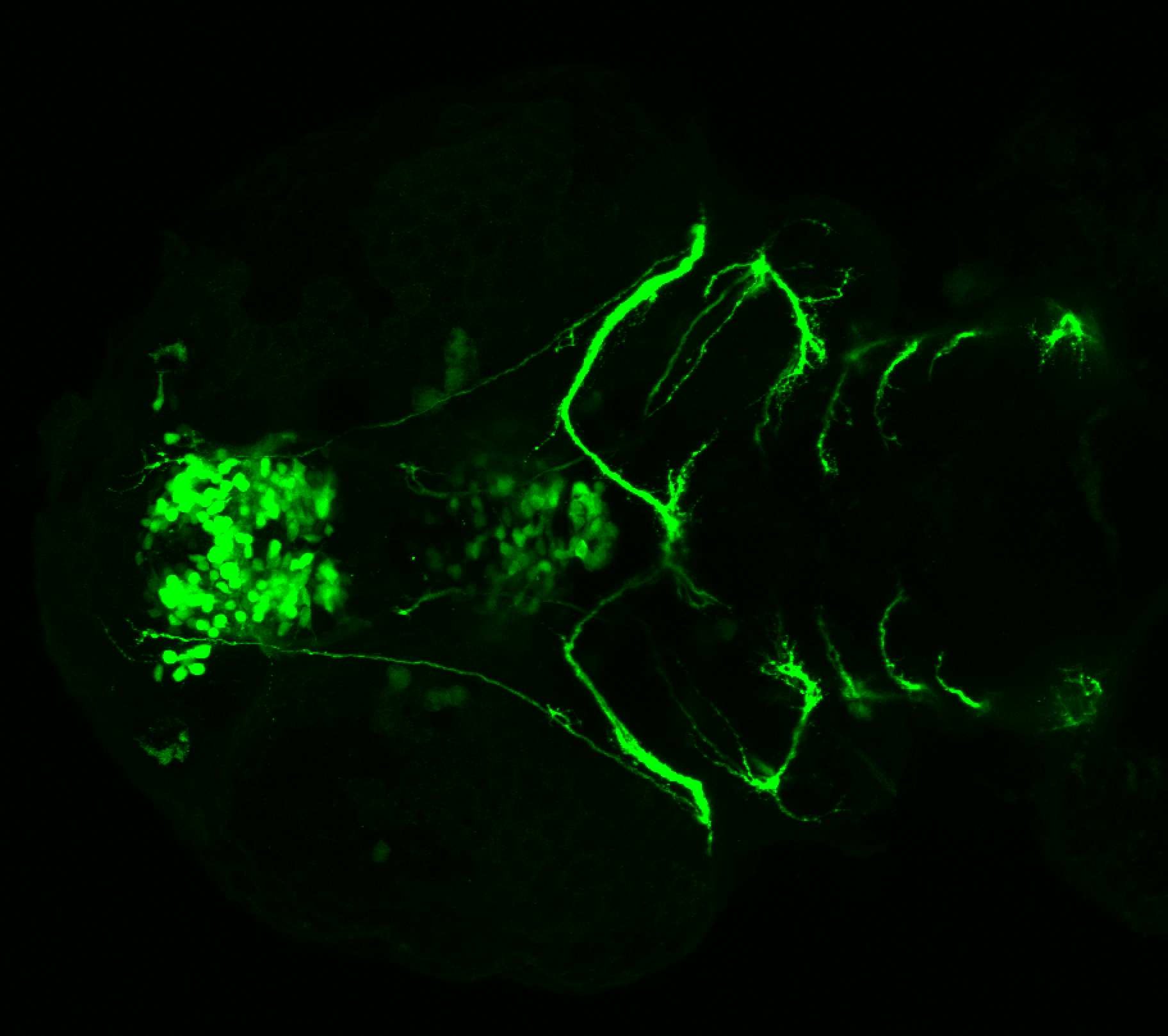
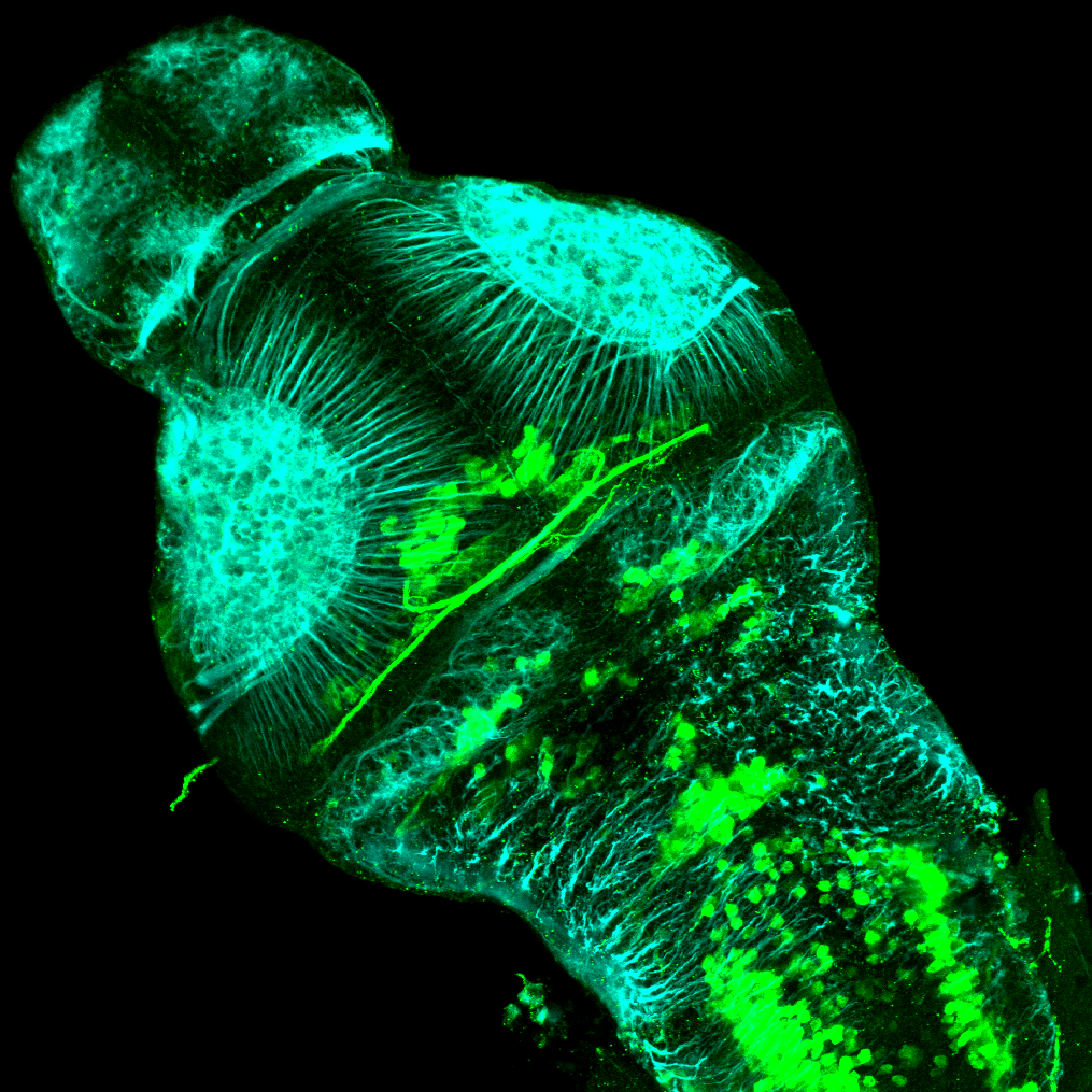
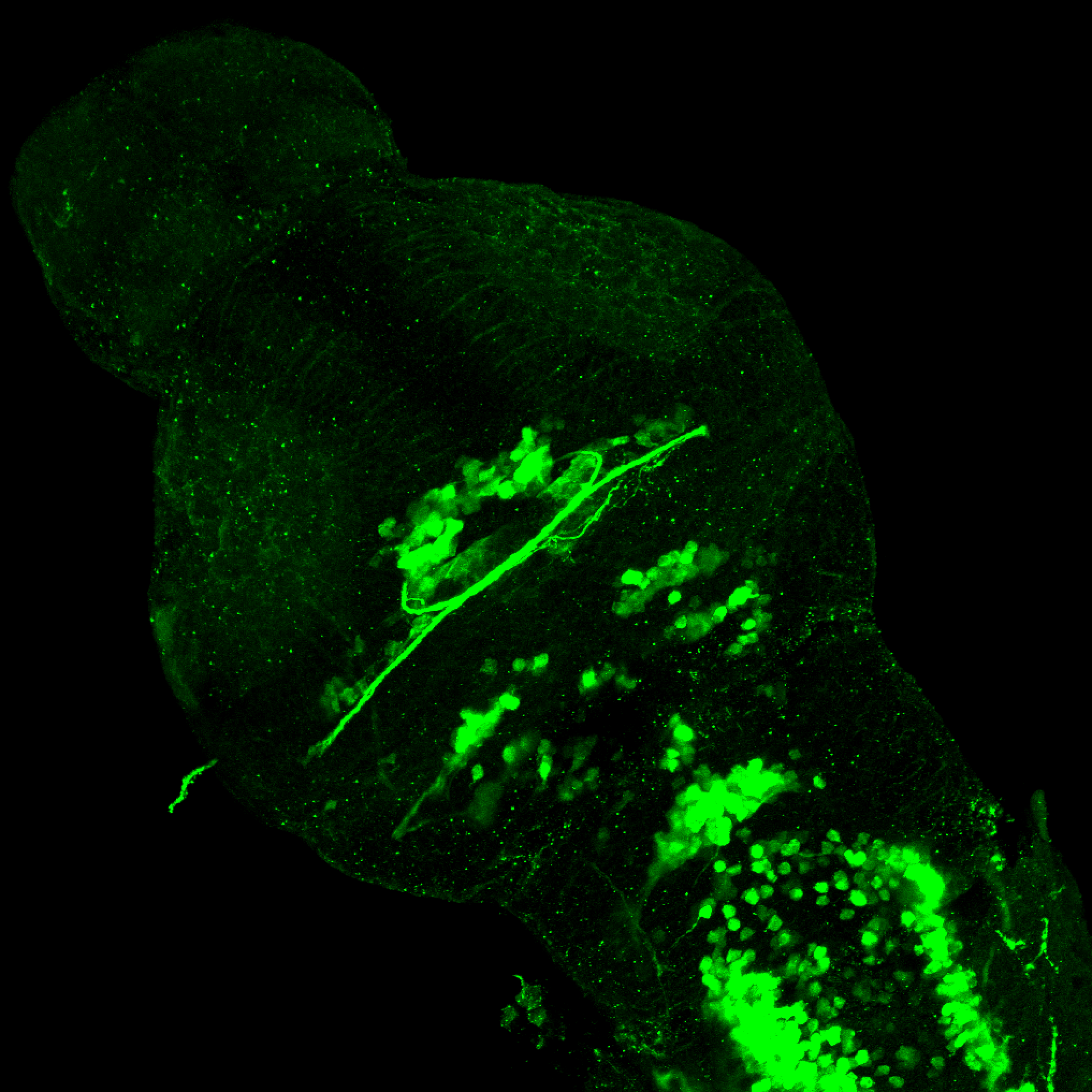
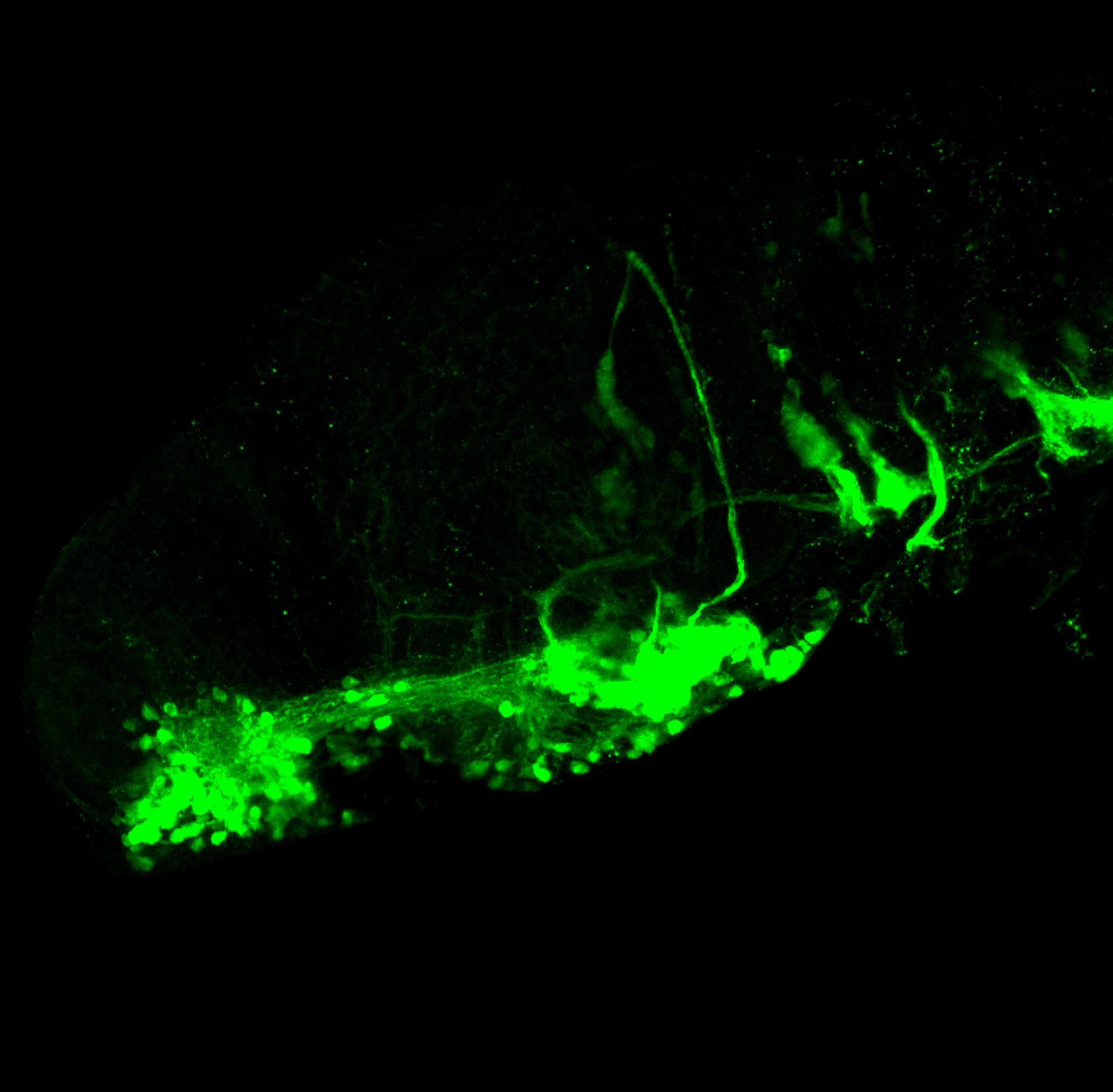
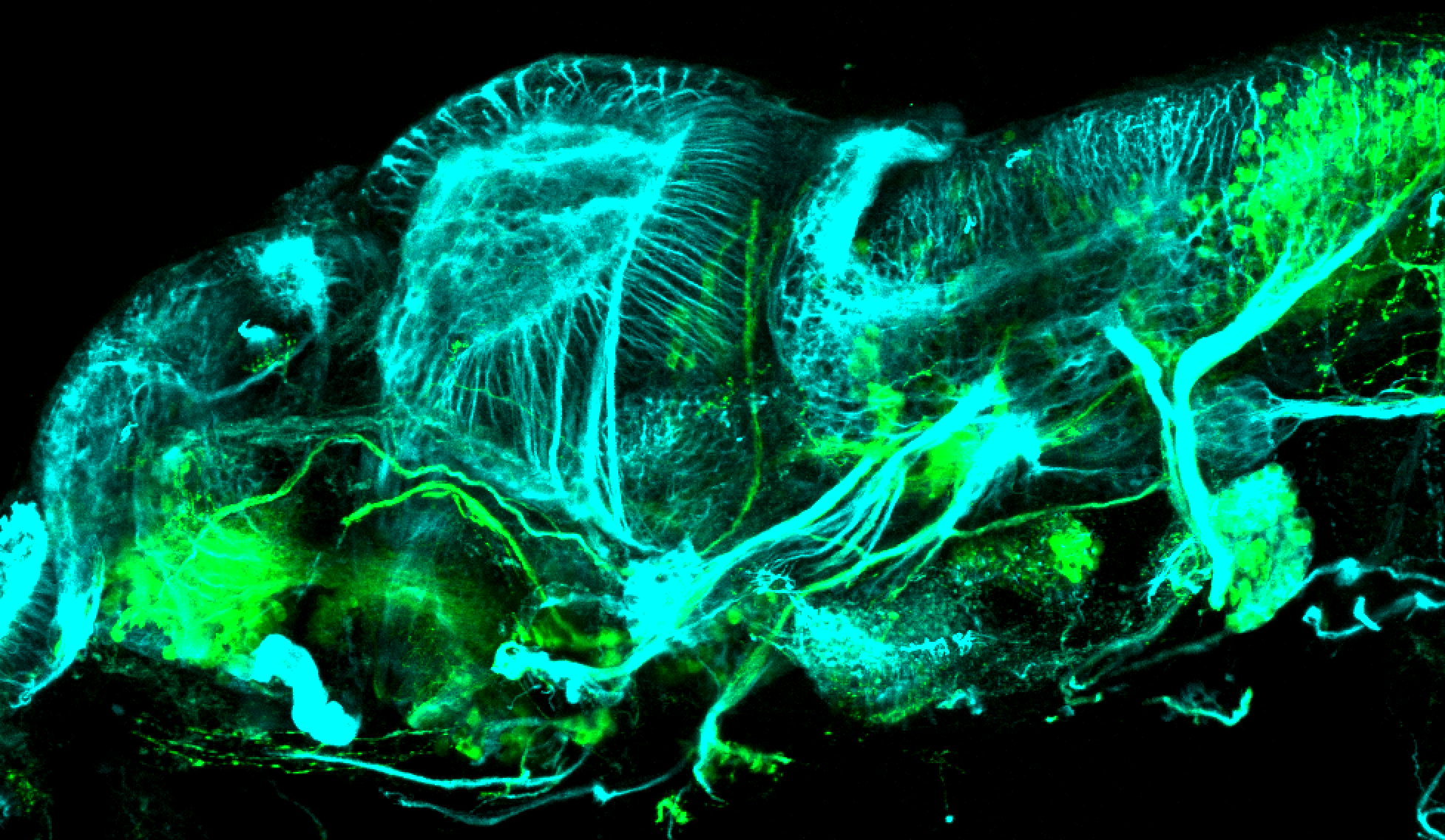
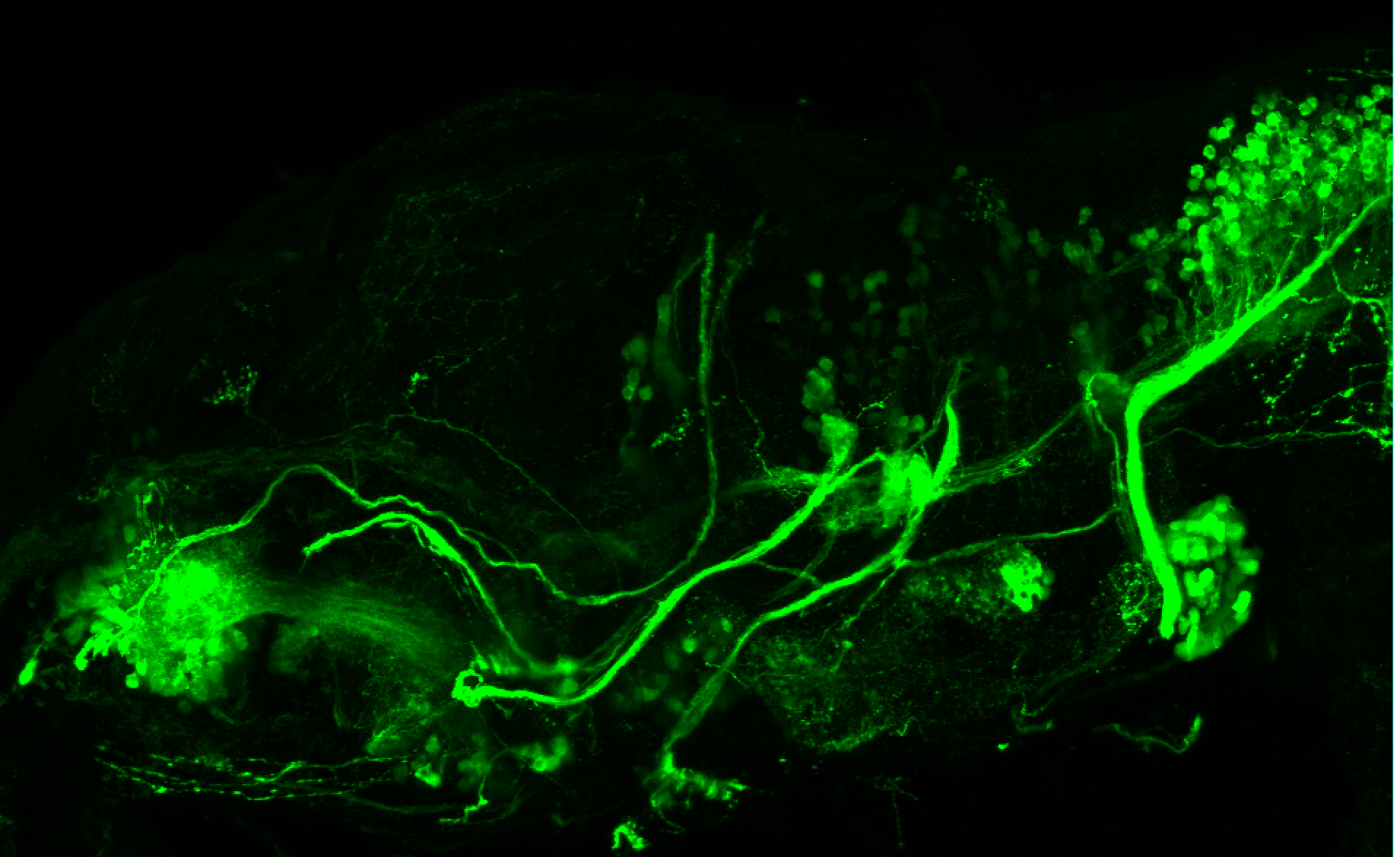
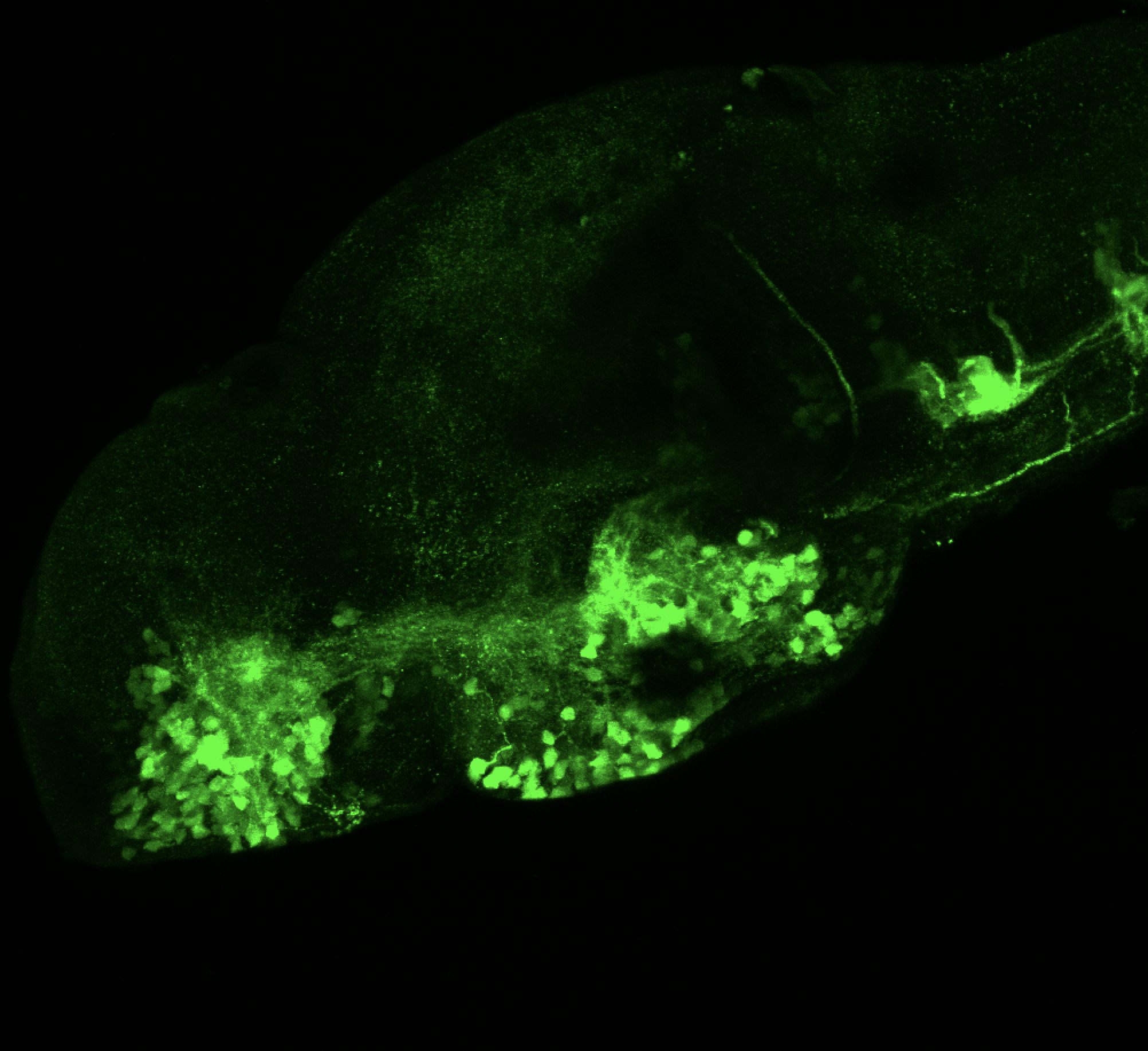
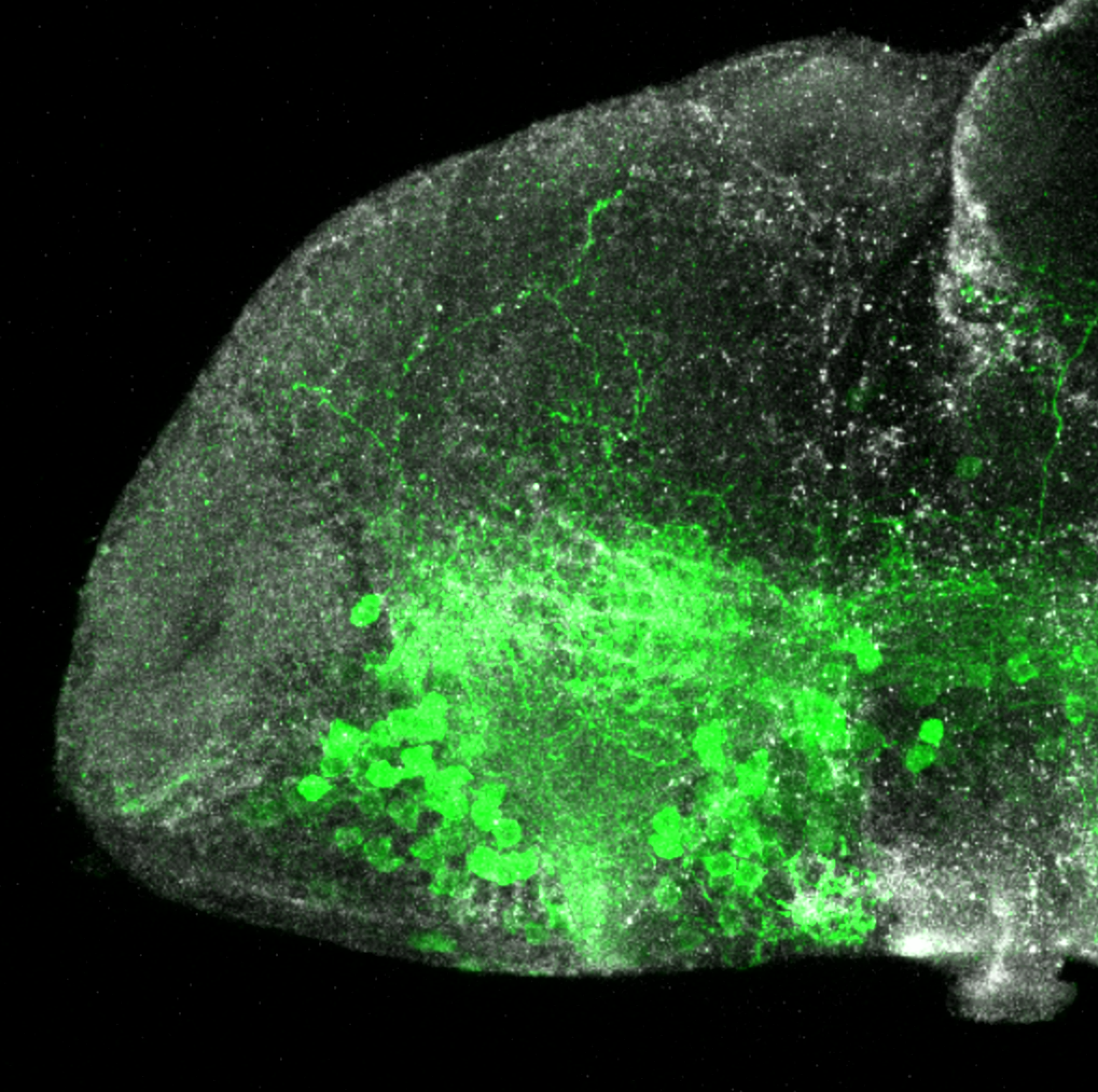
This transgenic line expresses GFP in cranial motor neurons. It was made using a construct that fuses Islet-1 promotor/enhancer sequences to GFP.
More images of this transgenic
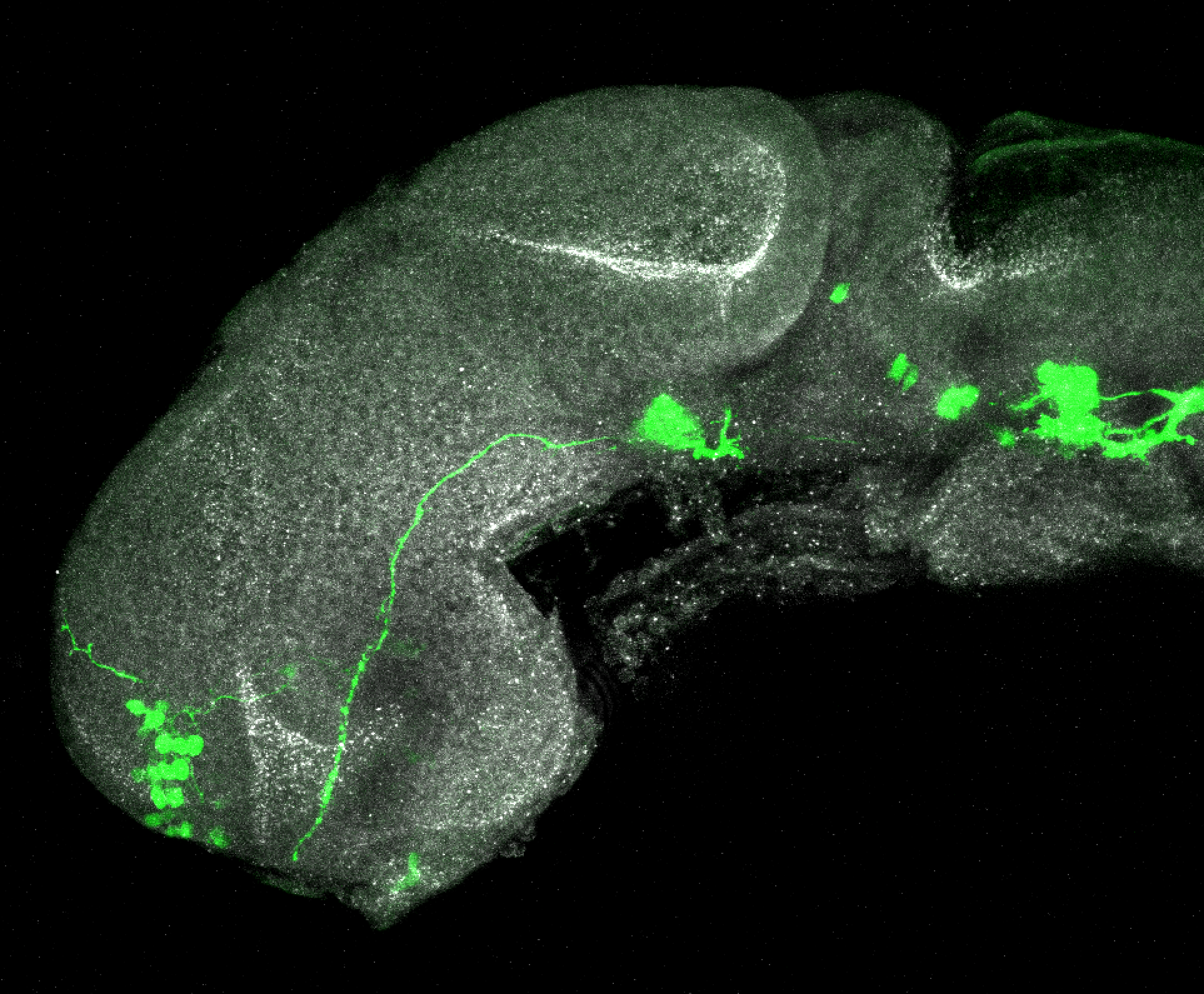
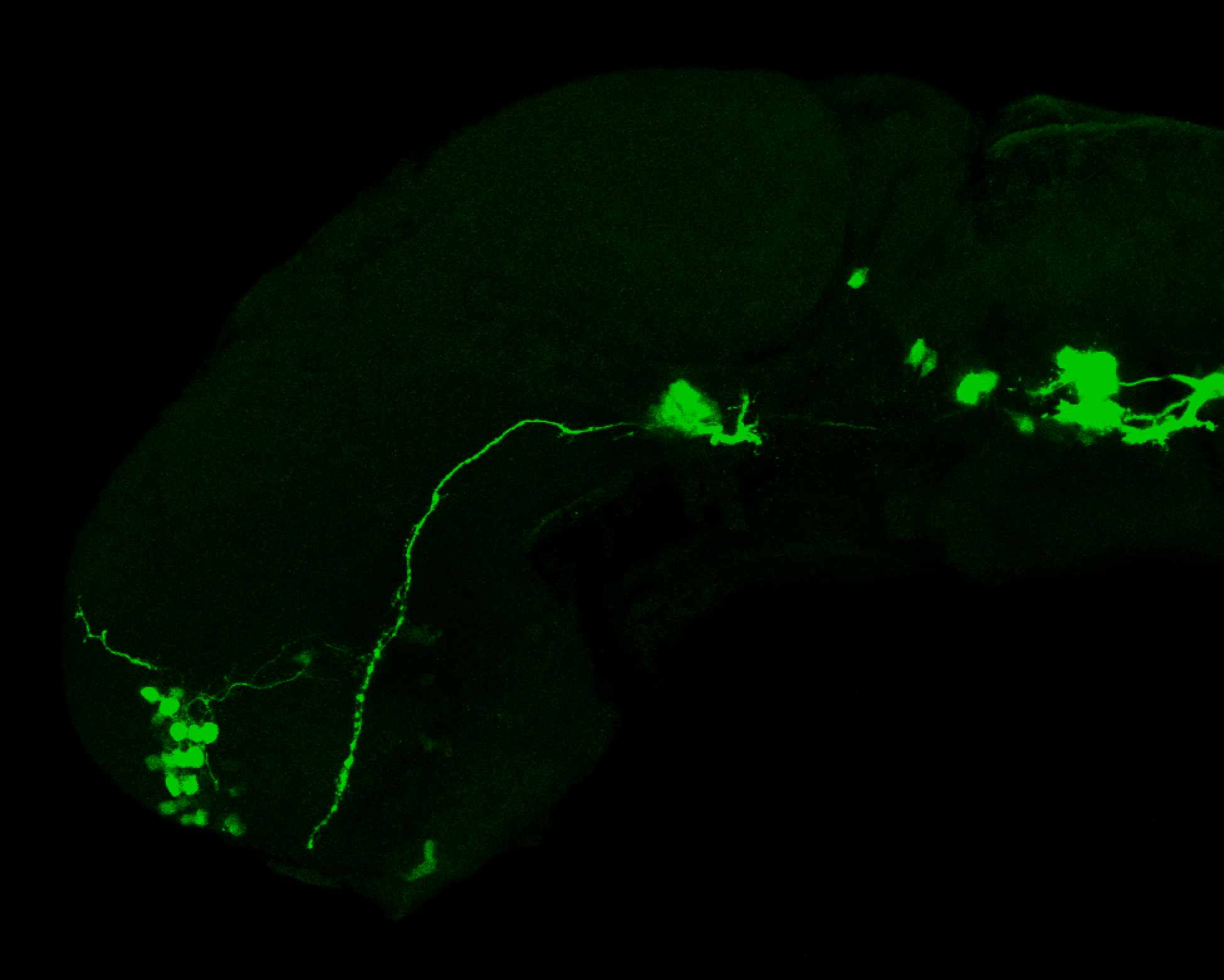
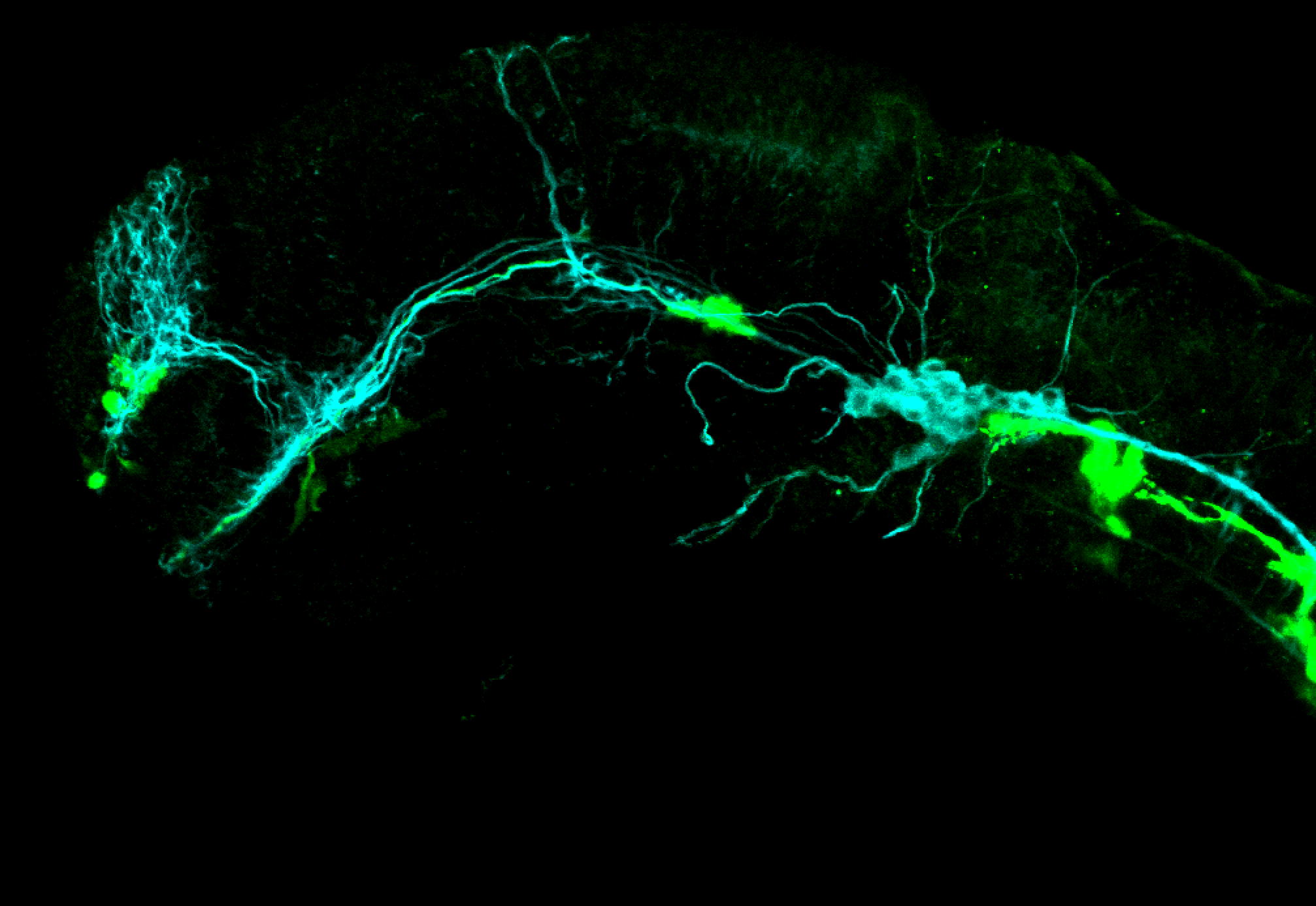
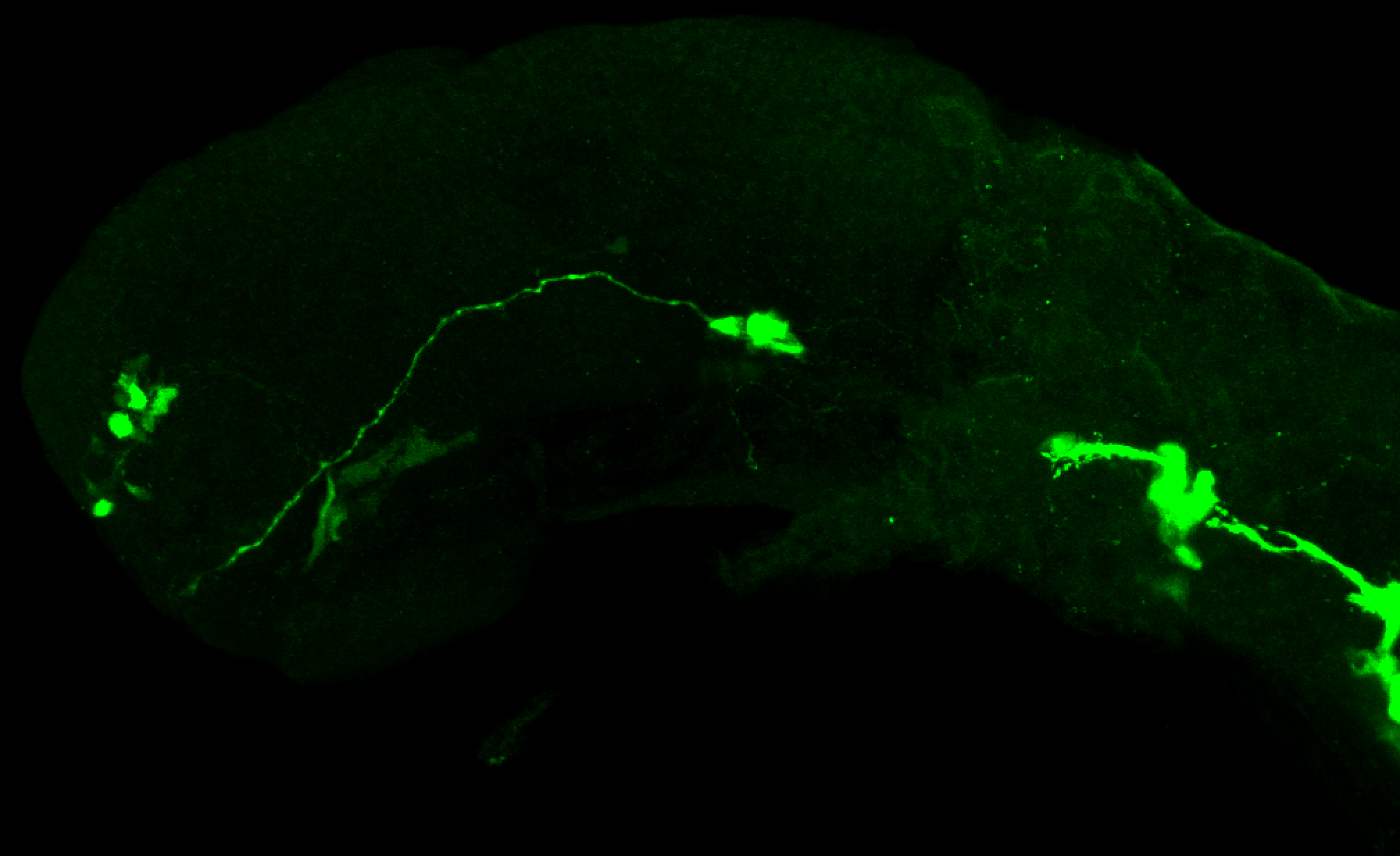
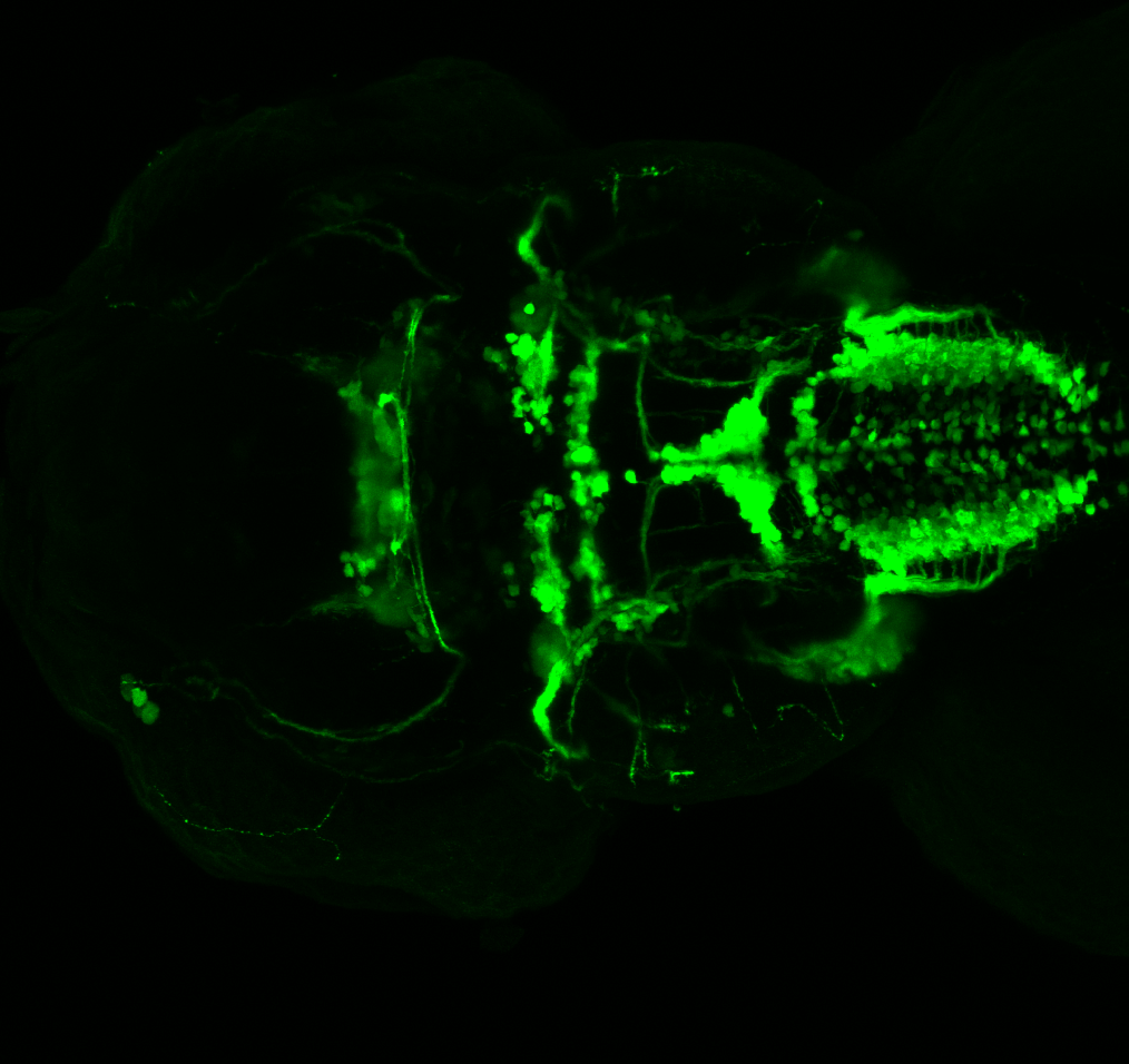
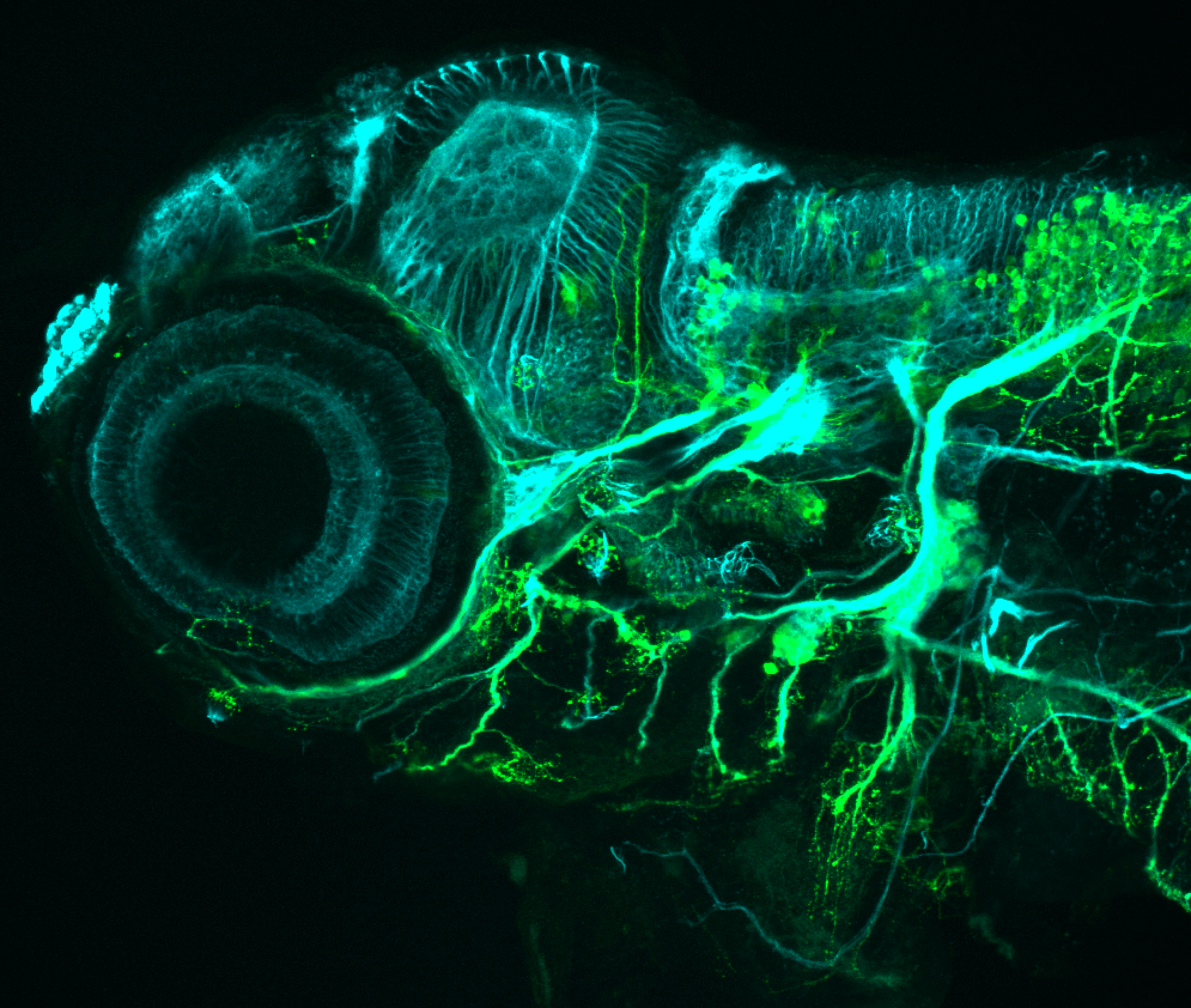
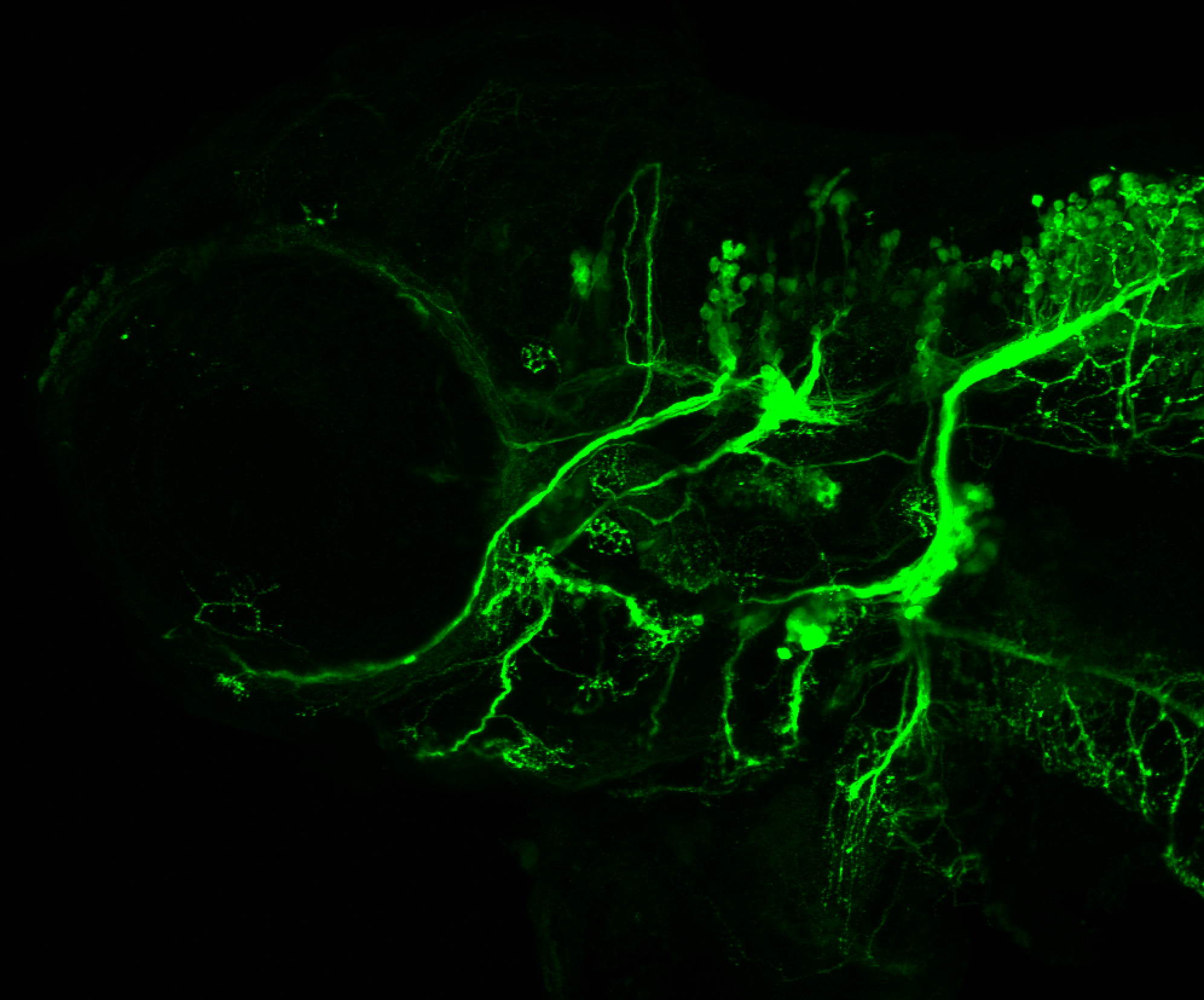
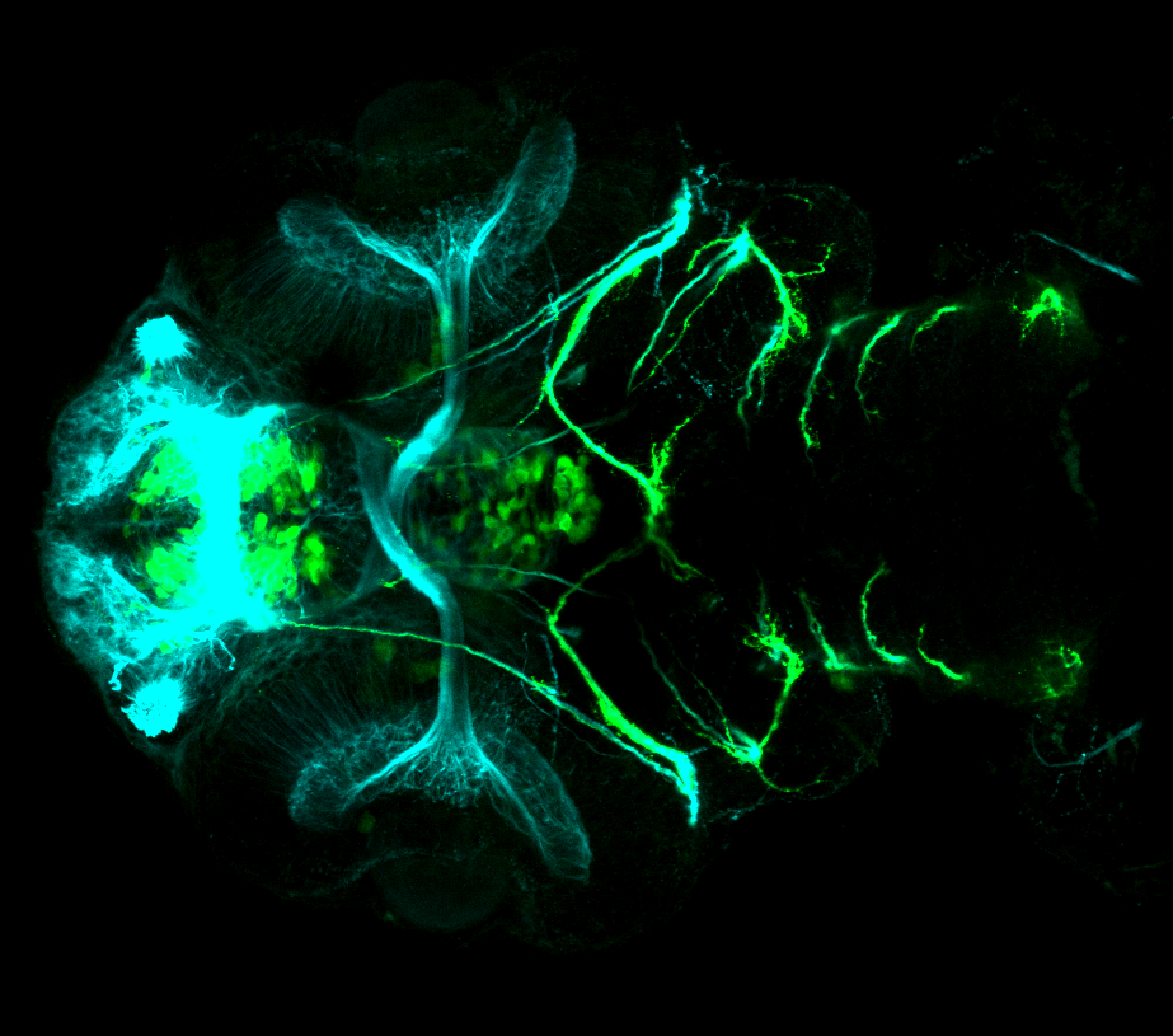
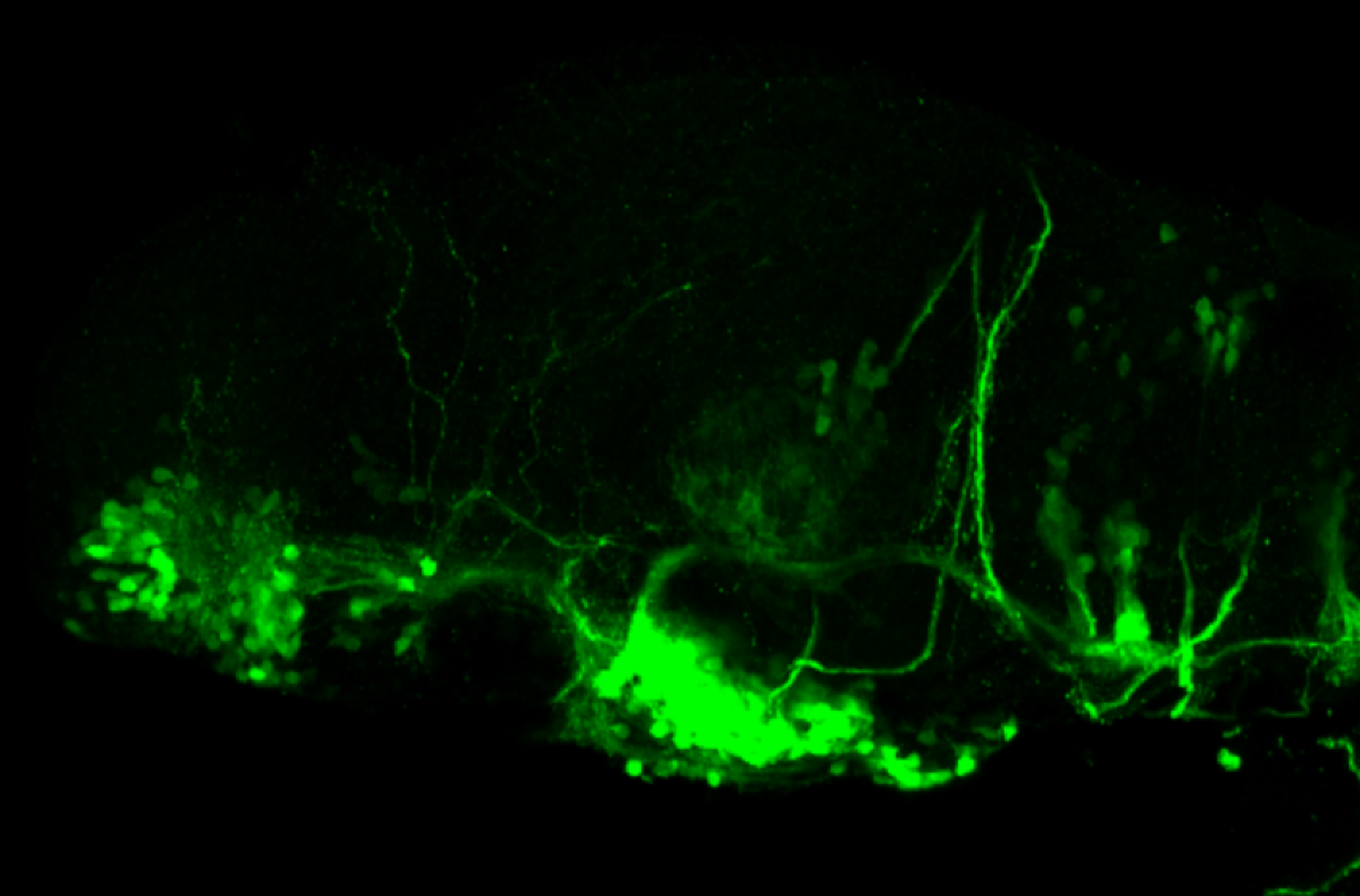
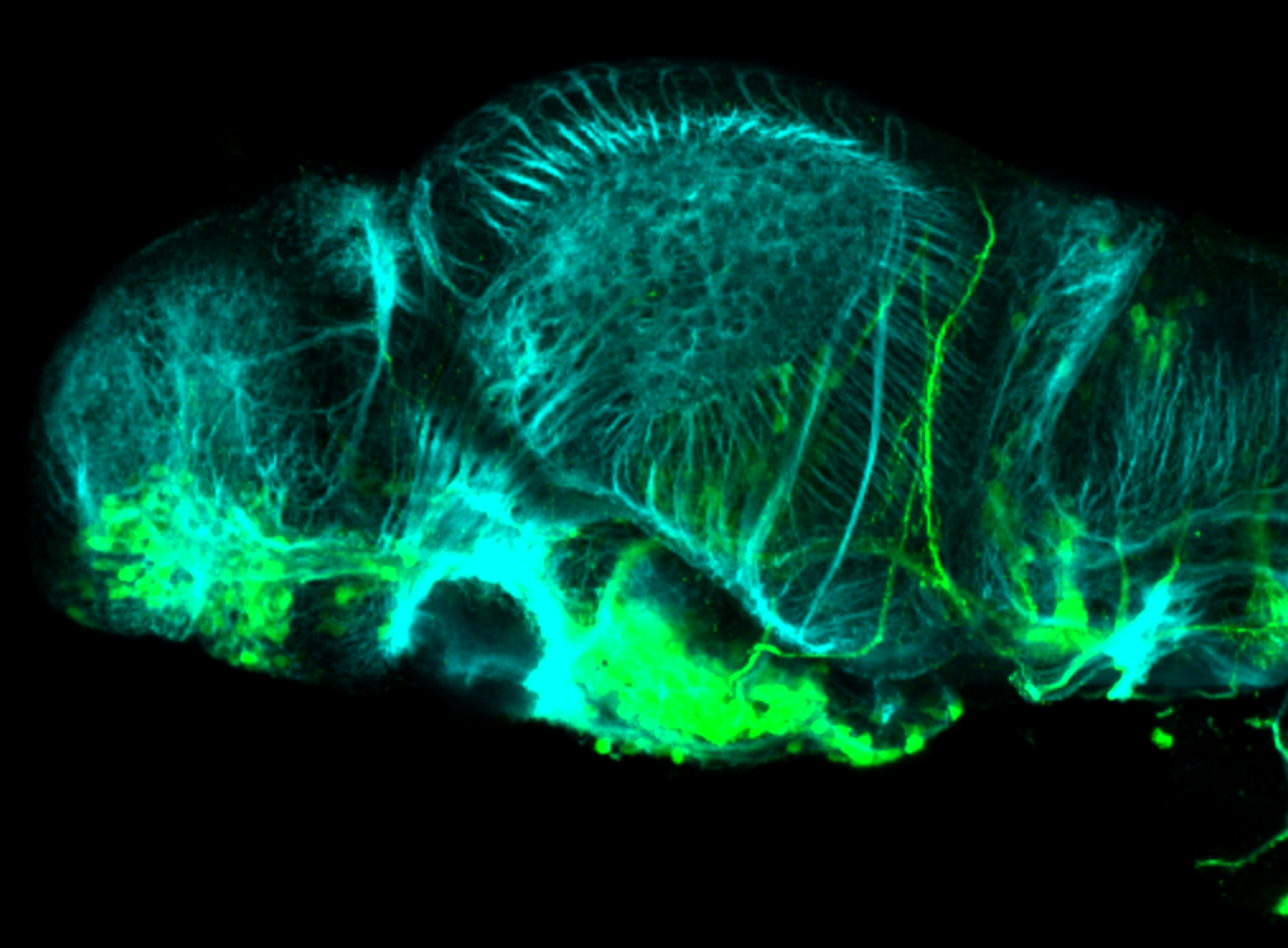
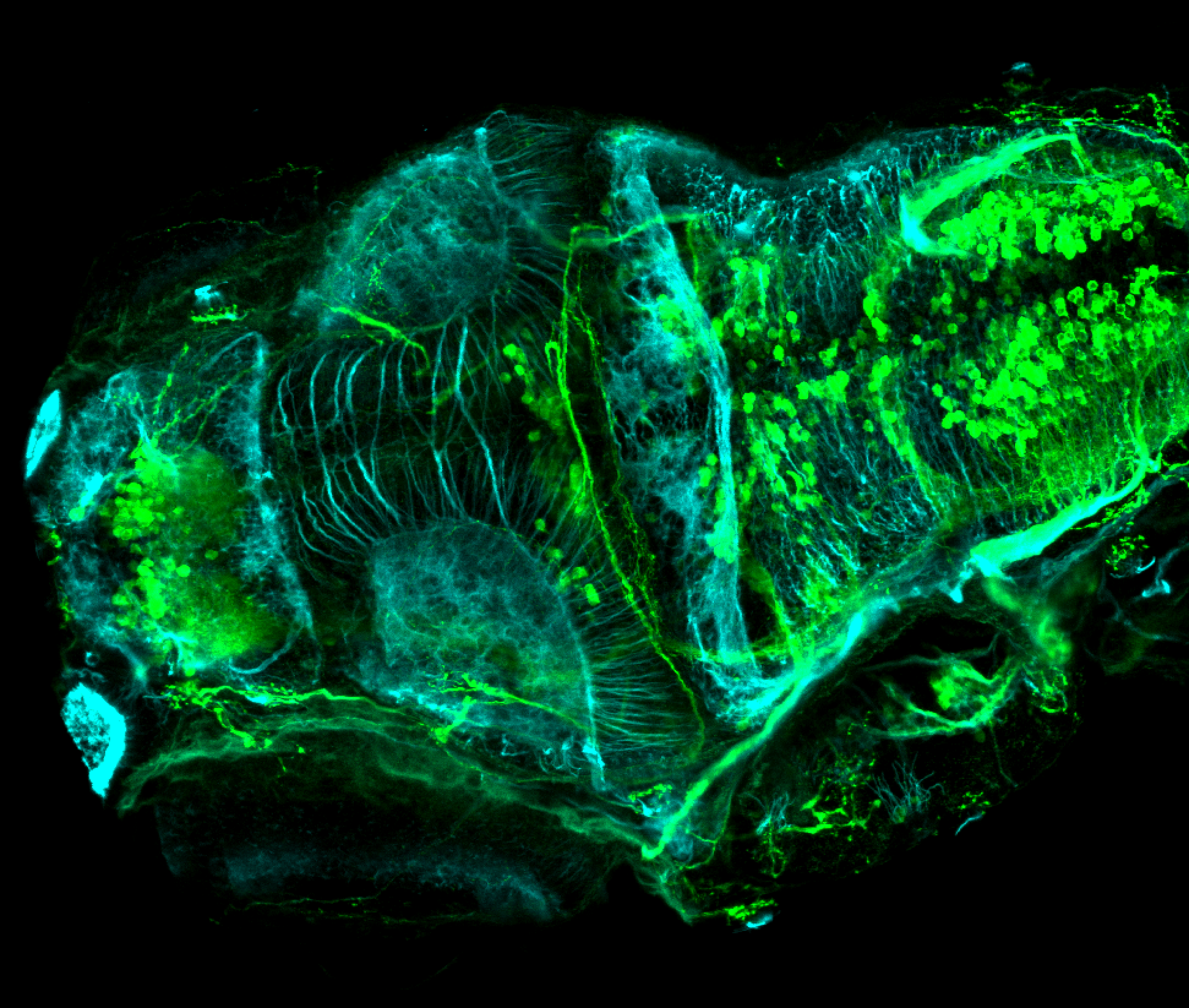
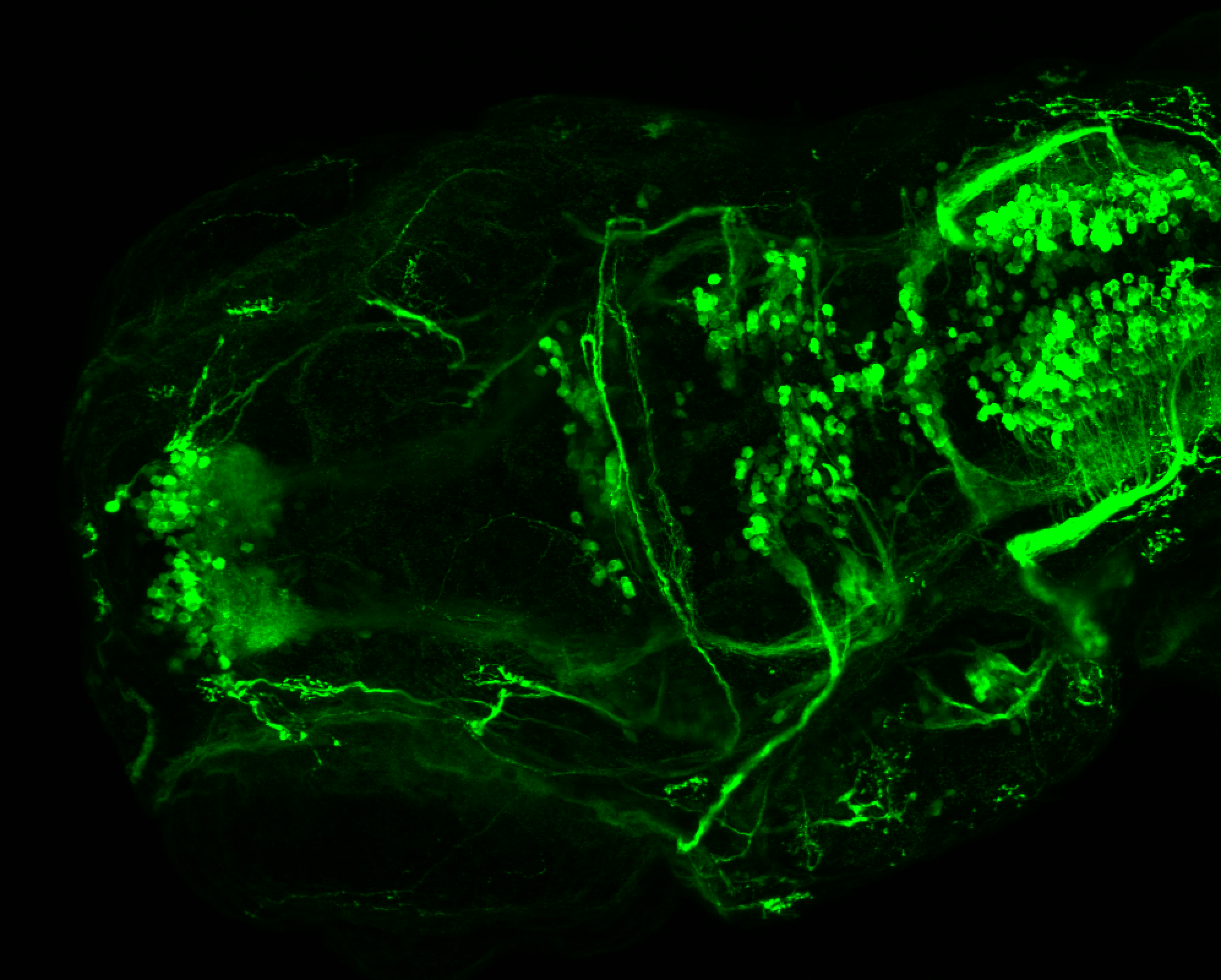
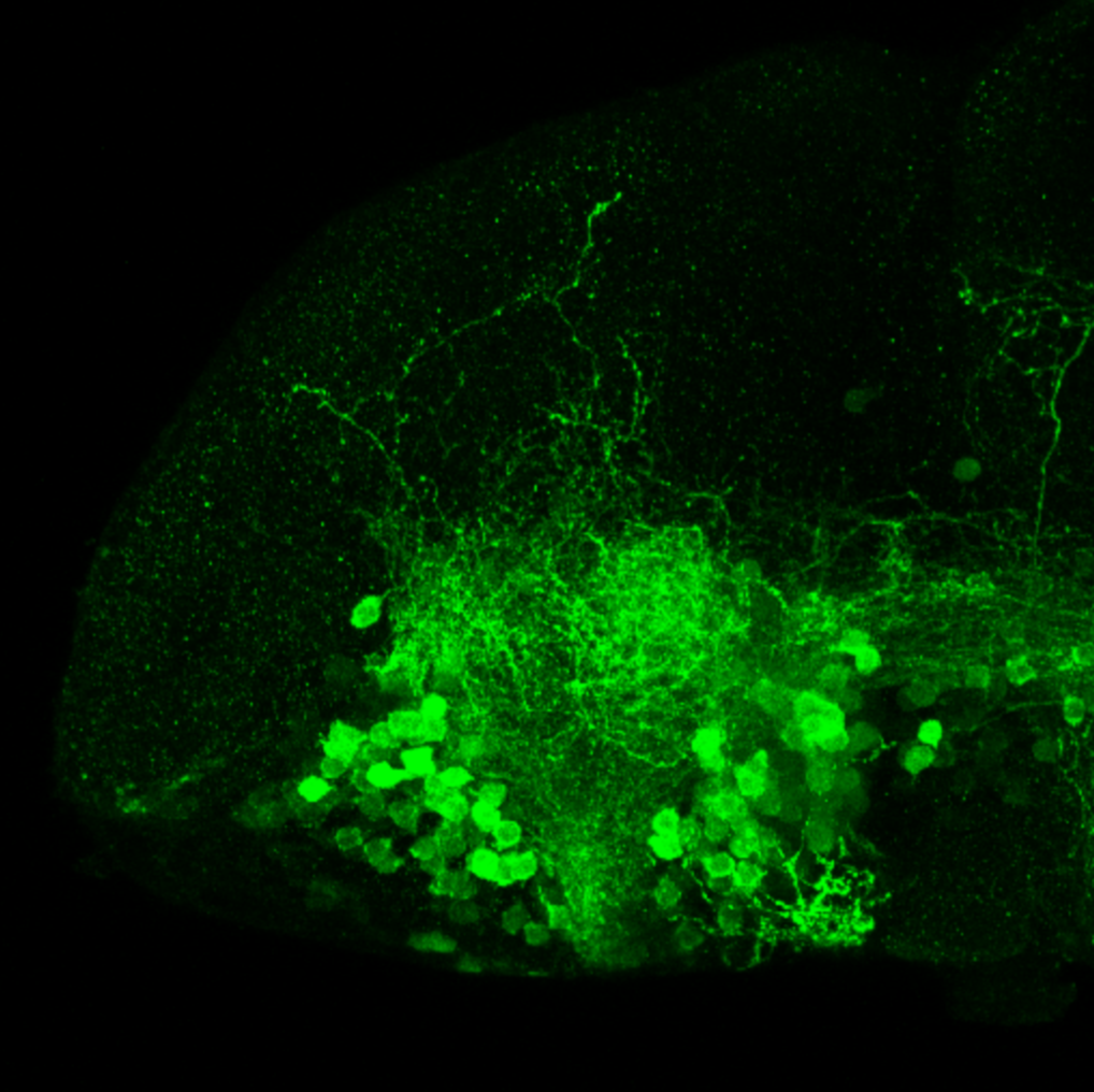
Expressed in:
cranial motor neurons, hindbrain, subpallium, preoptic area.
Key Publications
Higashijima, S., Hotta, Y., and Okamoto, H. (2000)
Visualization of cranial motor neurons in live transgenic zebrafish expressing green fluorescent protein under the control of the islet-1 promoter/enhancer.
The Journal of neuroscience. 20(1):206-218
Suli, A., Mortimer, N., Shepherd, I., and Chien, C.B. (2006)
Netrin/DCC signaling controls contralateral dendrites of octavolateralis efferent neurons.
The Journal of neuroscience. 26(51):13328-13337.
Schoppik, D., Bianco, I.H., Prober, D.A., Douglass, A.D., Robson, D.N., Li, J.M.B., Greenwood, J.S.F., Soucy, E., Engert, F., Schier, A.F. (2017)
Gaze-stabilizing central vestibular neurons project asymmetrically to extraocular motoneuron pools. The Journal of neuroscience. 37(47):11353-11365.
Rebman, J.K., Kirchoff, K.E., Walsh, G.S. (2016)
Cadherin-2 Is Required Cell Autonomously for Collective Migration of Facial Branchiomotor Neurons.
PLoS One. 11:e0164433.
Barsh, G.R., Isabella, A.J., Moens, C.B. (2017)
Vagus Motor Neuron Topographic Map Determined by Parallel Mechanisms of hox5 Expression and Time of Axon Initiation.
Current biology : CB. 27(24):3812-3825.e3.
Cox, J.A., Lamora, A., Johnson, S.L., and Voigt, M.M. (2011)
Diverse mechanisms for assembly of branchiomeric nerves.
Developmental Biology. 357(2):305-17.



