About
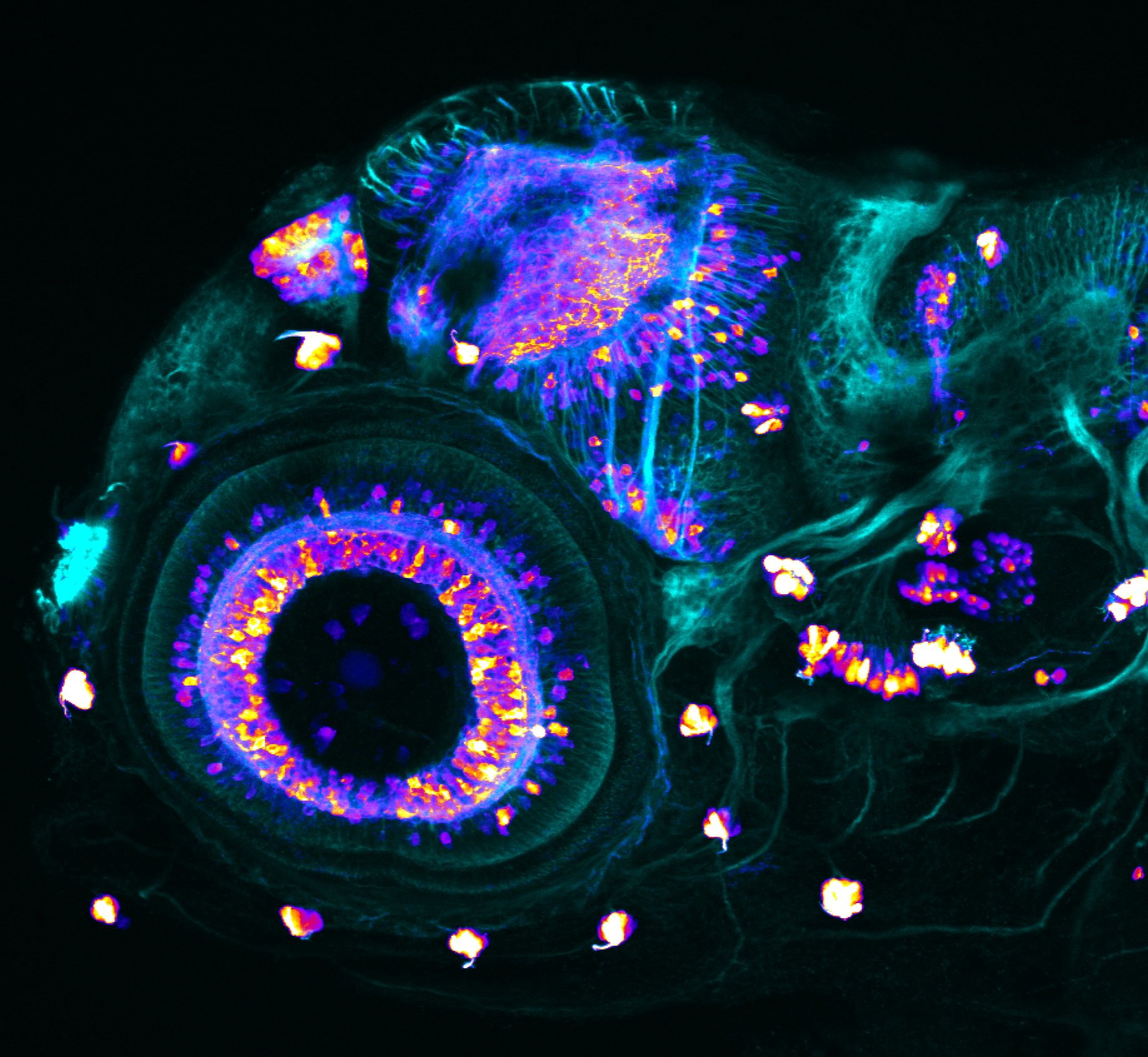
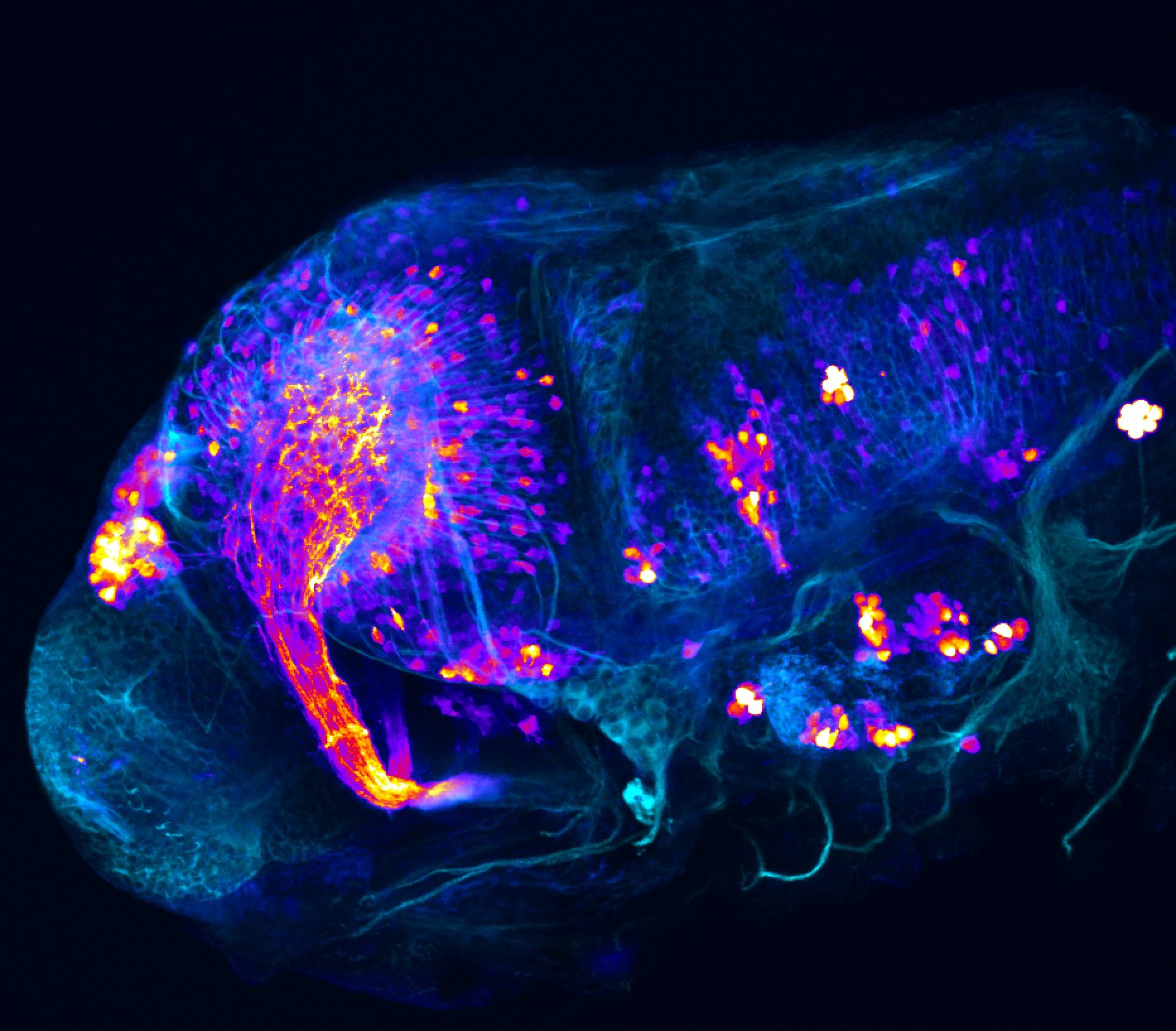
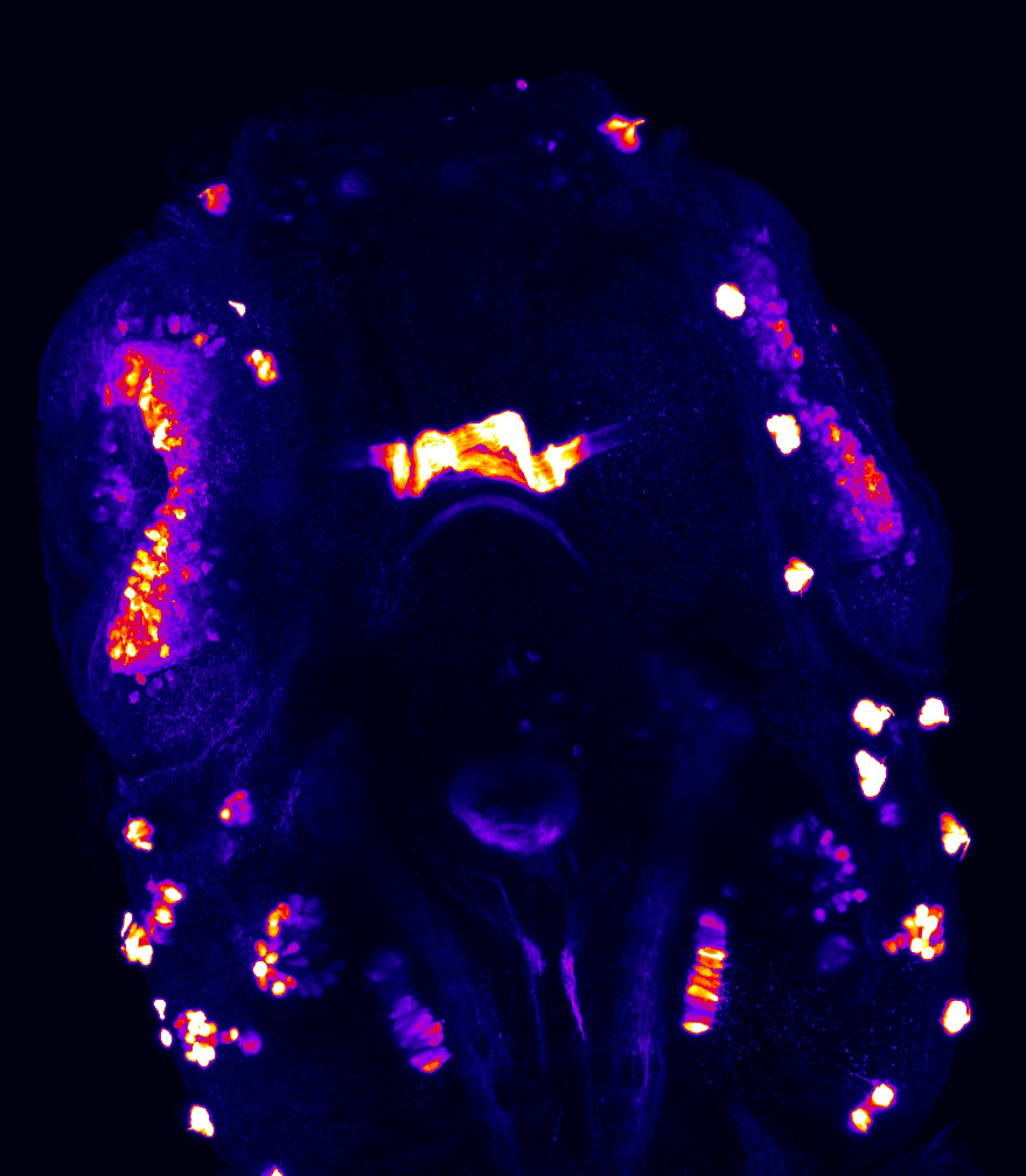
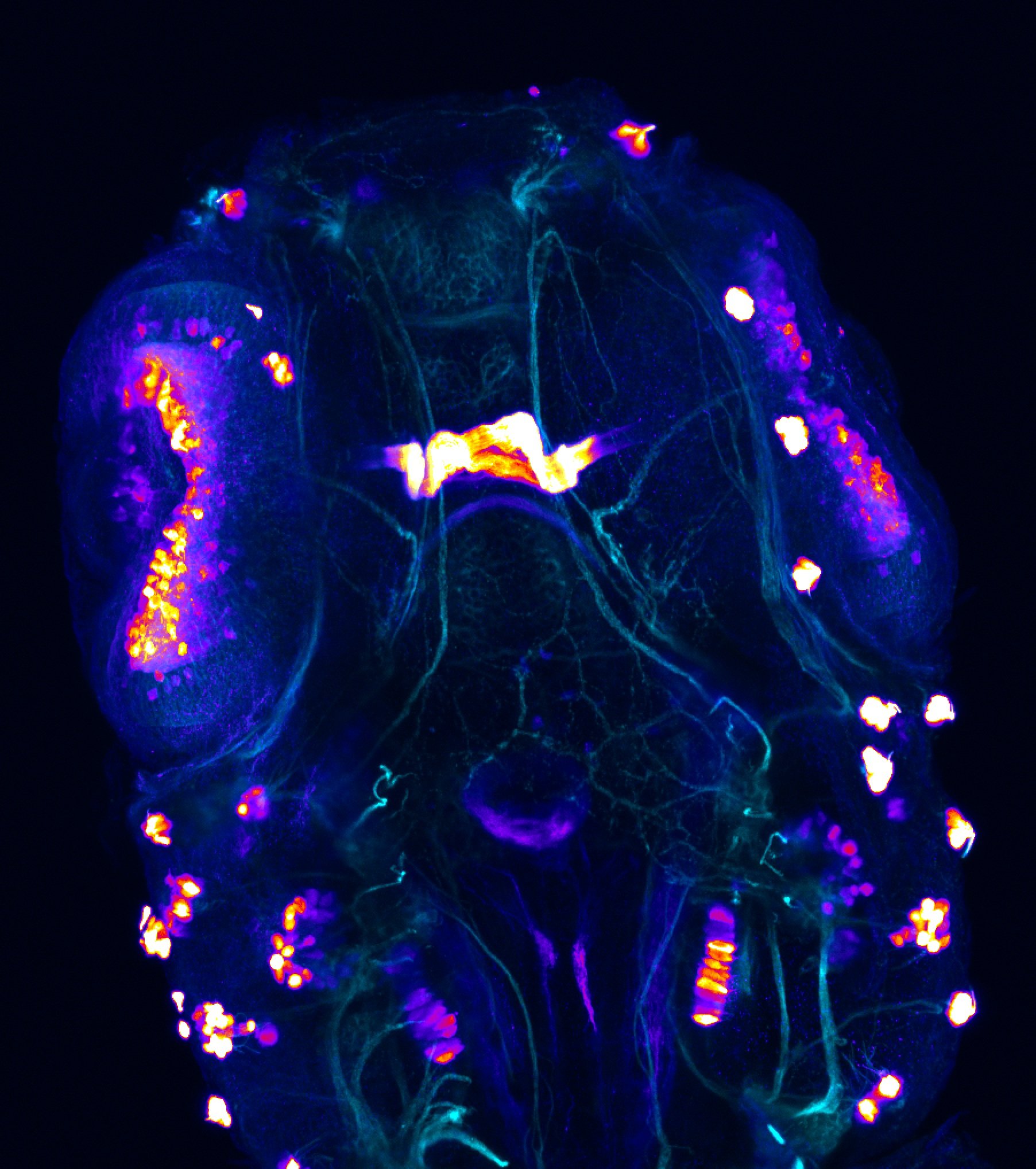
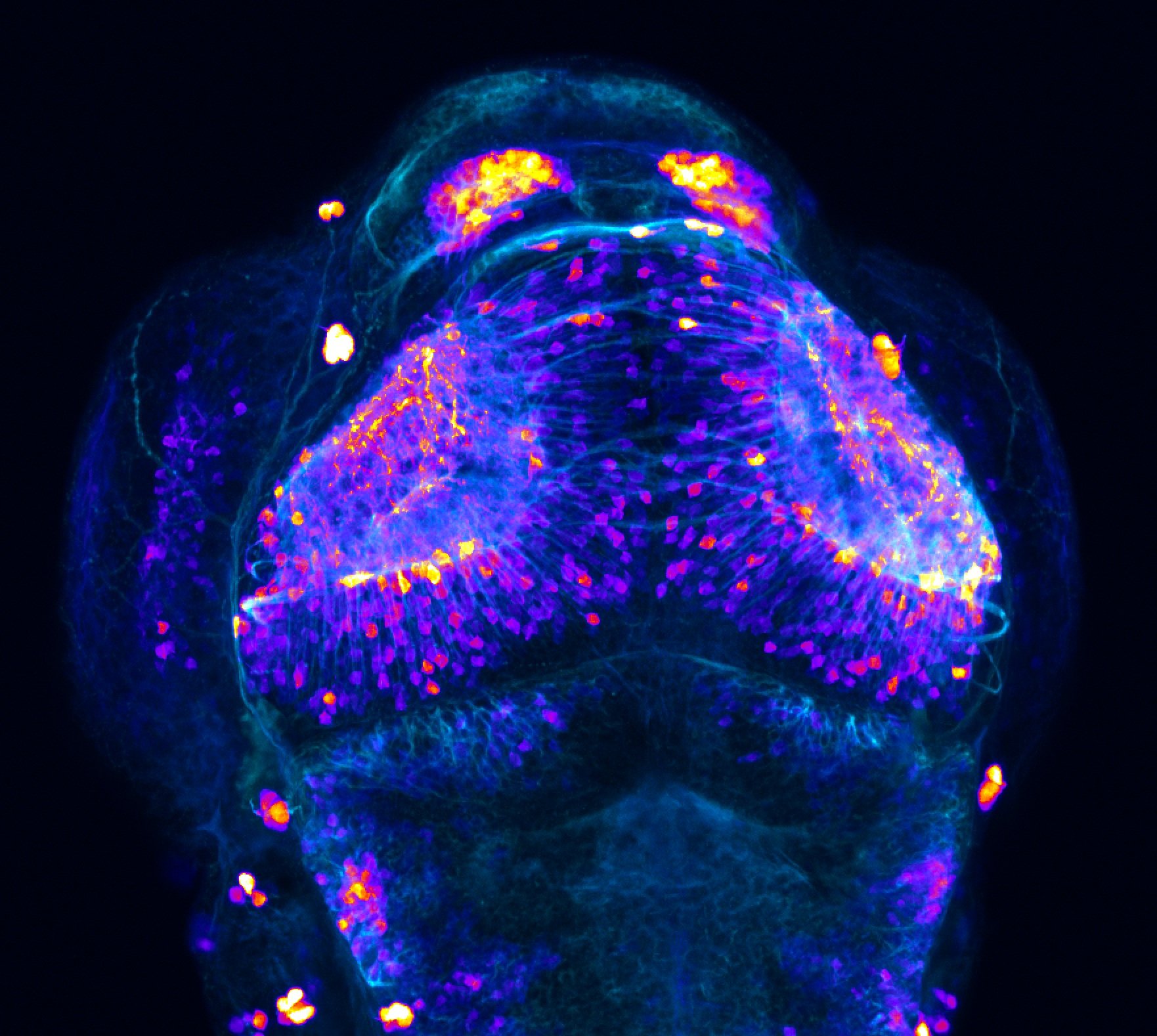
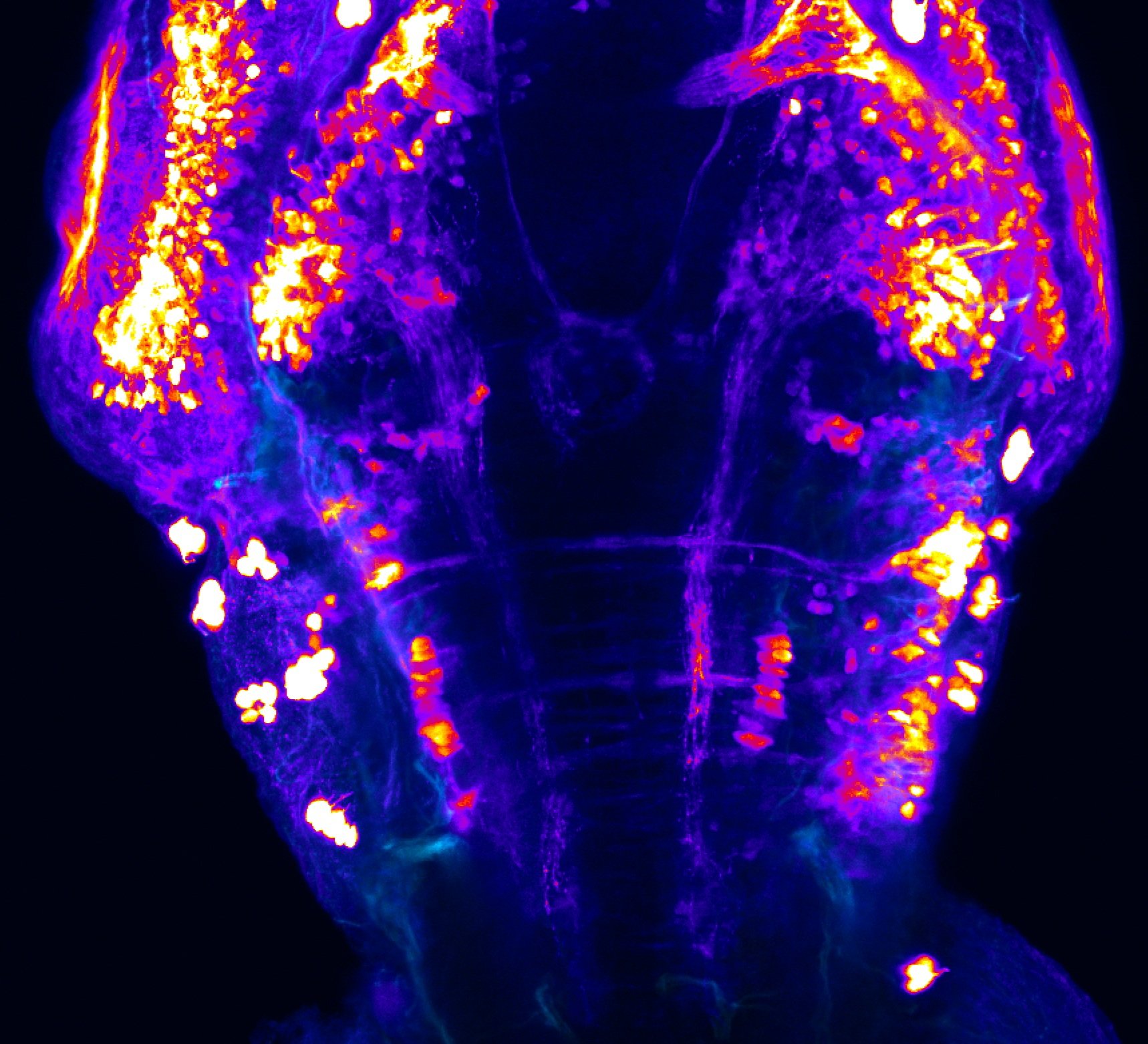
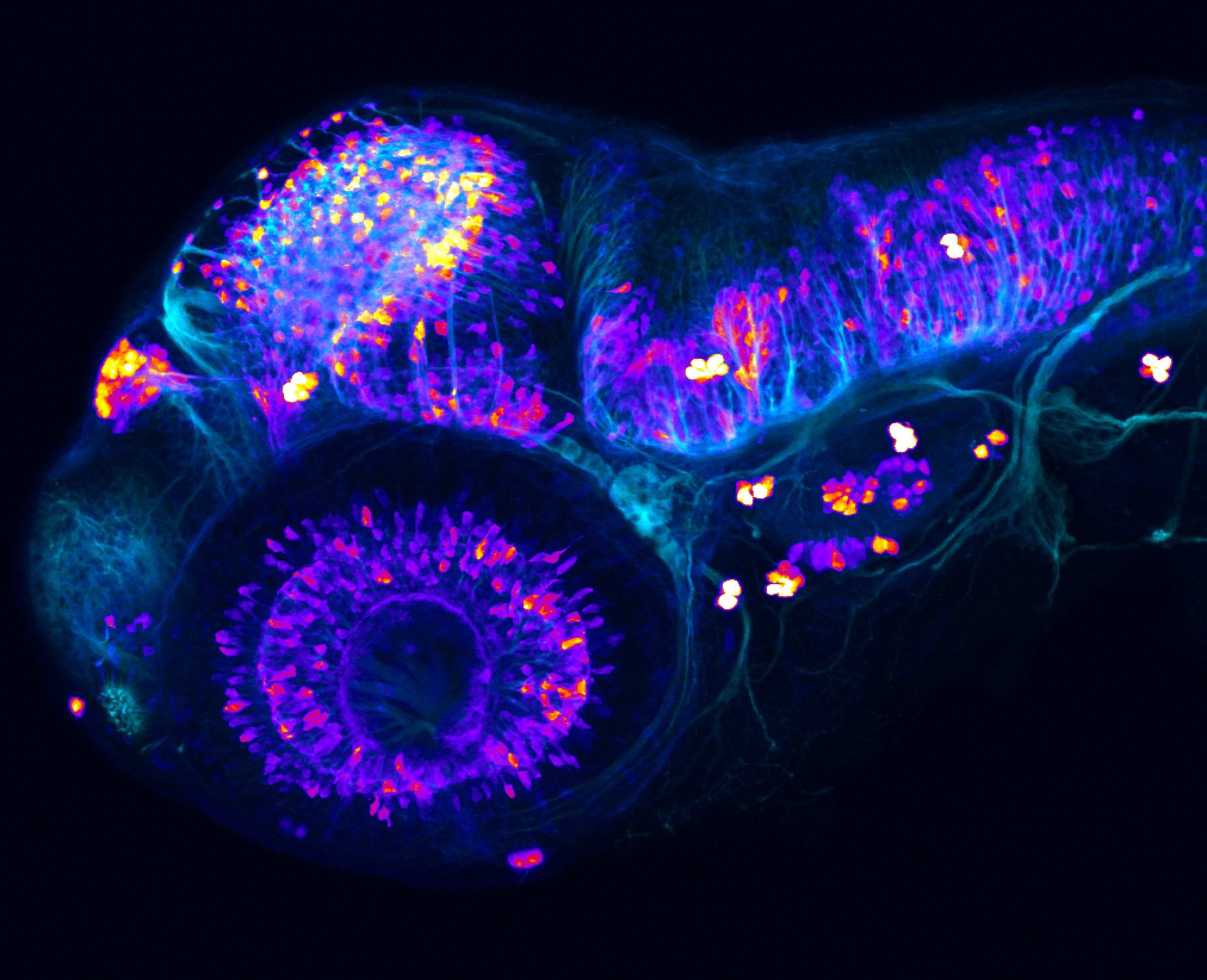
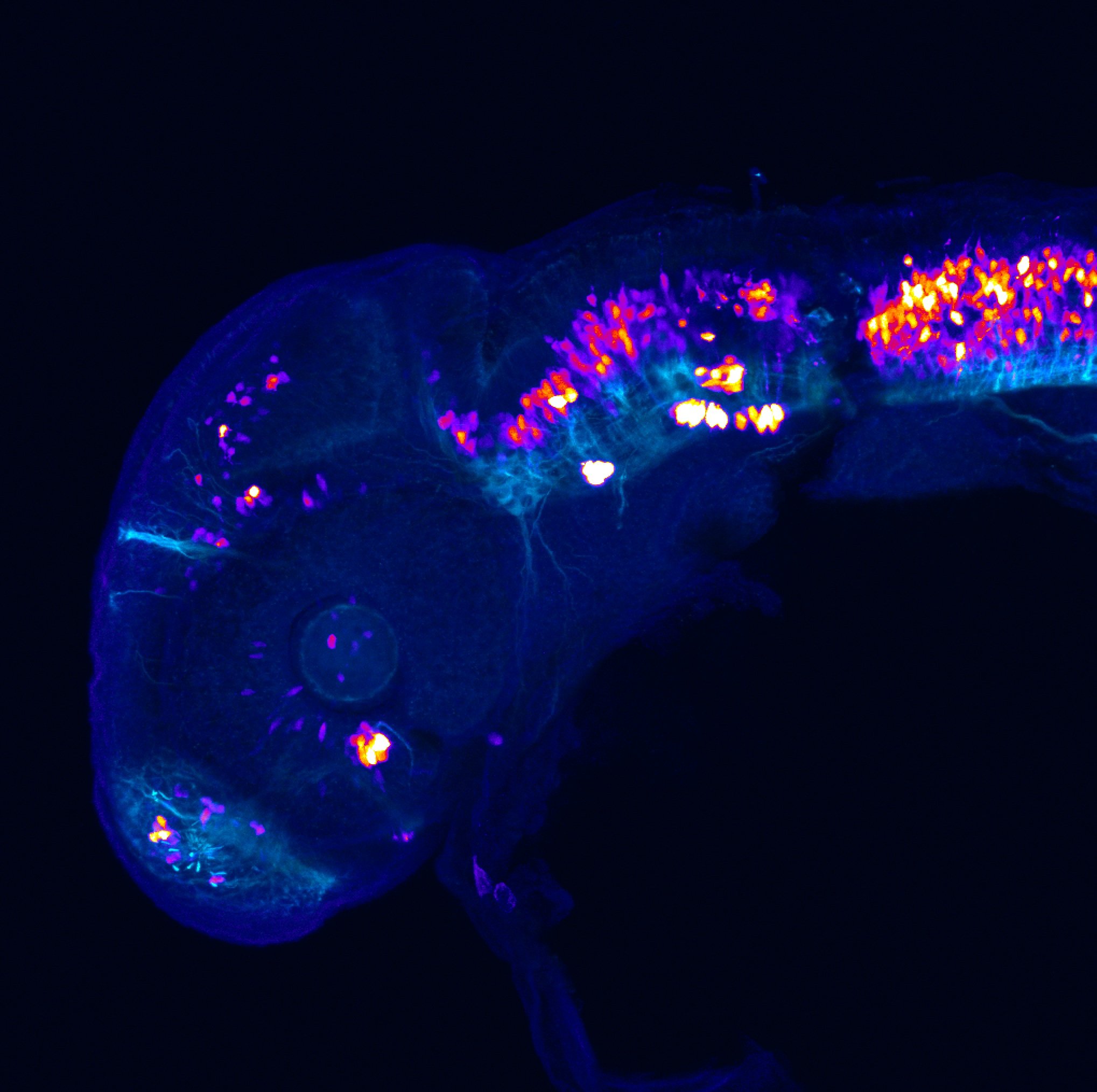
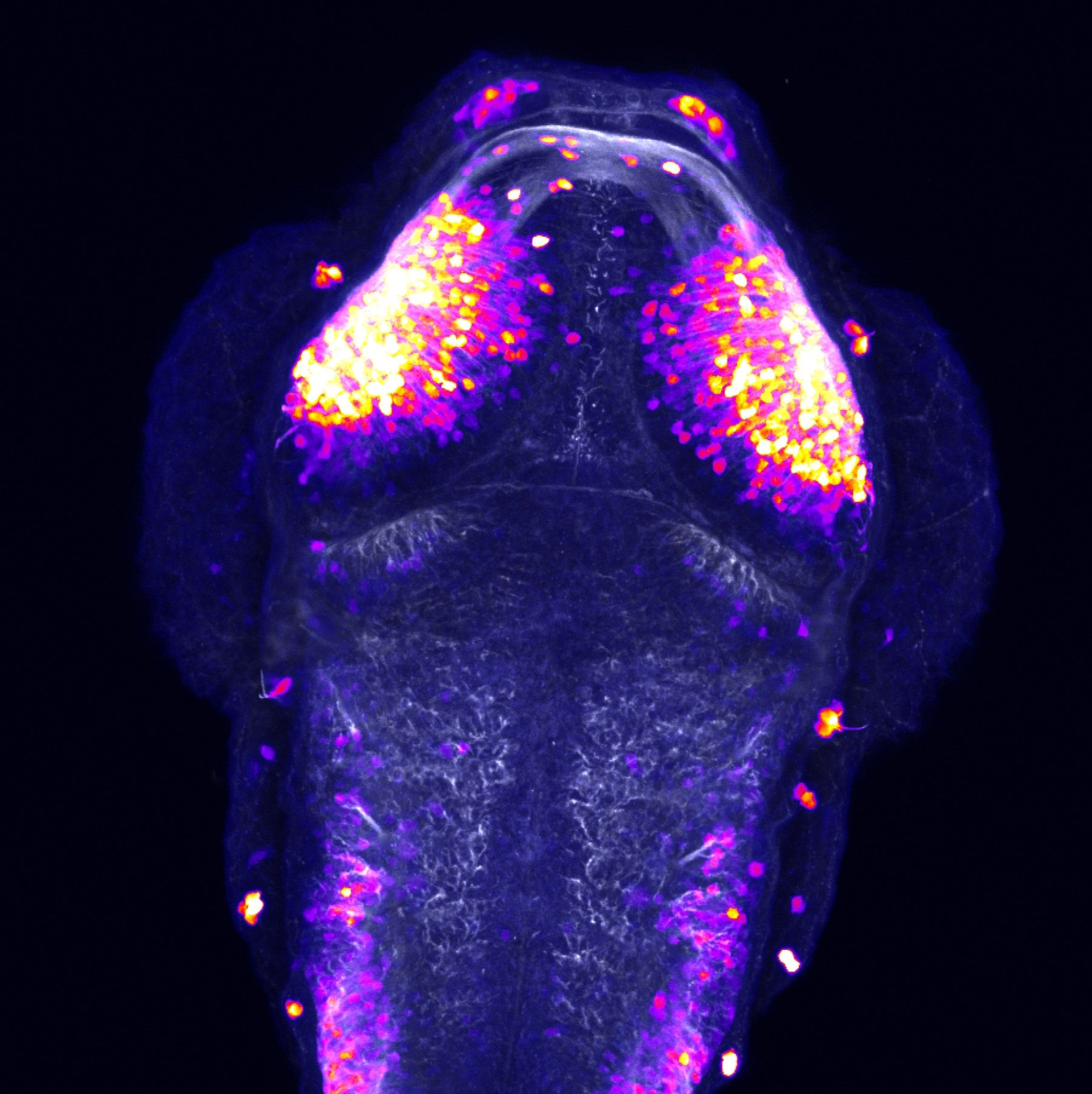
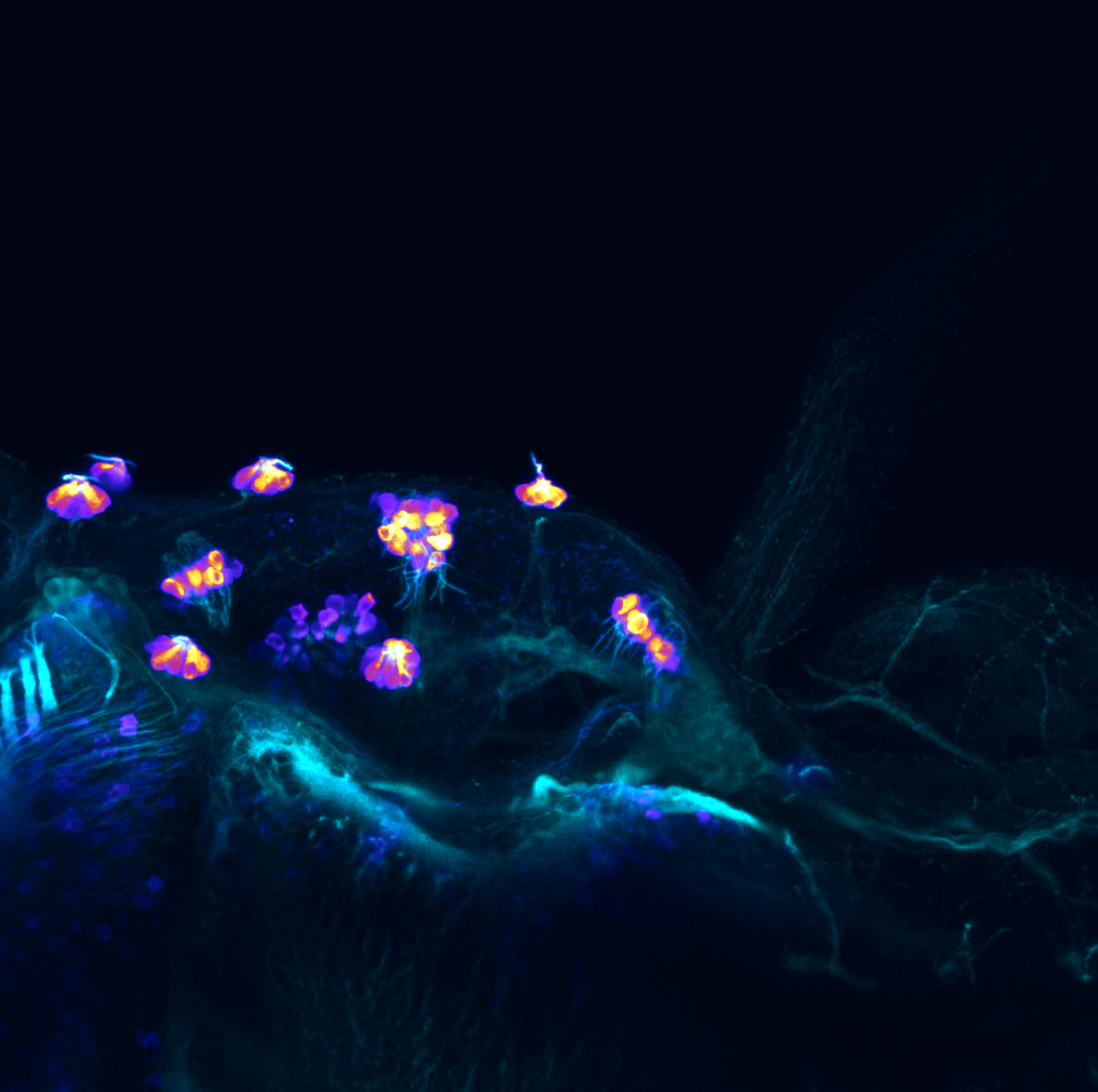
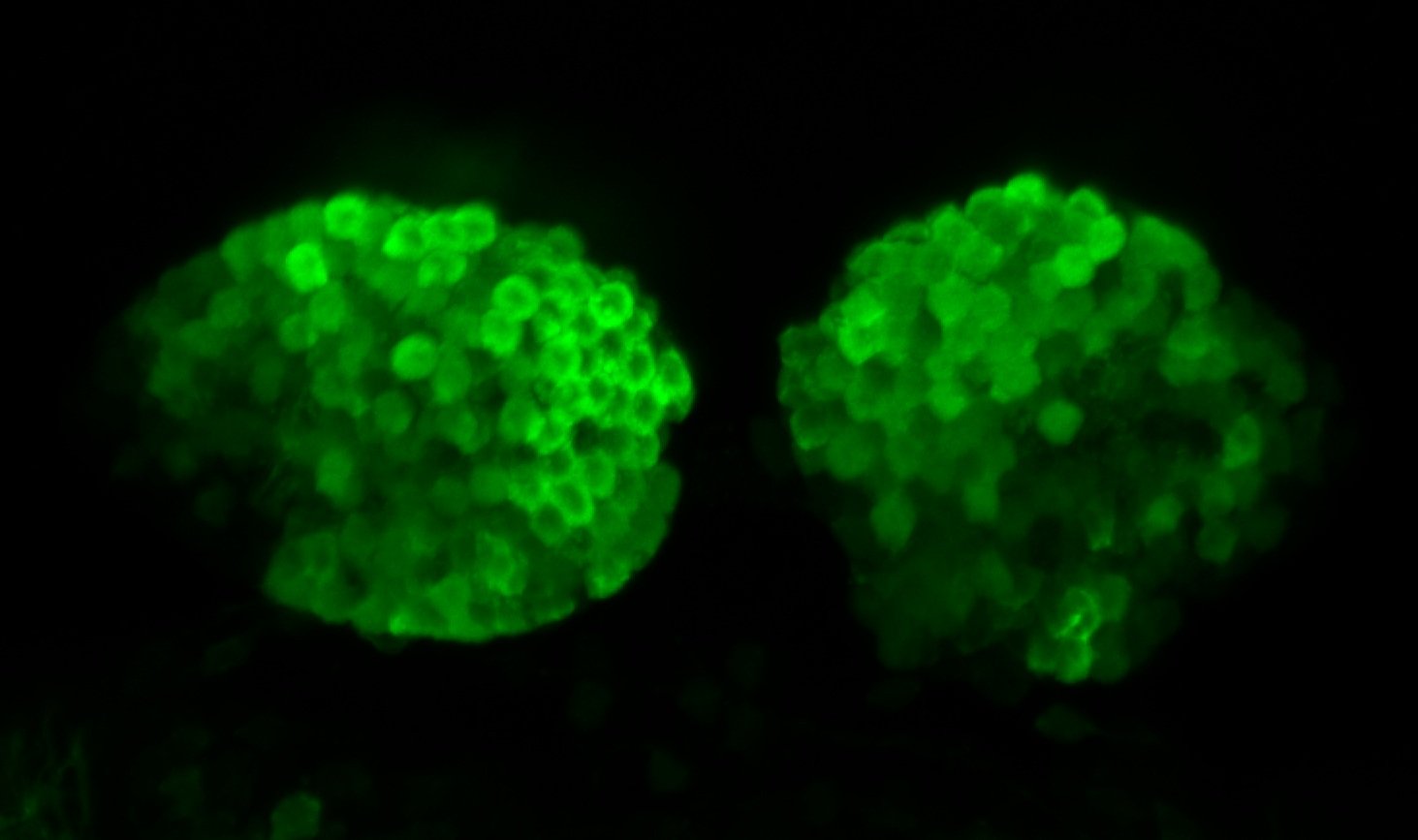
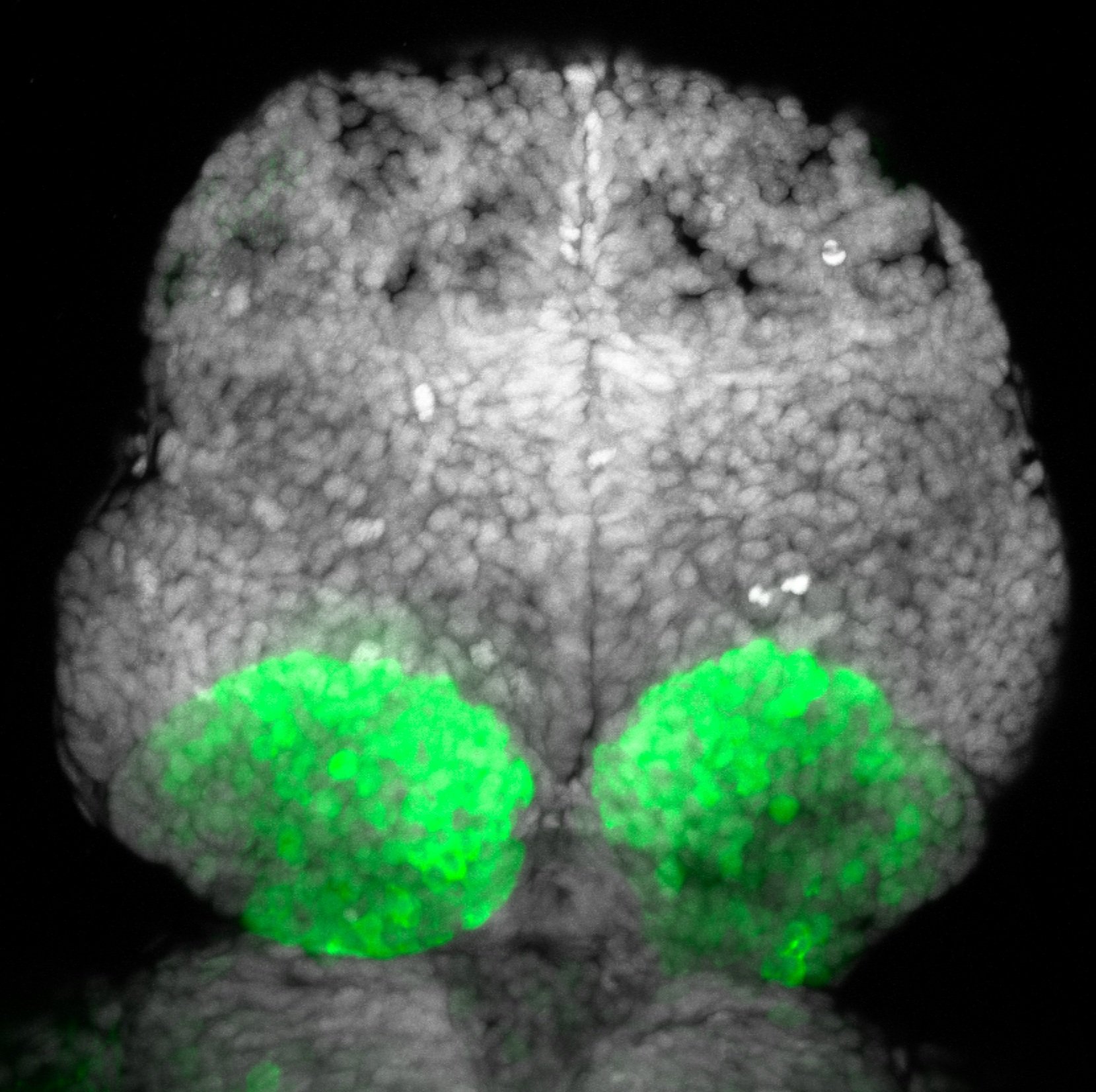
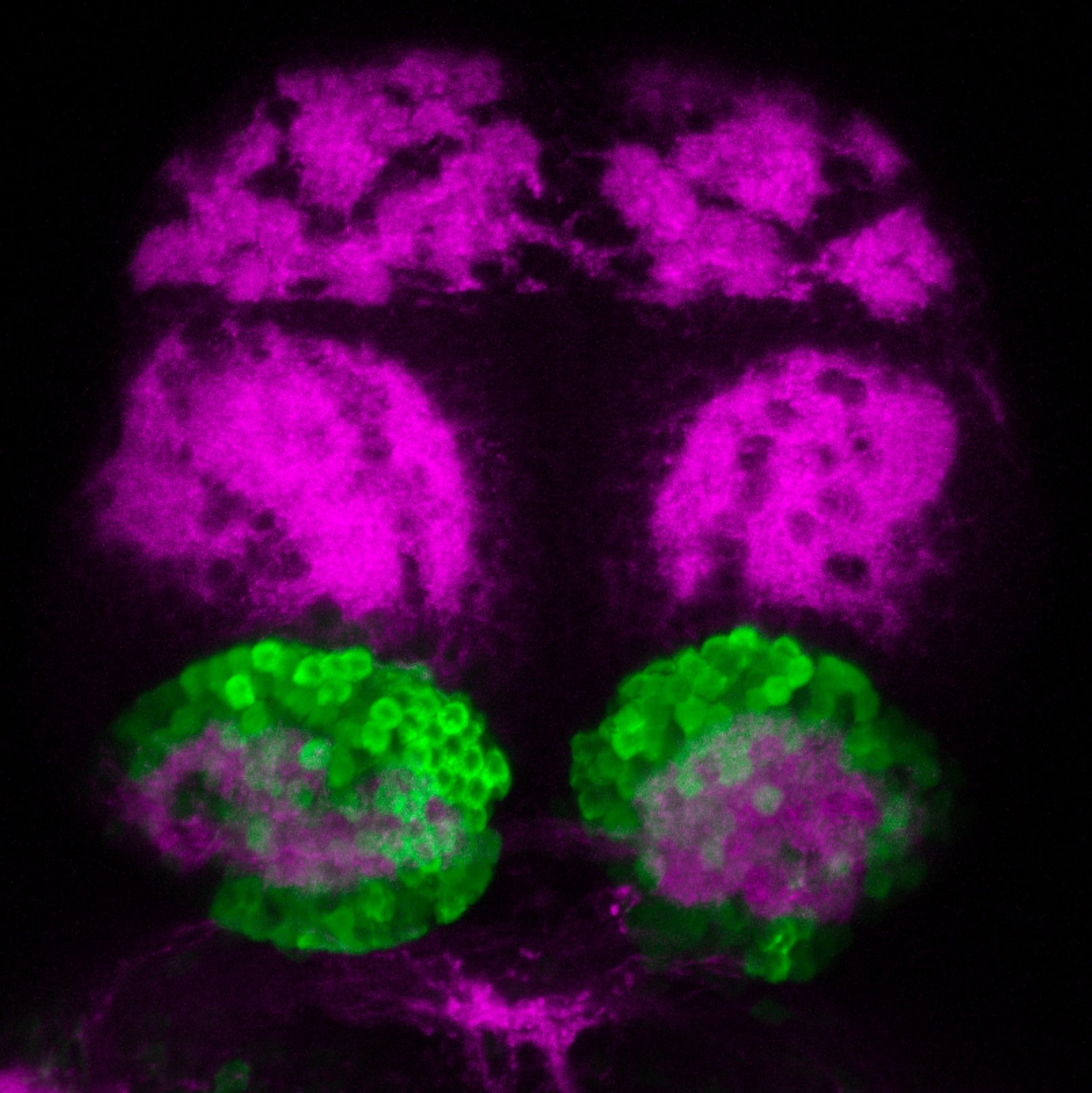
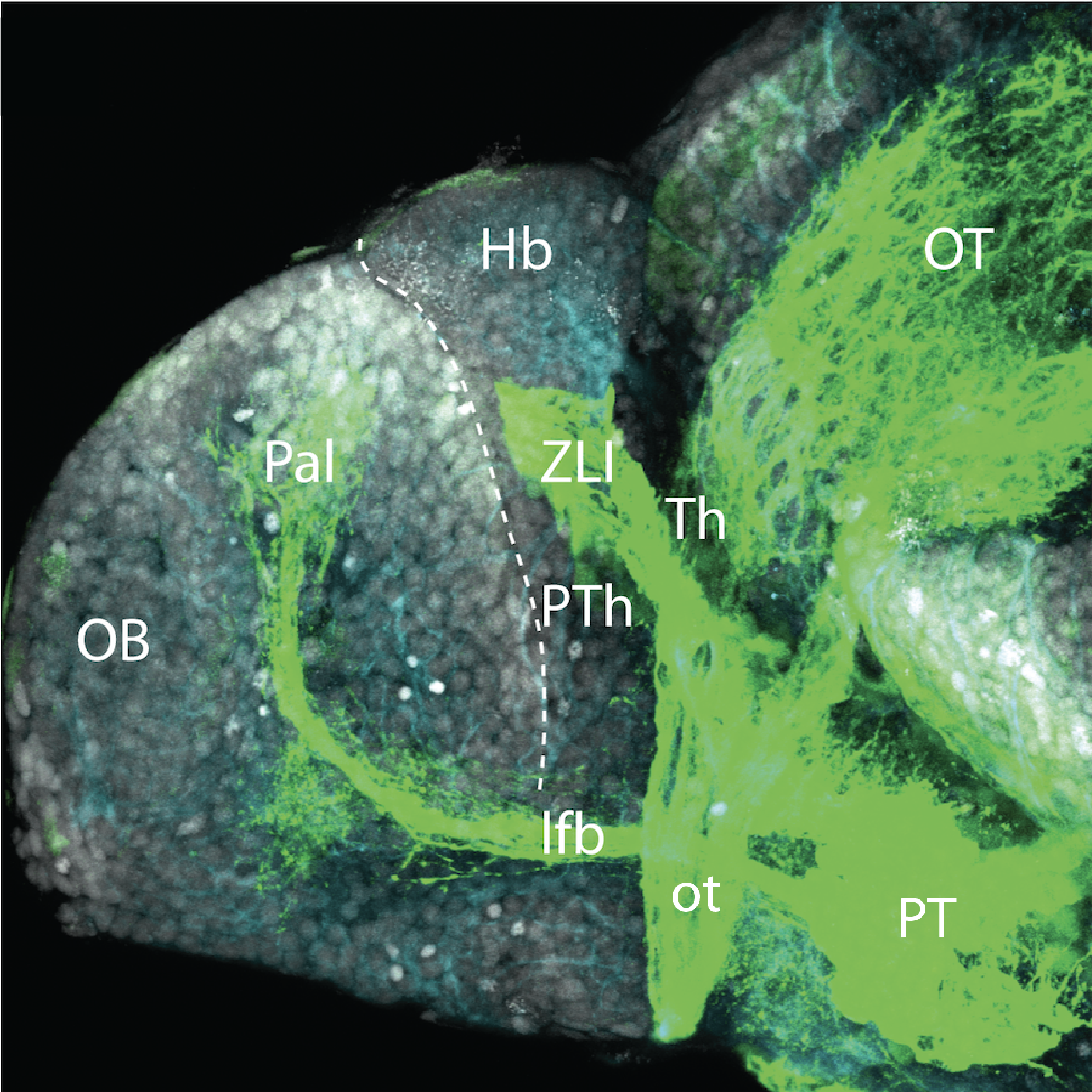
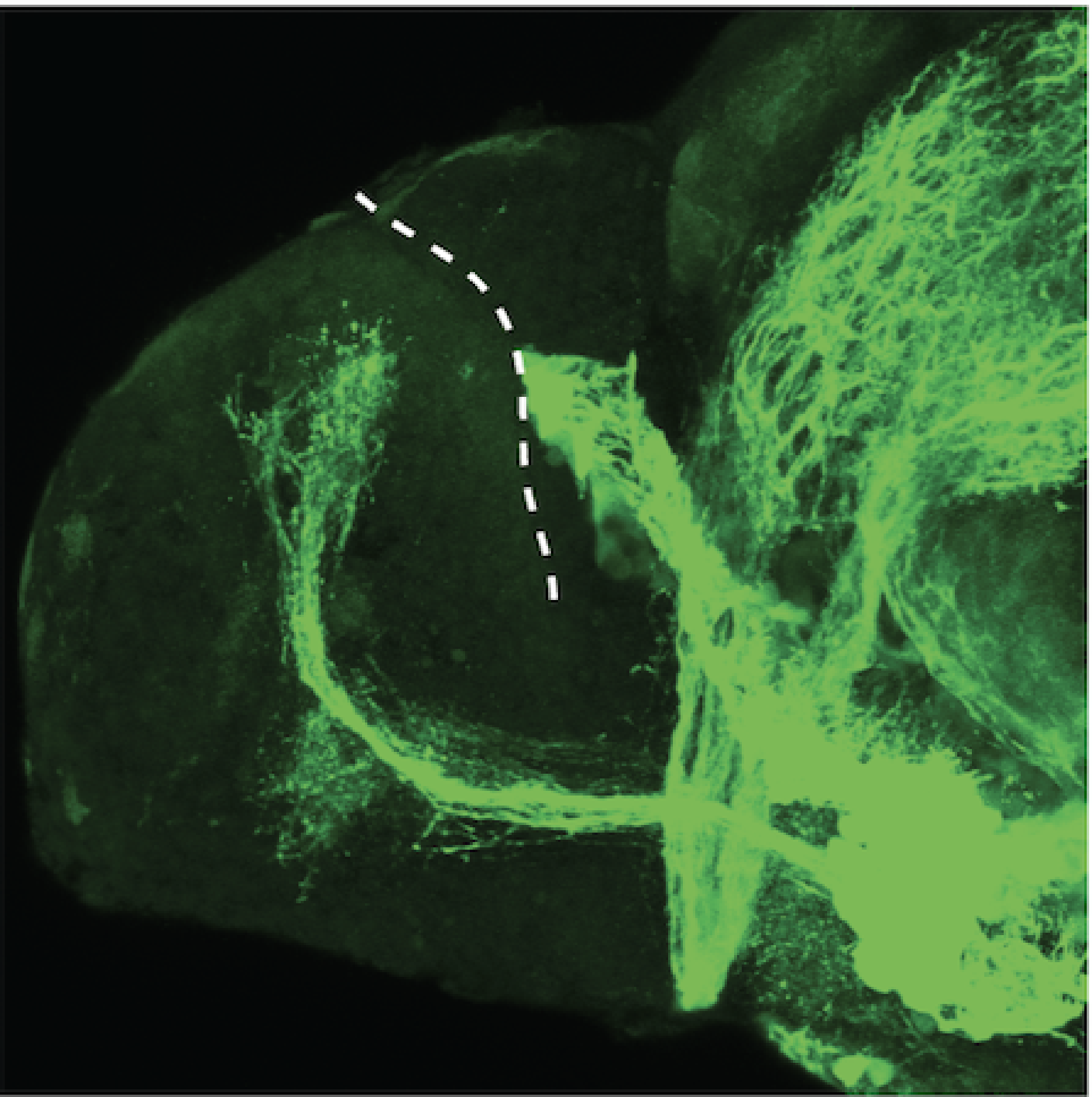
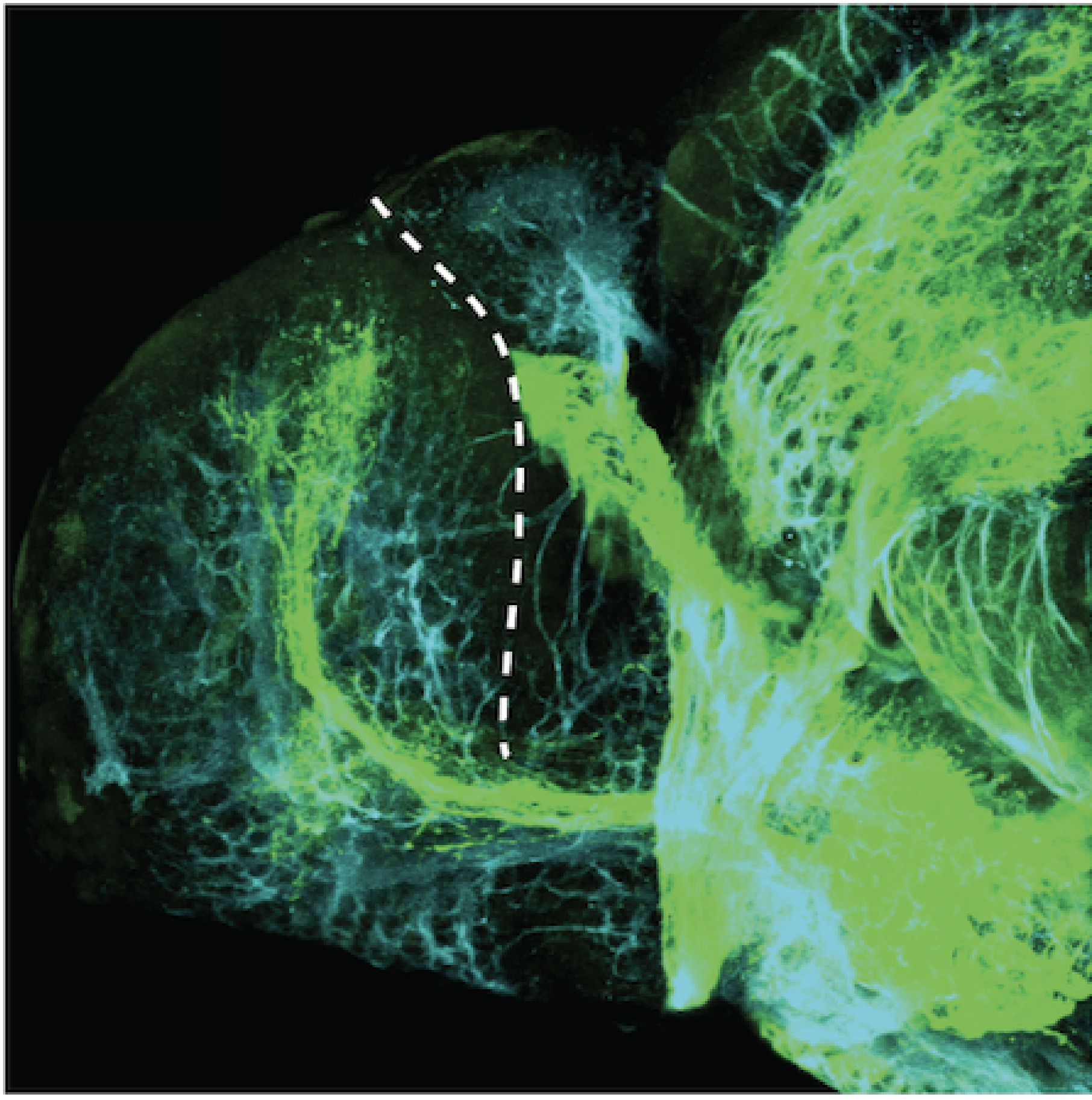
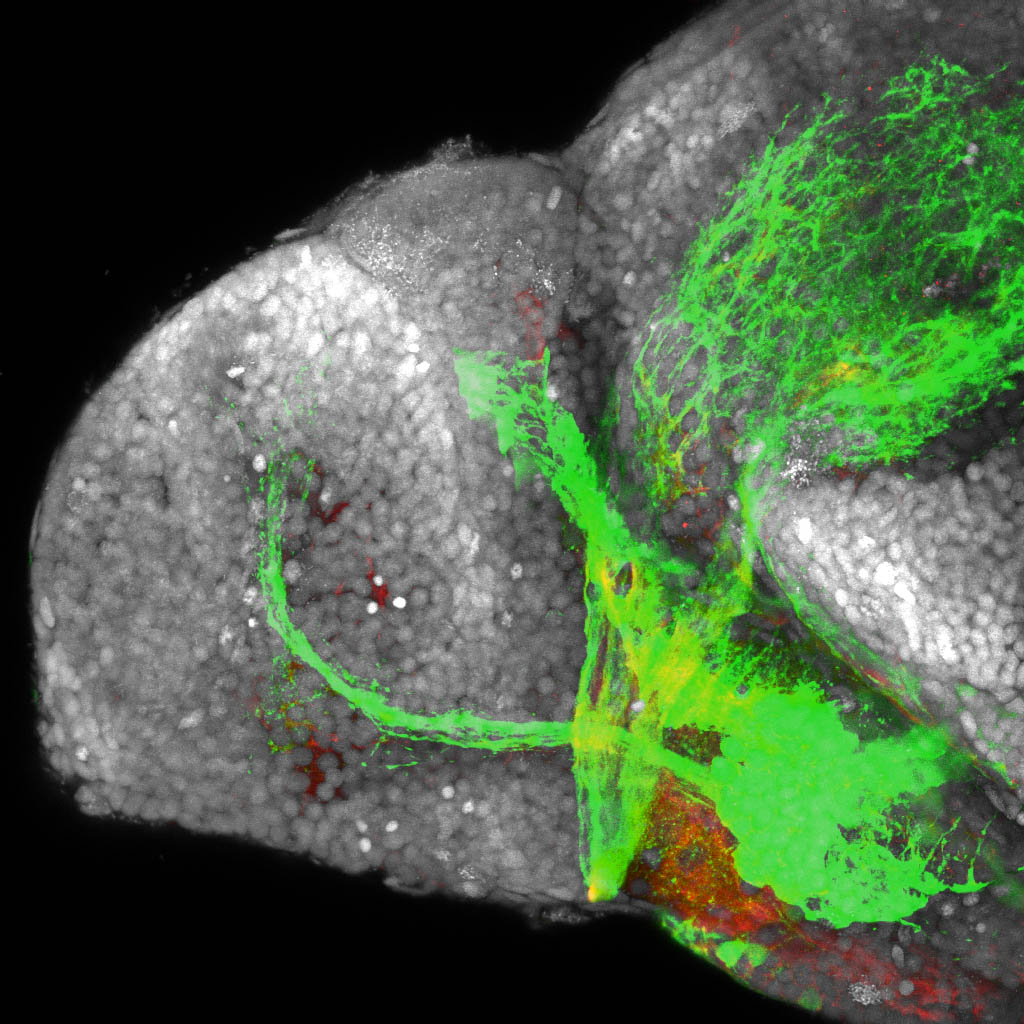
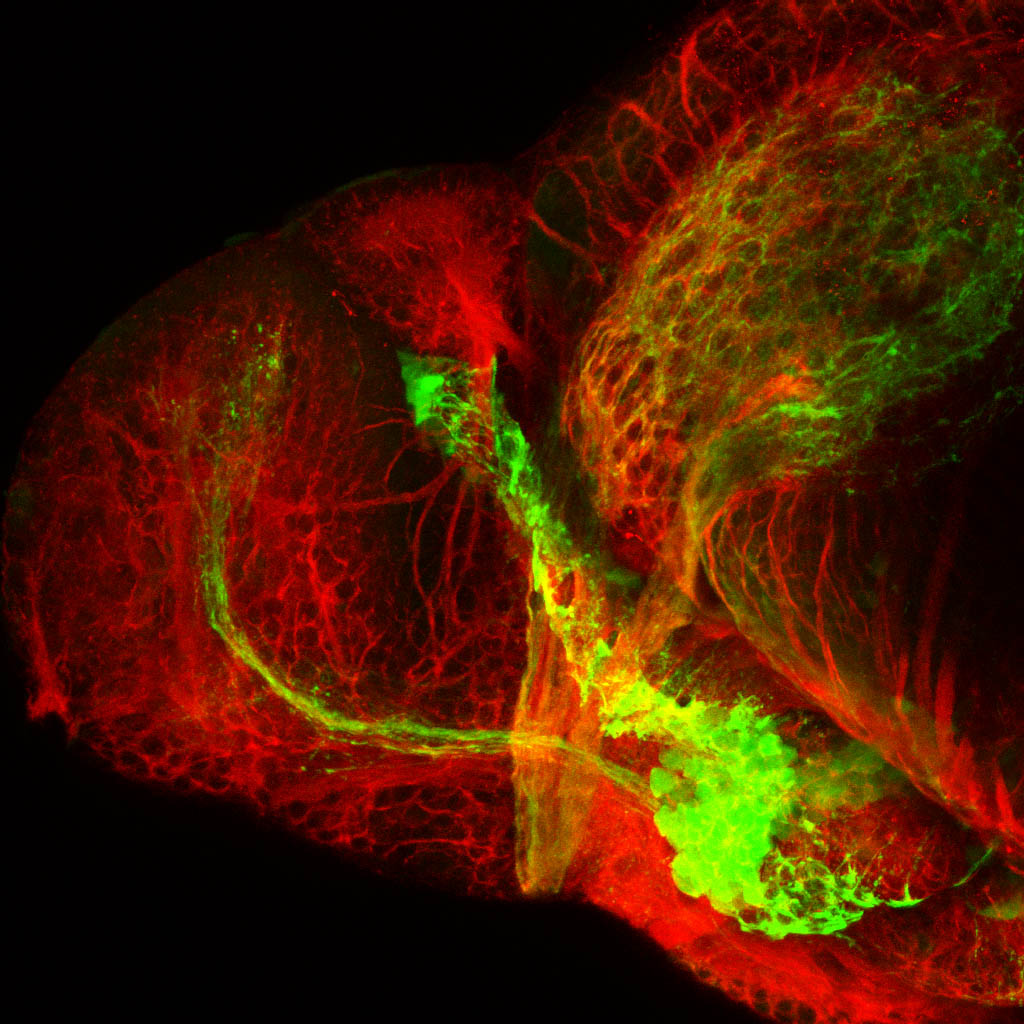
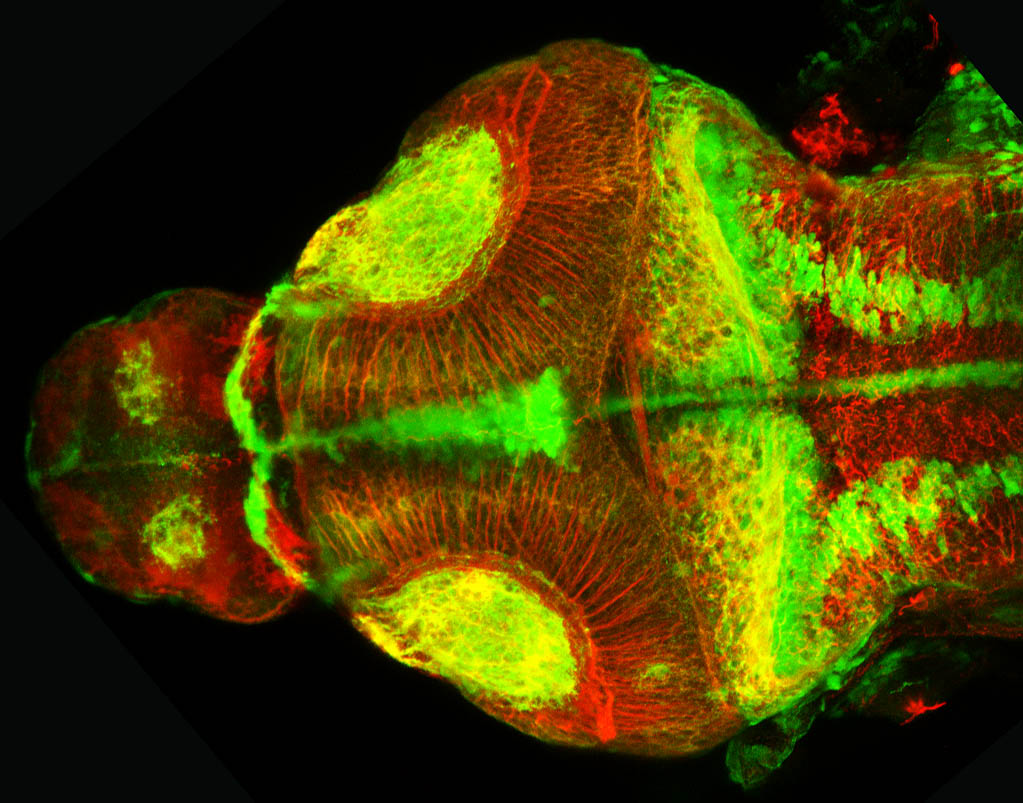
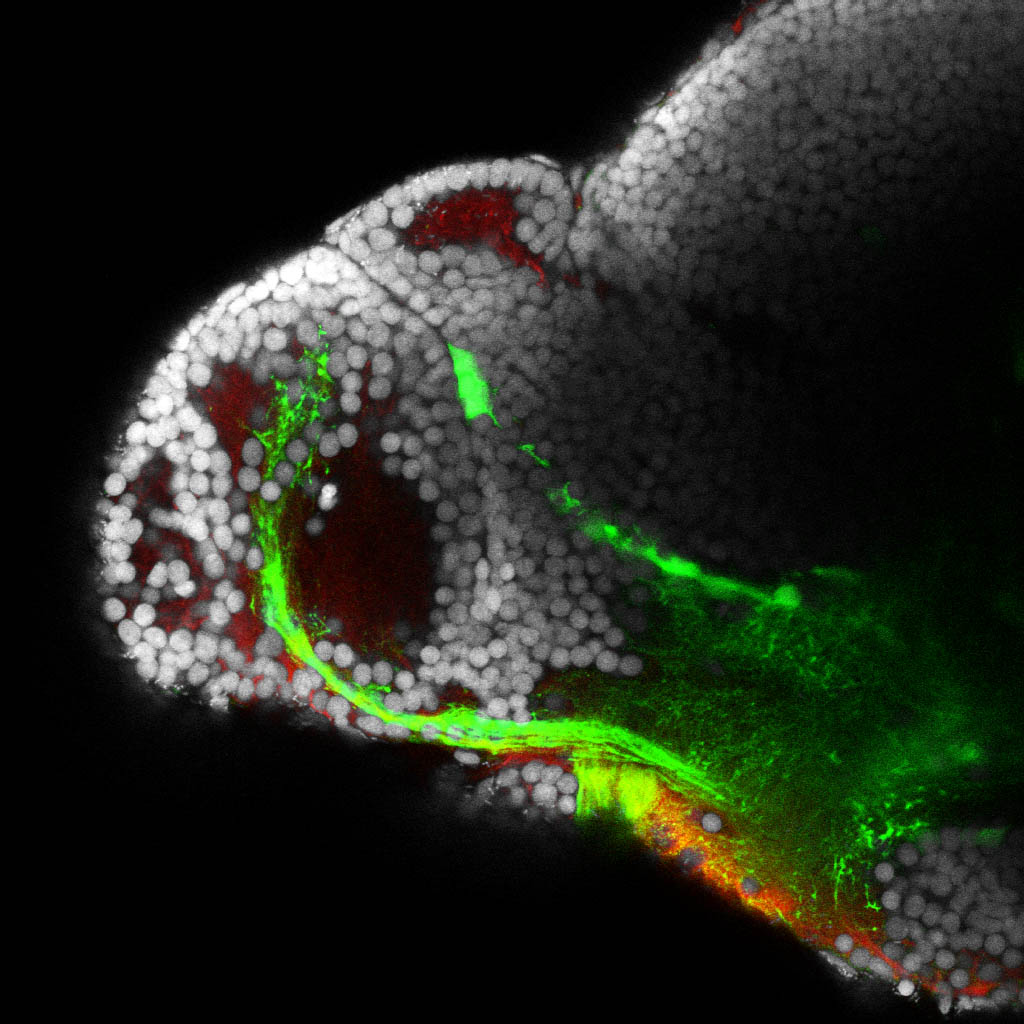
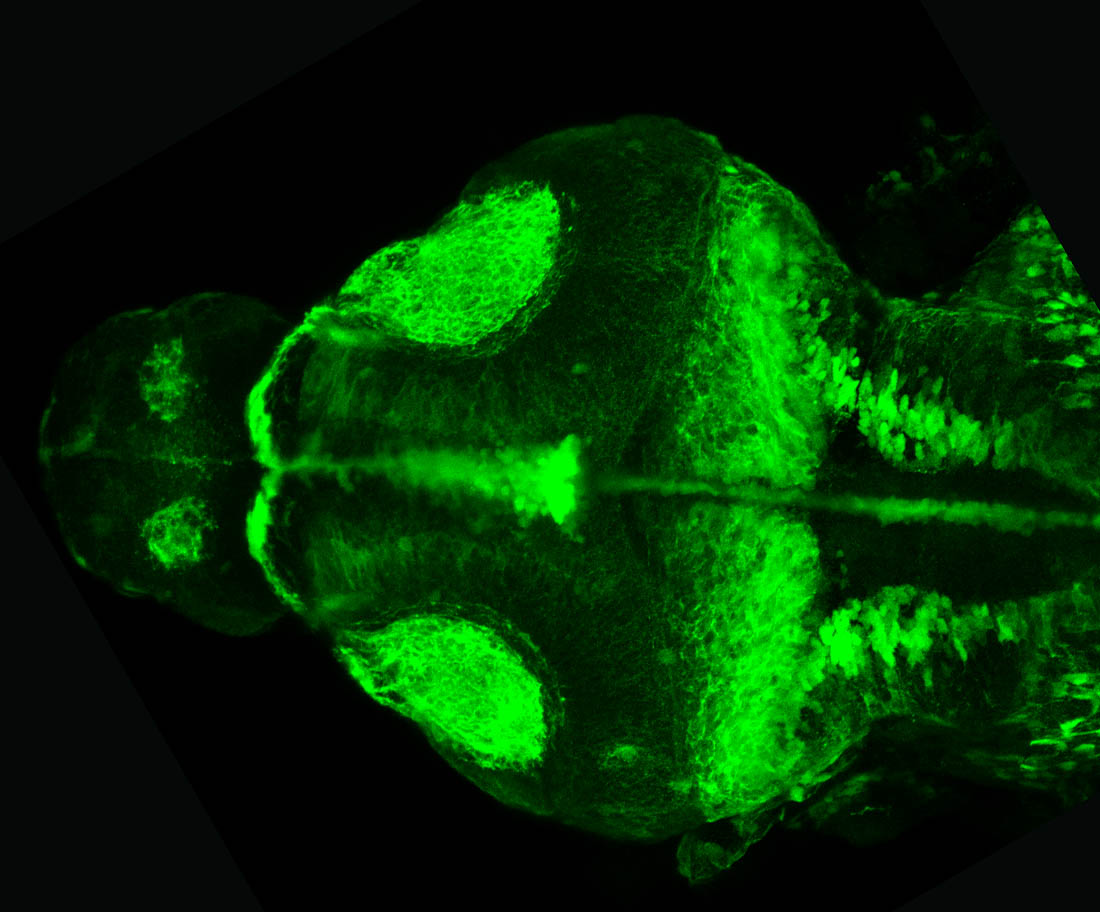
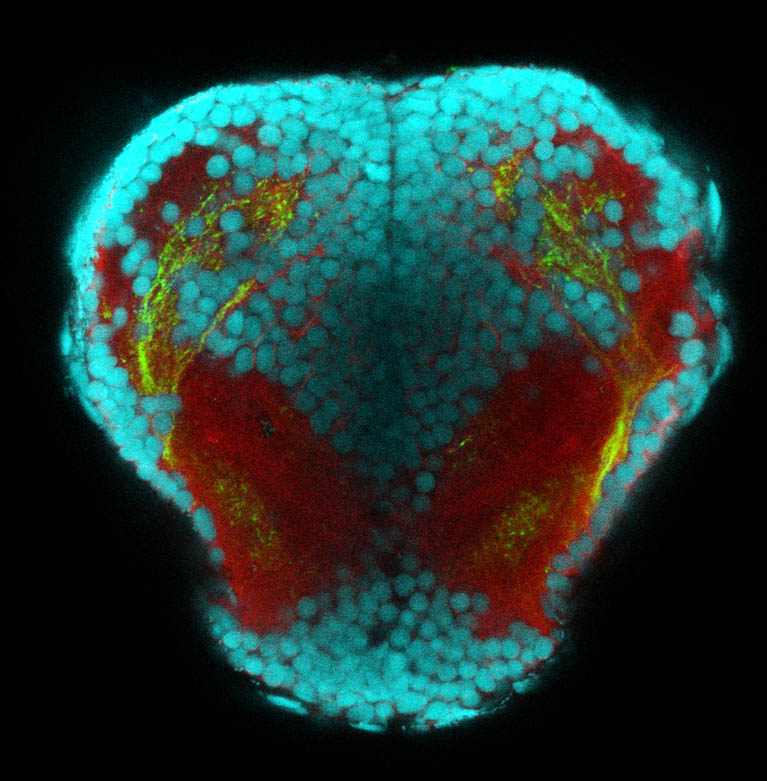
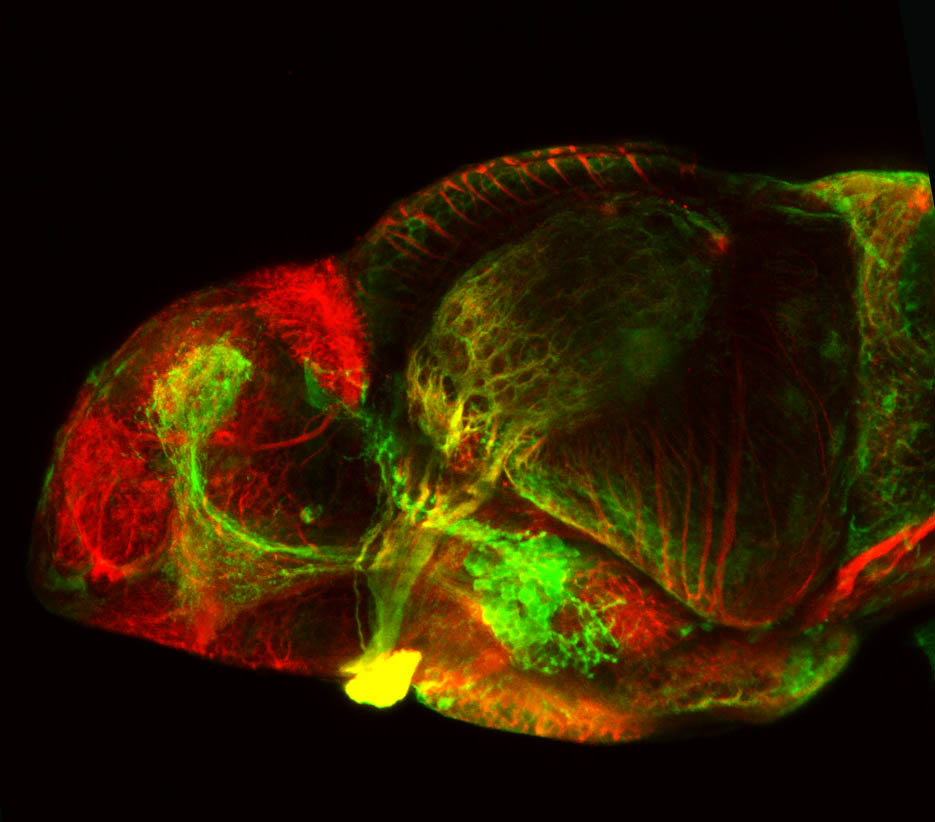
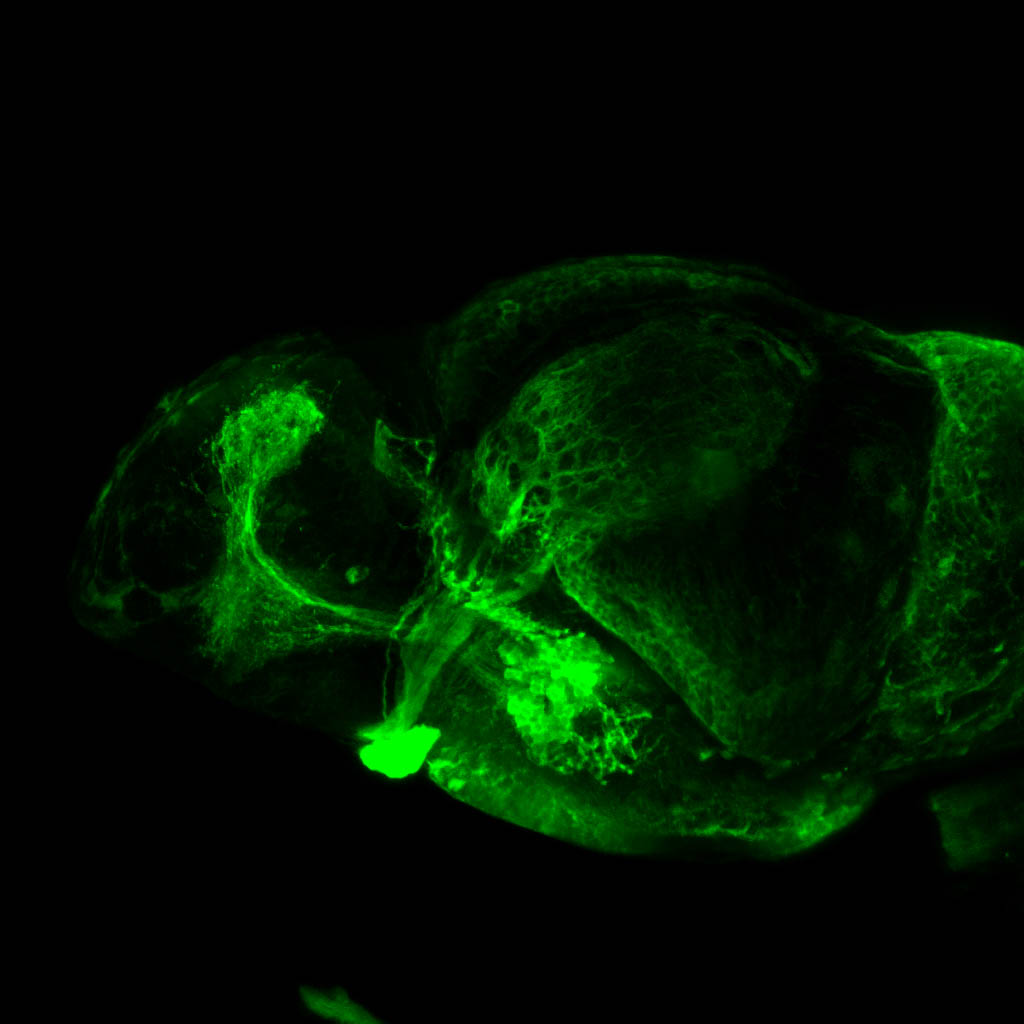
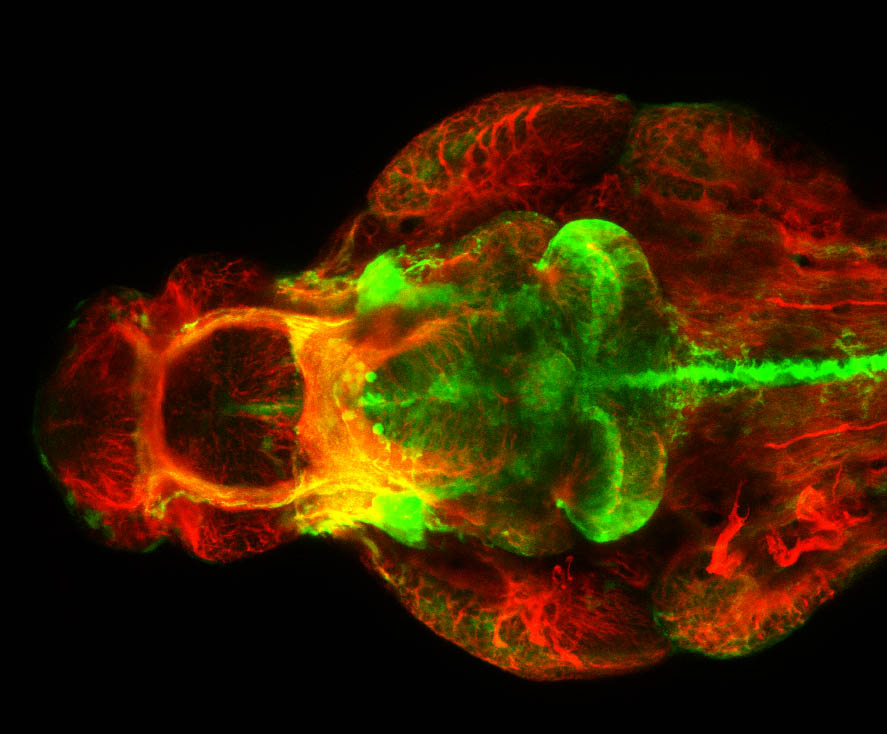
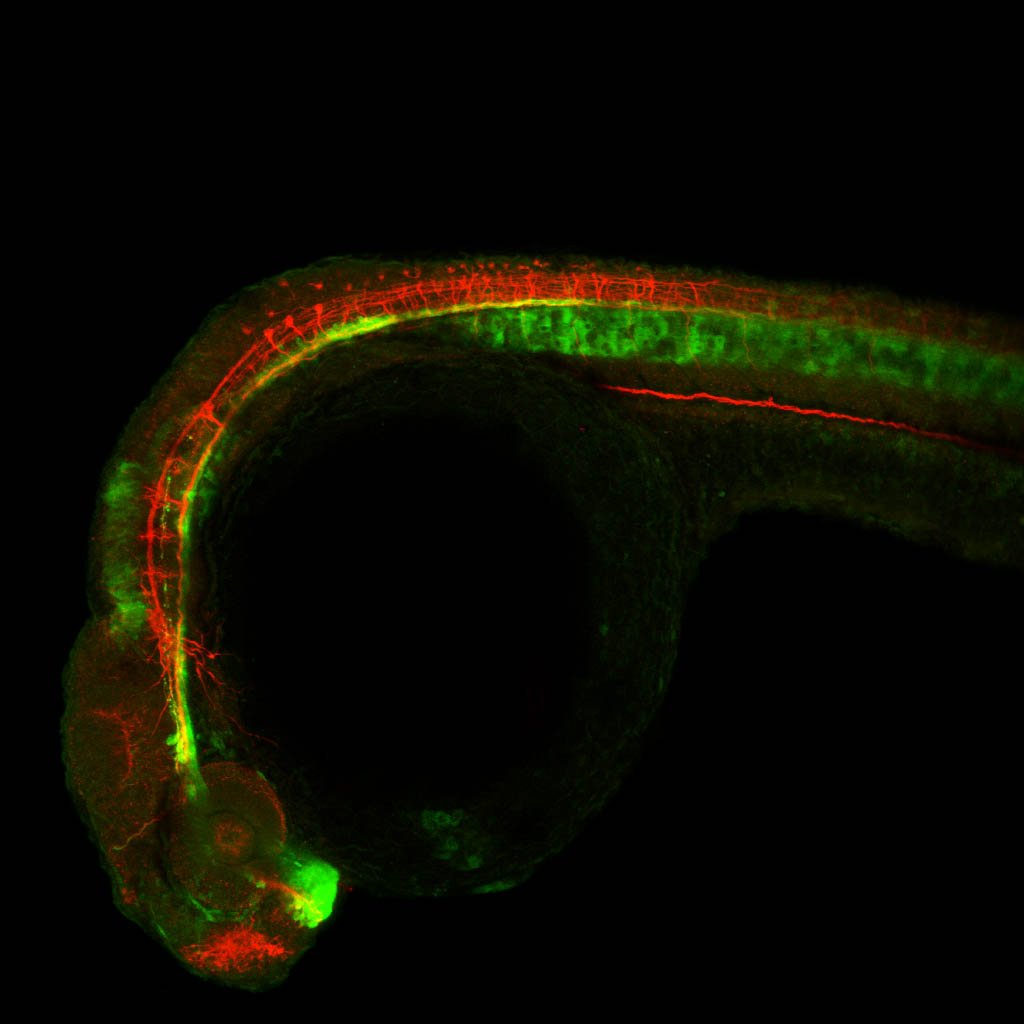
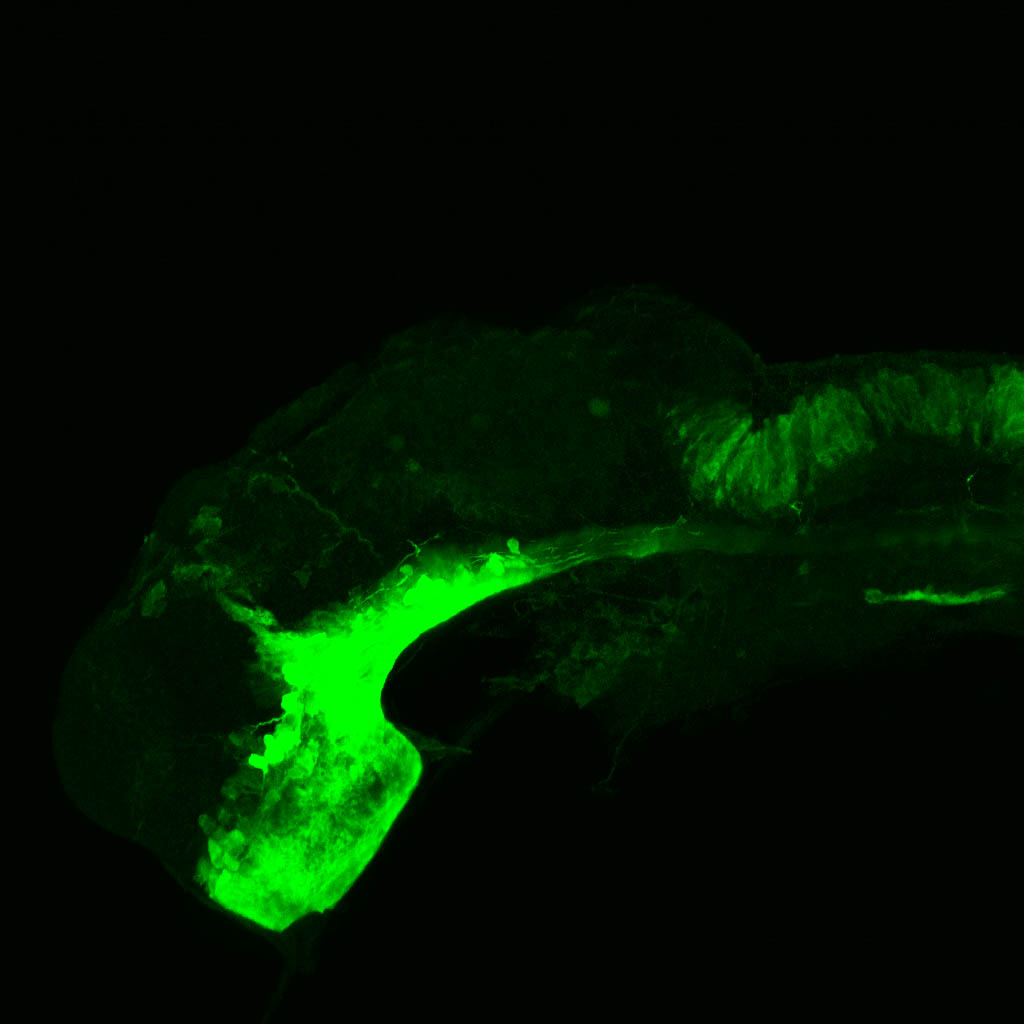
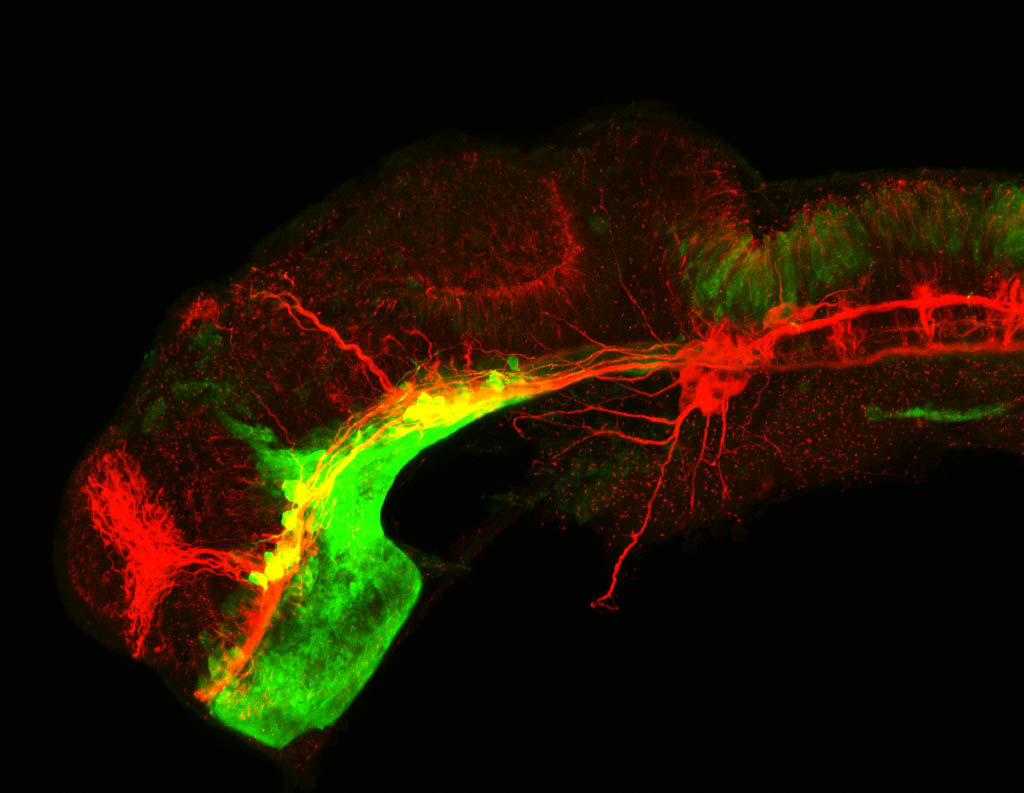
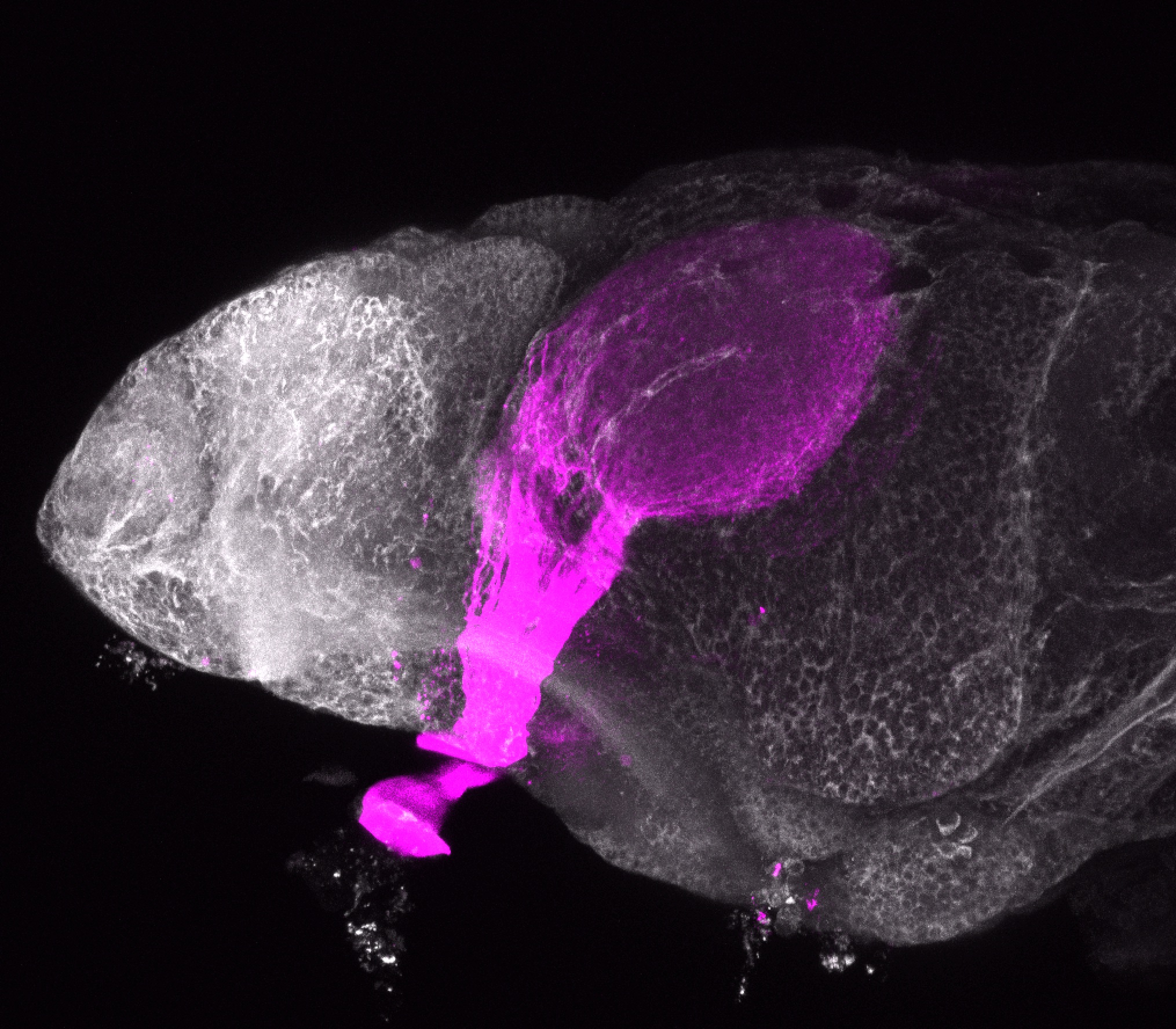
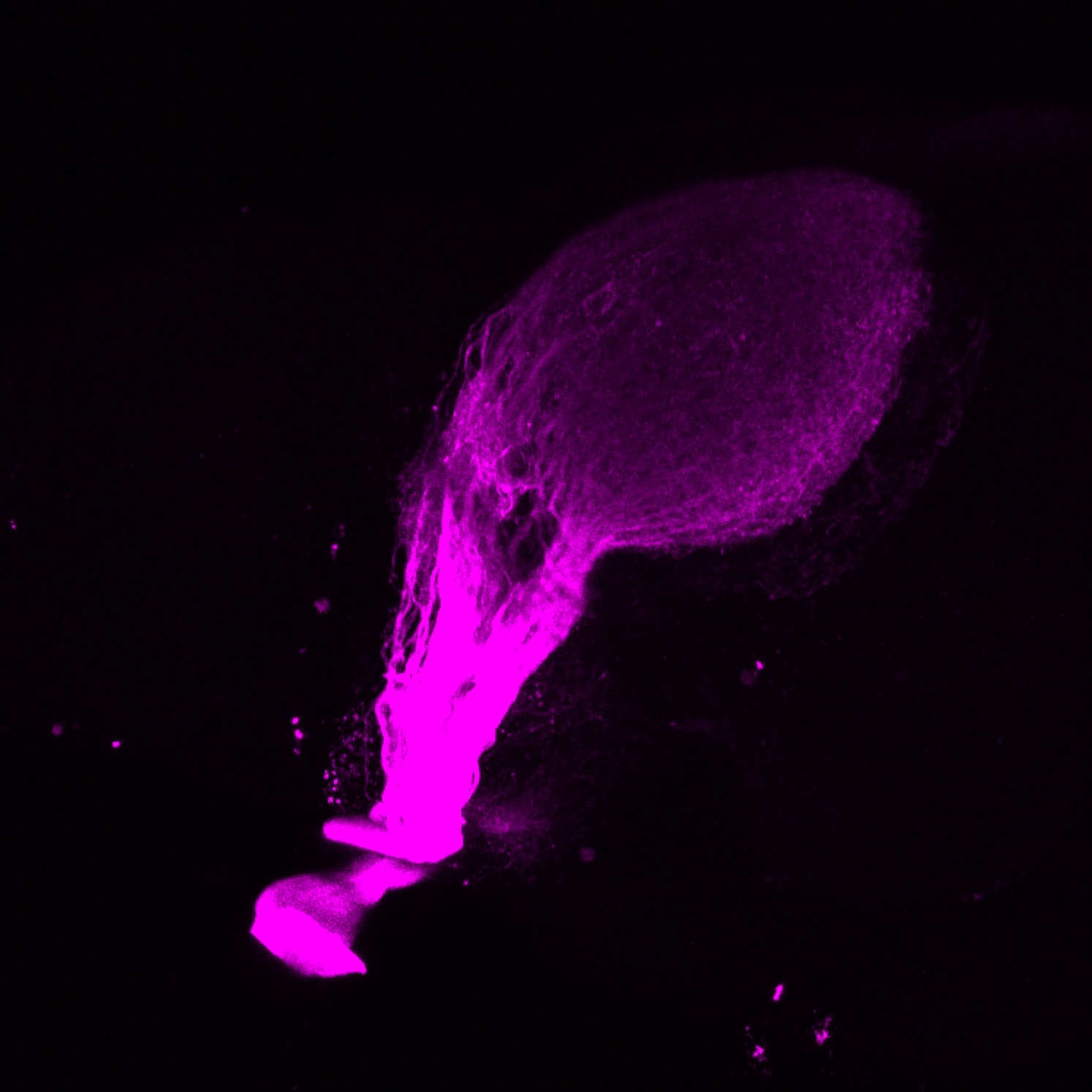
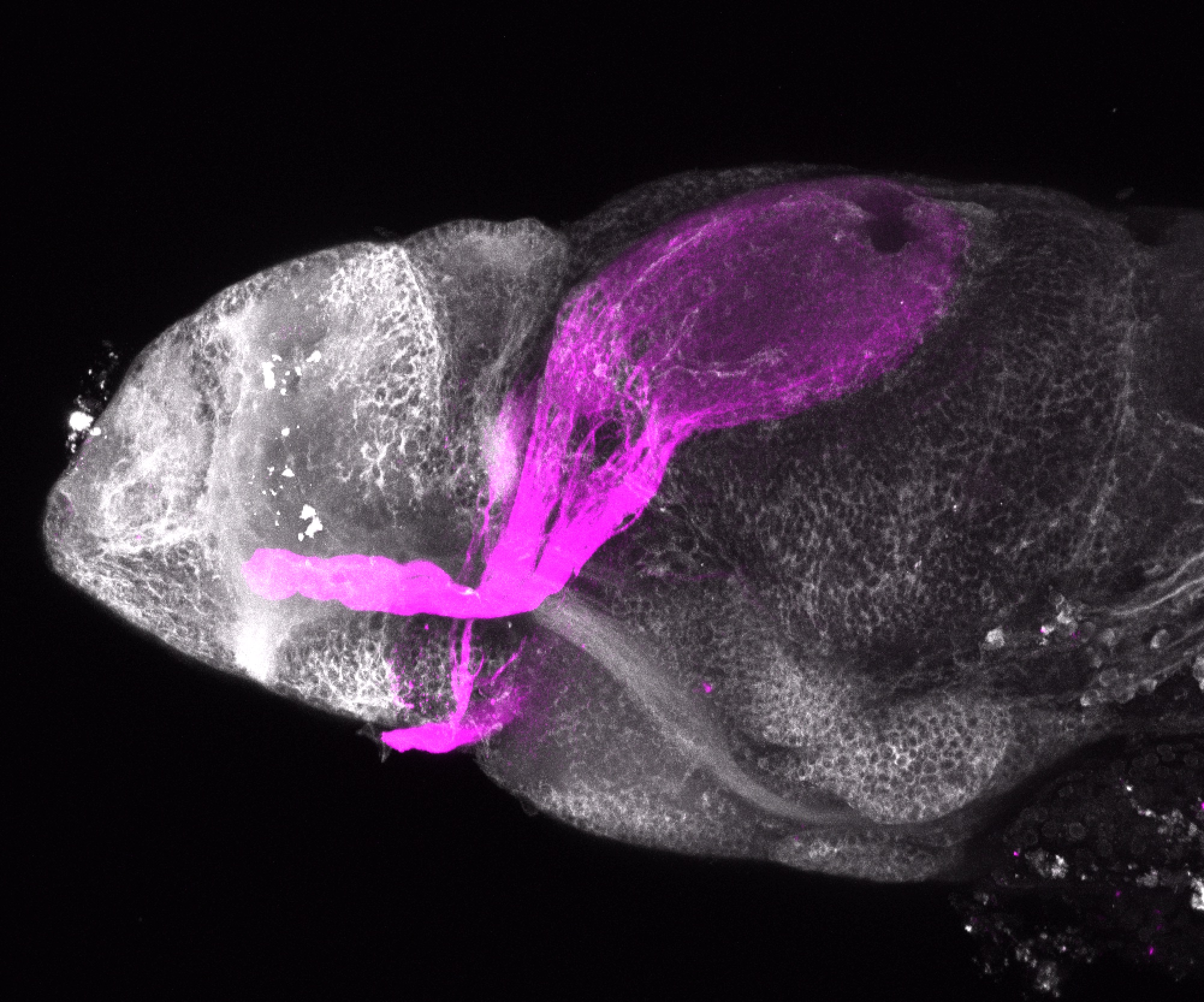
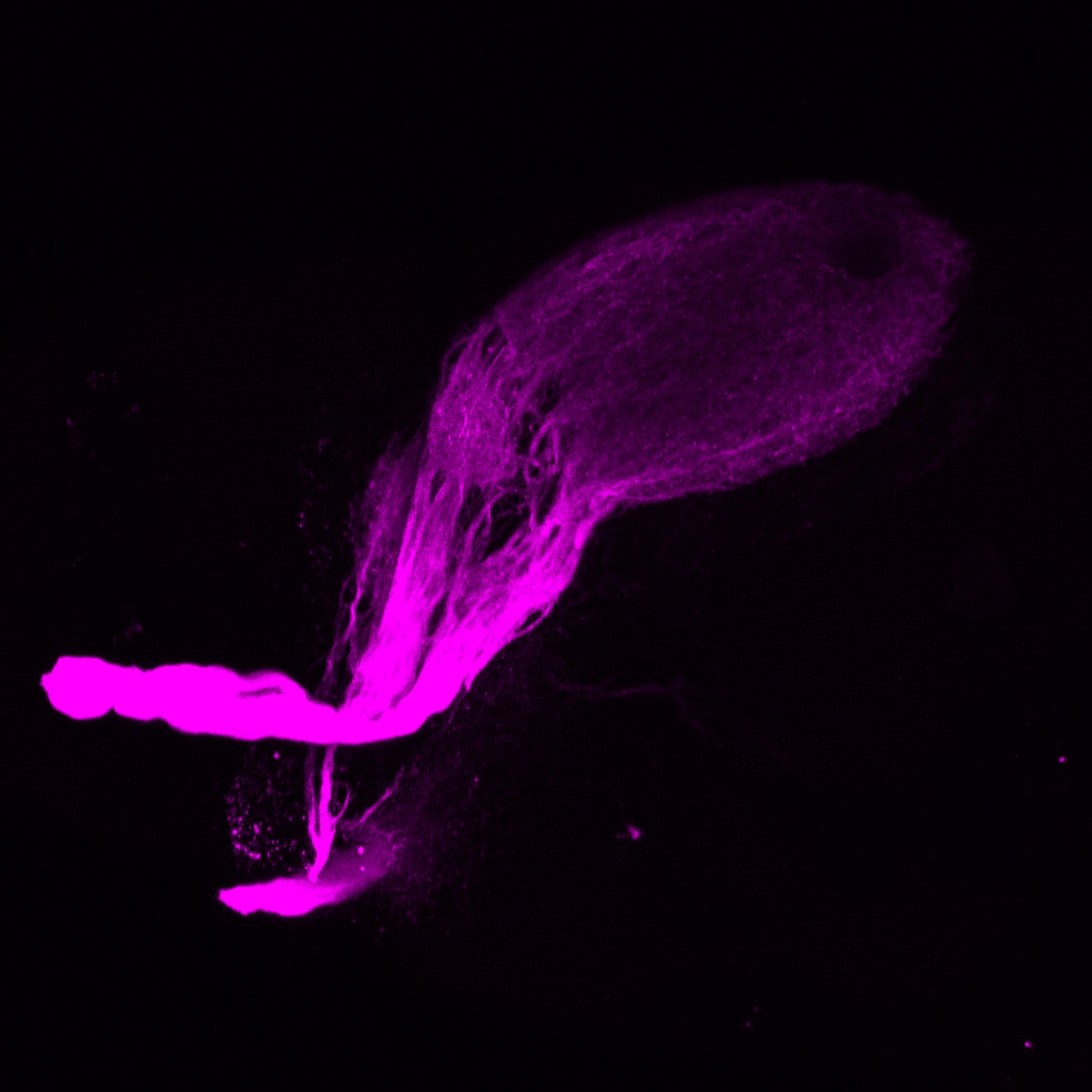
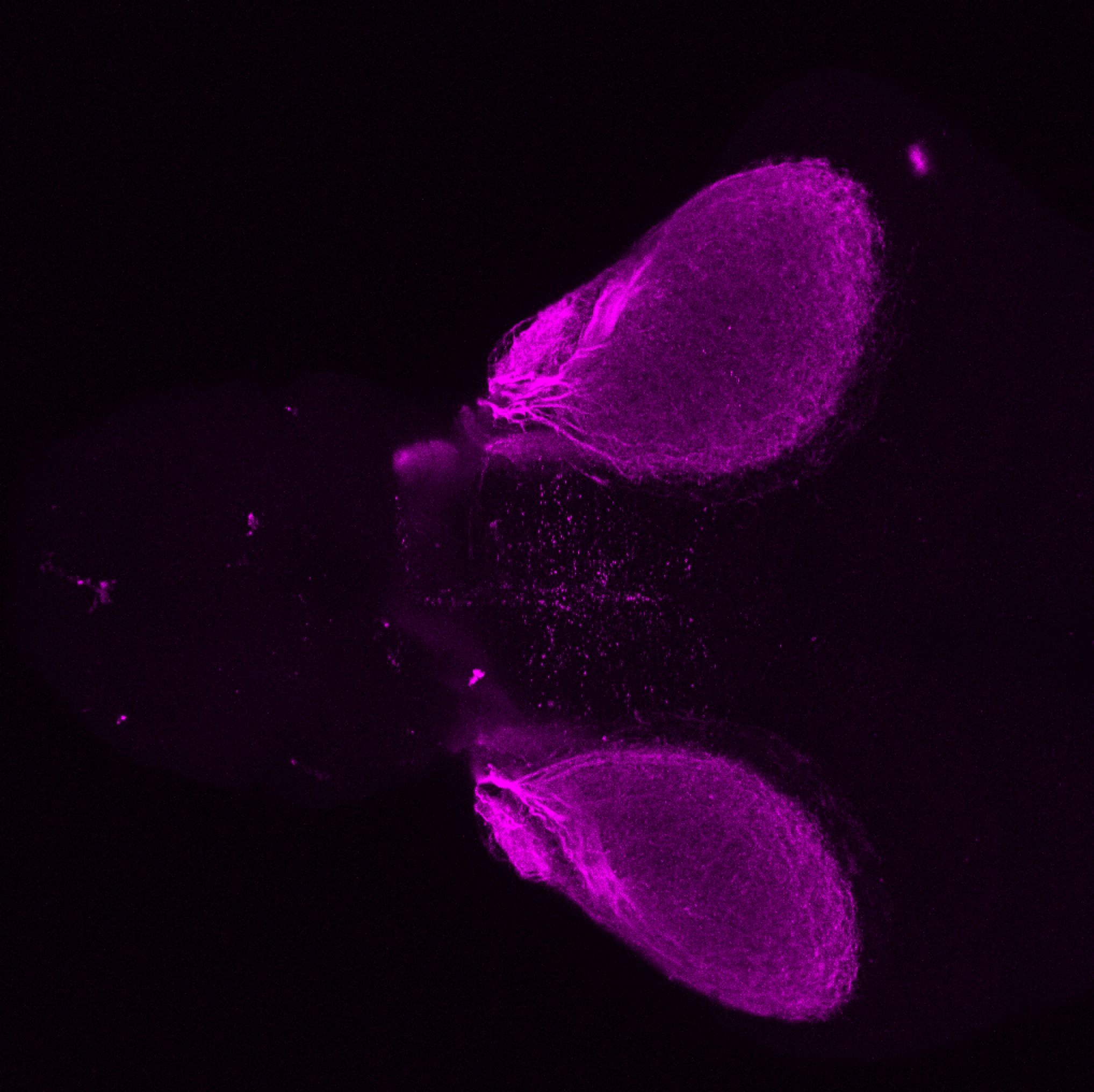
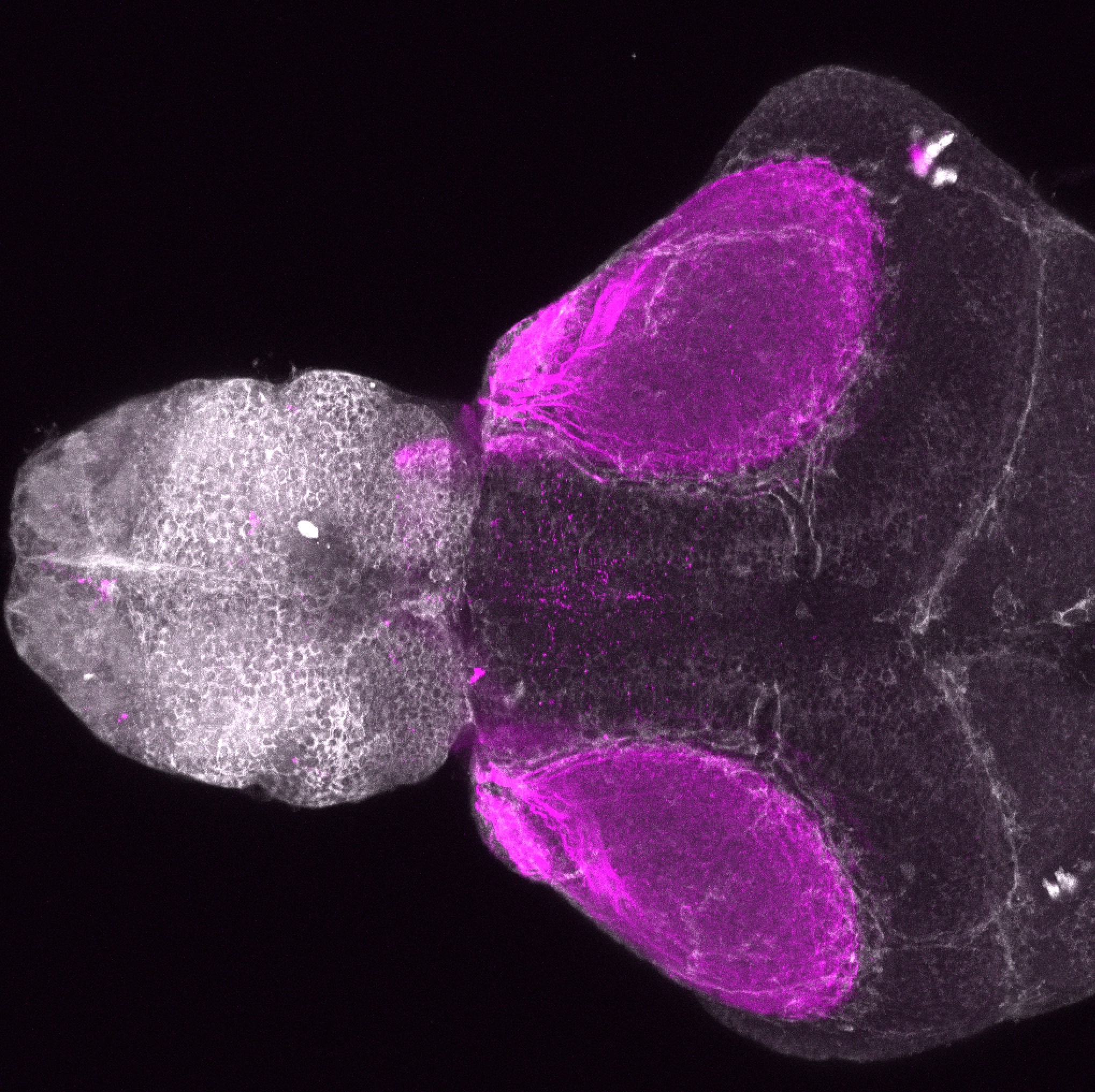
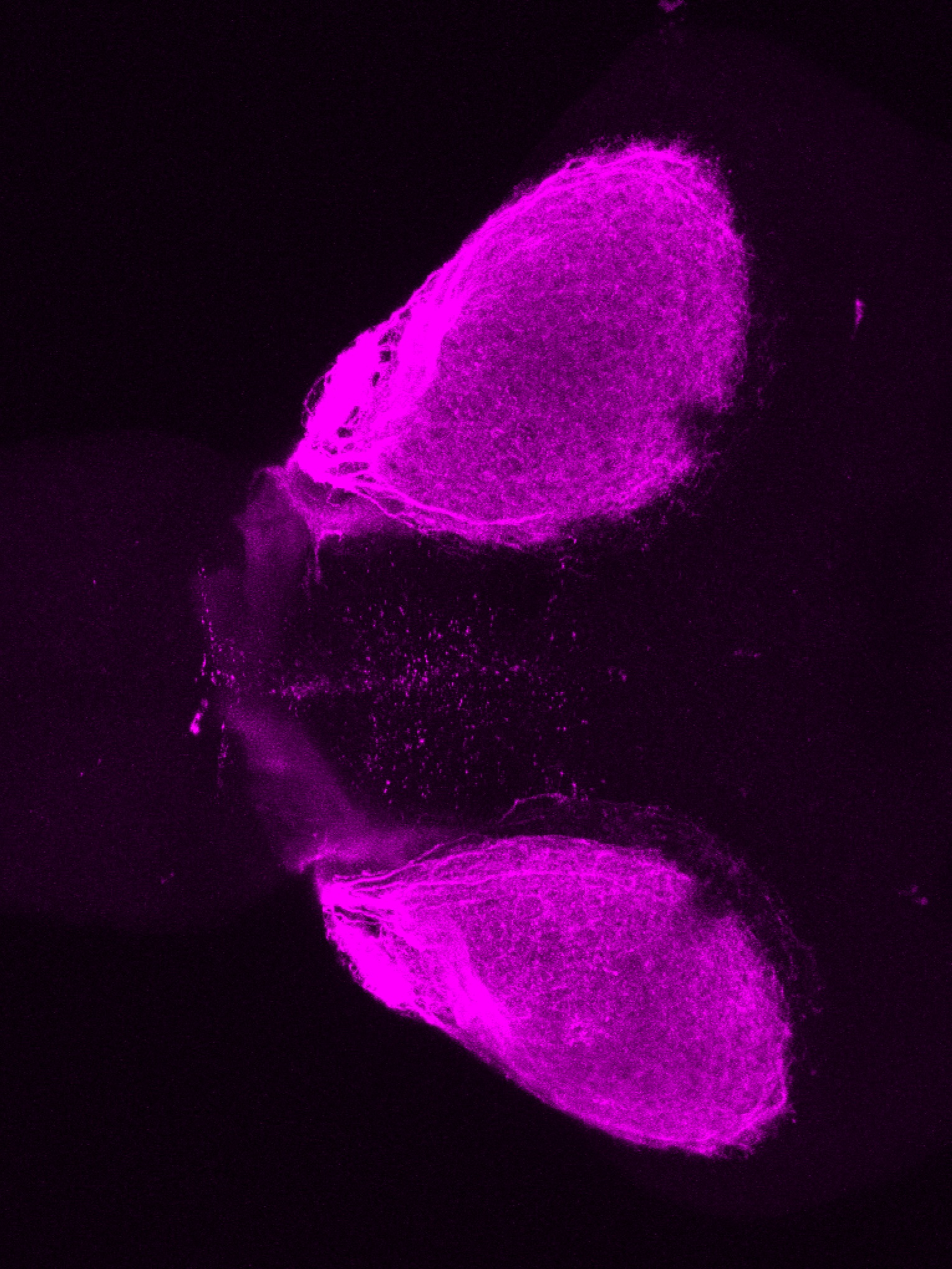
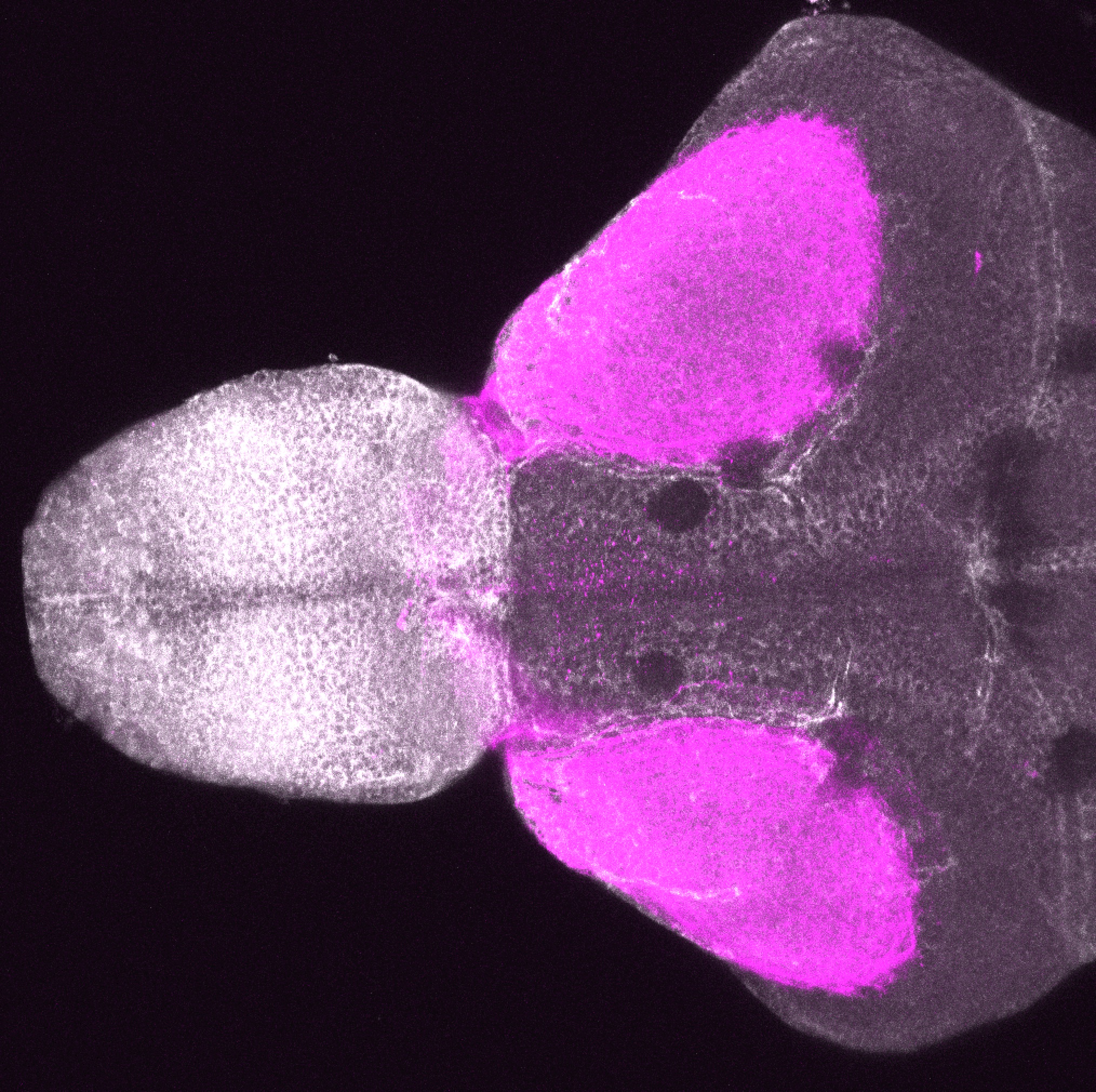
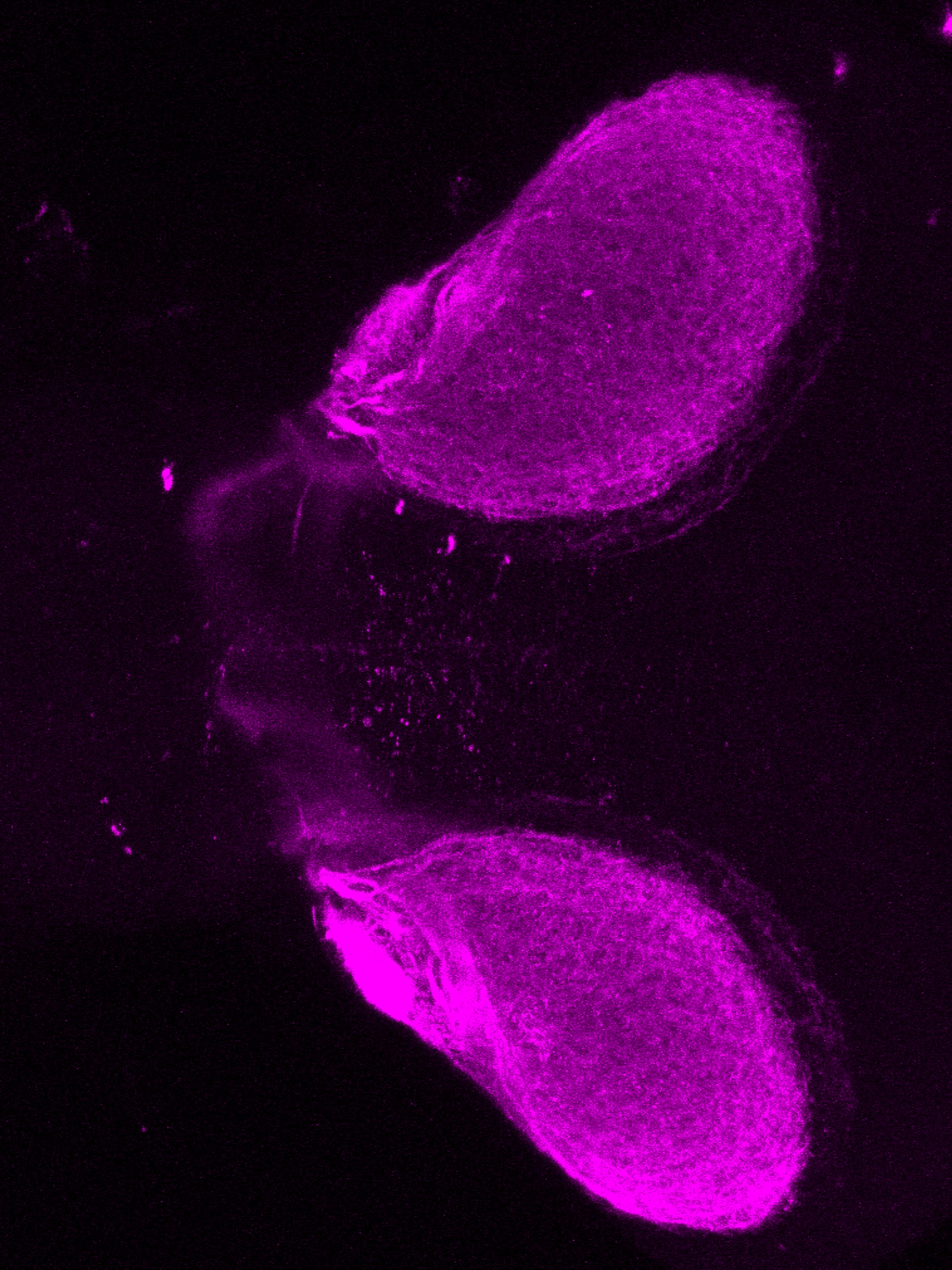
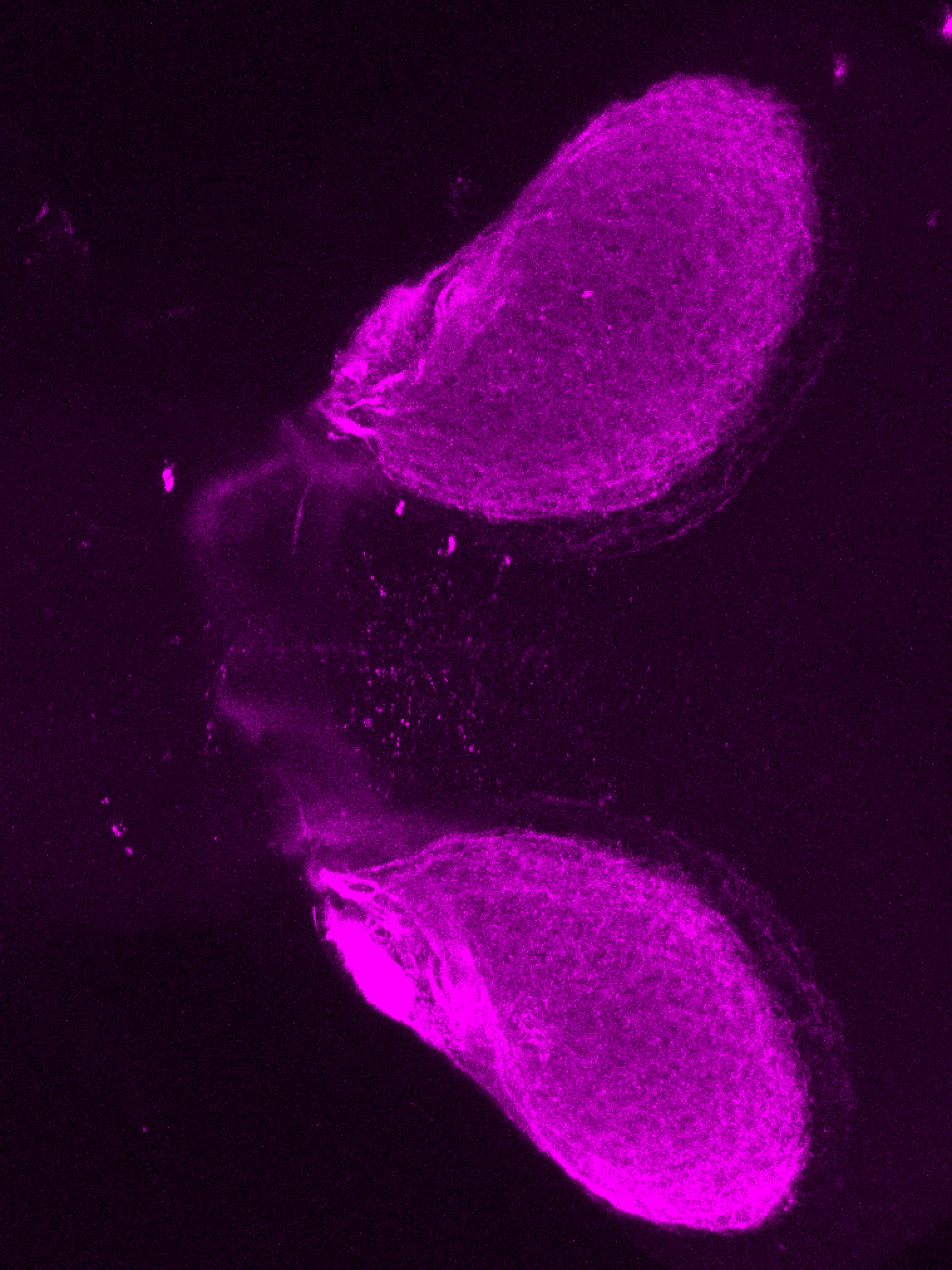
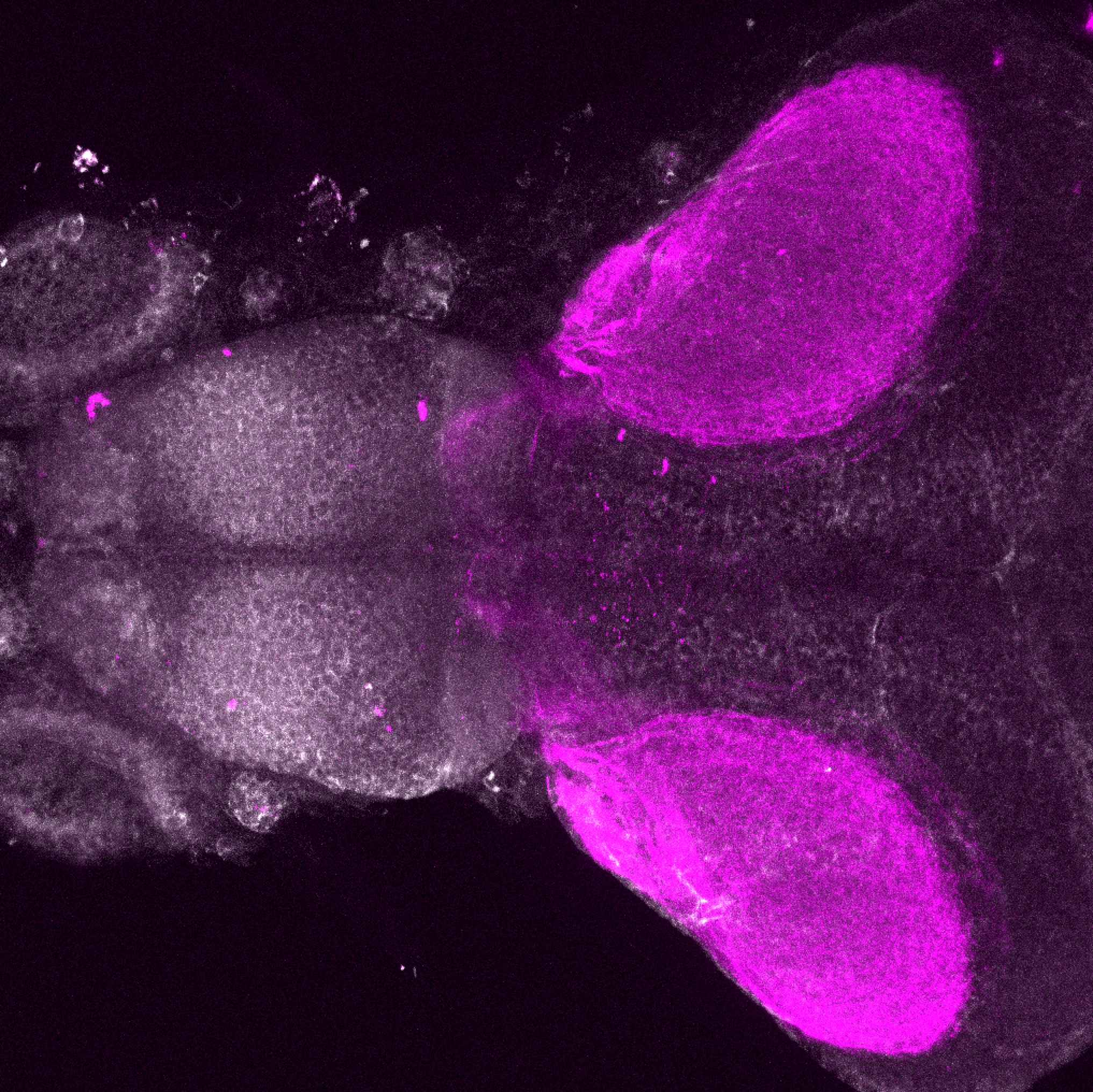
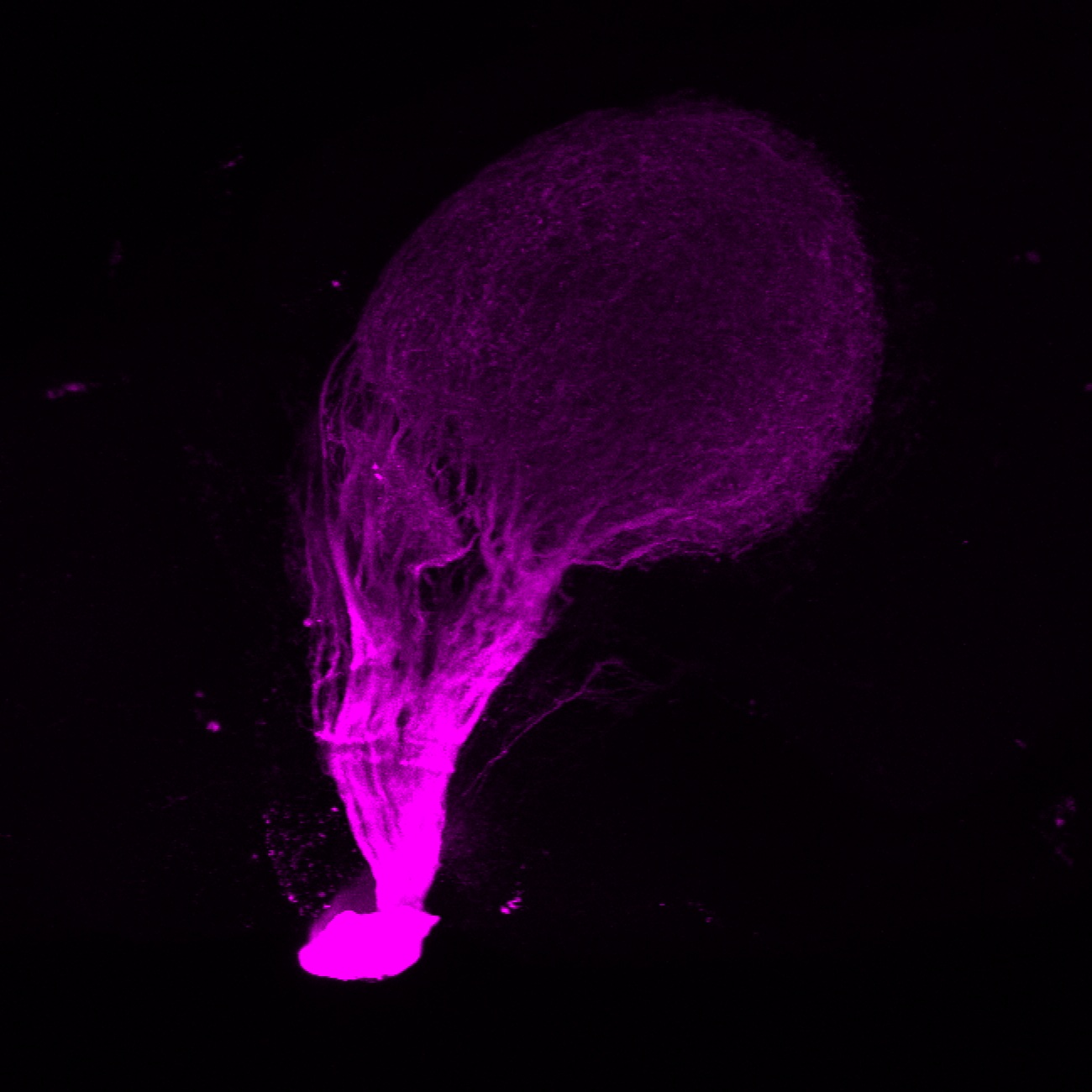
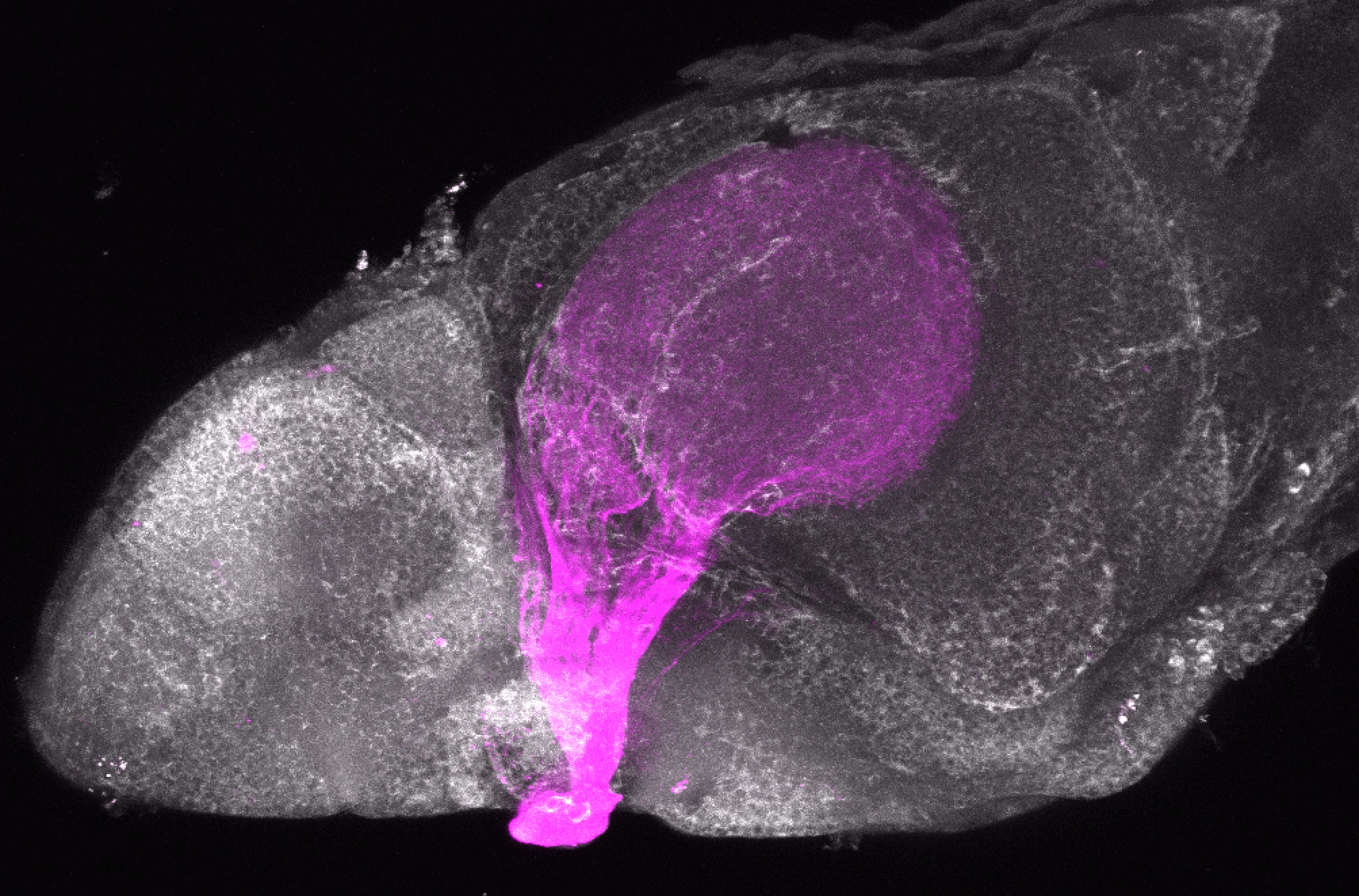
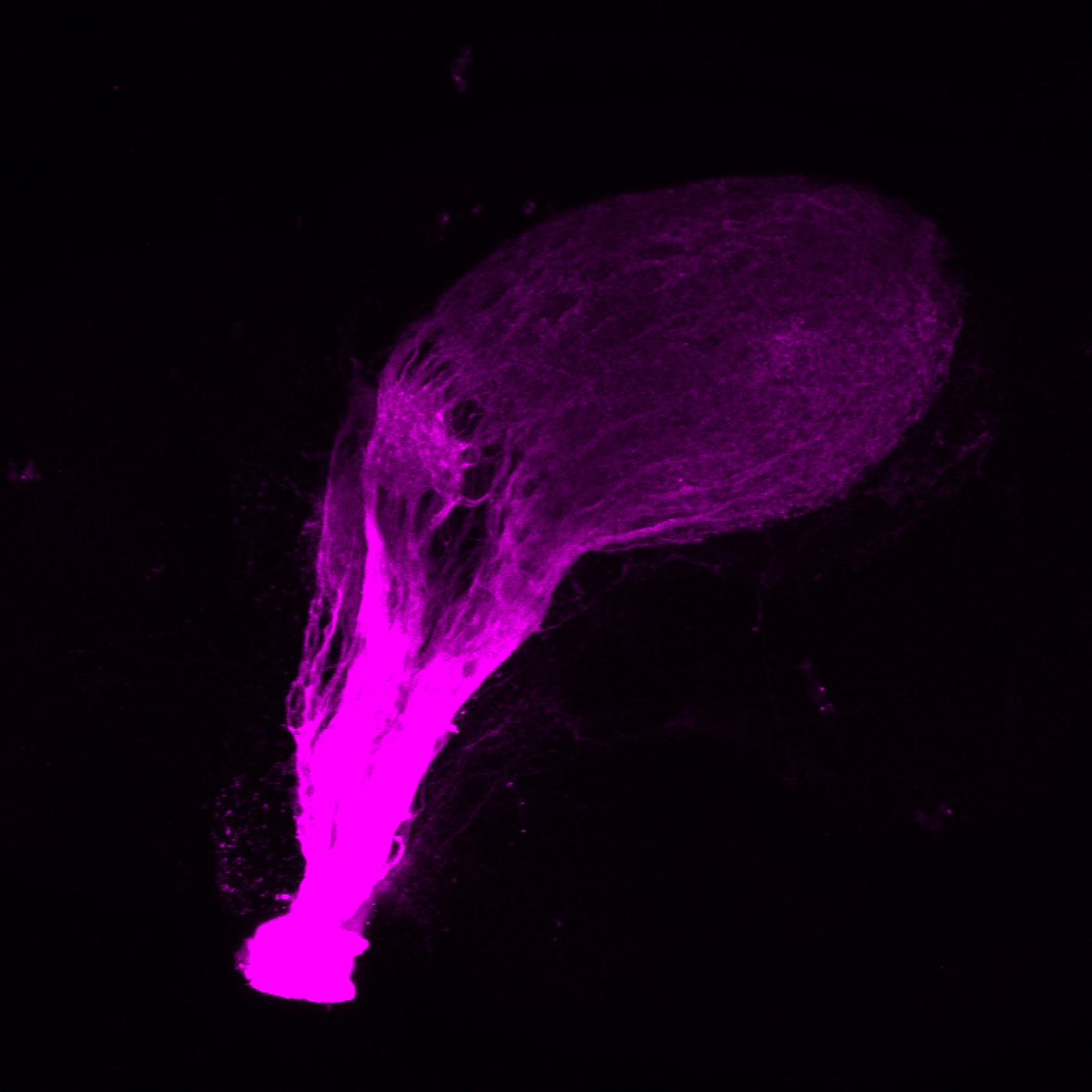
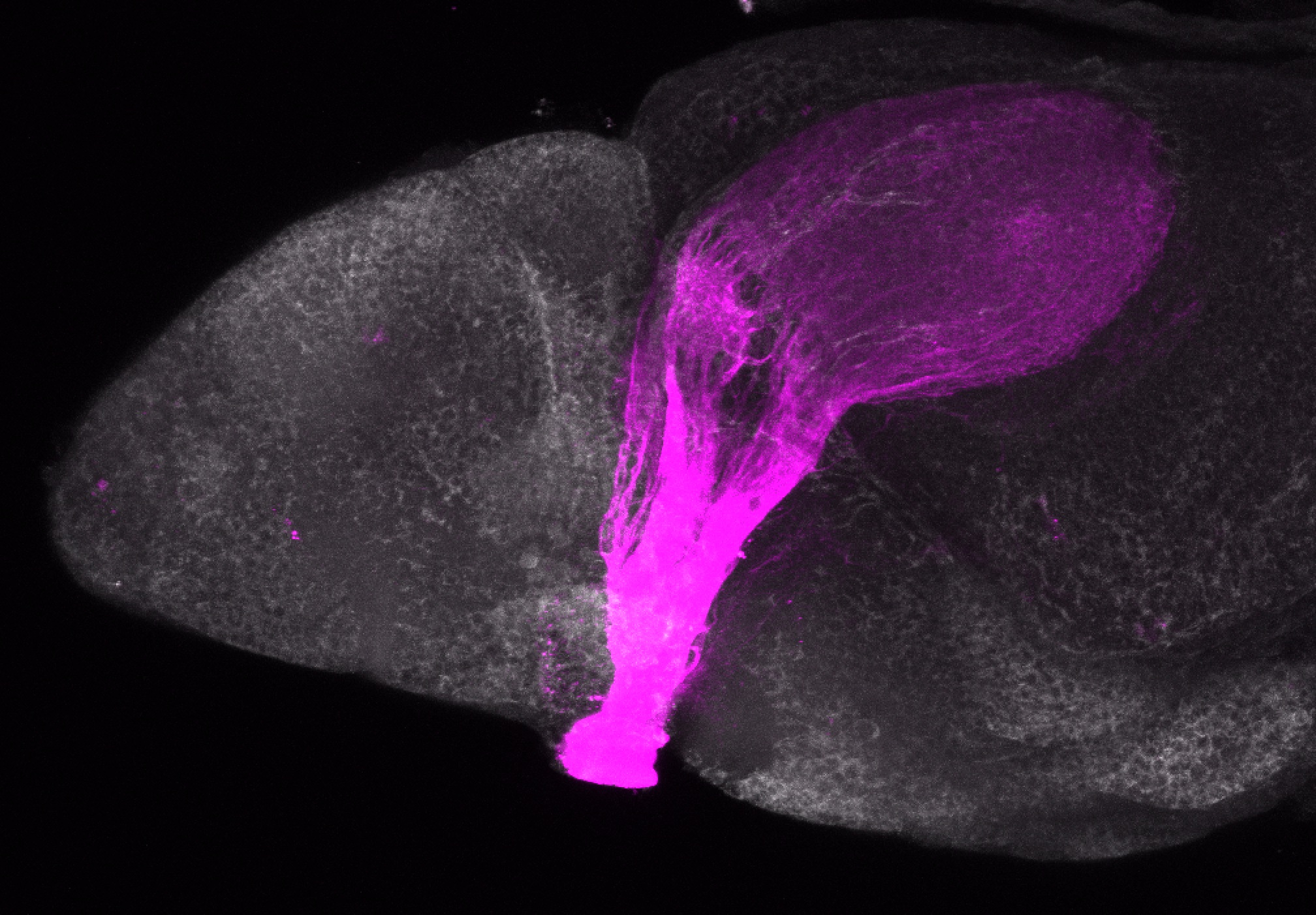
atonal bHLH transcription factor 7 is turned on in retinal ganglion cells as they transition from proliferating neuroblast to differentiated neuron. The atoh7 promoter in this transgenic line drives the expression of a membrane tagged version of RFP so the axons of the RGCs are also labelled so the optic nerve and tract projecting from the retina to the optic tectum can be distinguished.
Expressed in:
Retinal ganglion cells, cilliary marginal zone, retina, optic nerve. optic tract, optic tectum.
Key Publications
Zolessi, F.R., Poggi, L., Wilkinson, C.J., Chien, C.B., and Harris, W.A. (2006)
Polarization and orientation of retinal ganglion cells in vivo.
Neural Development. 1:2.