About
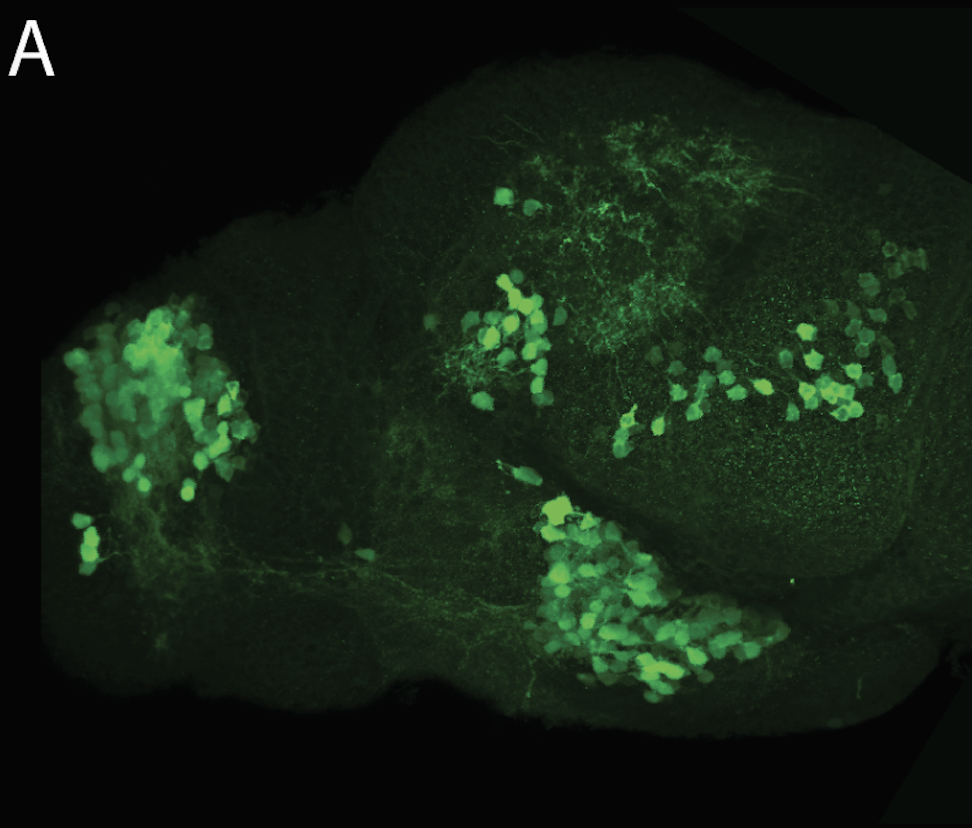
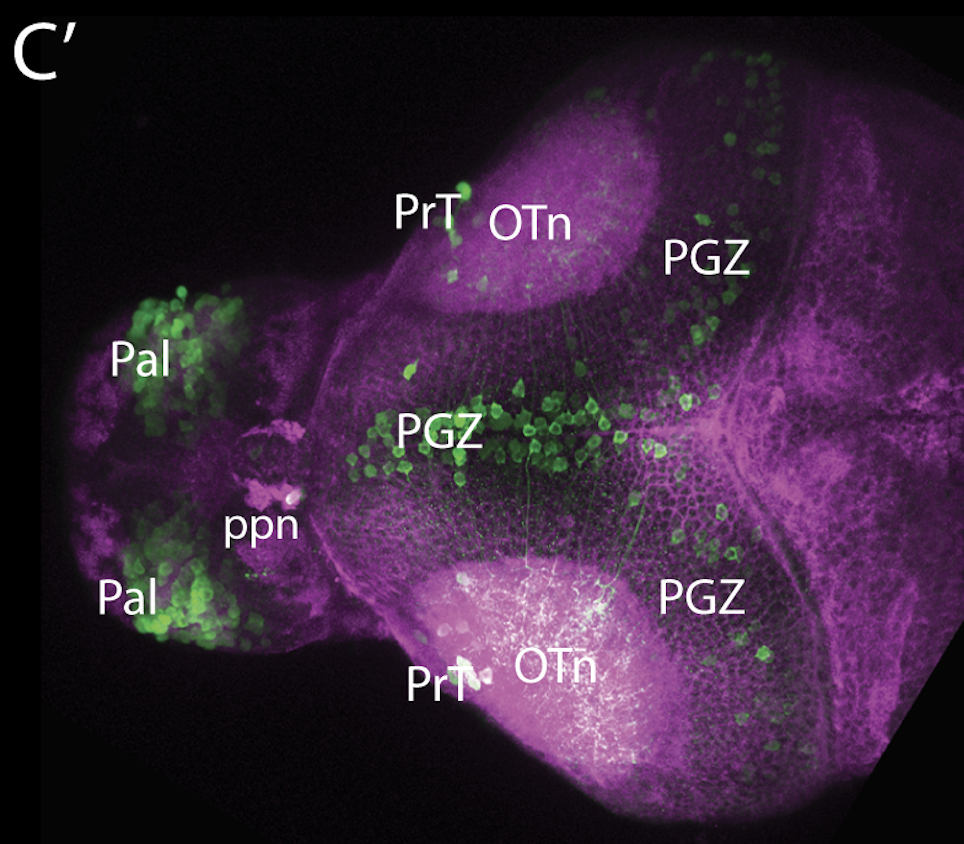
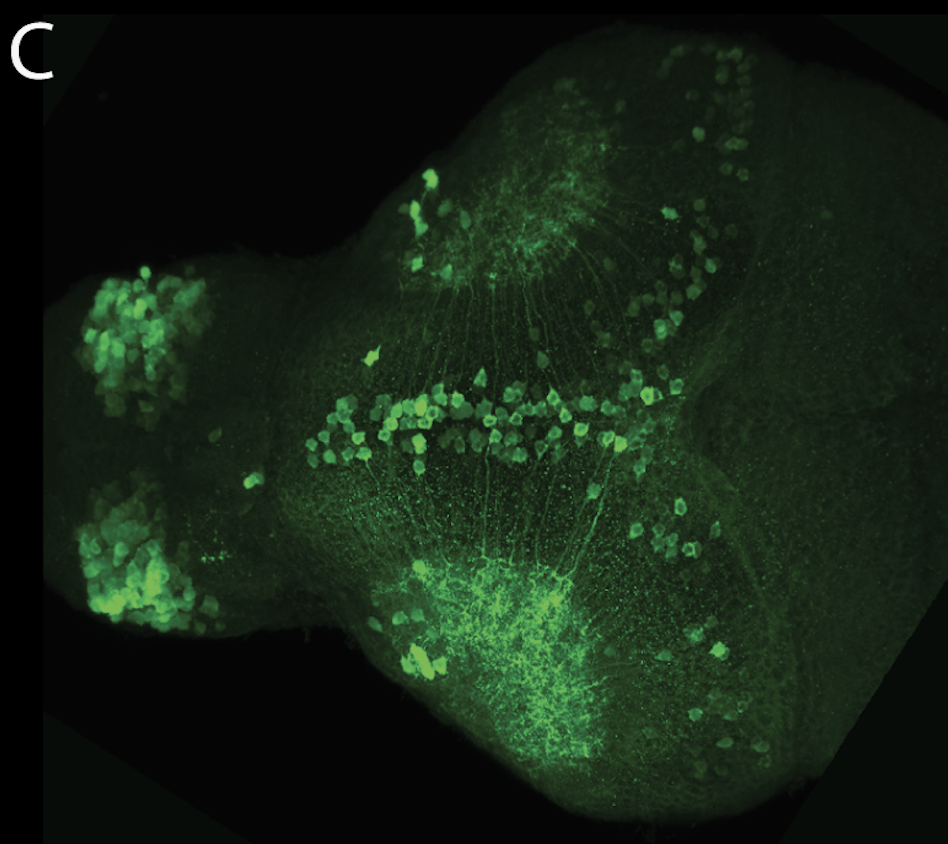
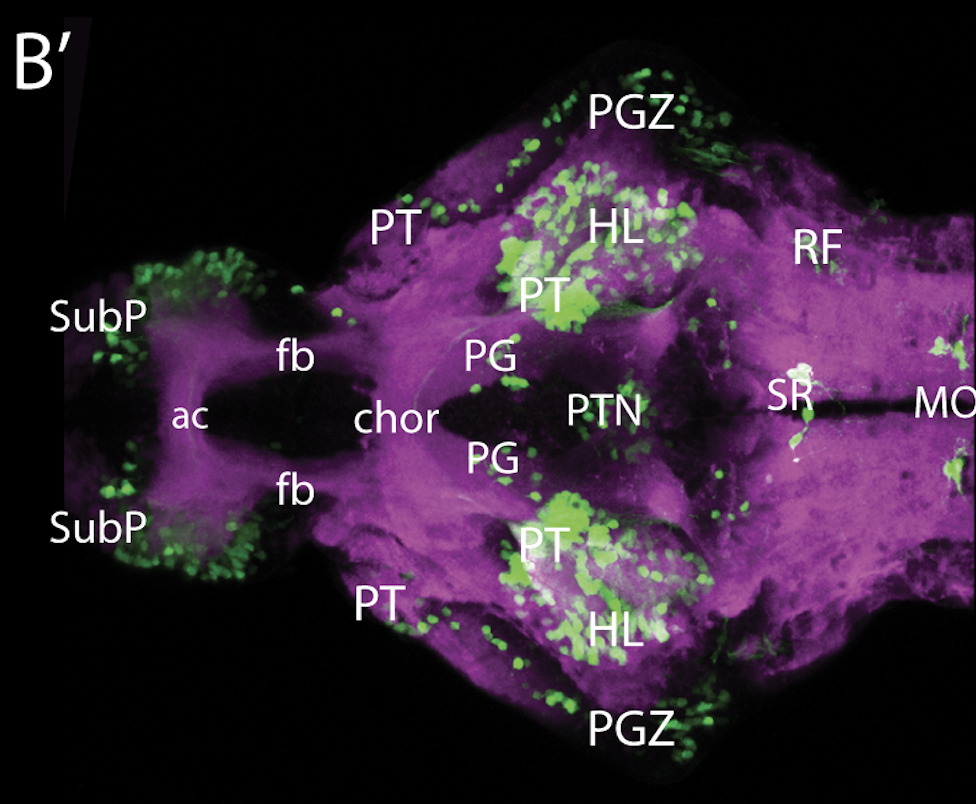
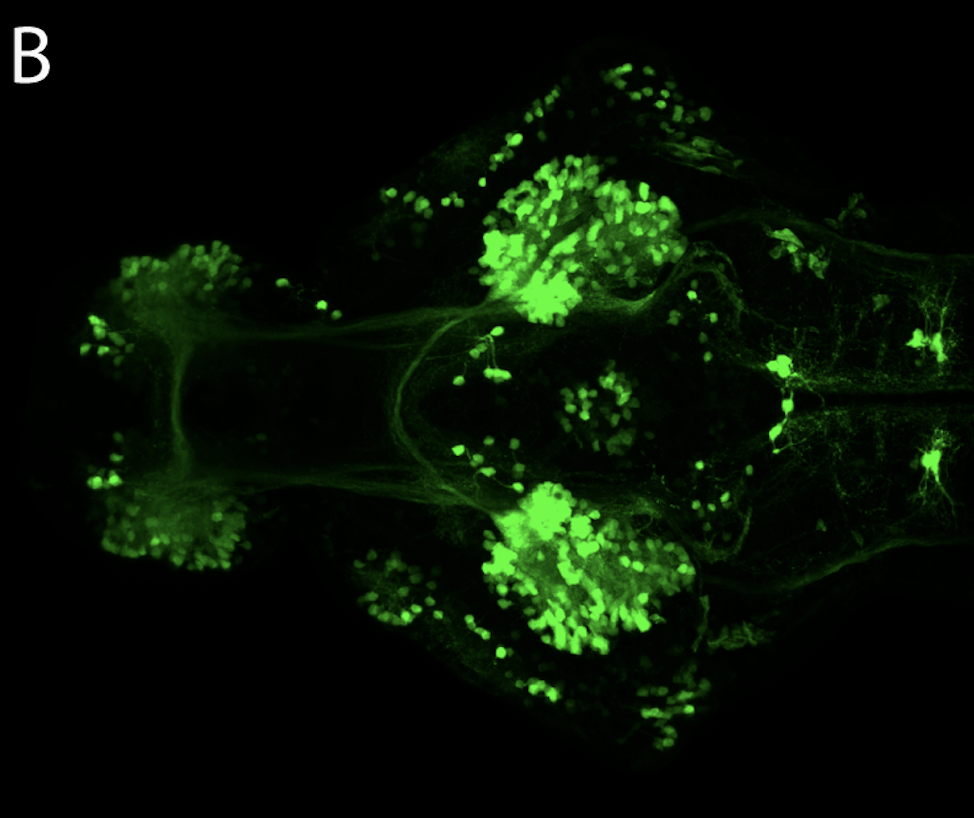
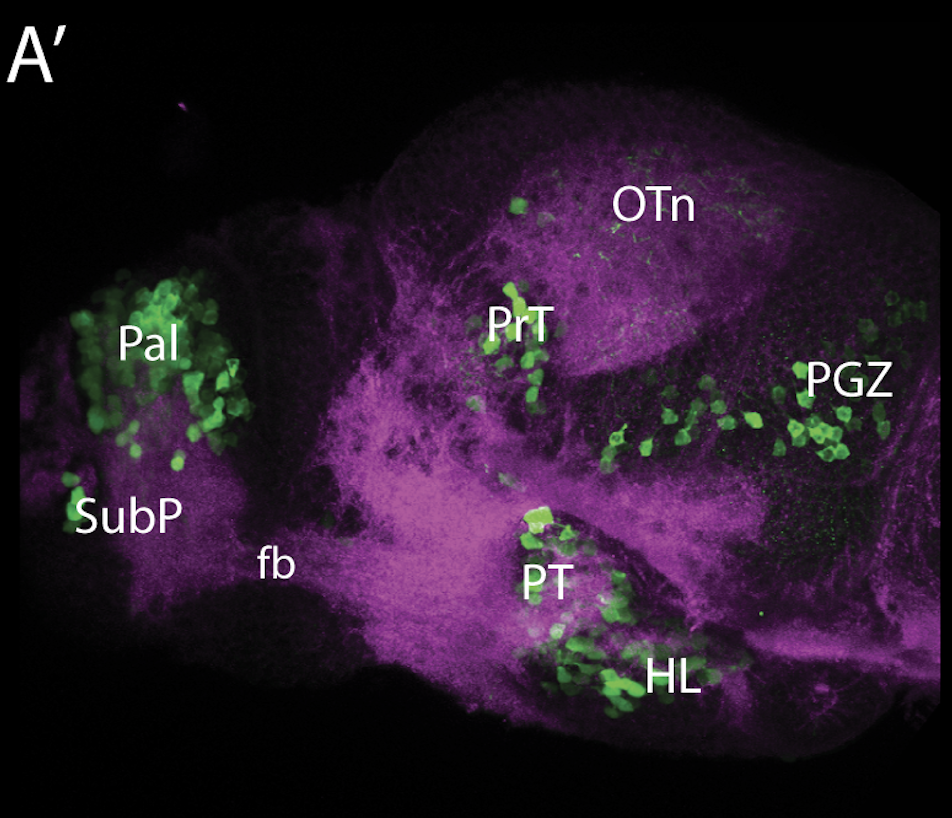
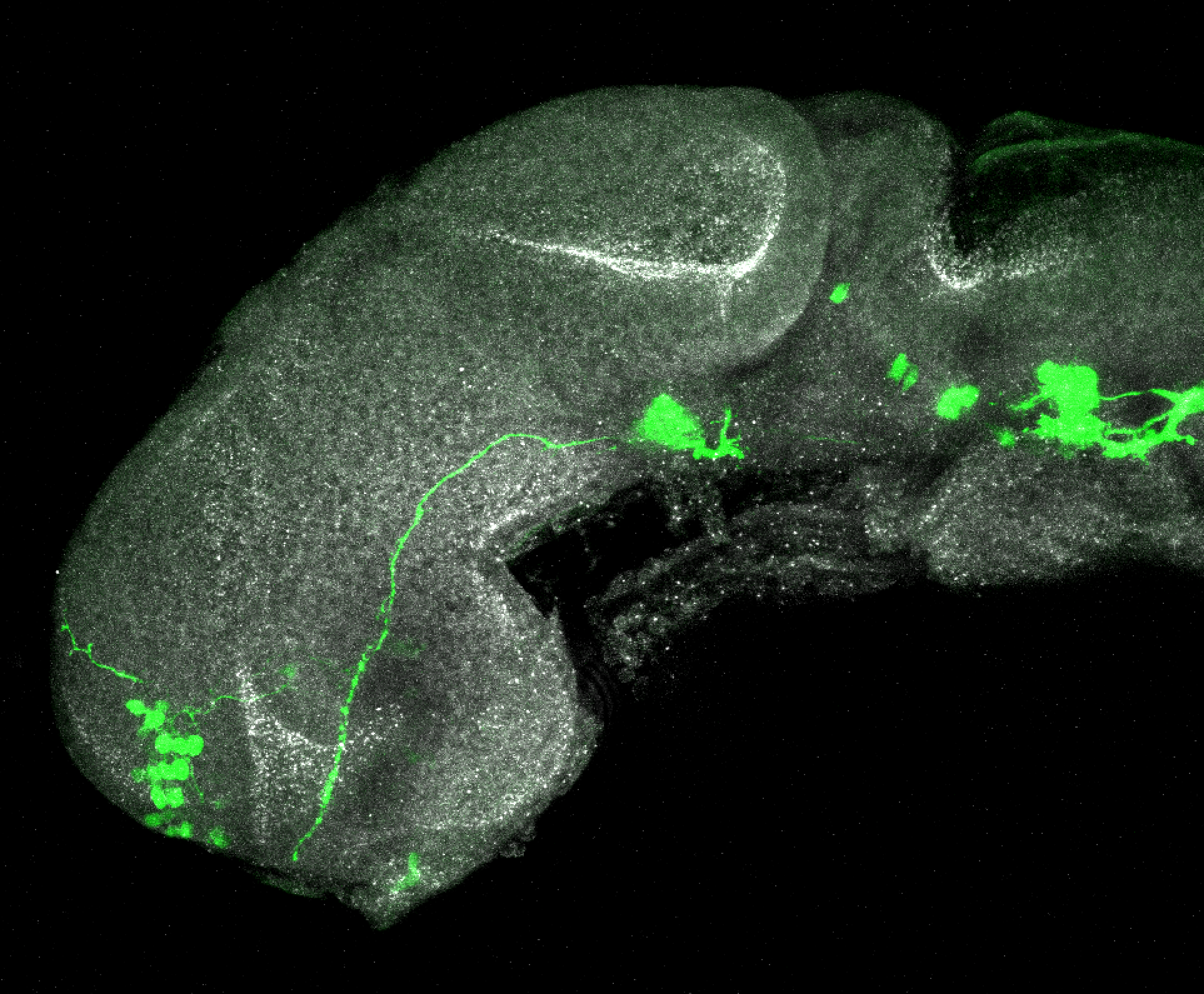
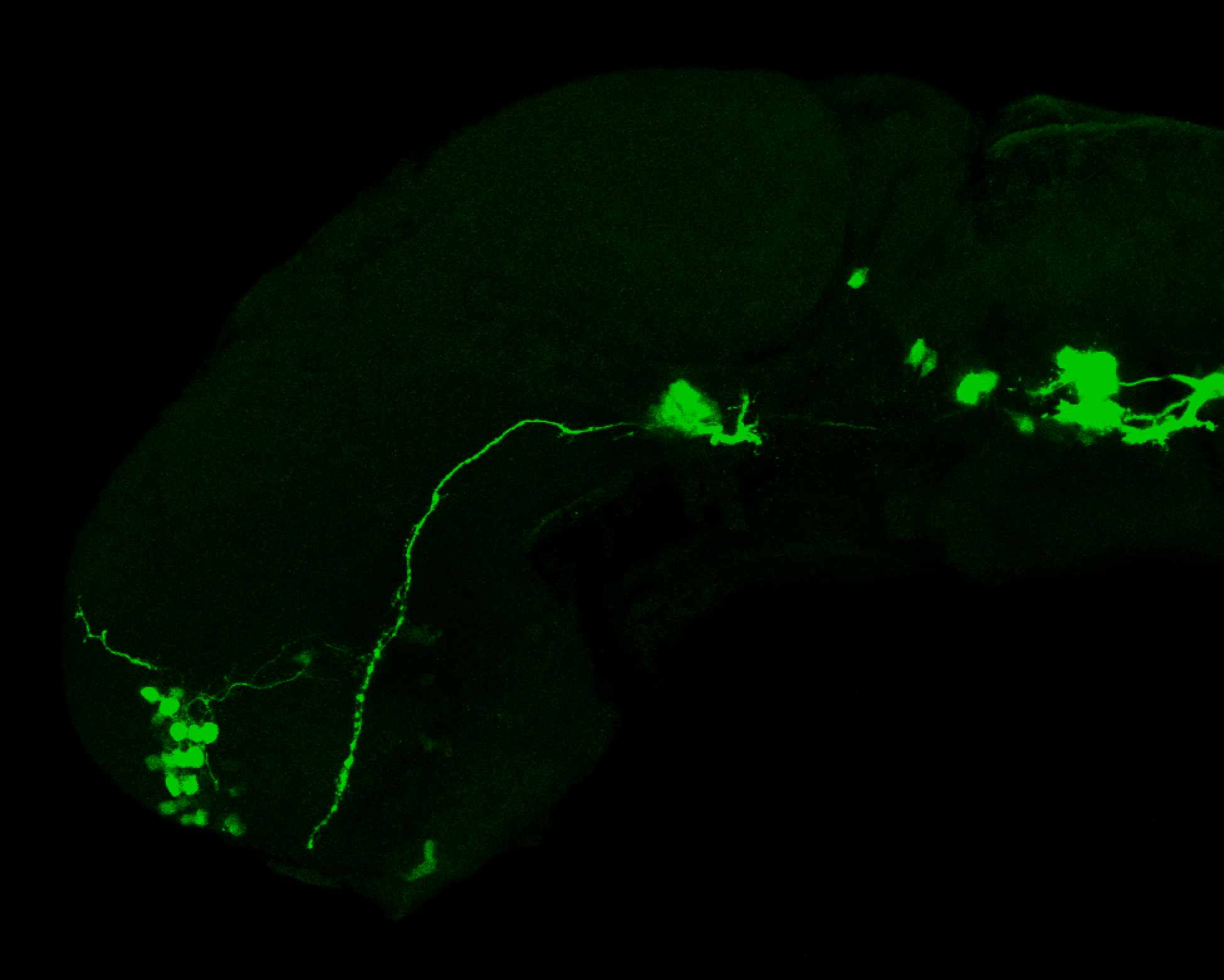
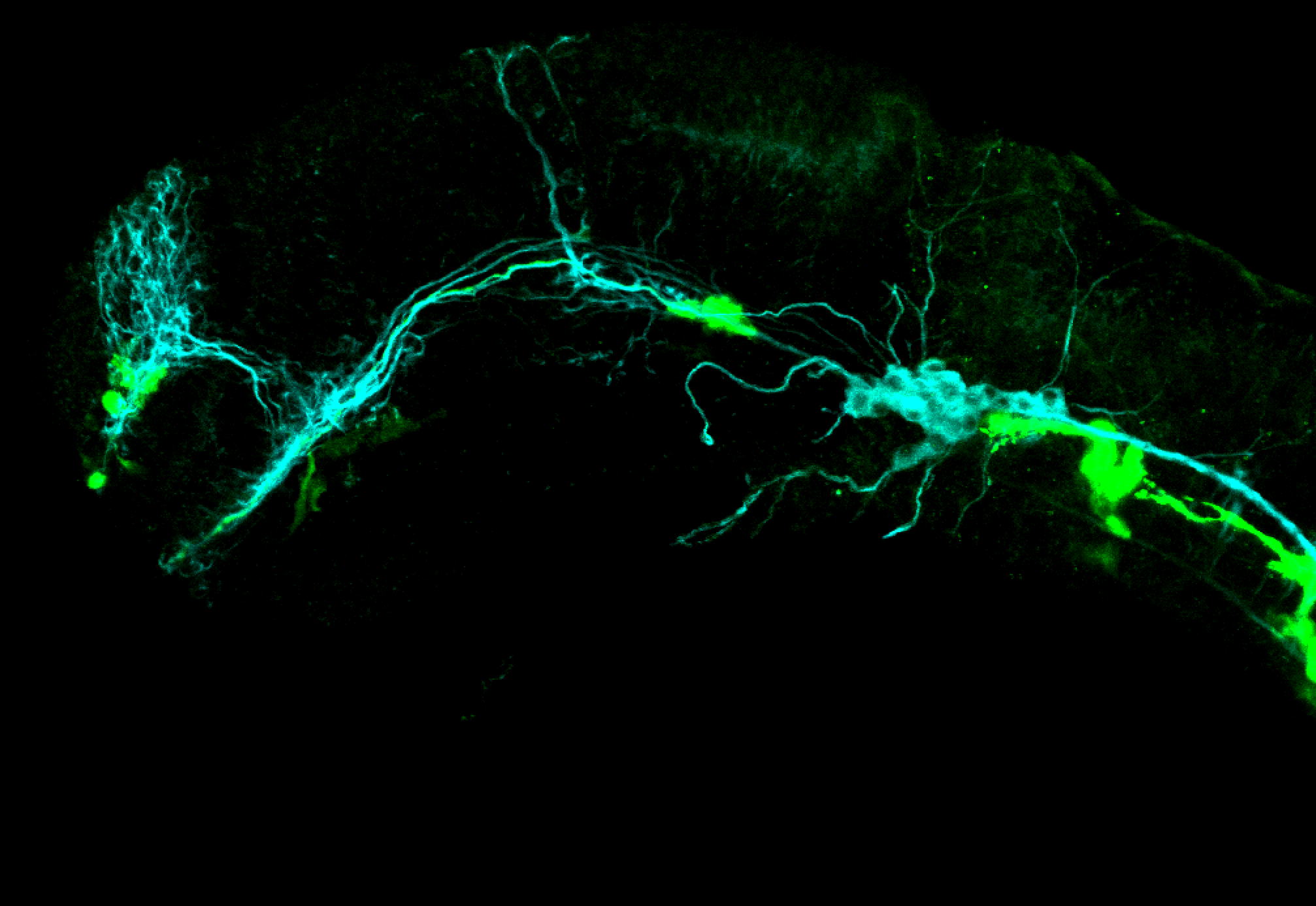
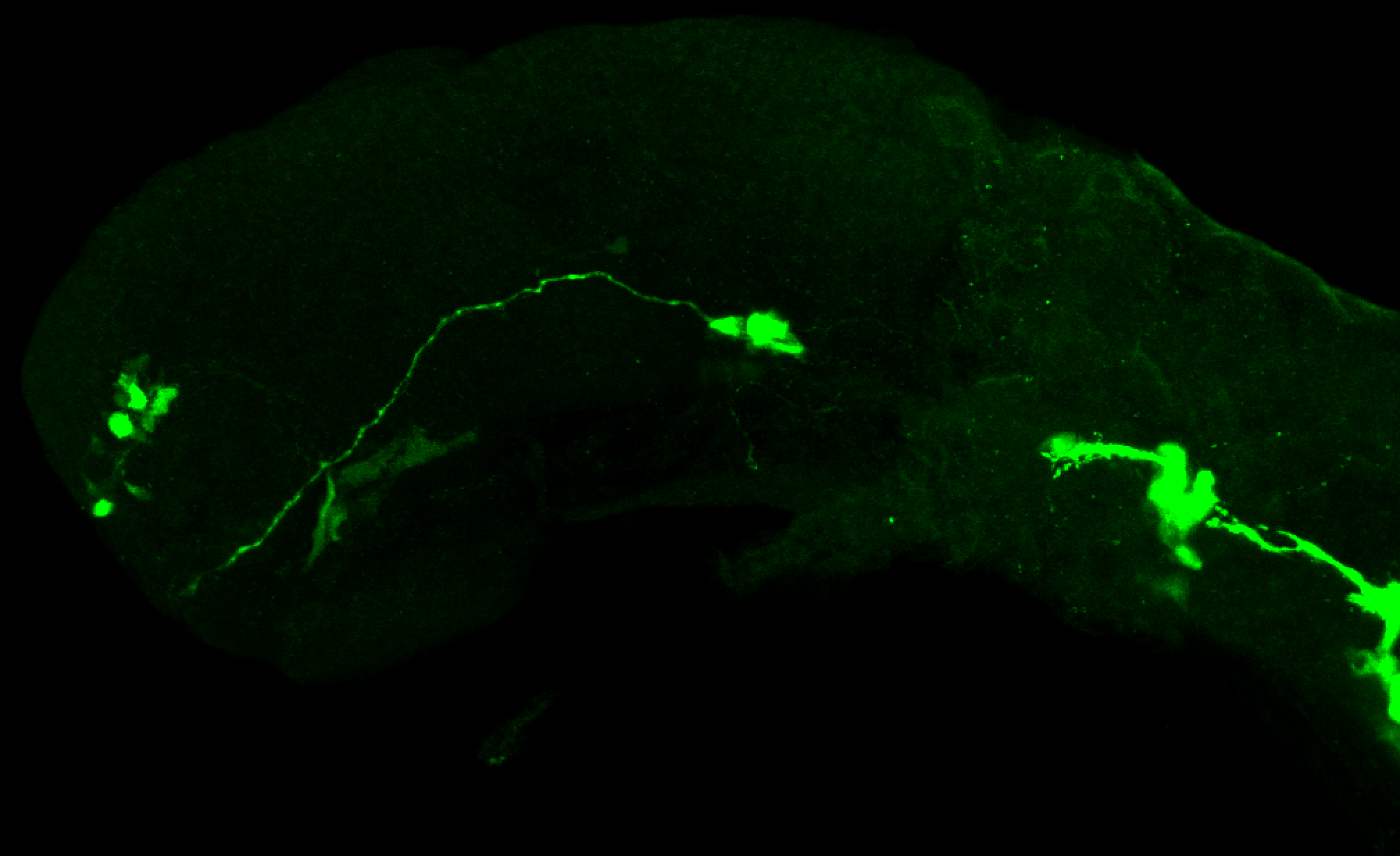
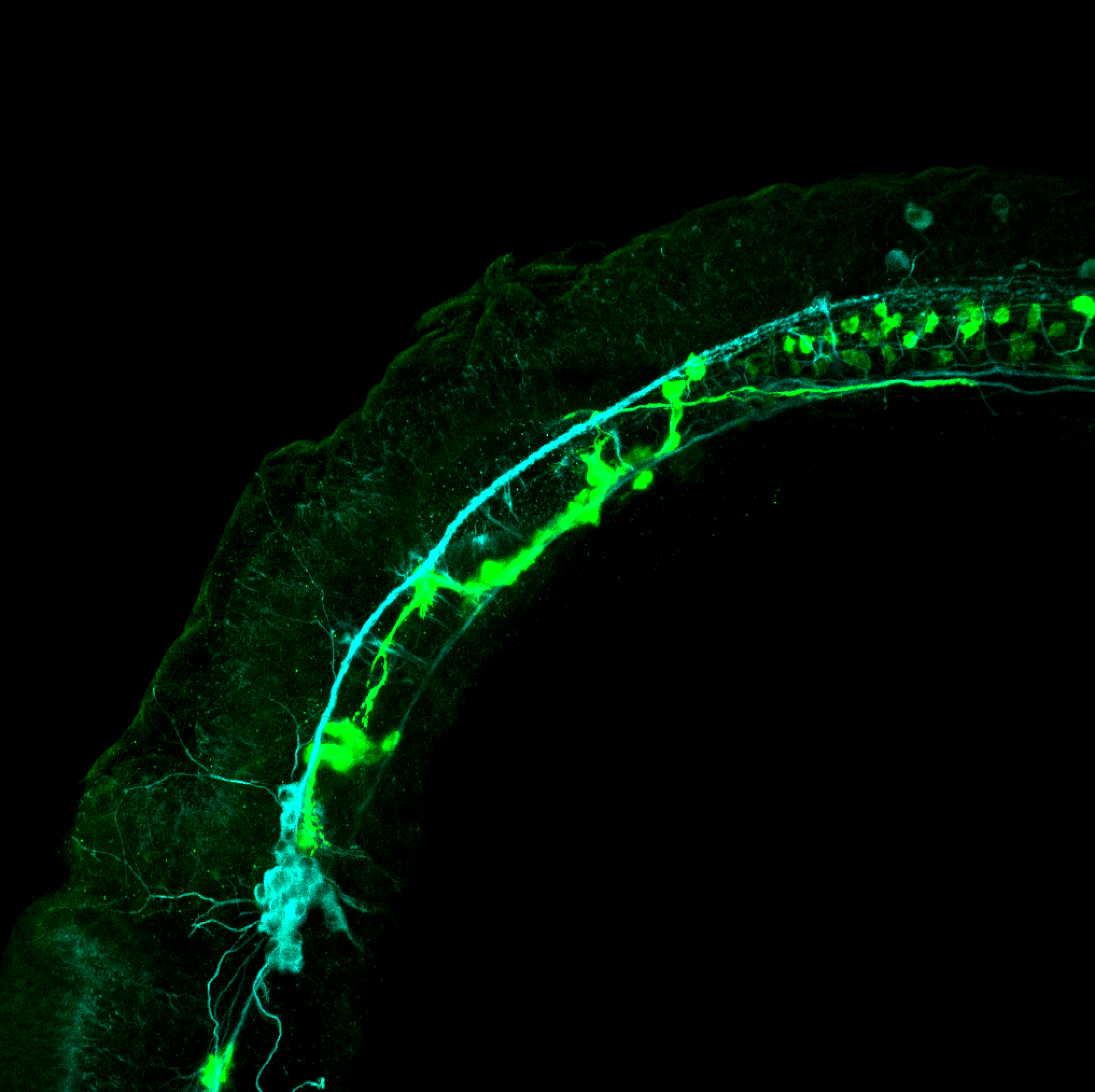
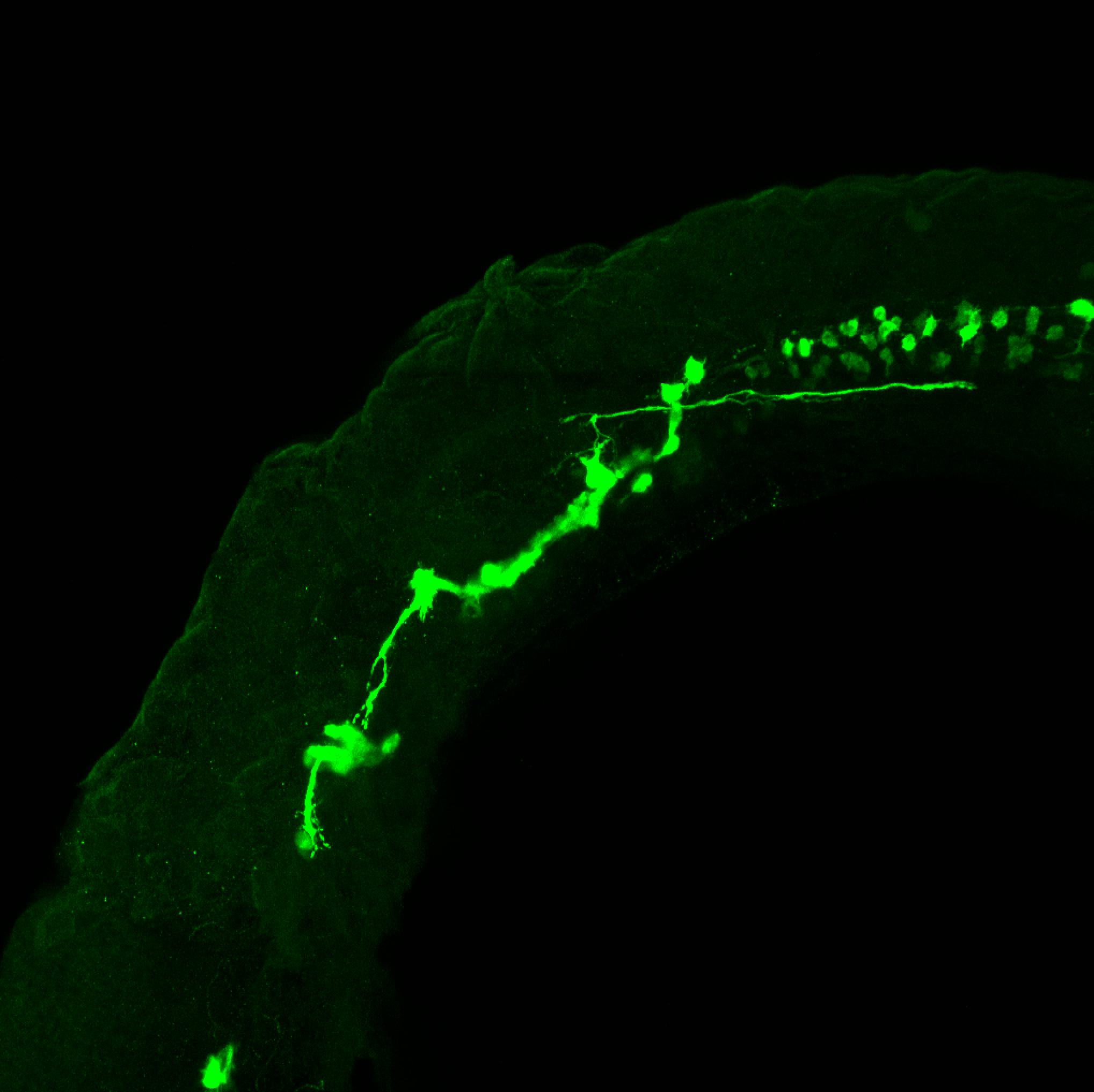
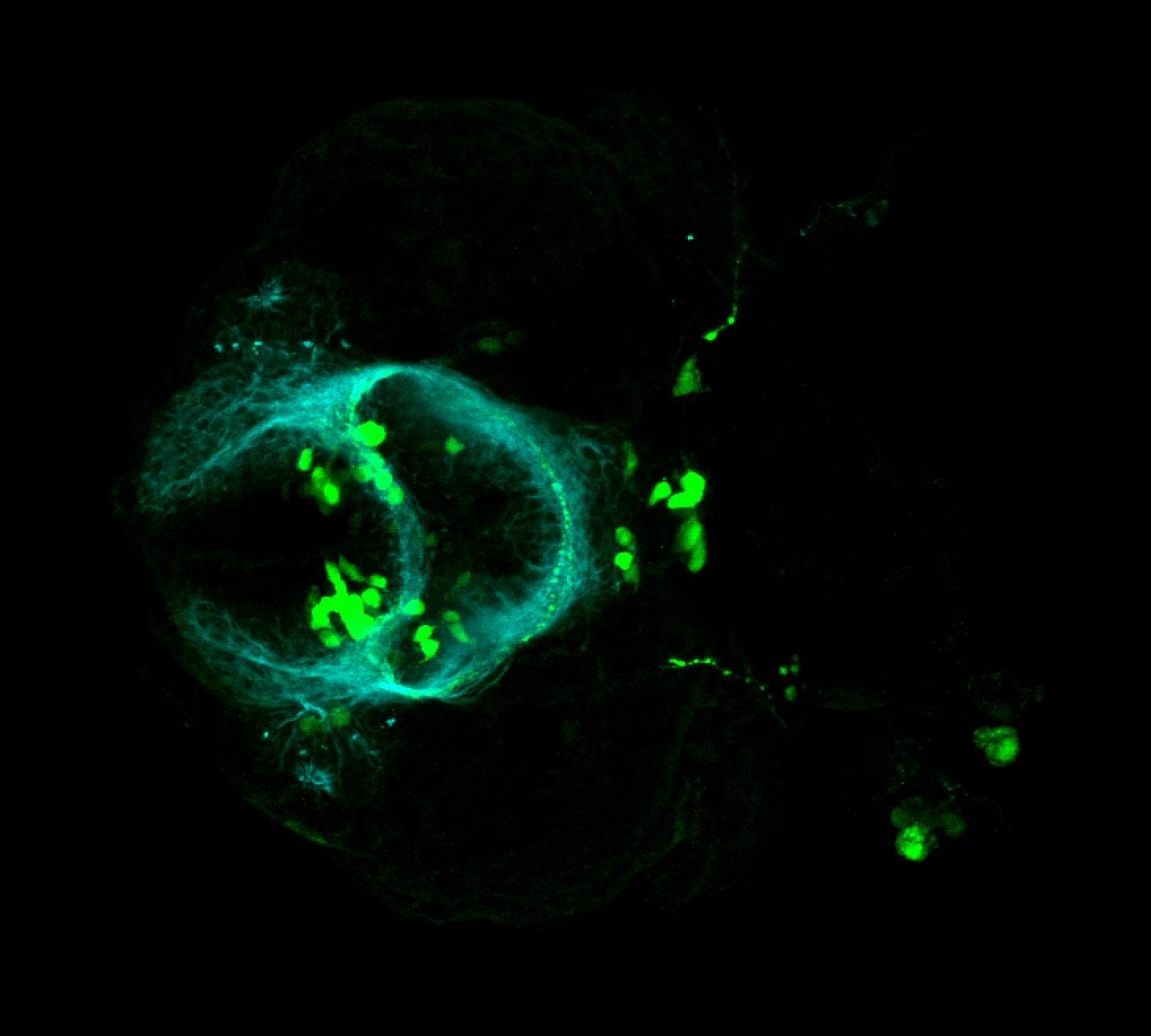
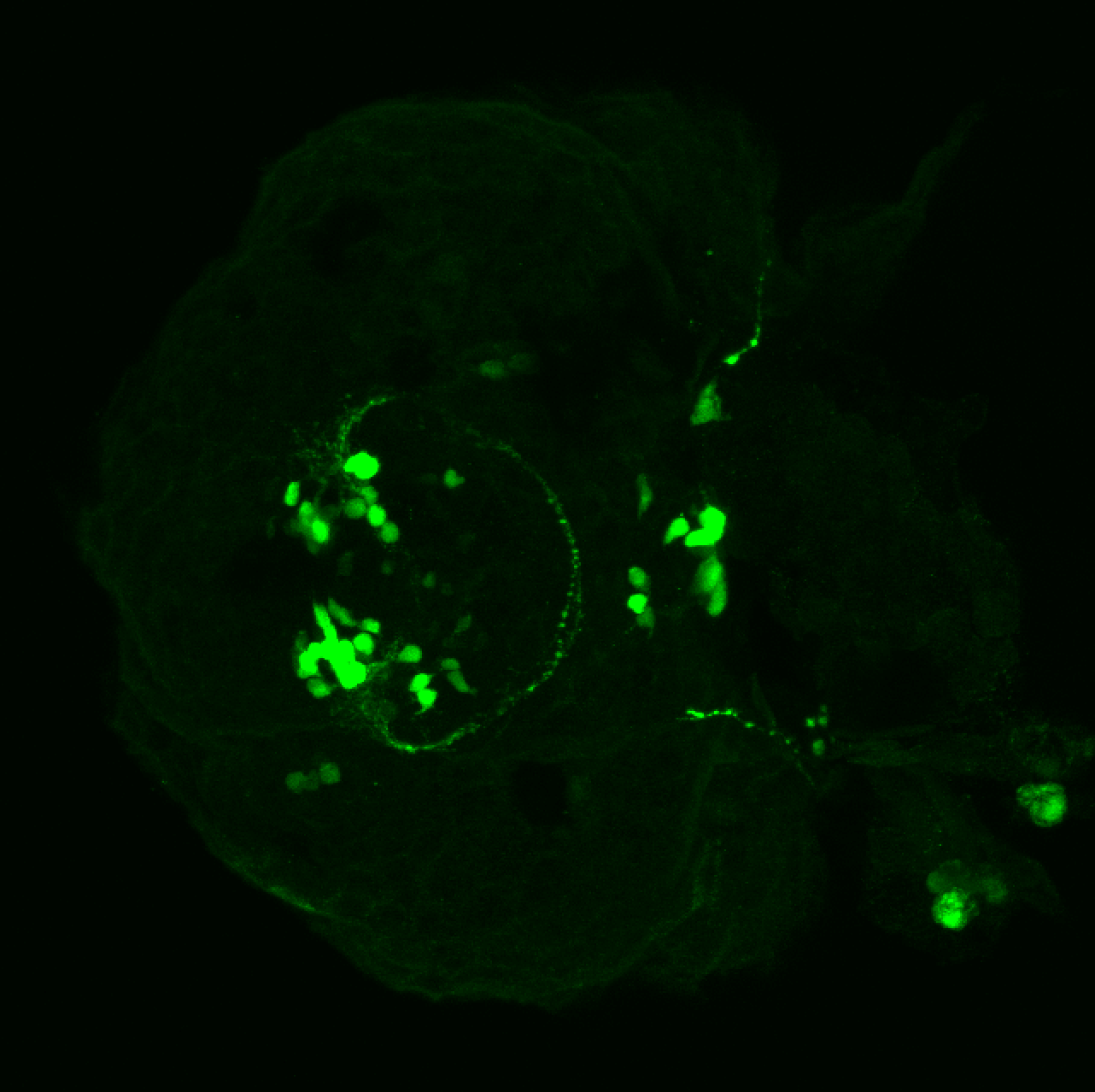
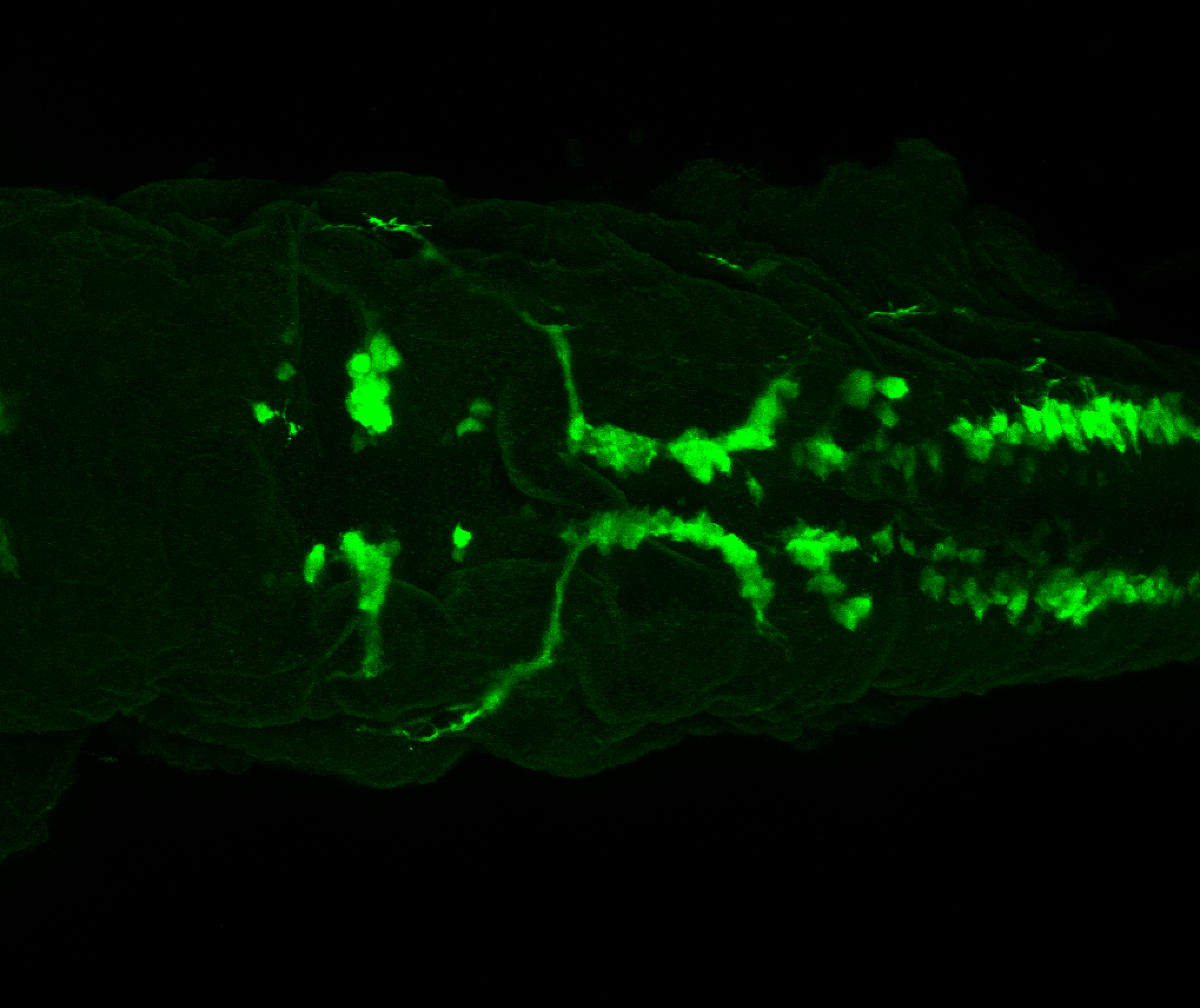
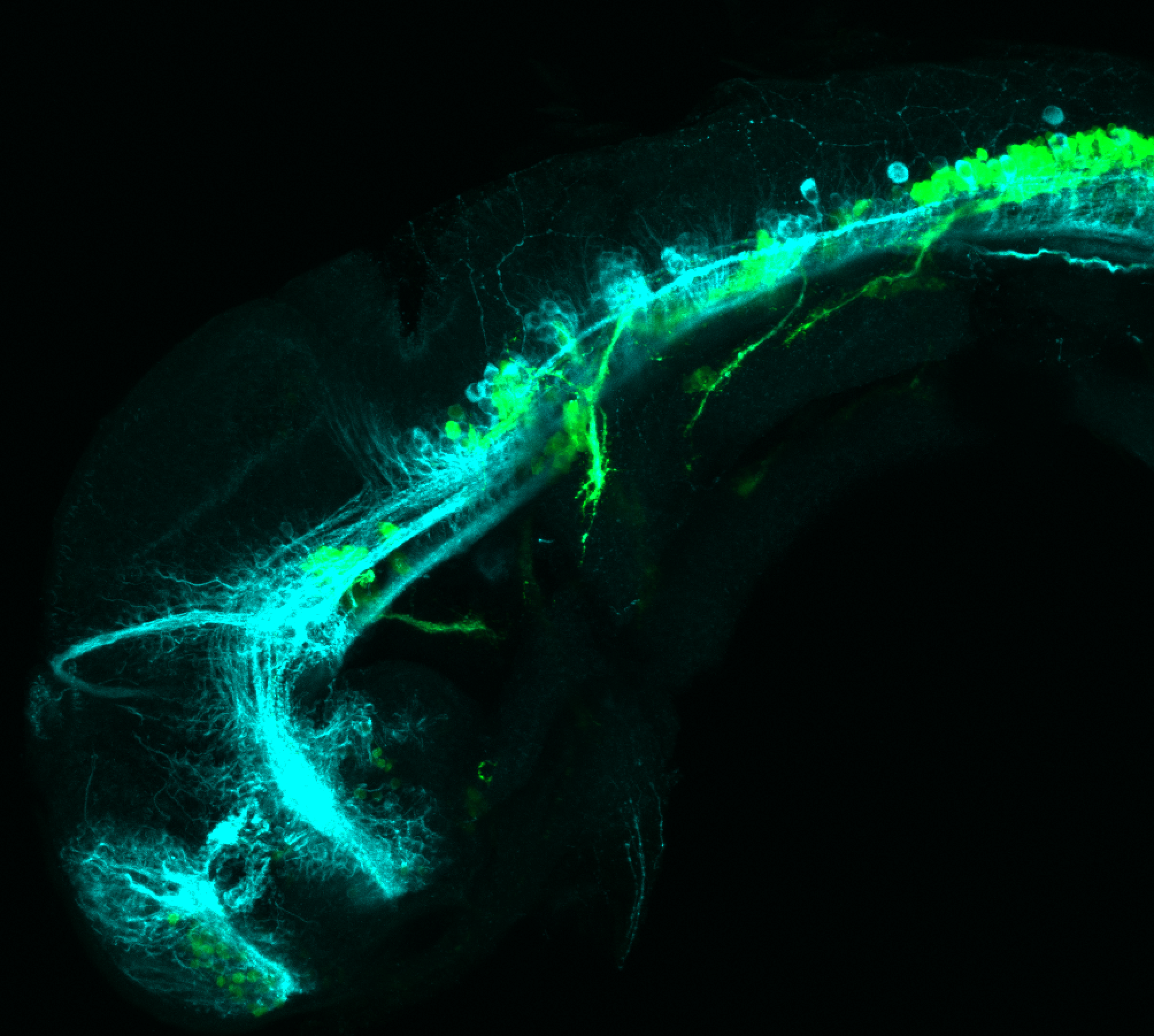
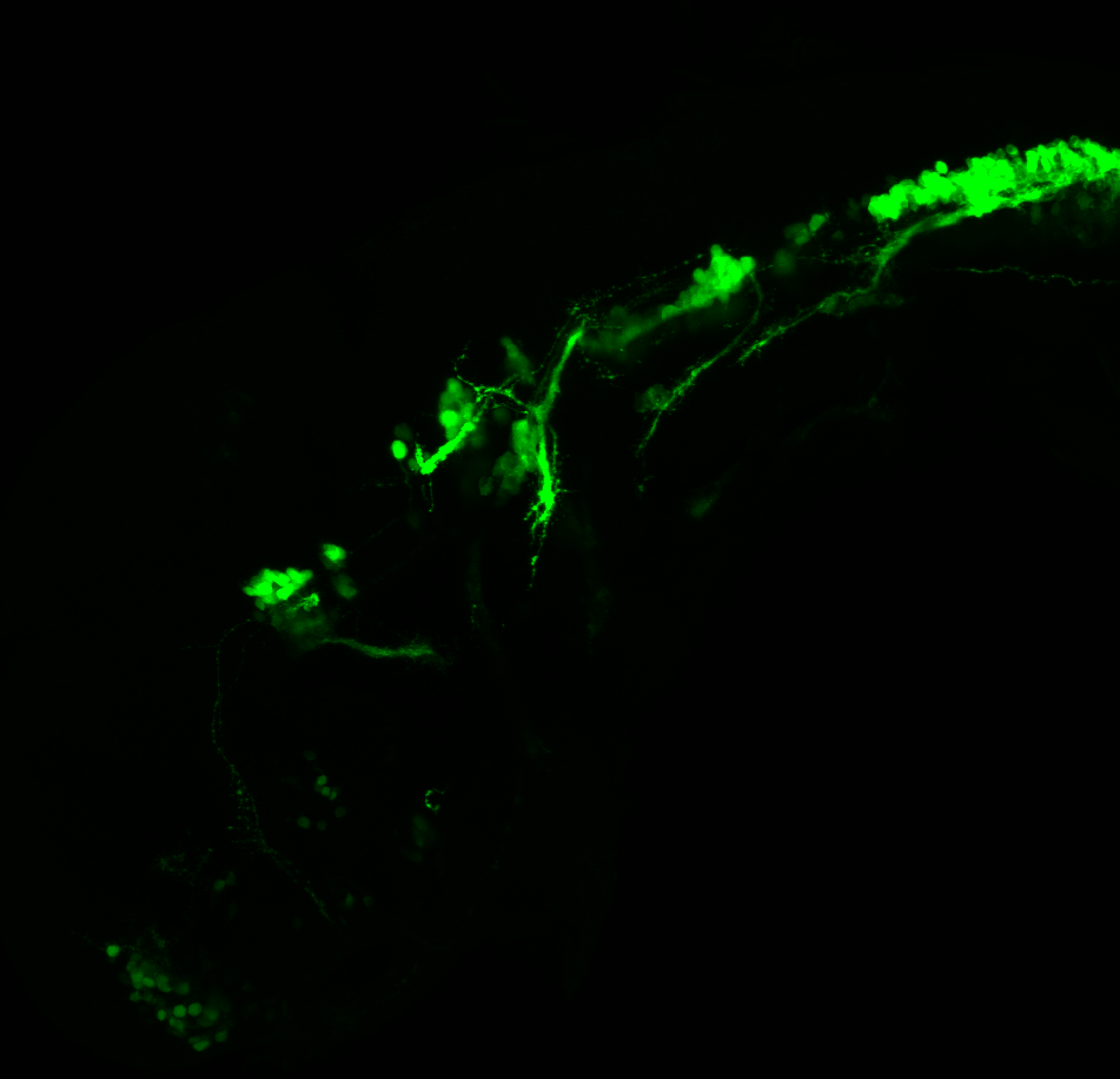
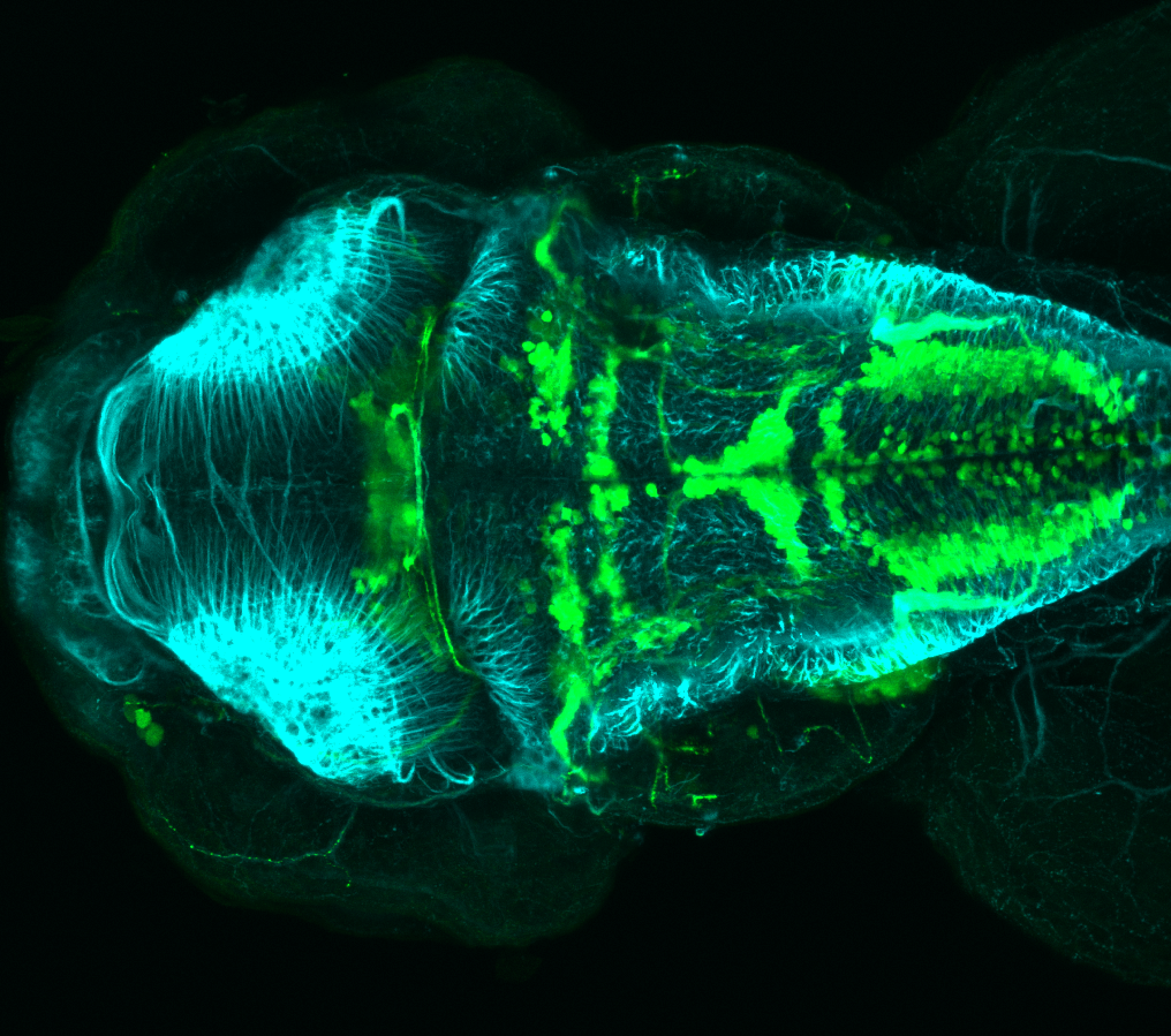
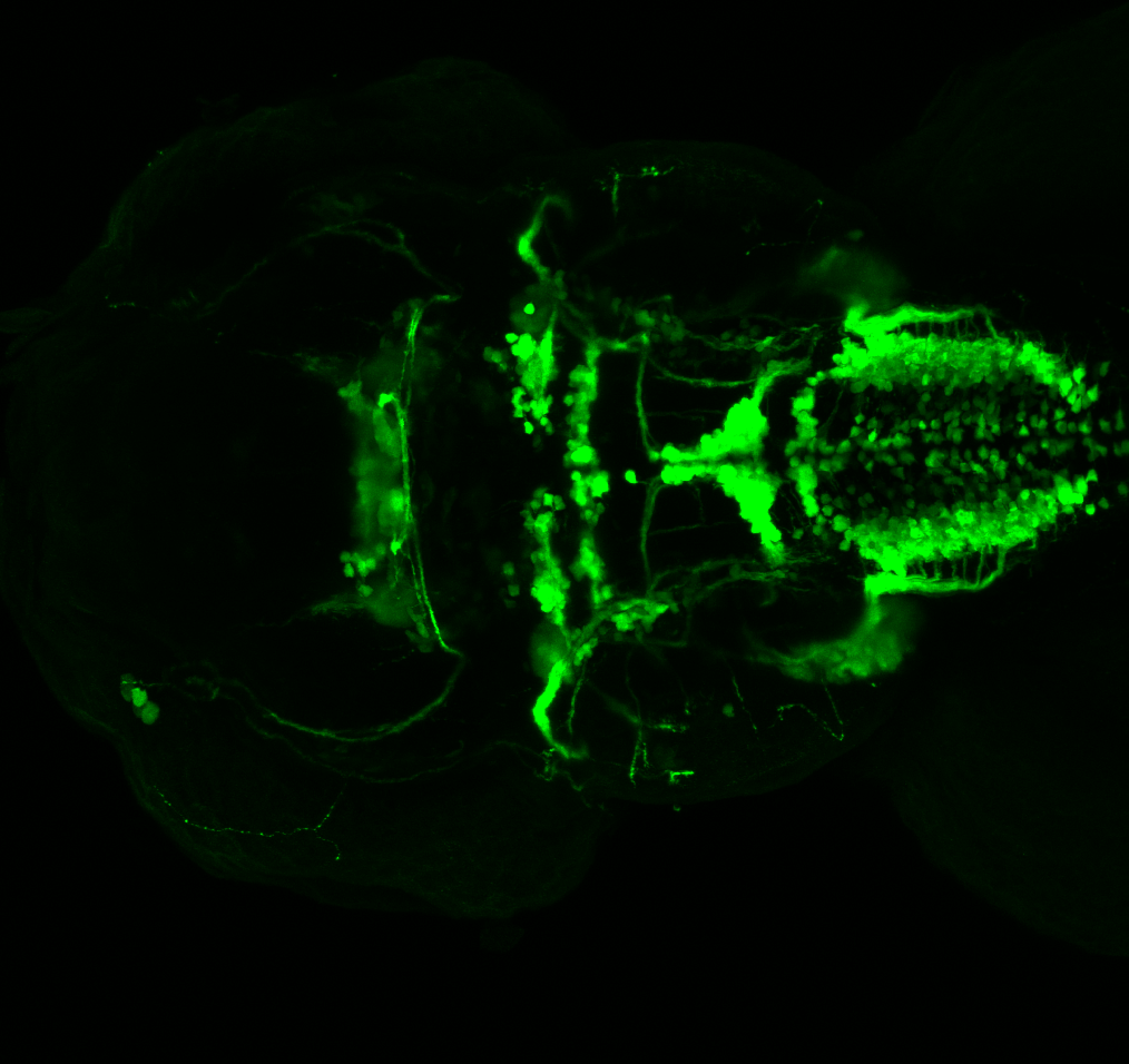
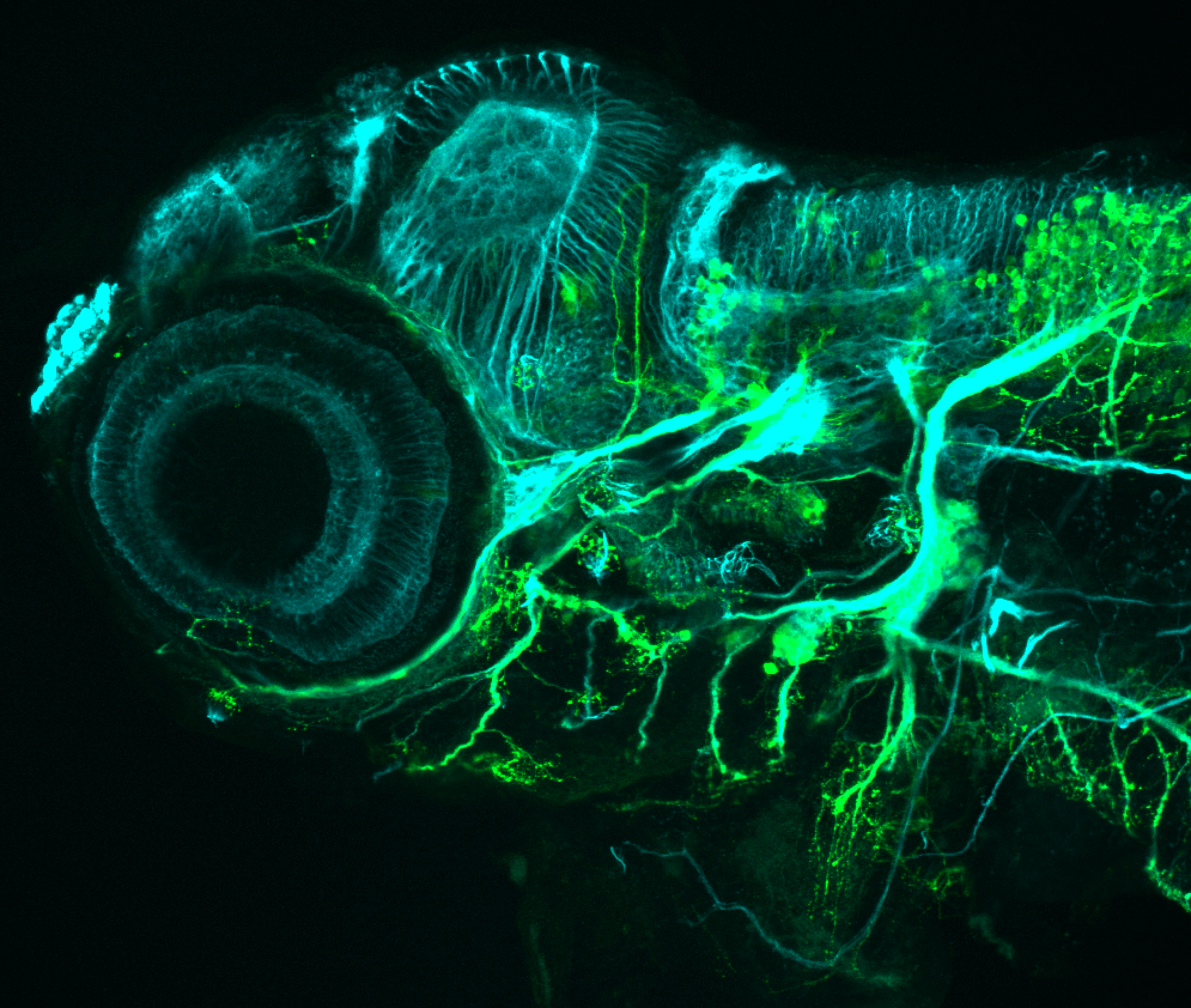
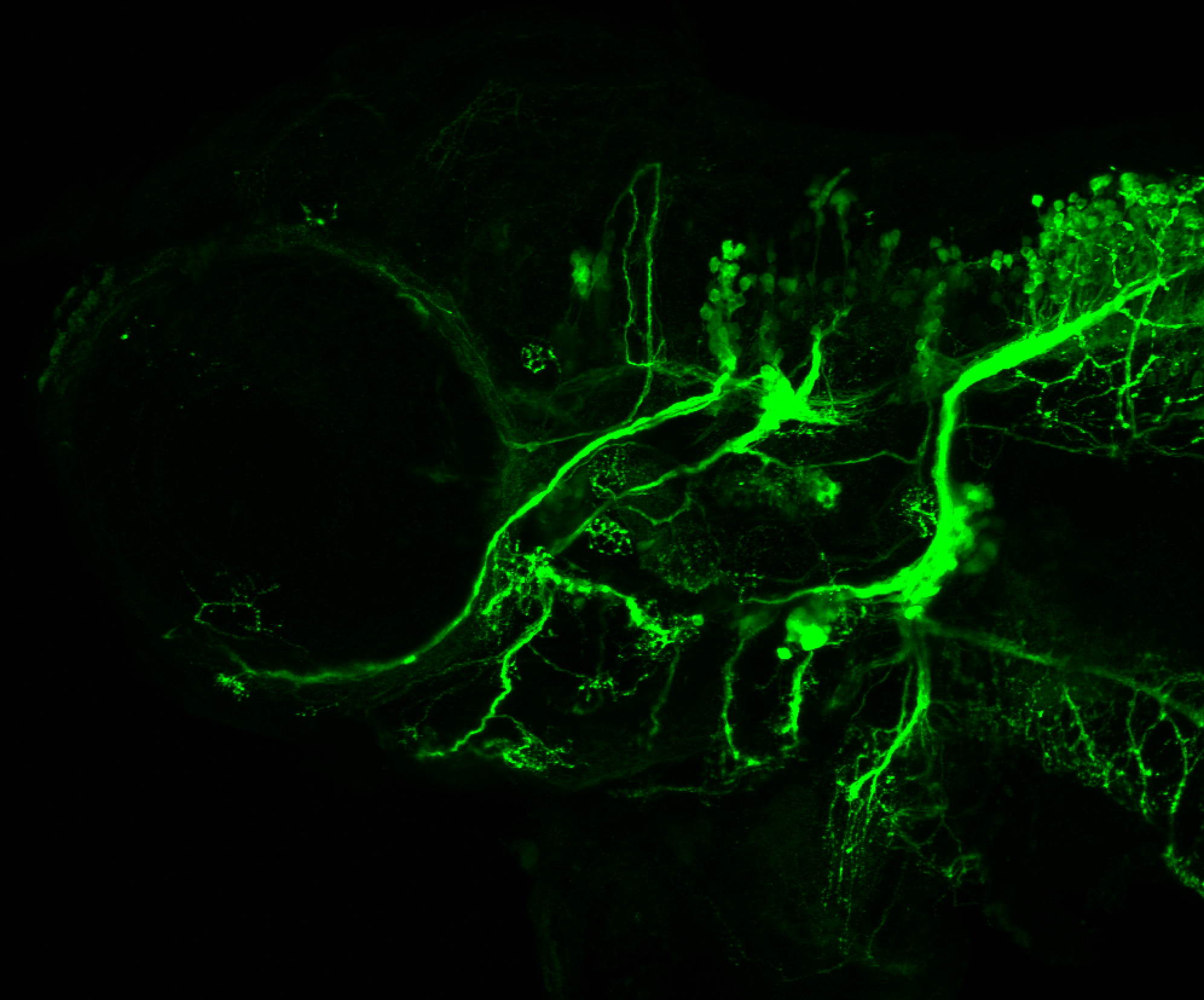
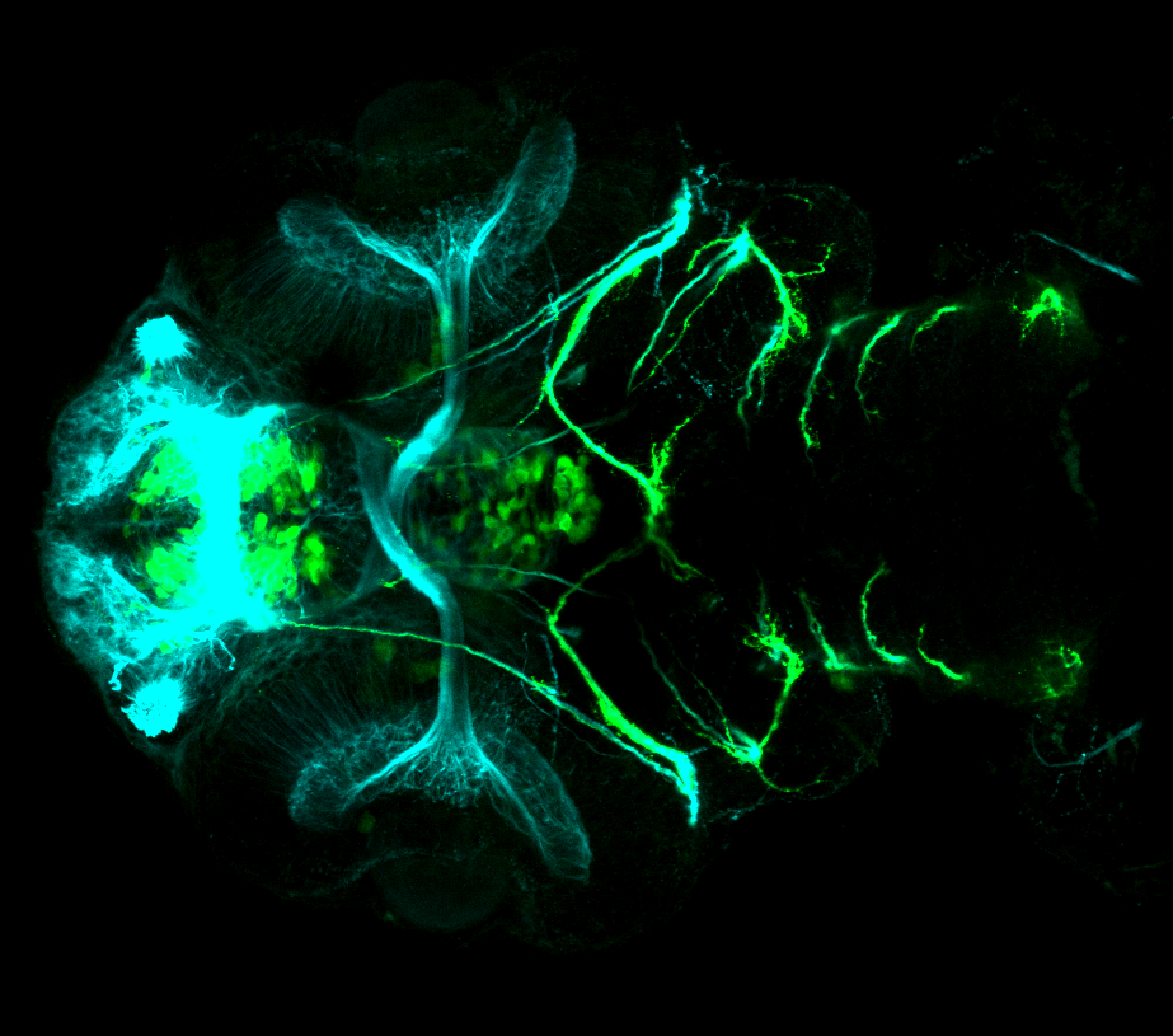
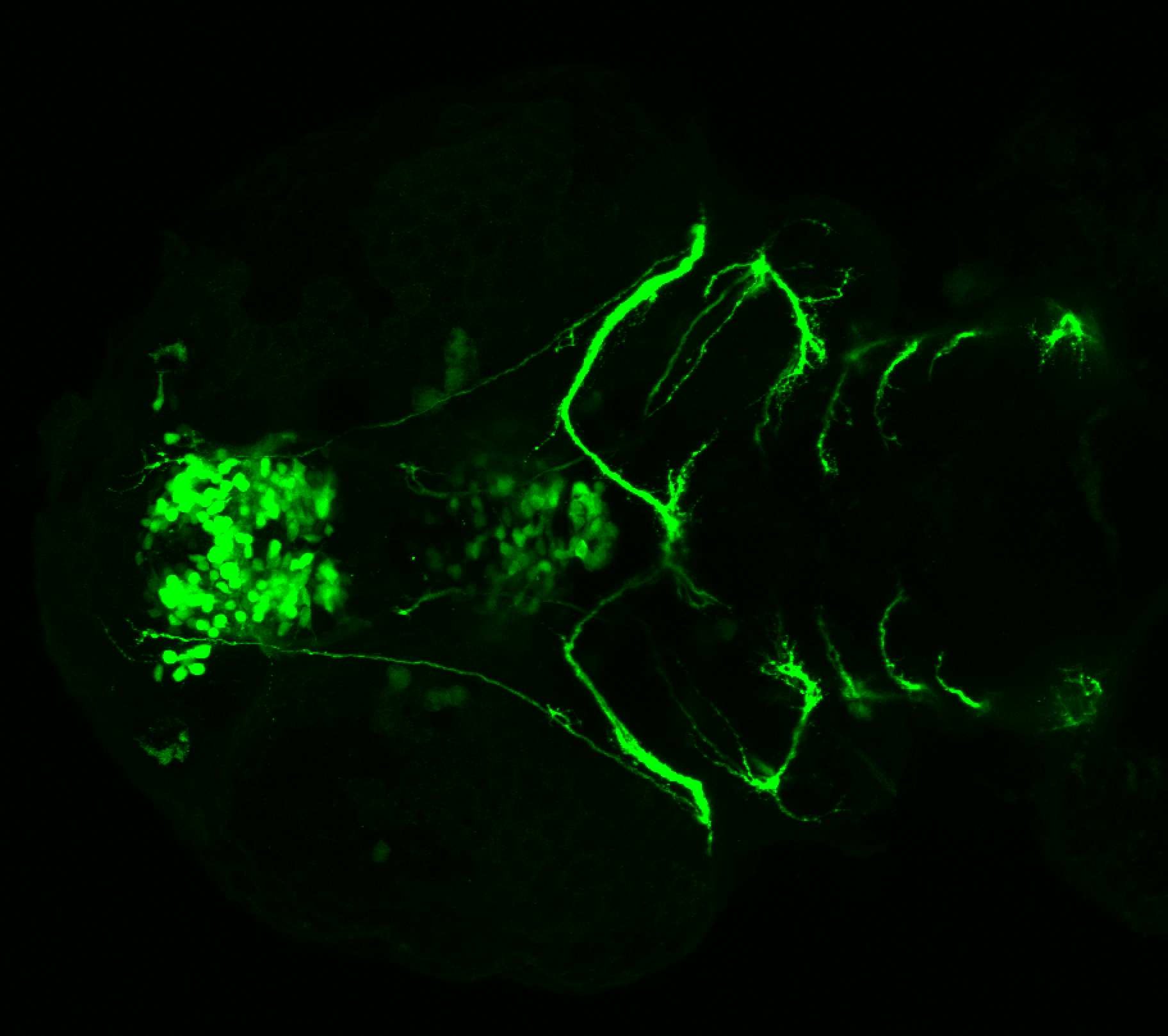
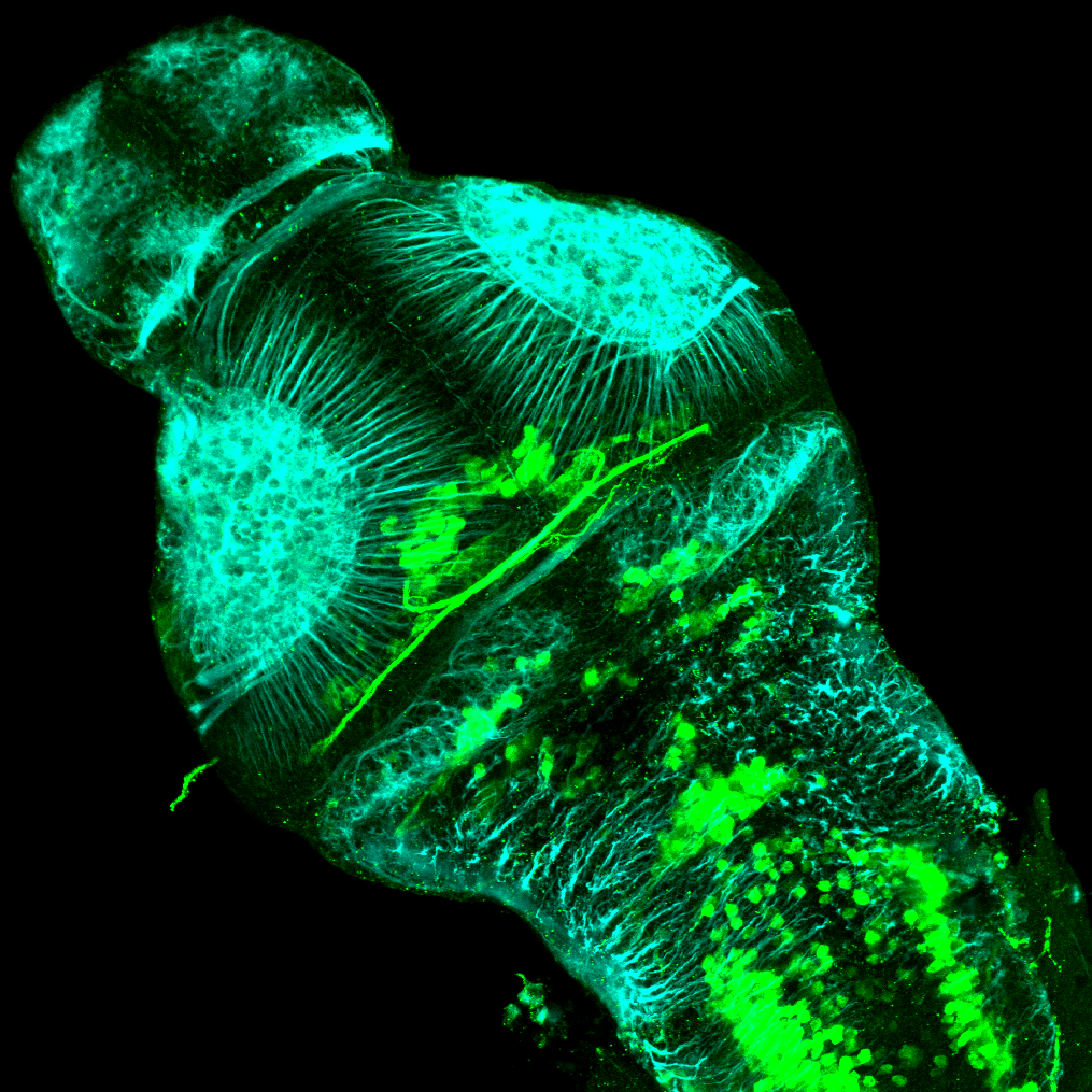
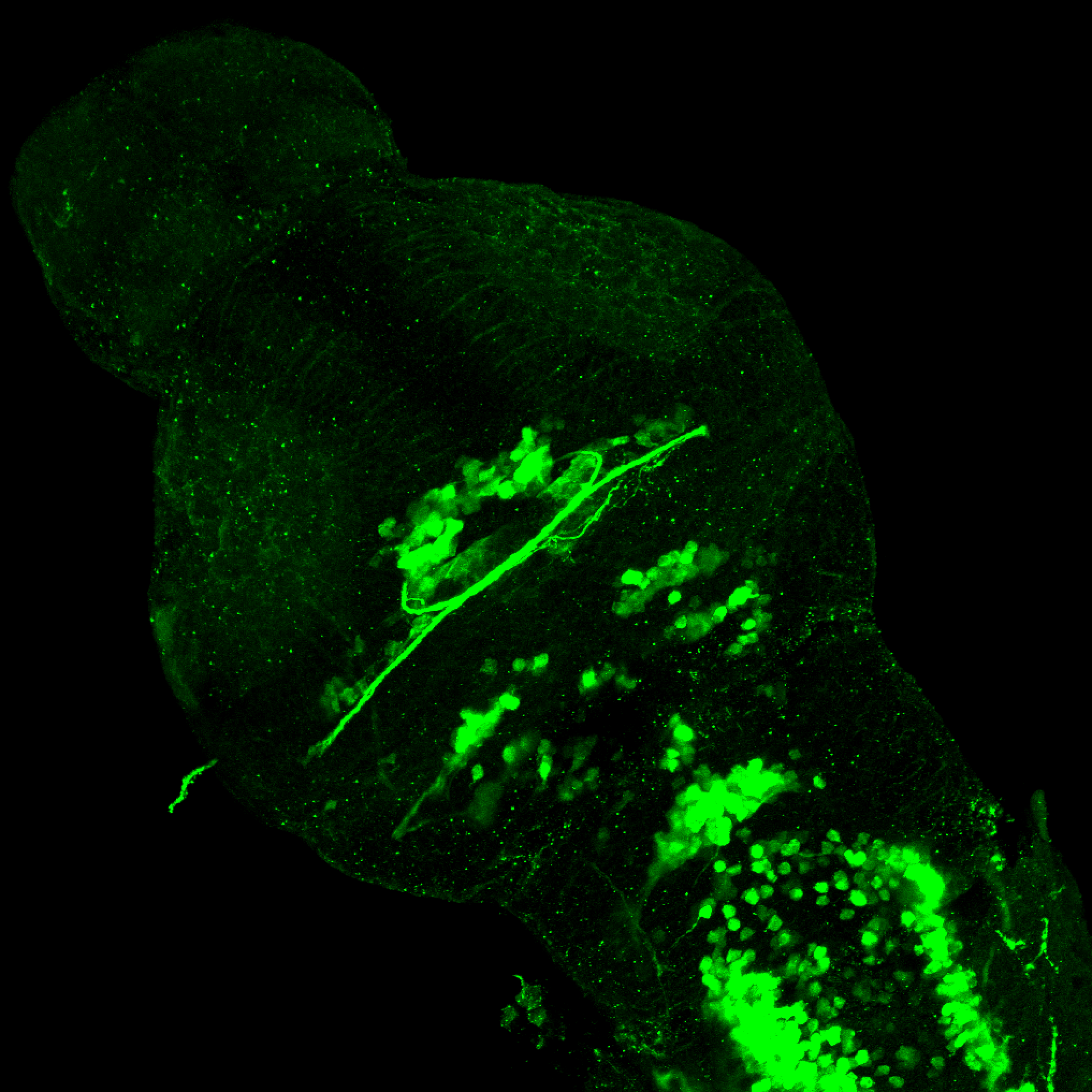
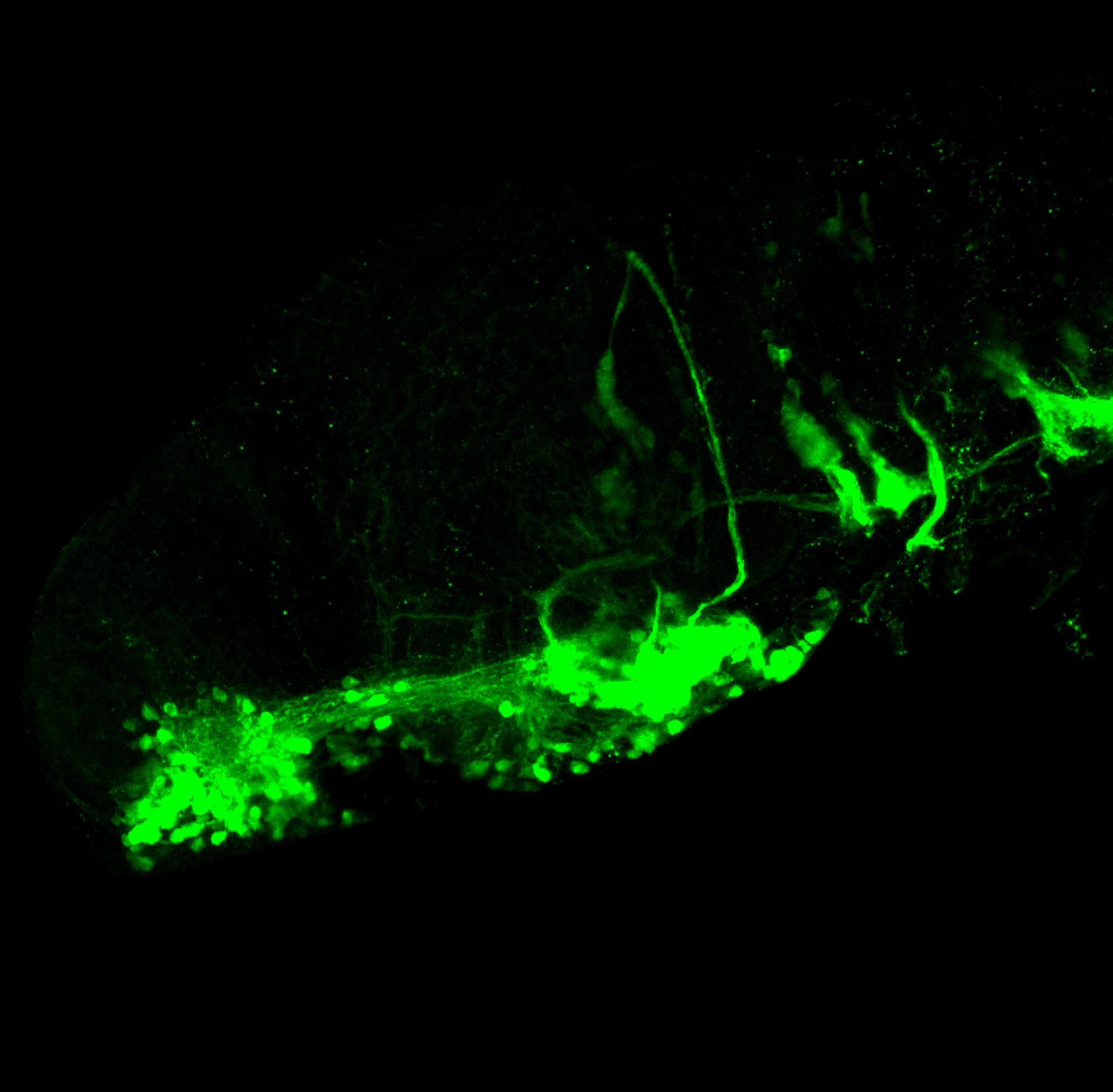
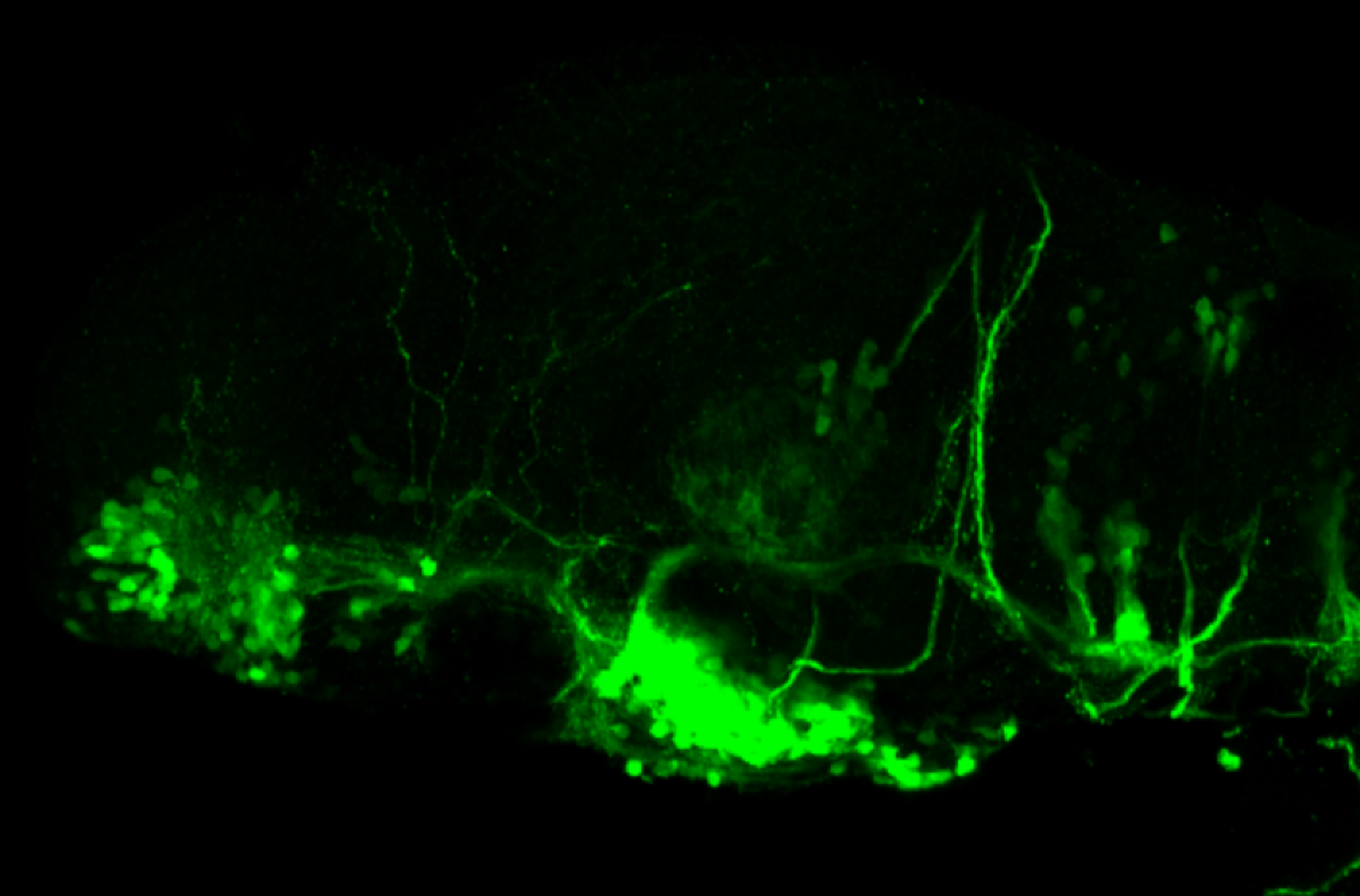
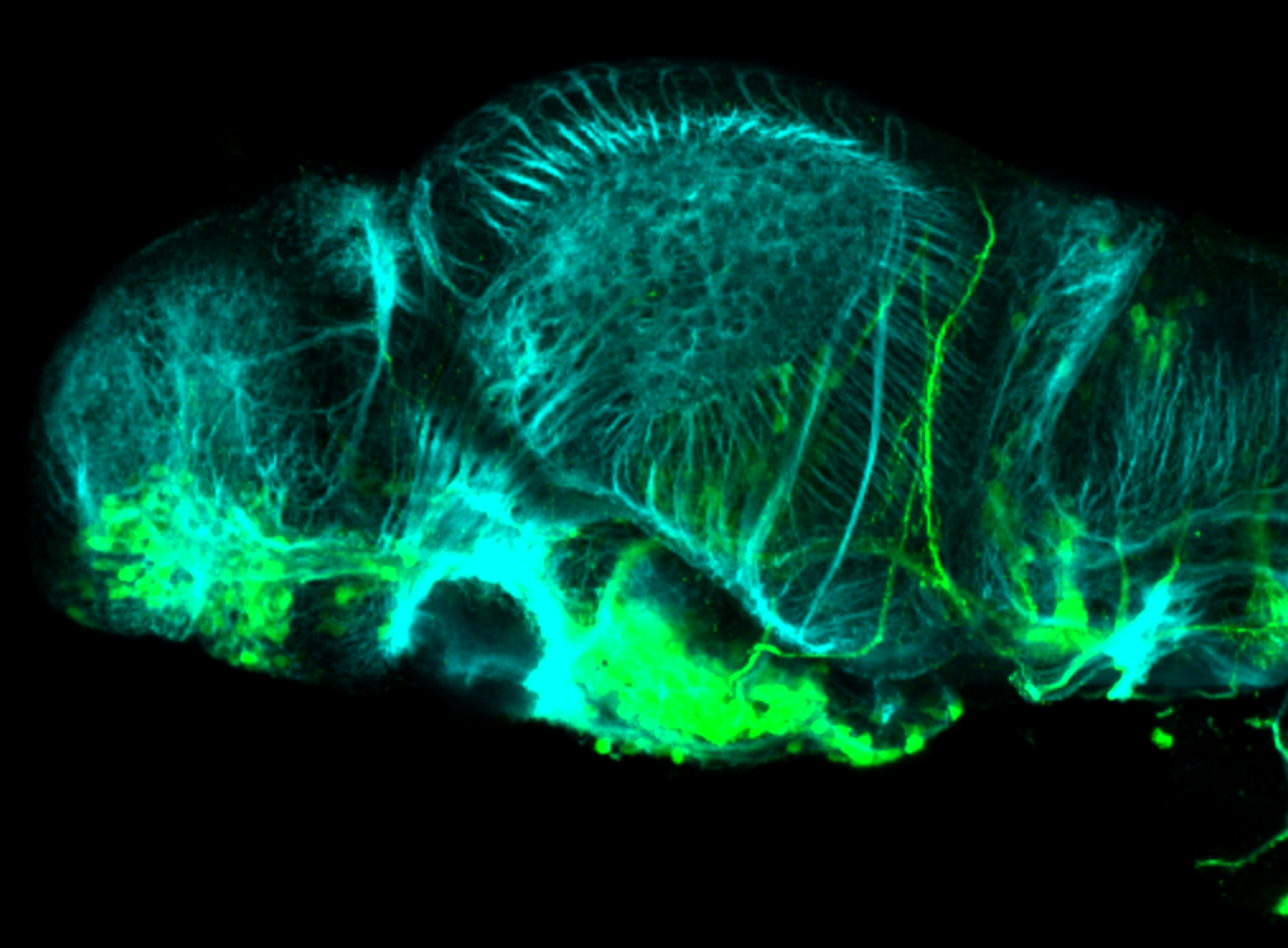
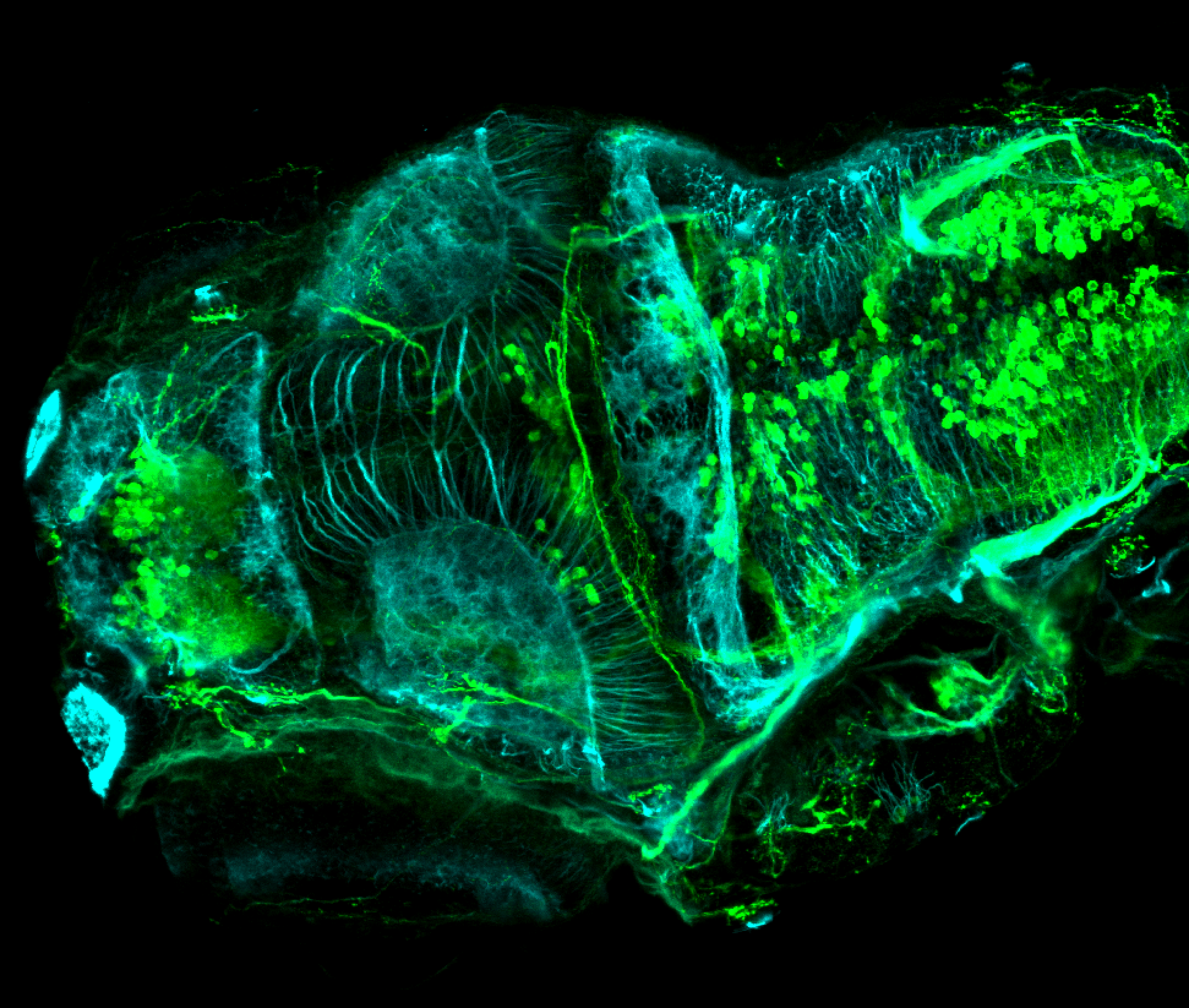
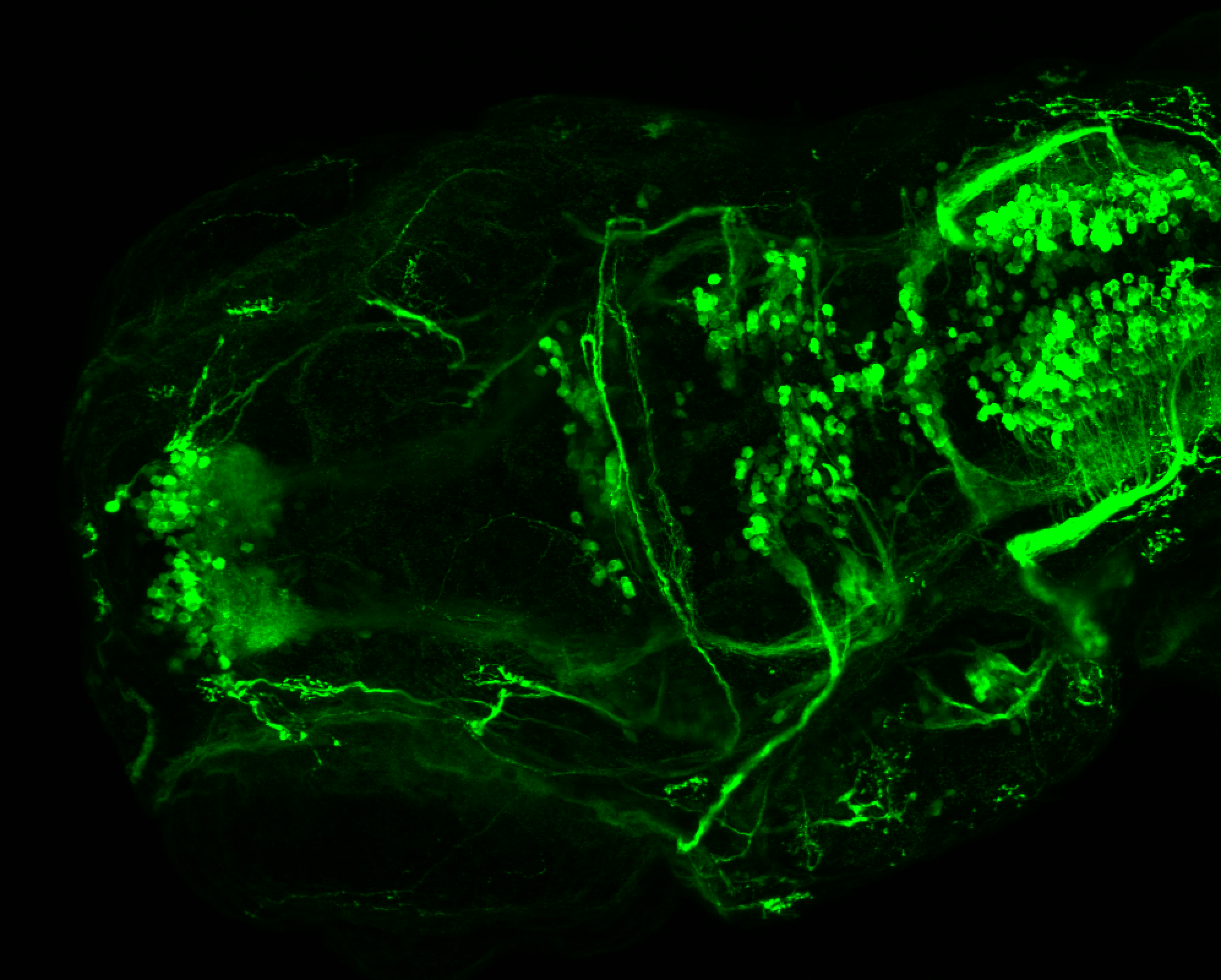
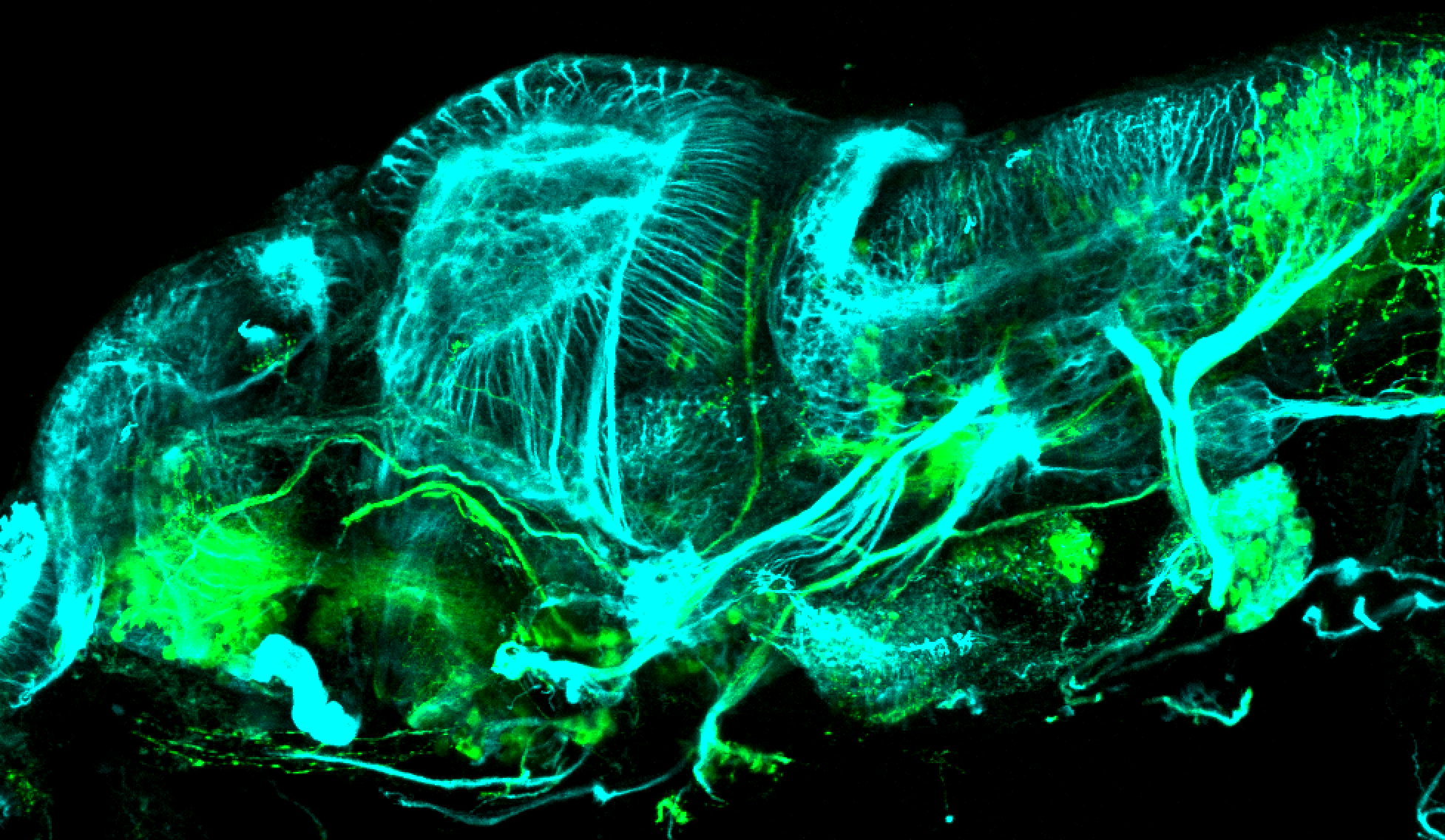
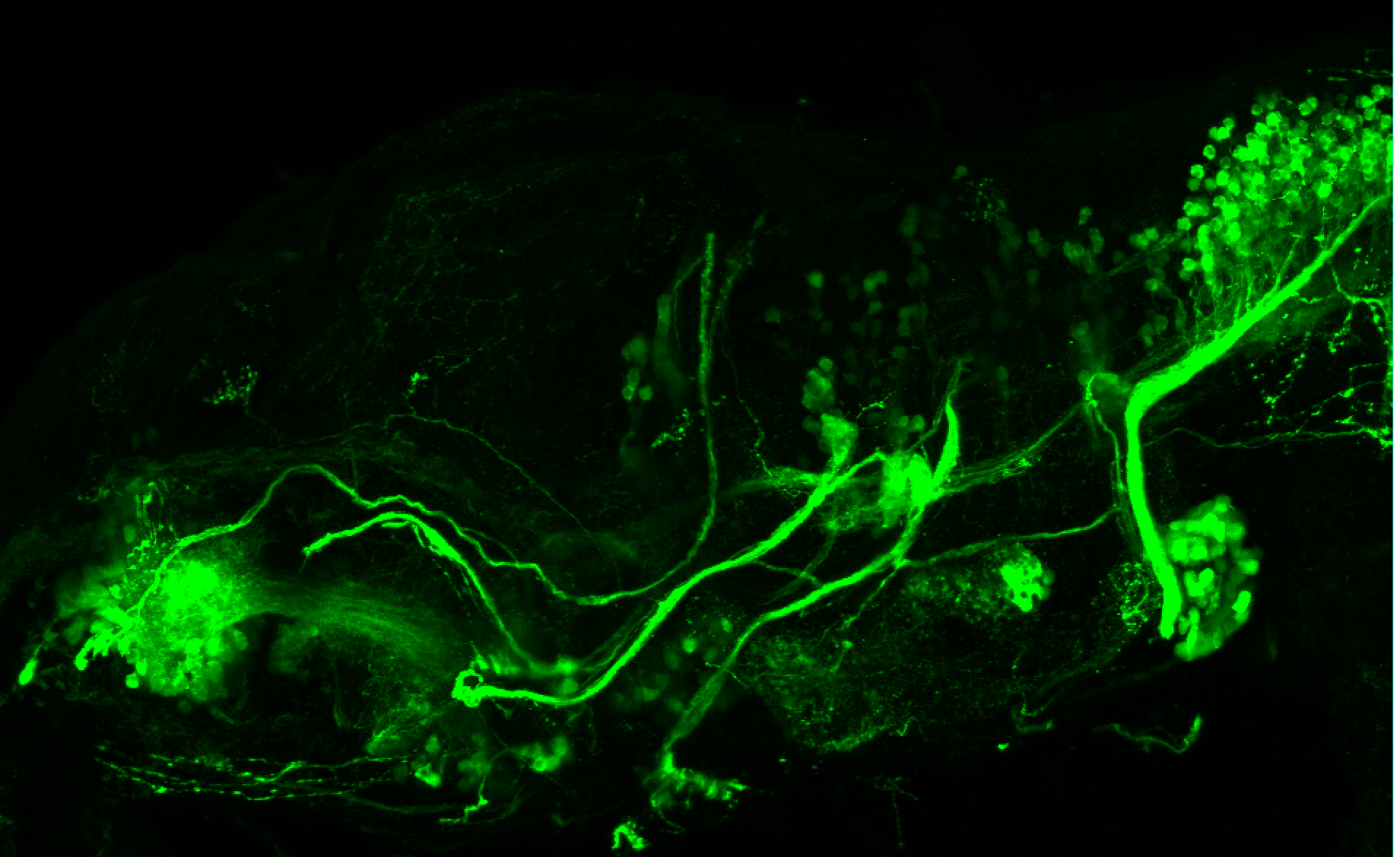
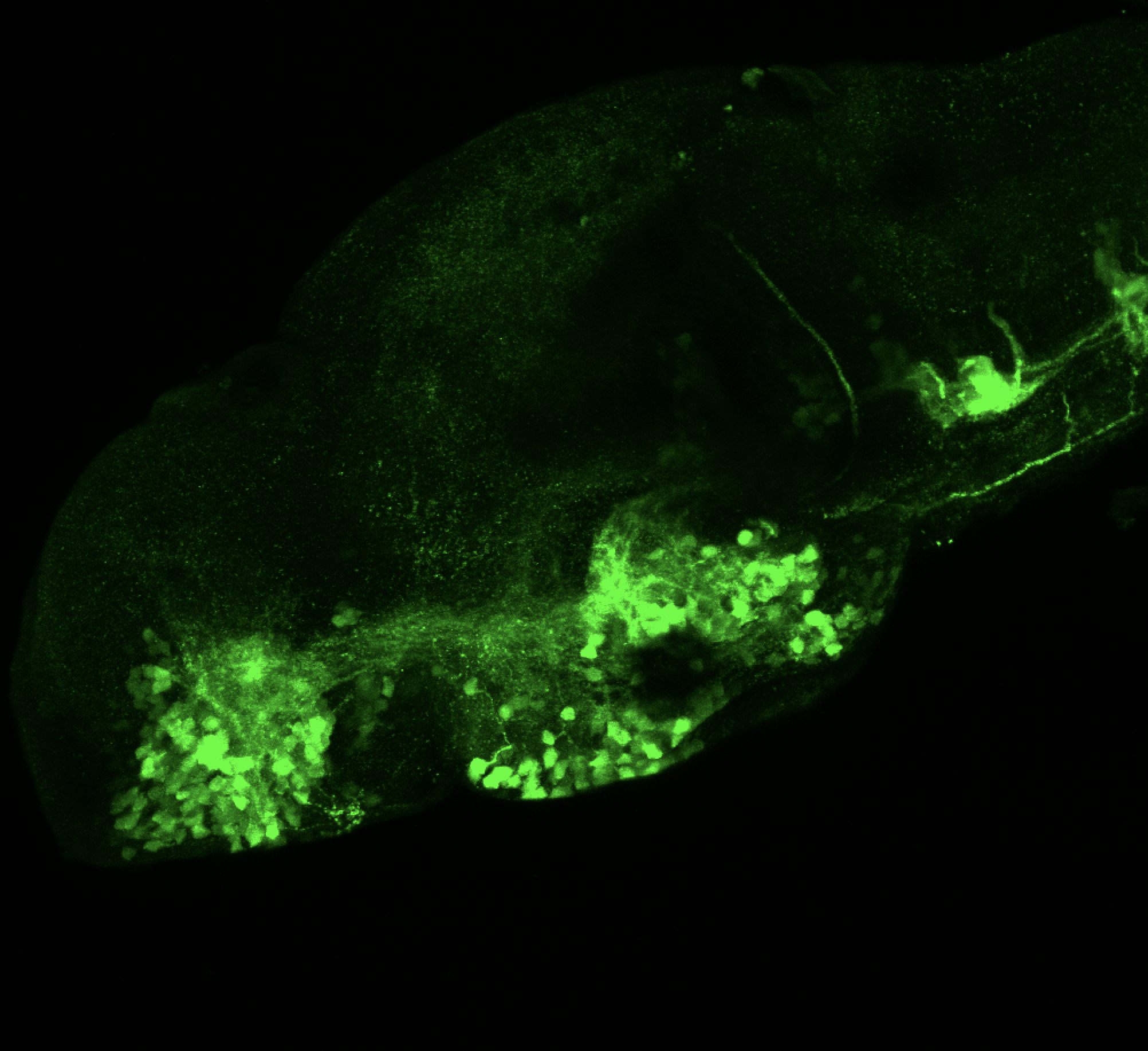
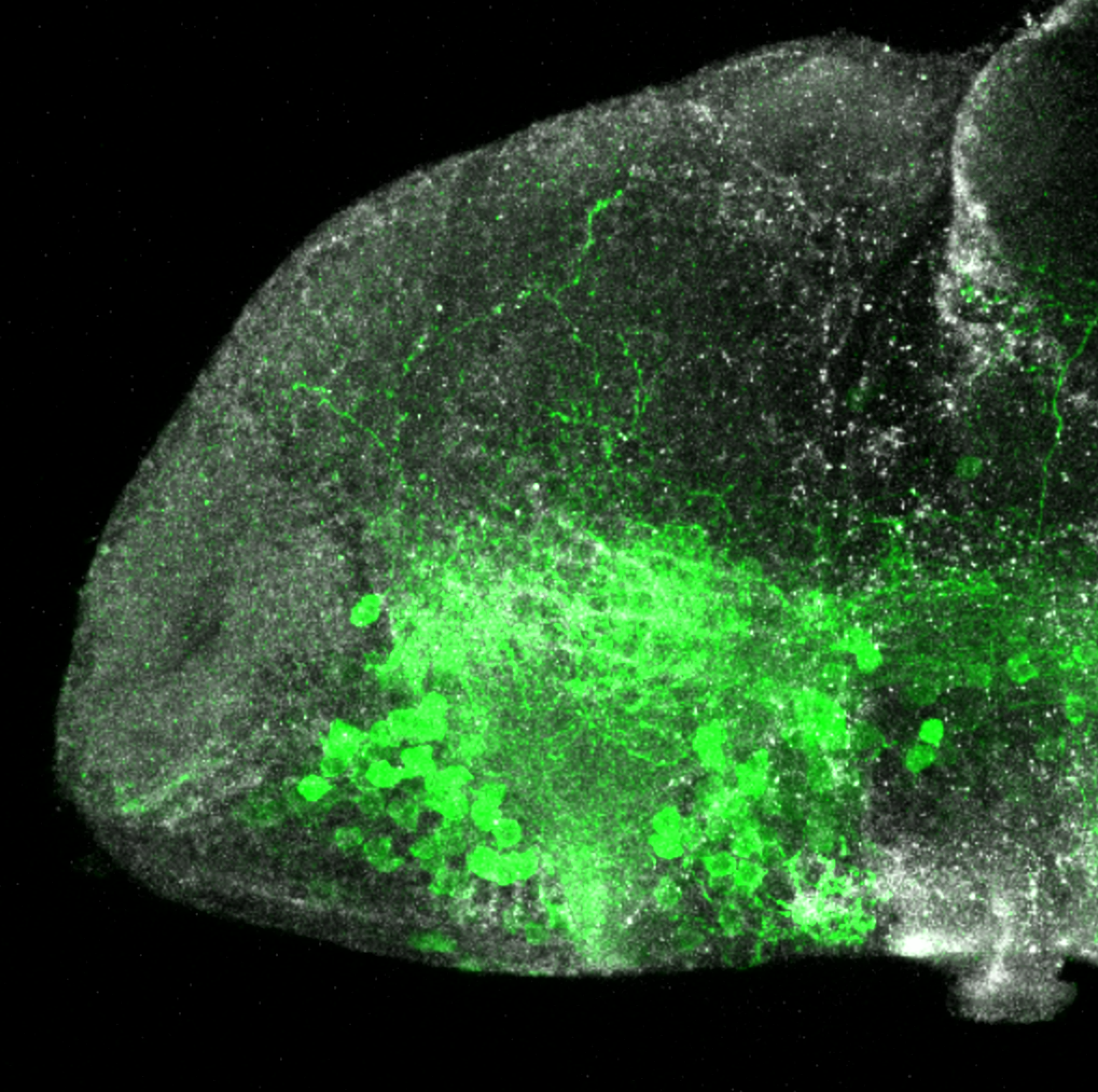
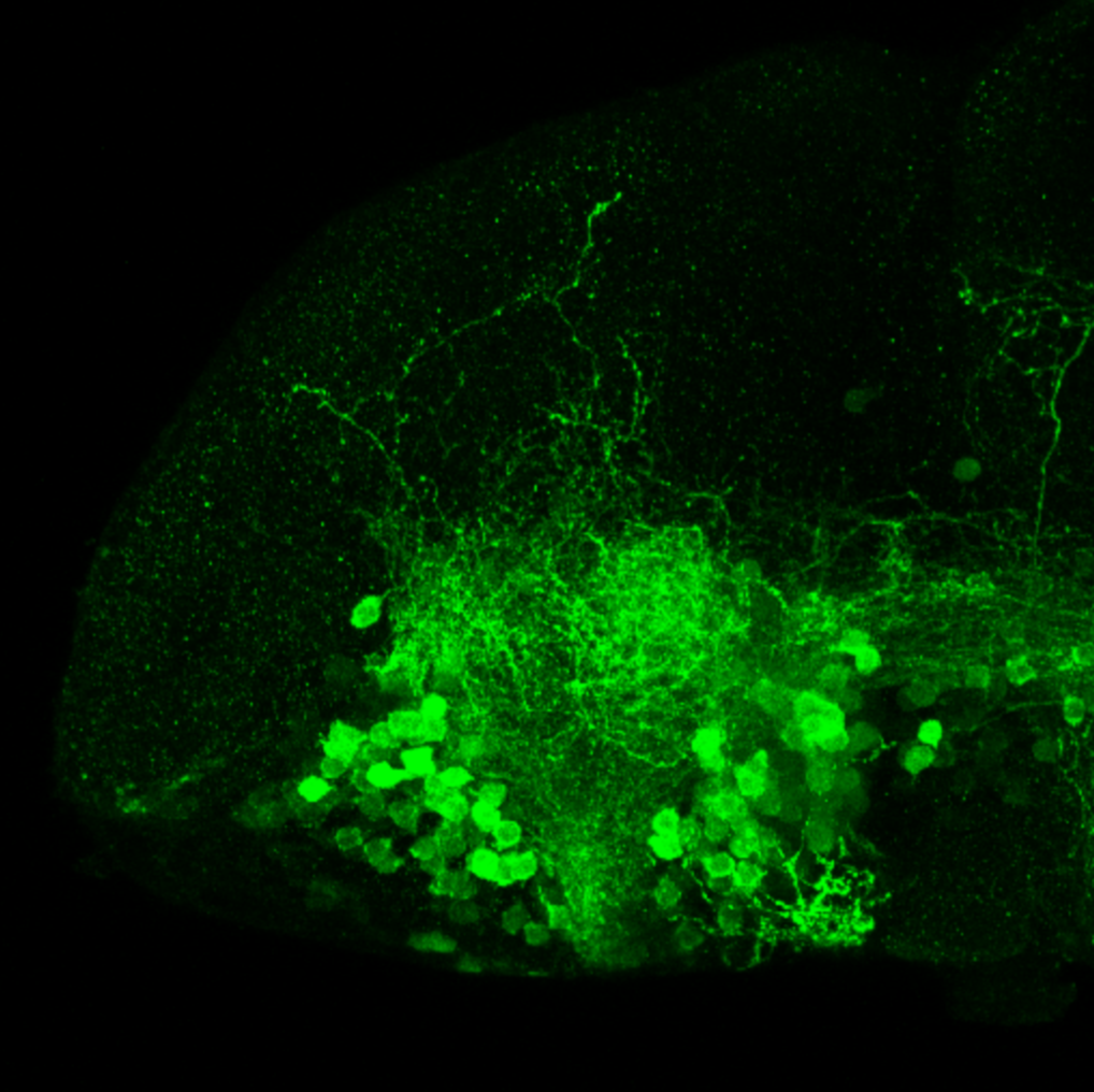
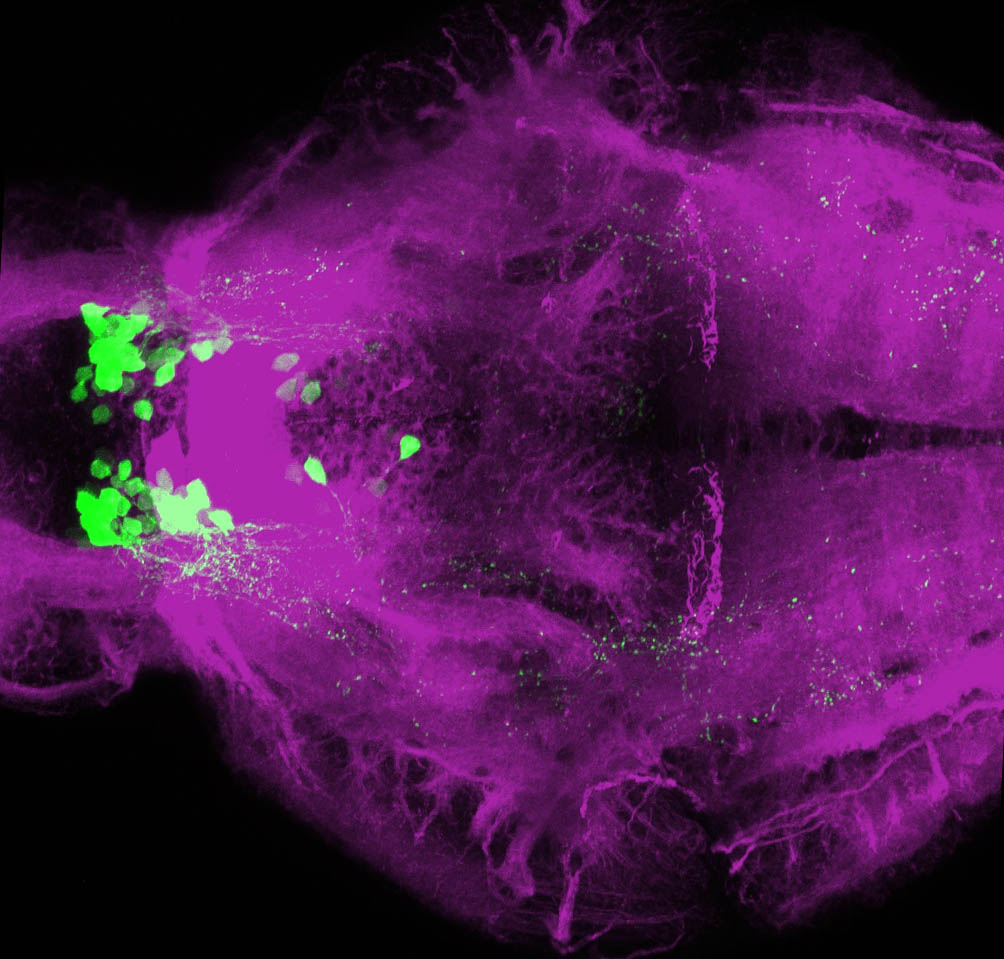
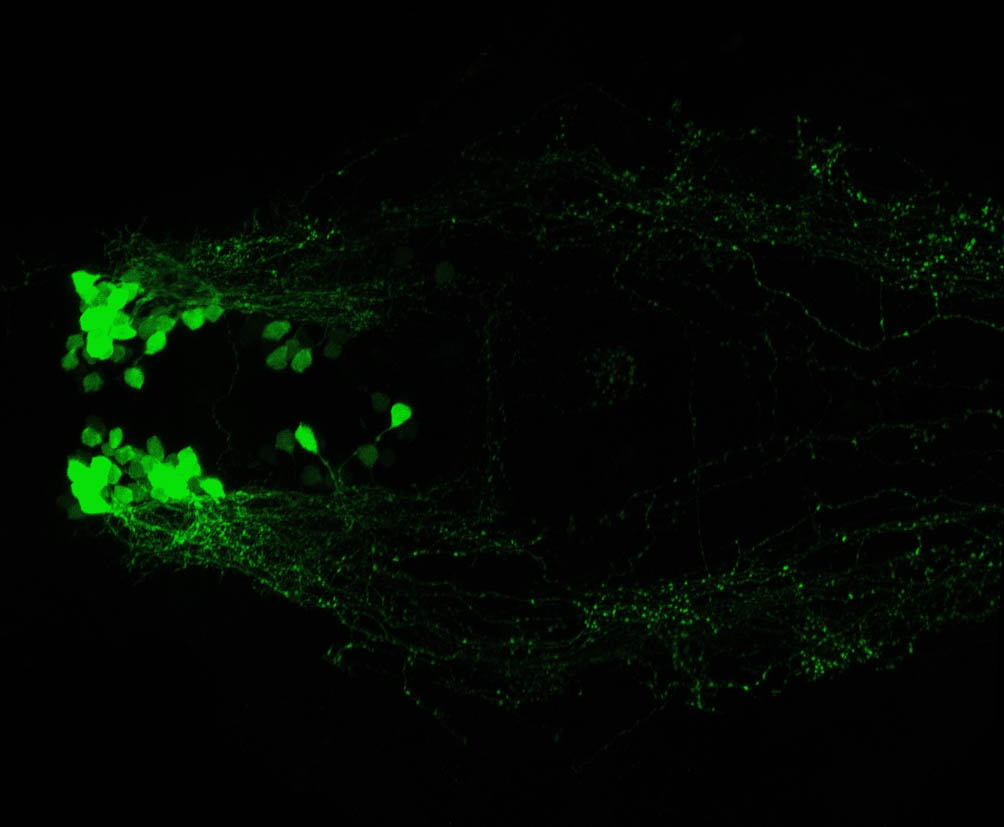
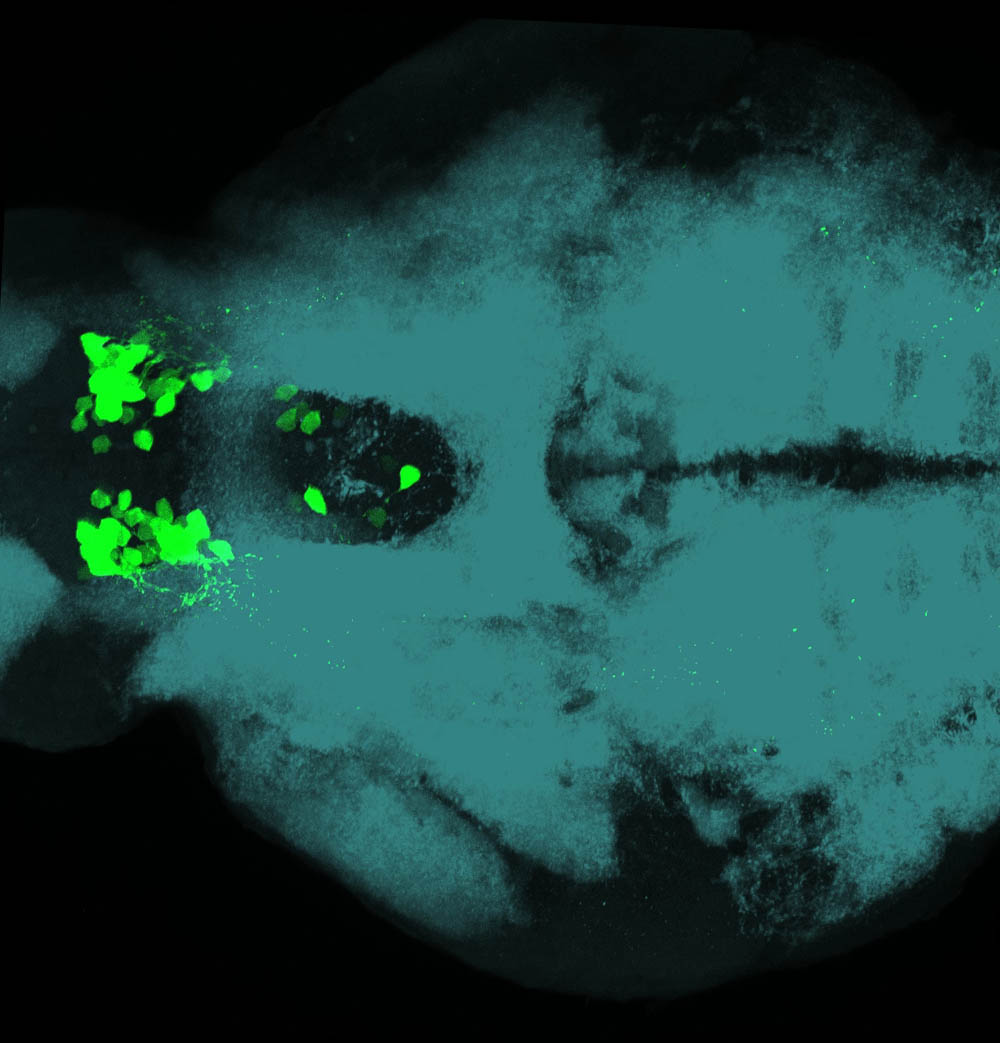
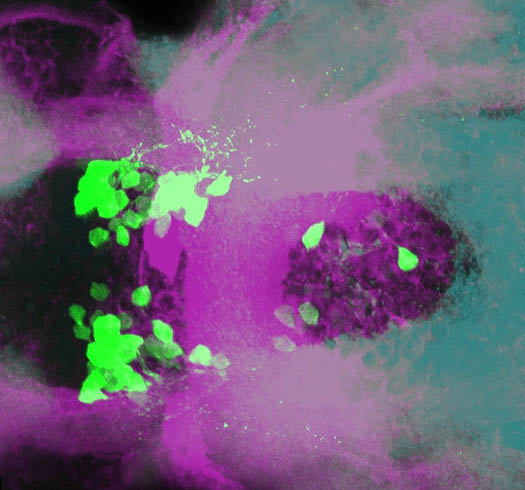
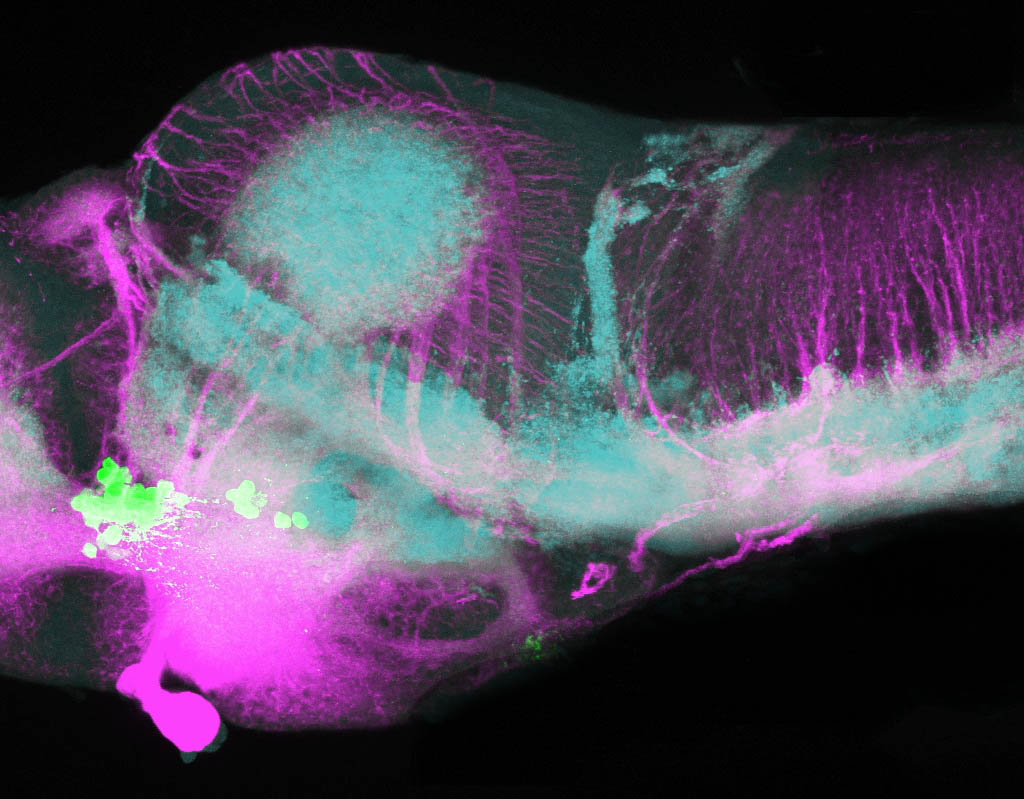
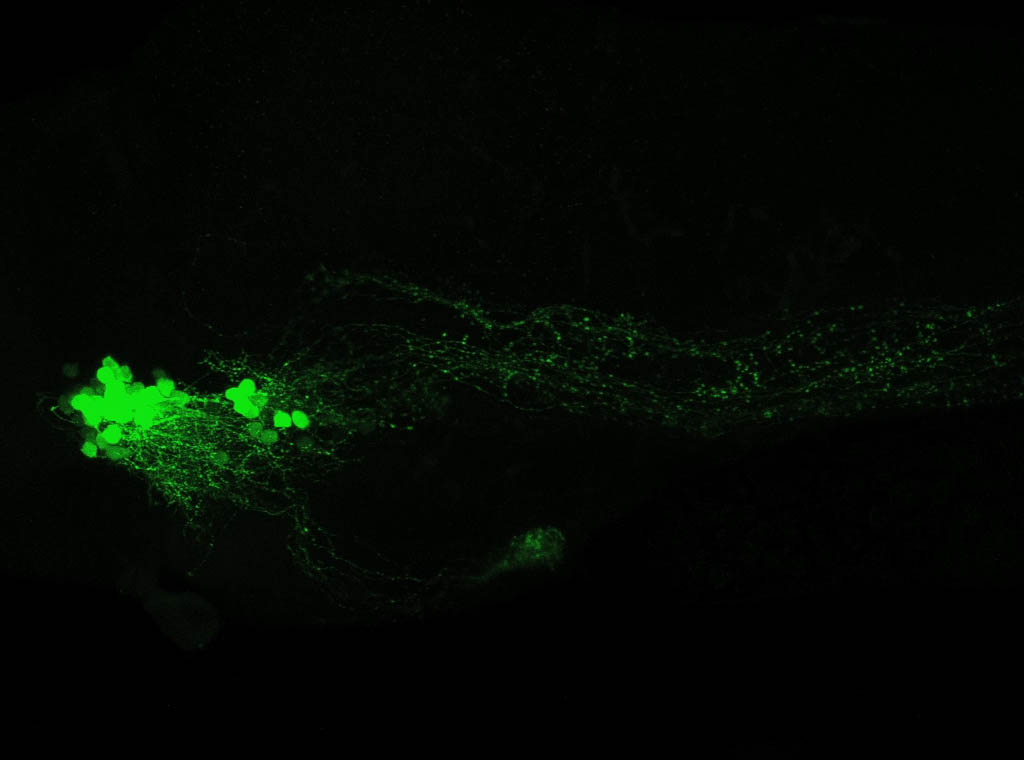
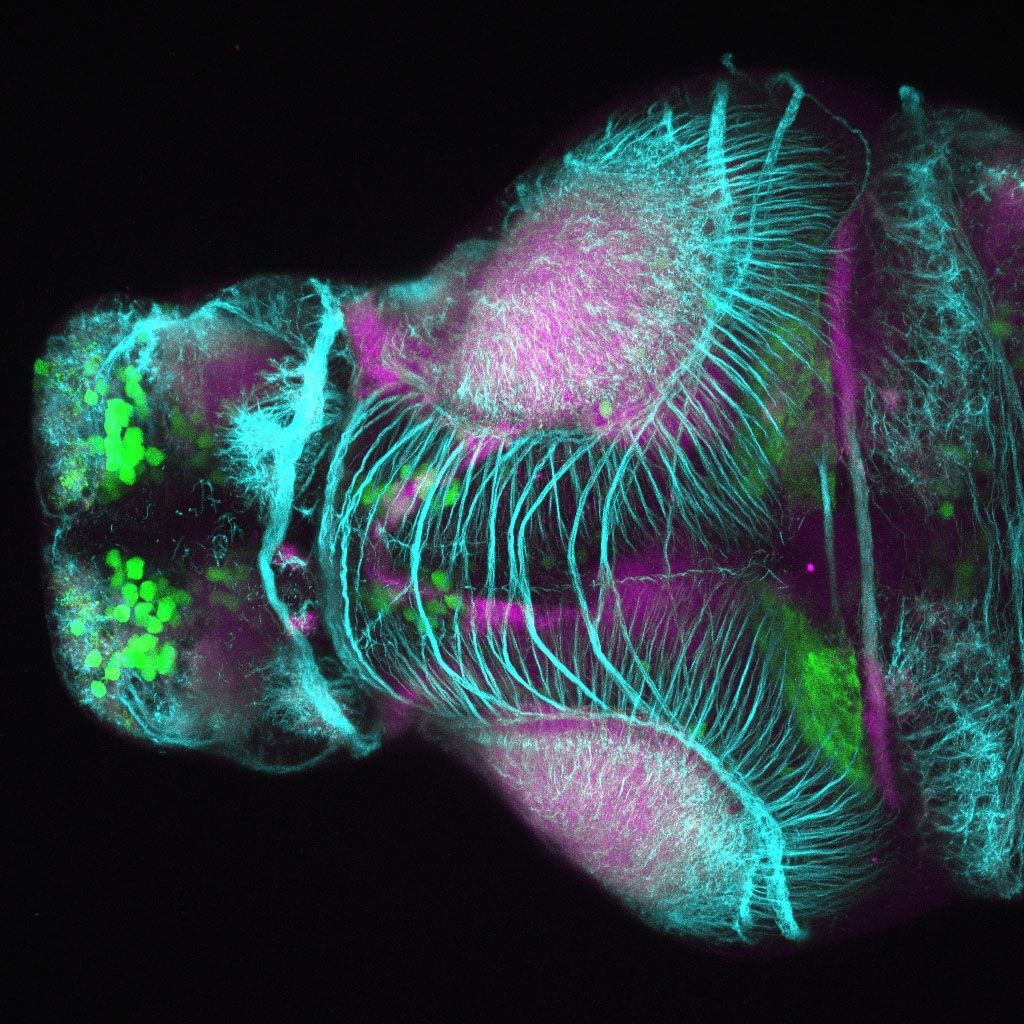
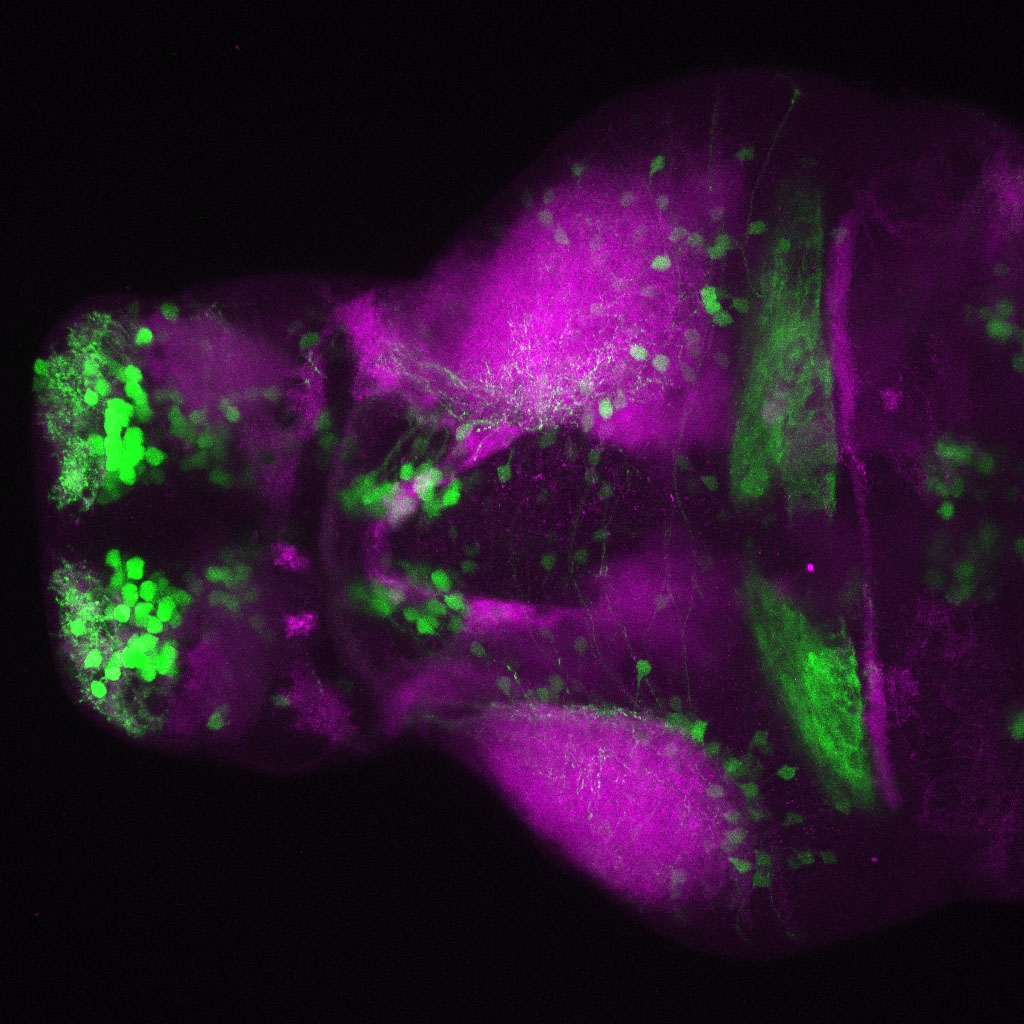
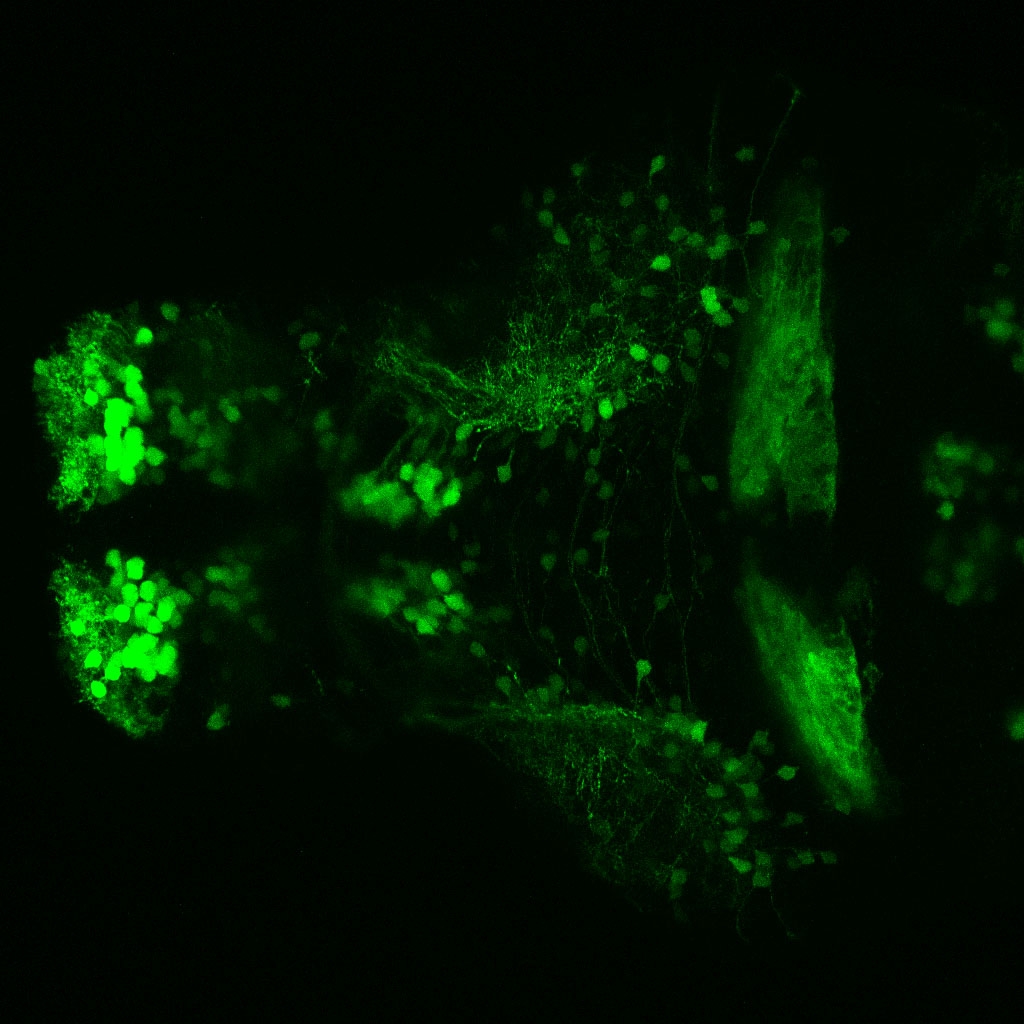
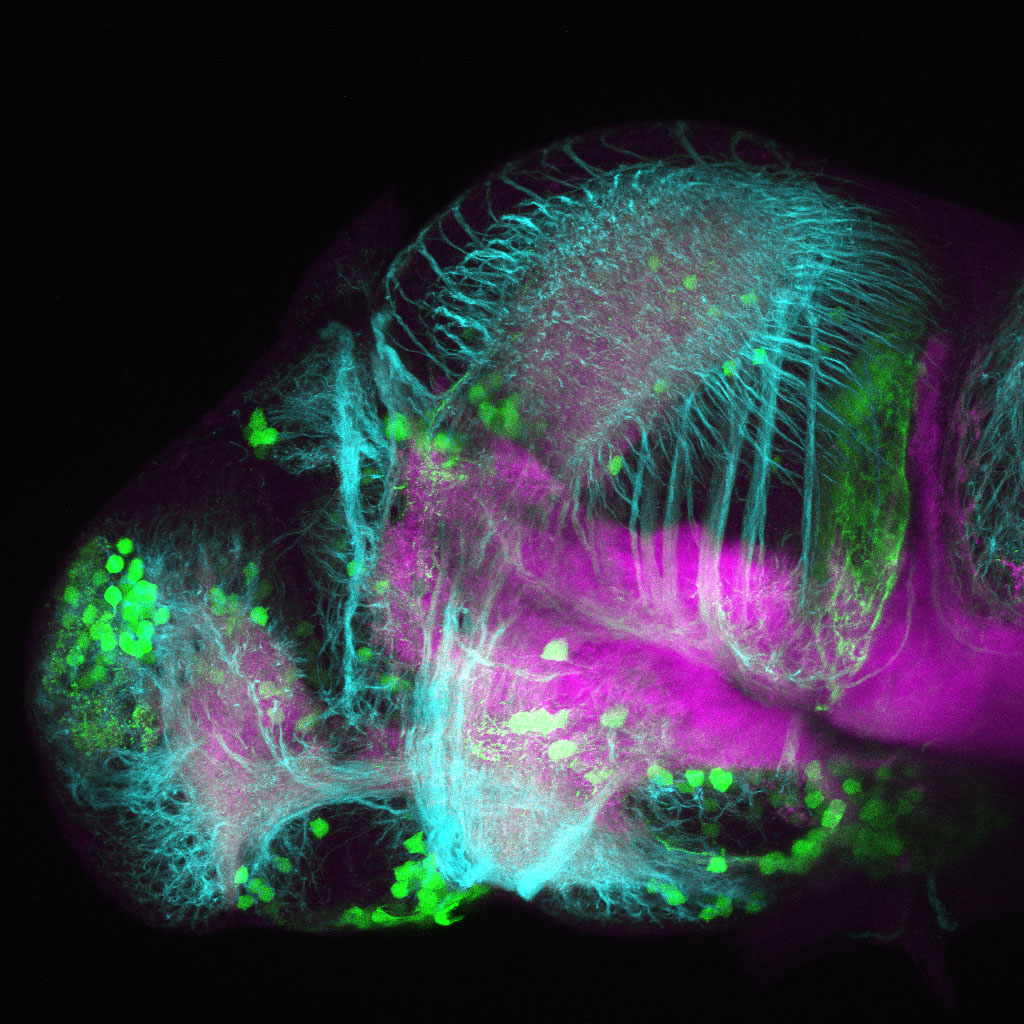
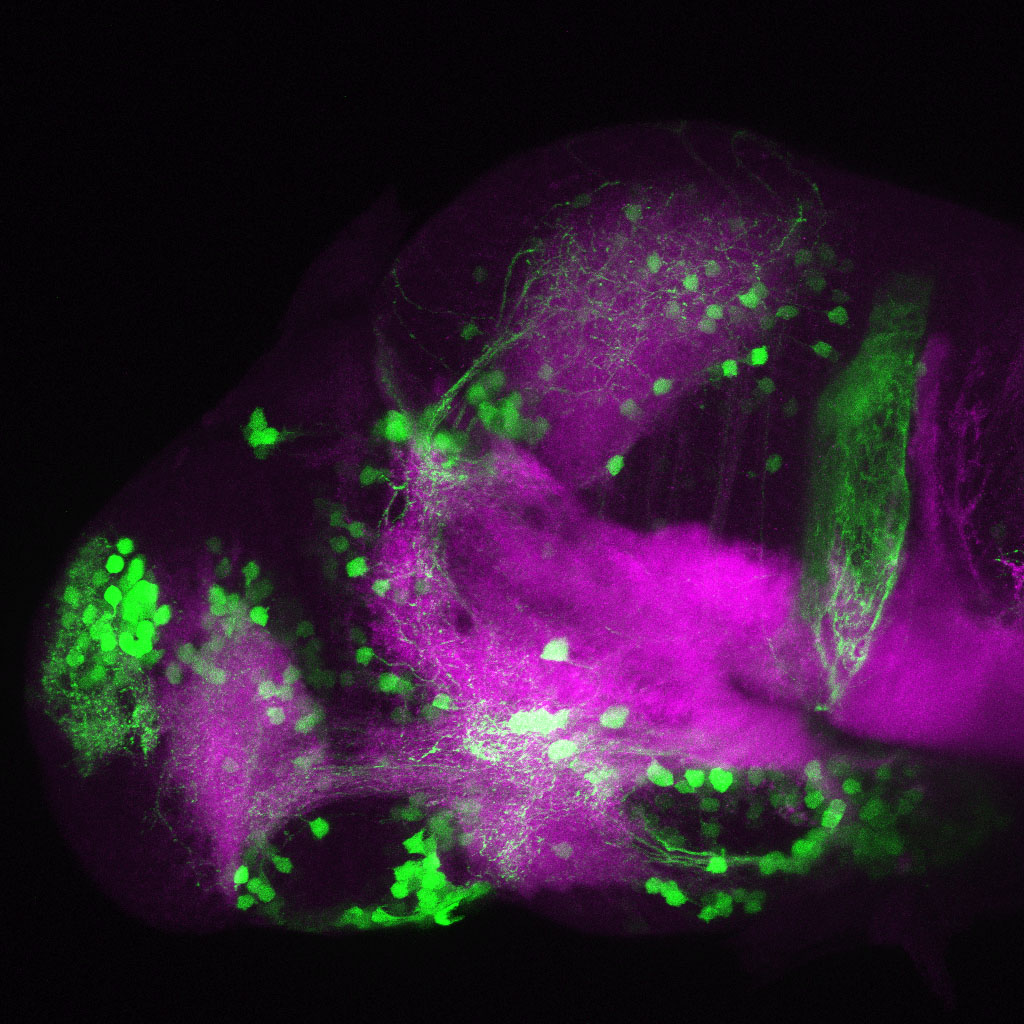
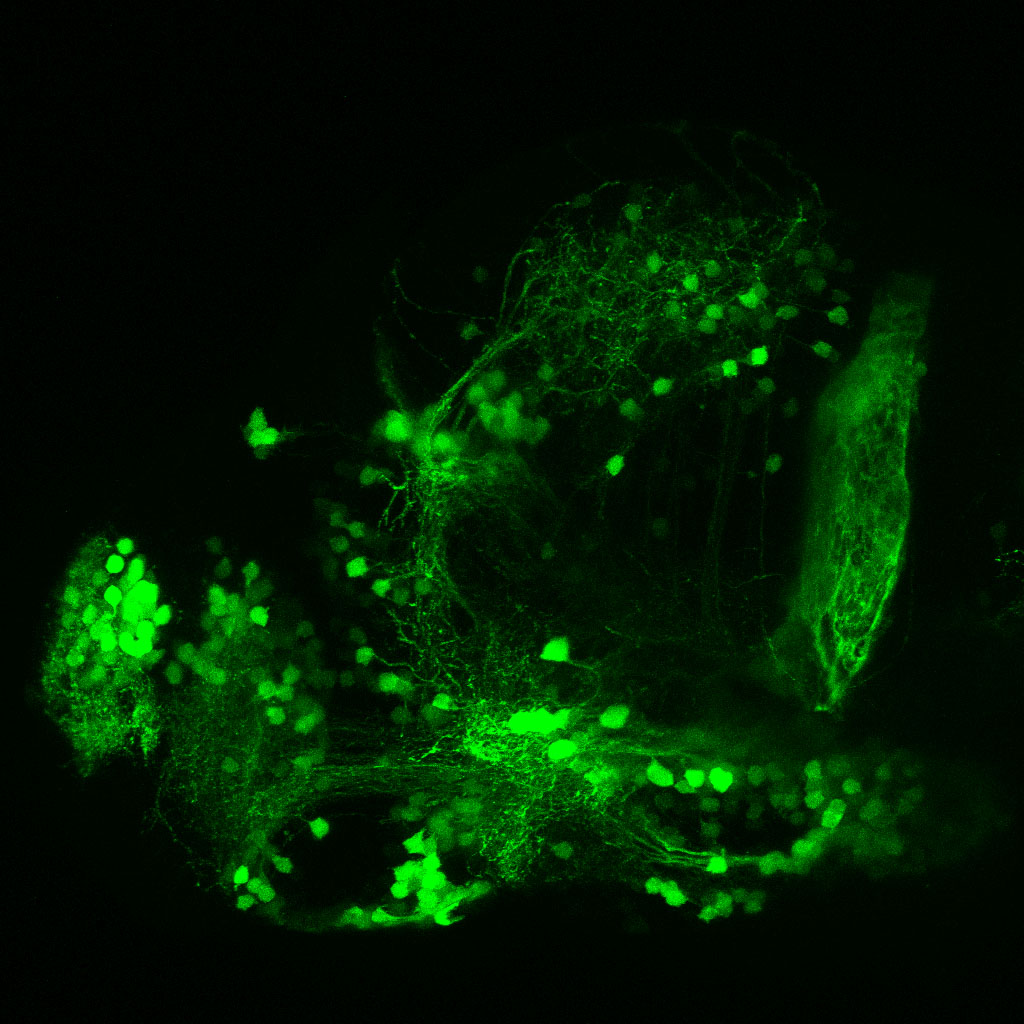
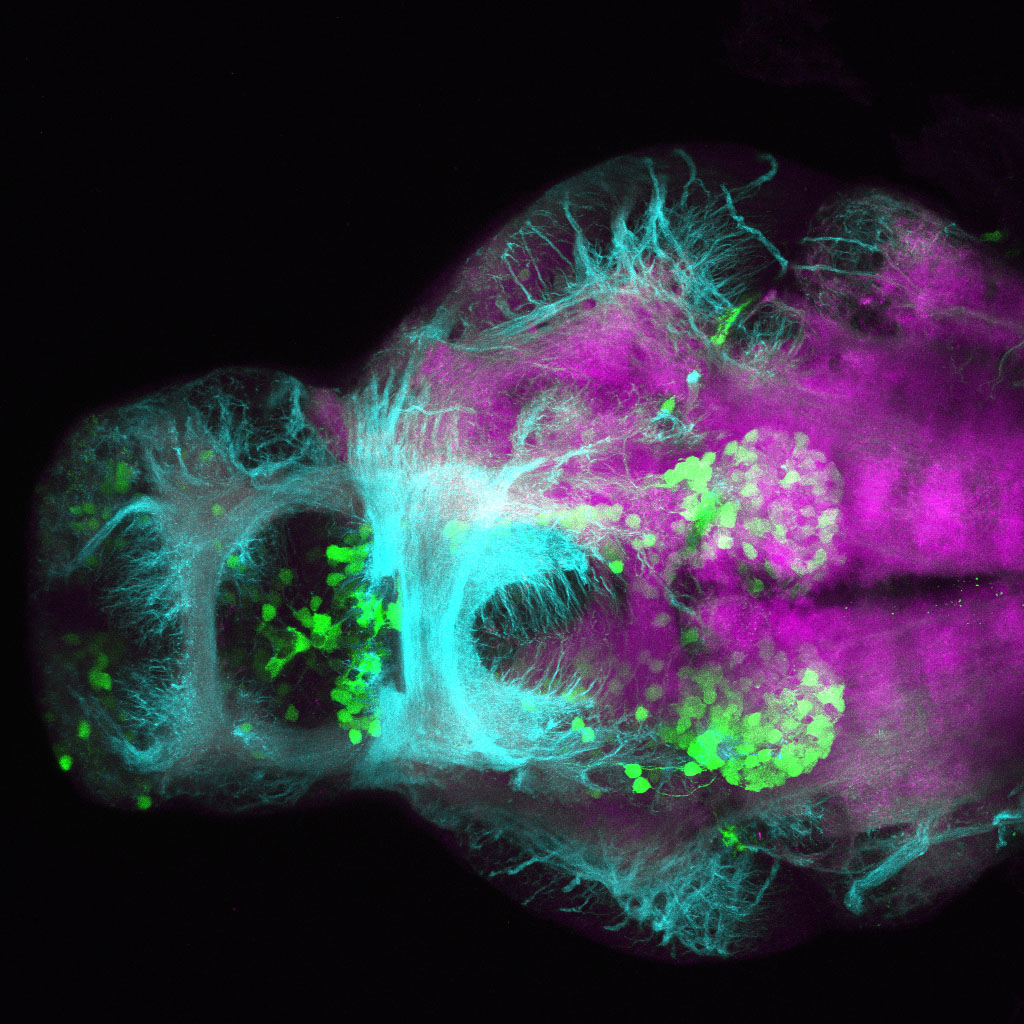
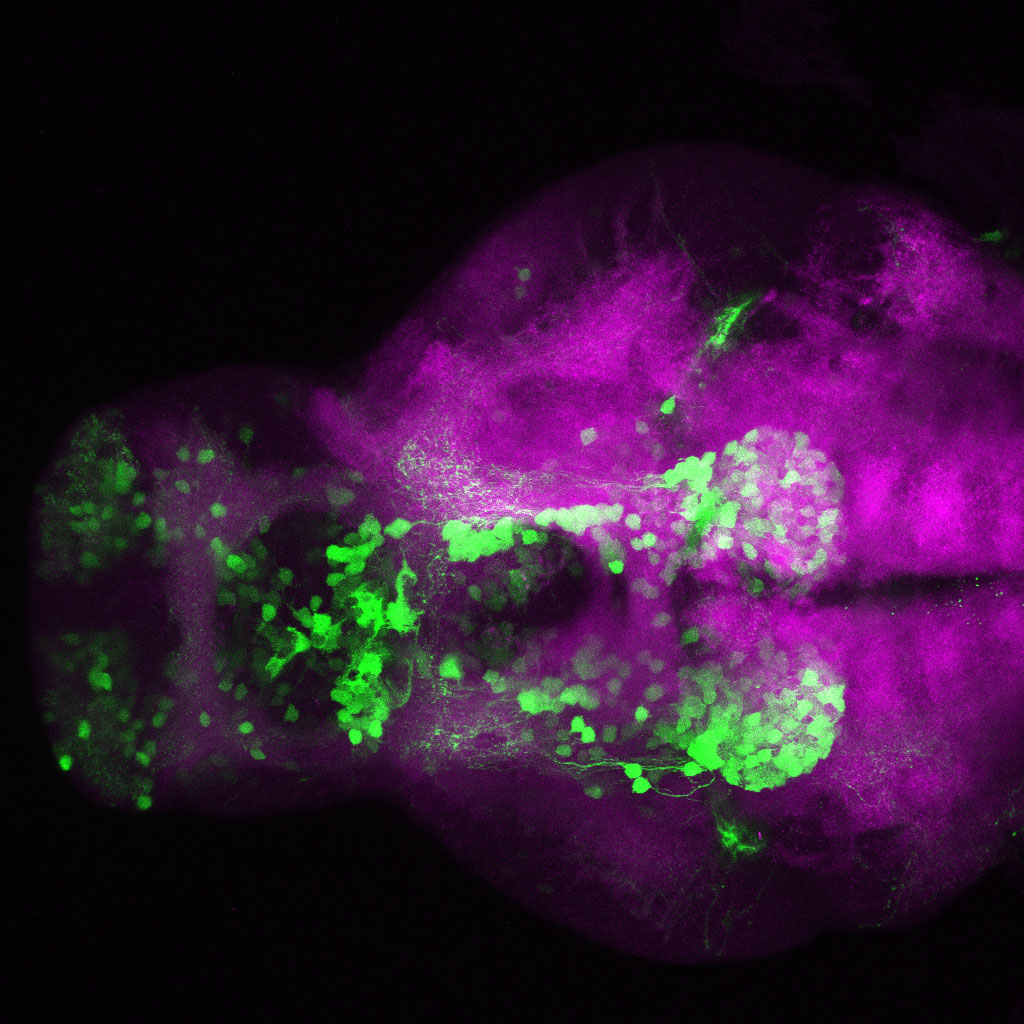
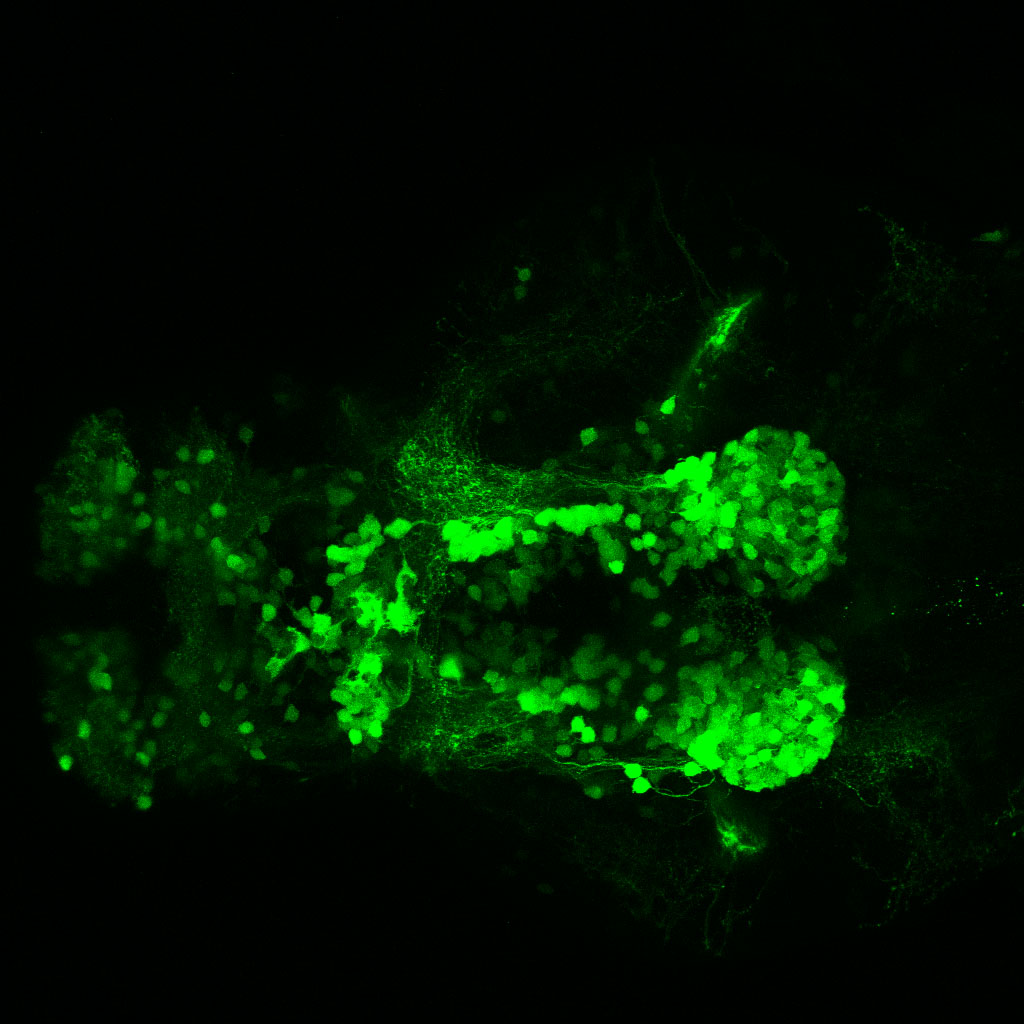
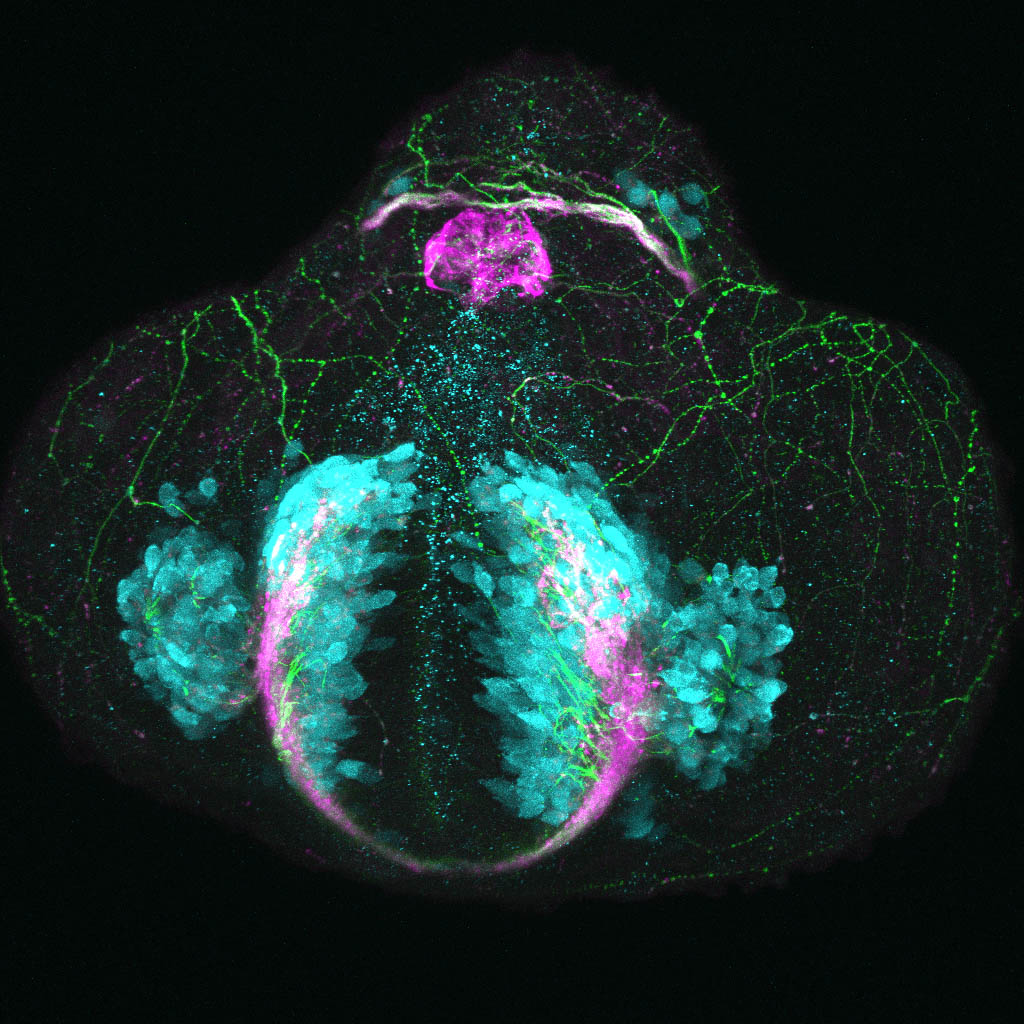
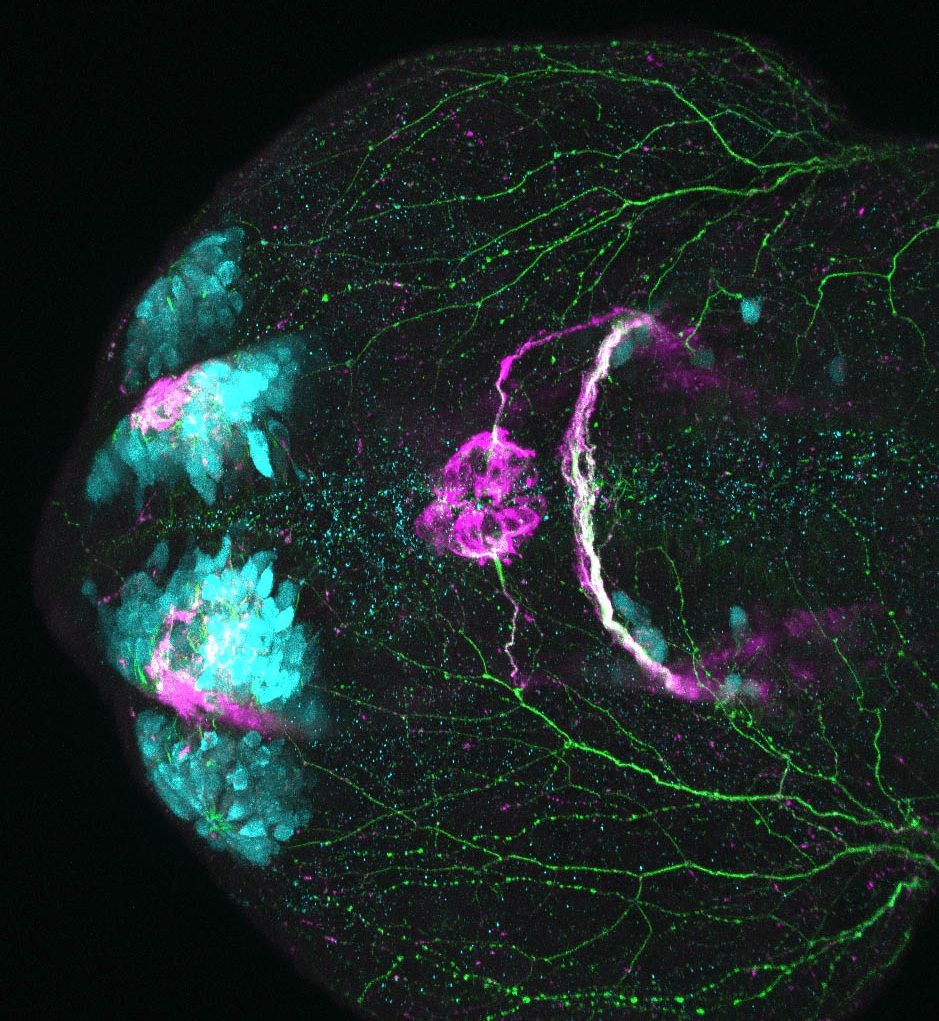
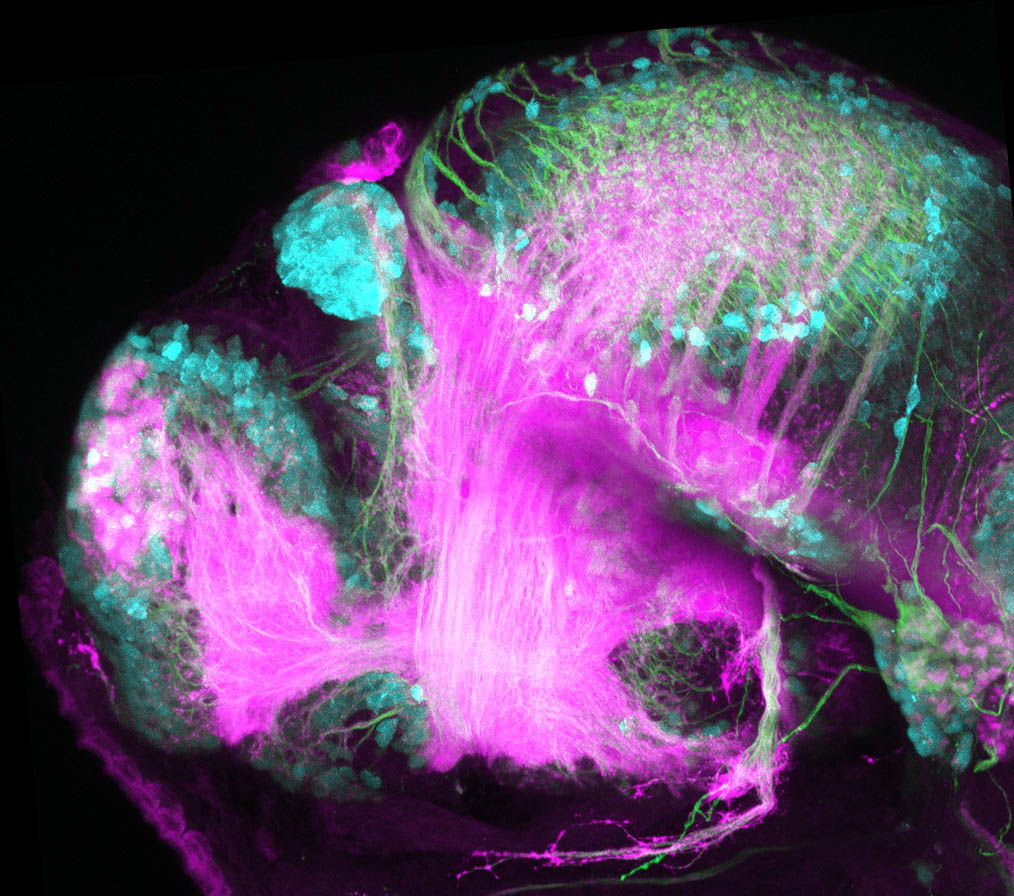
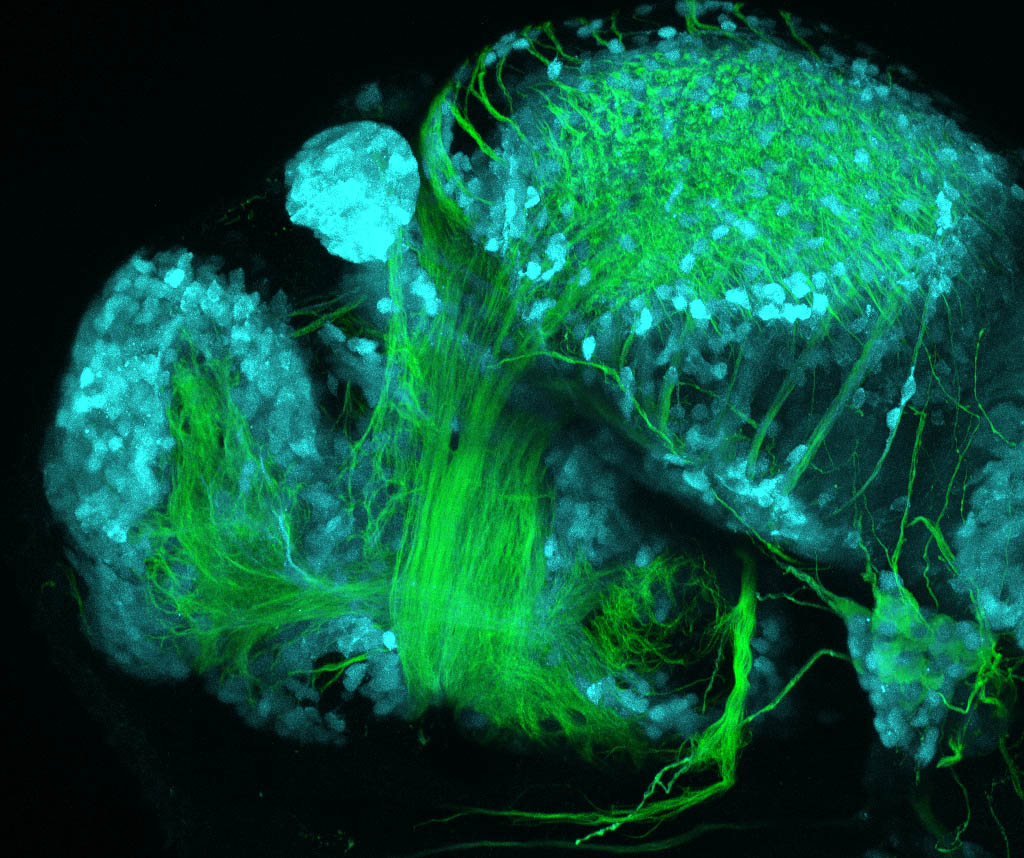
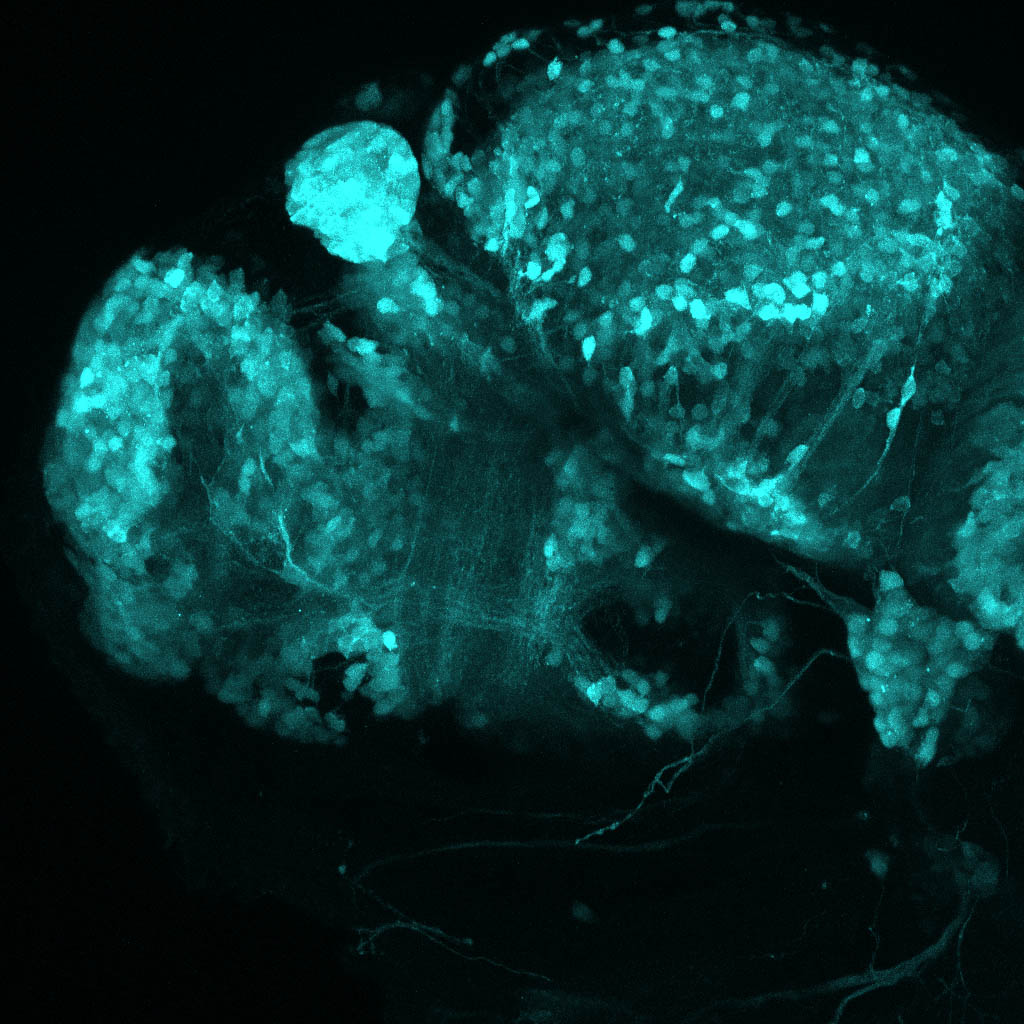
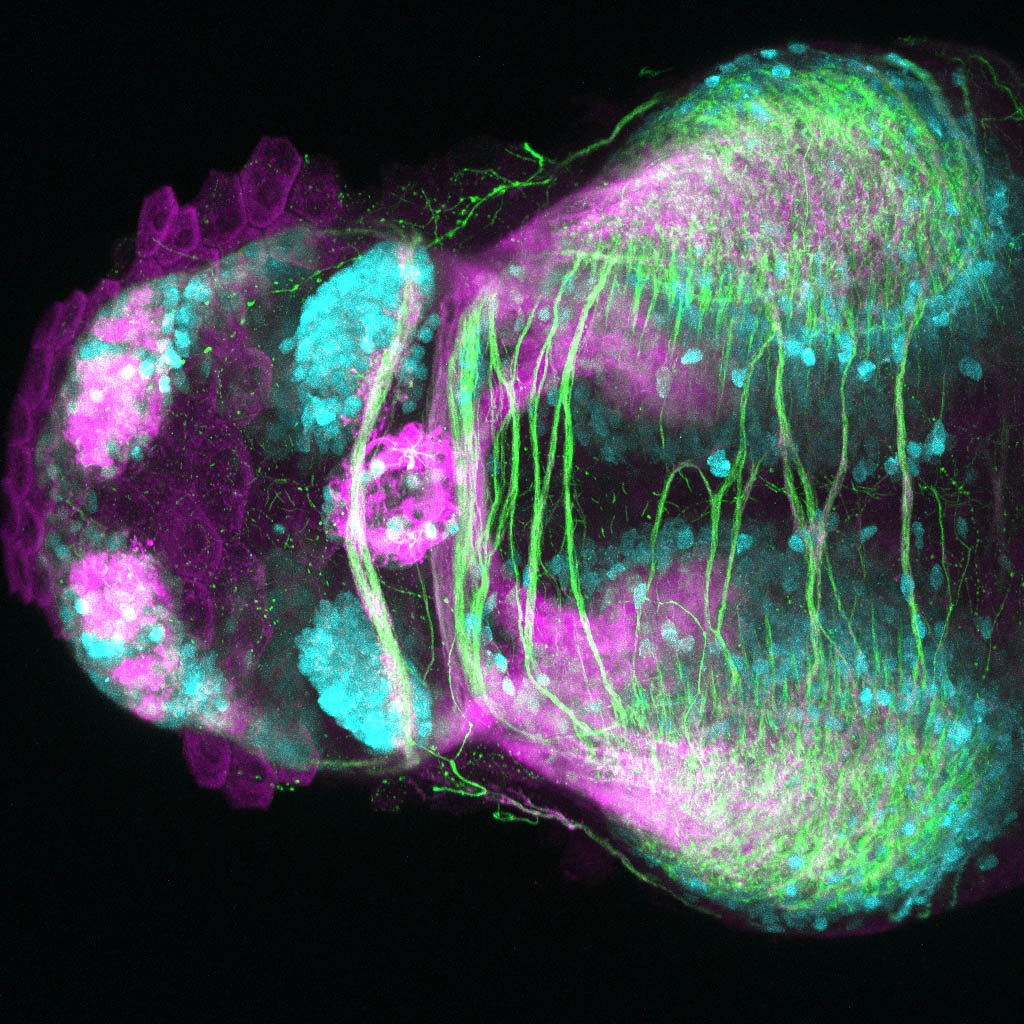
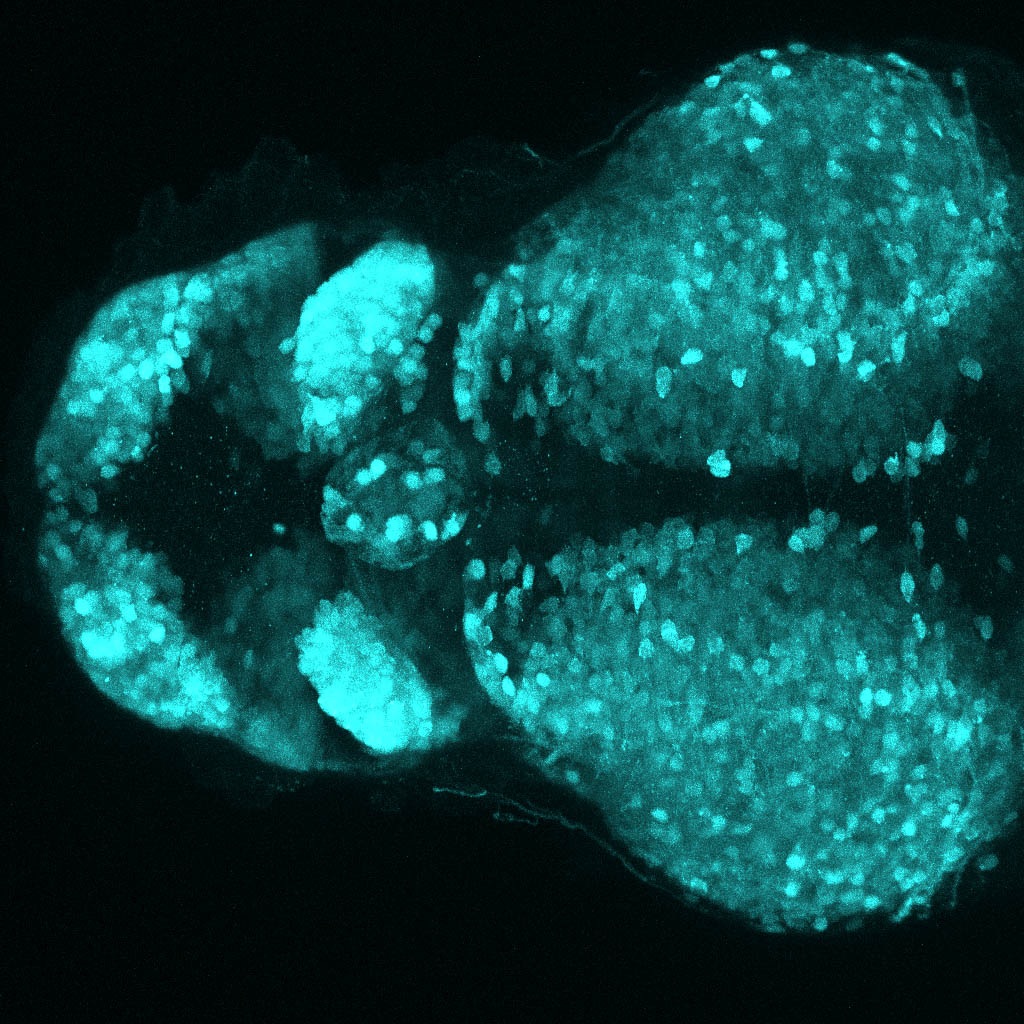
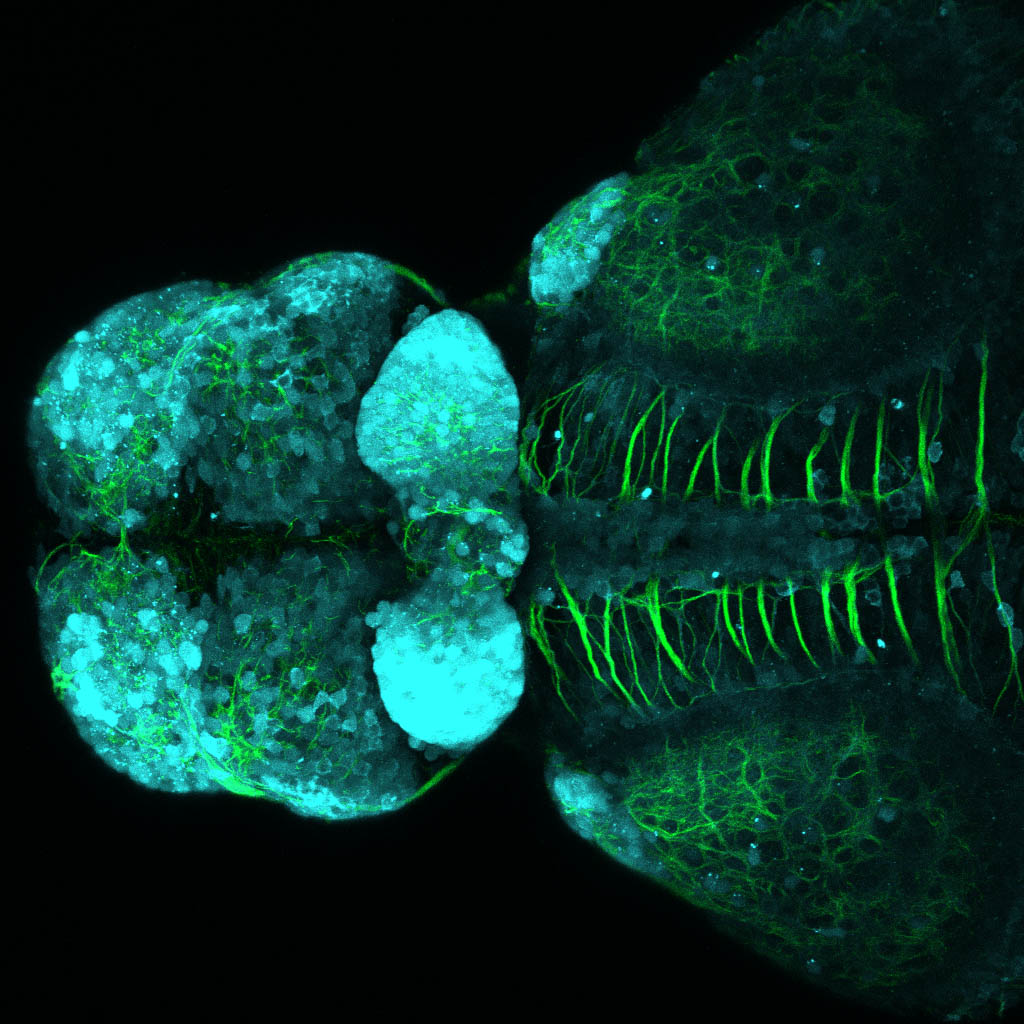
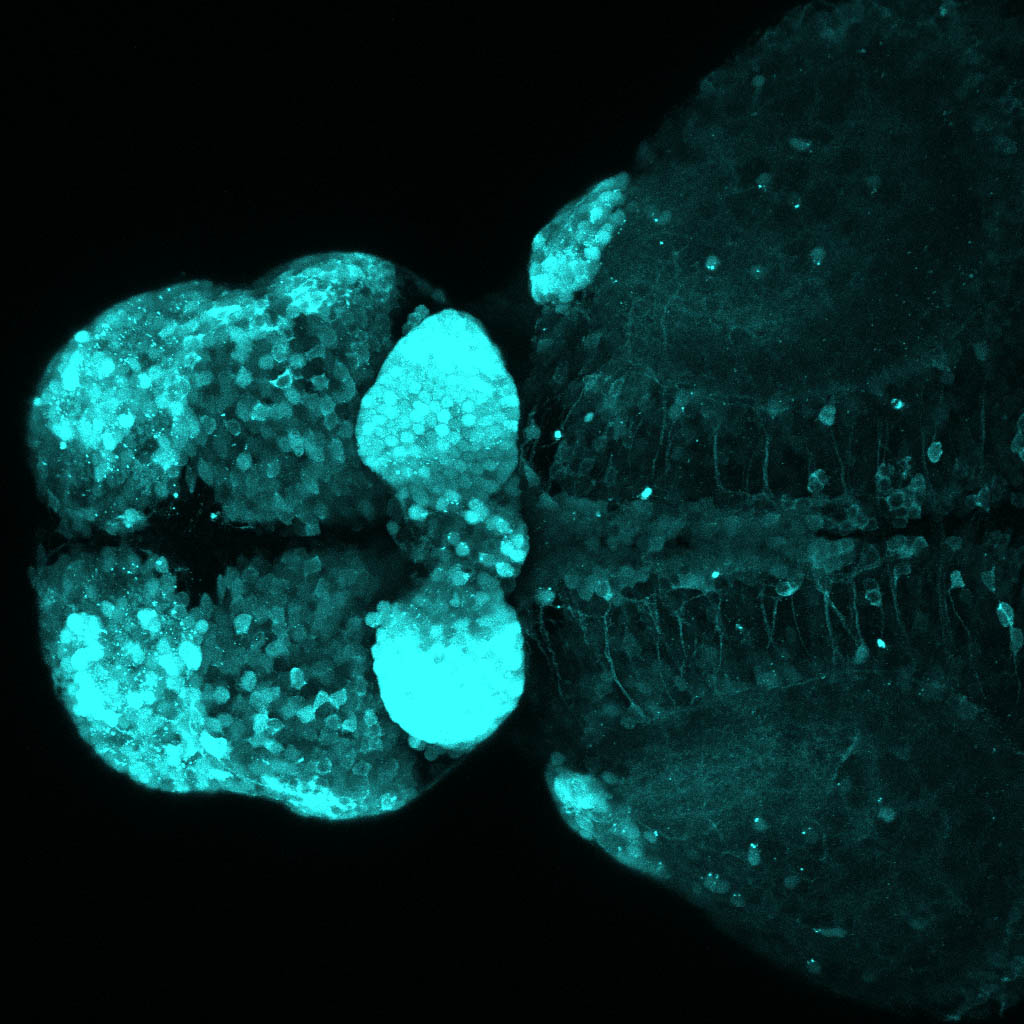
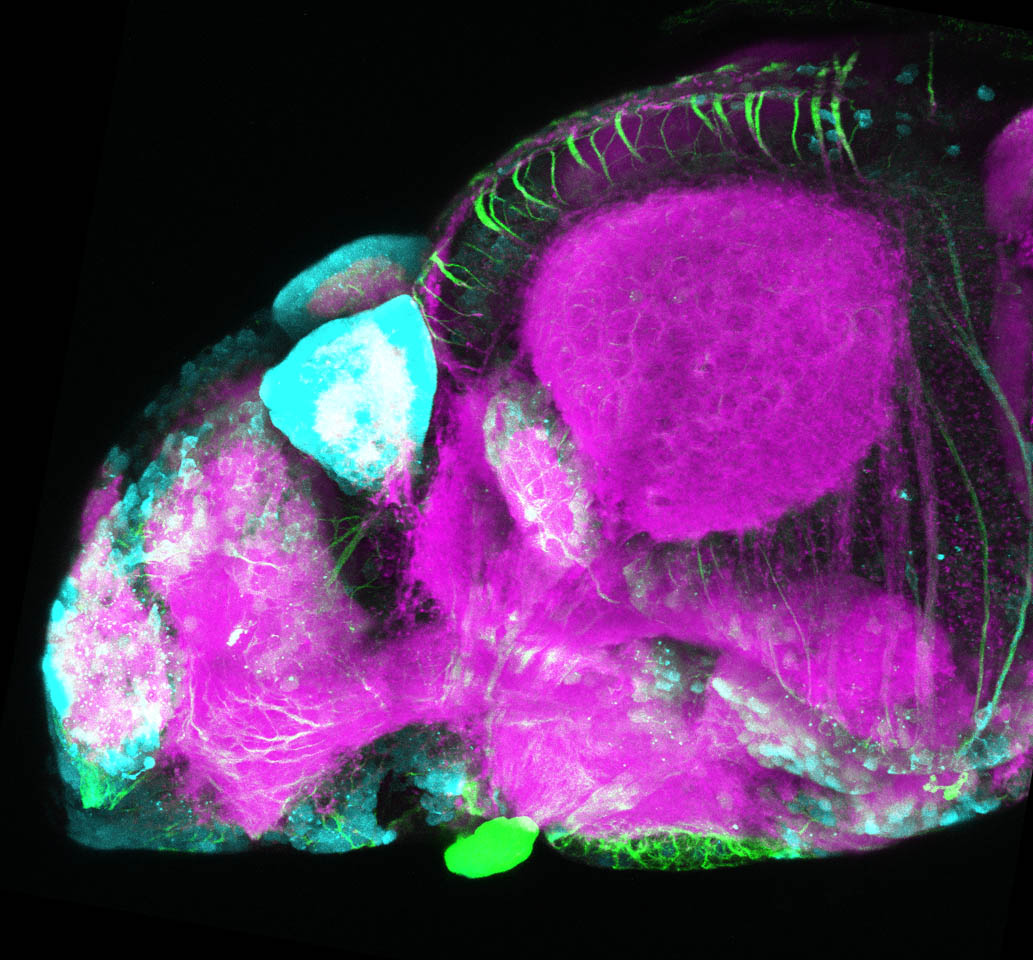
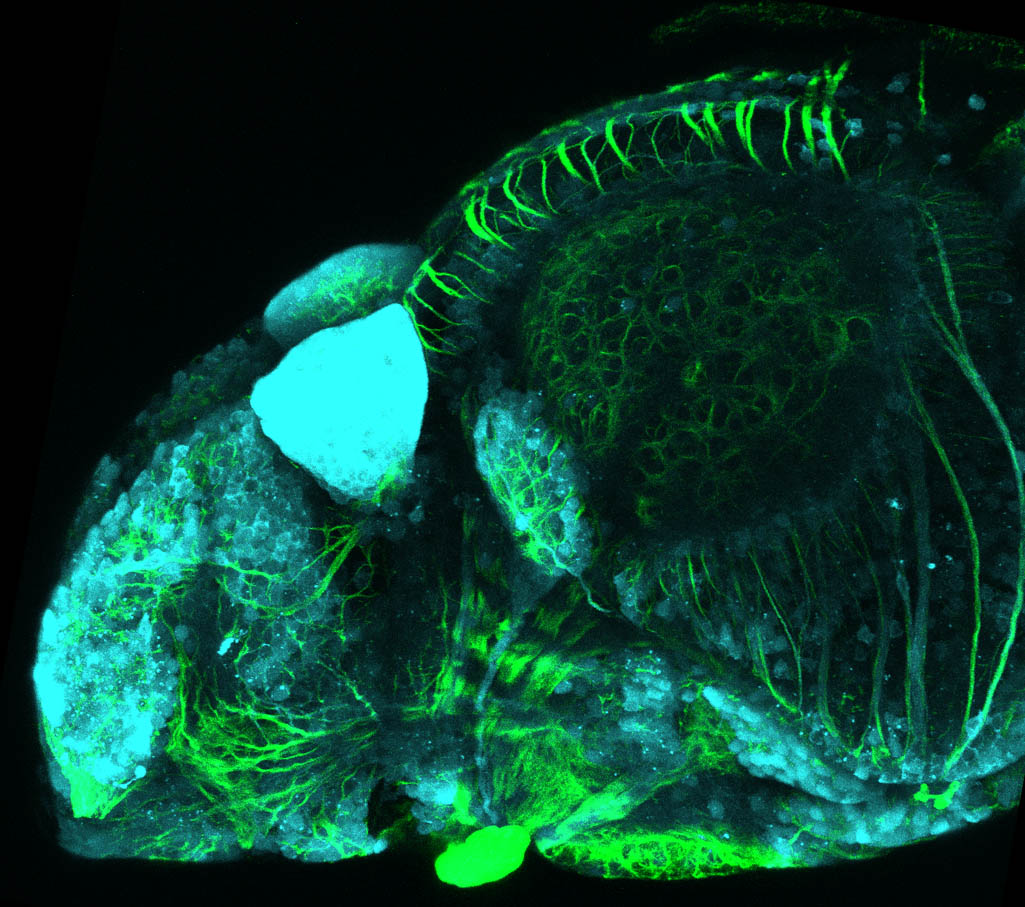
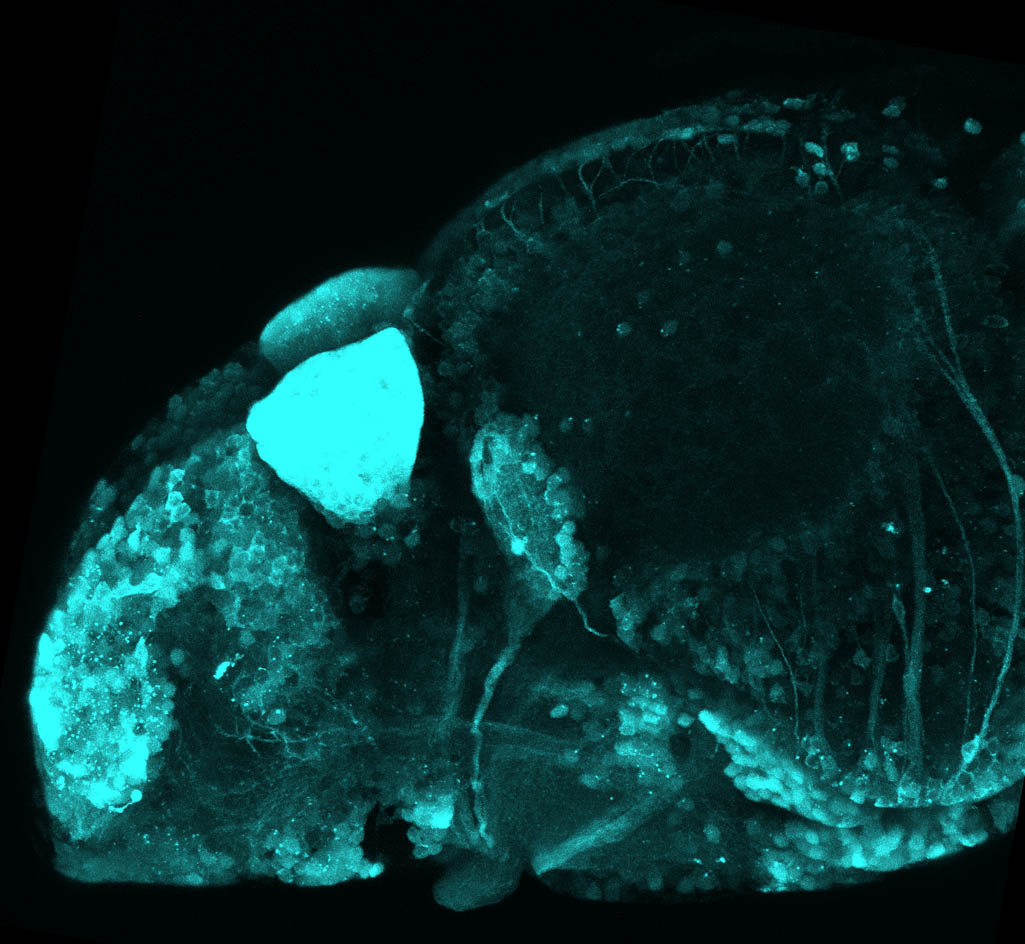
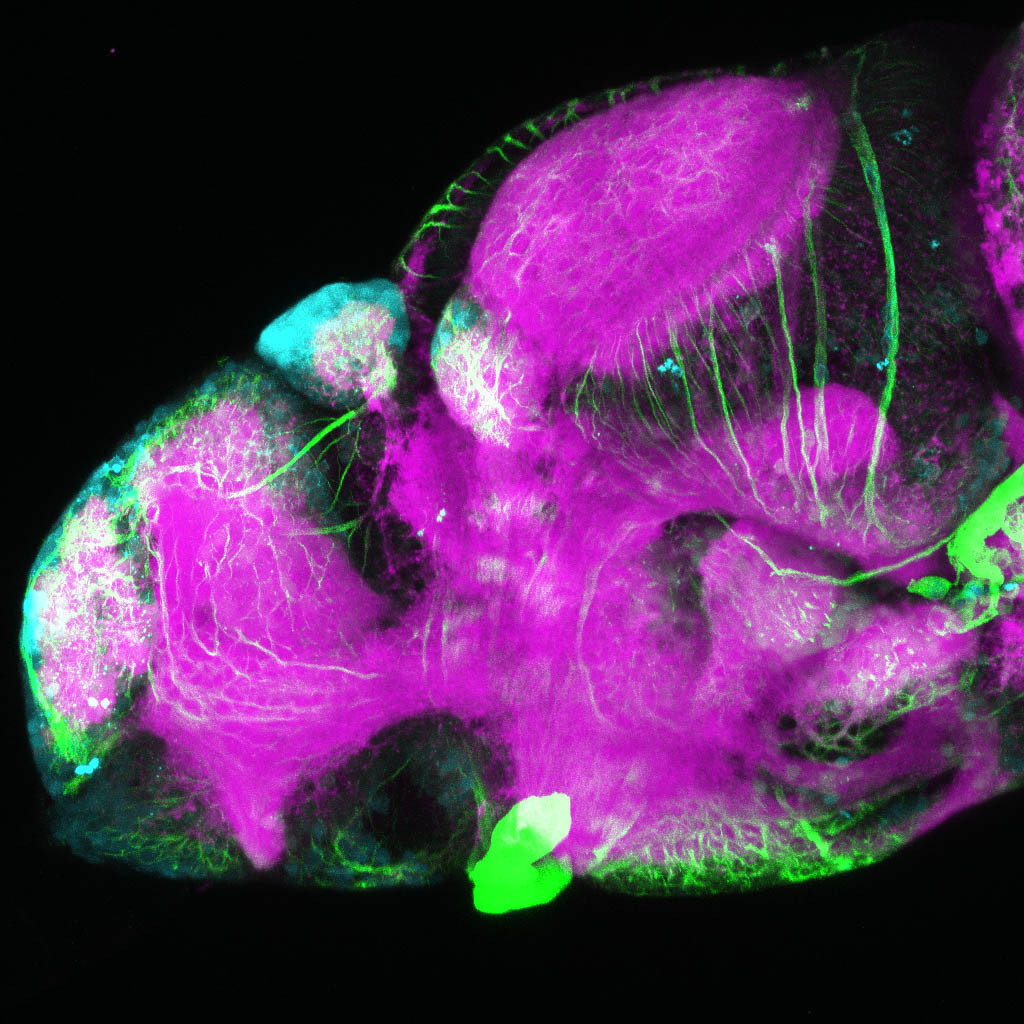
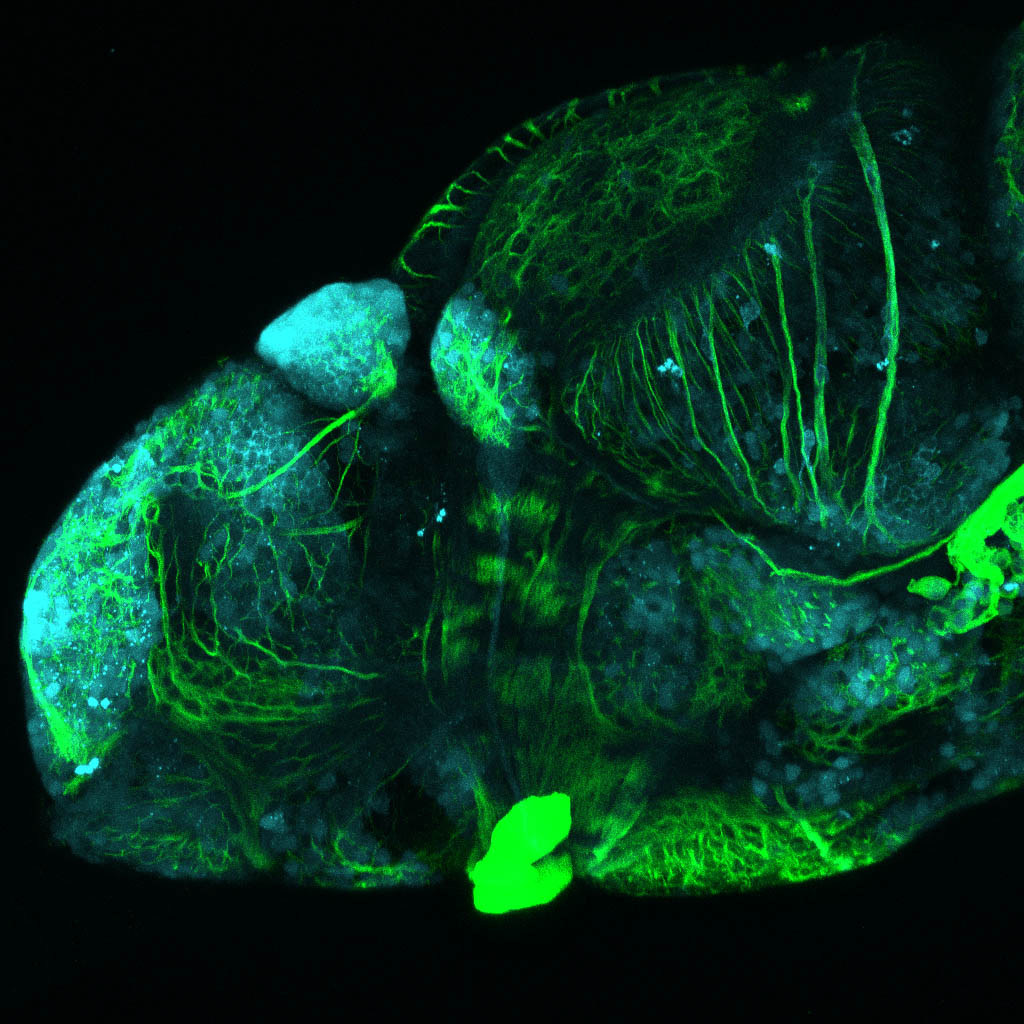
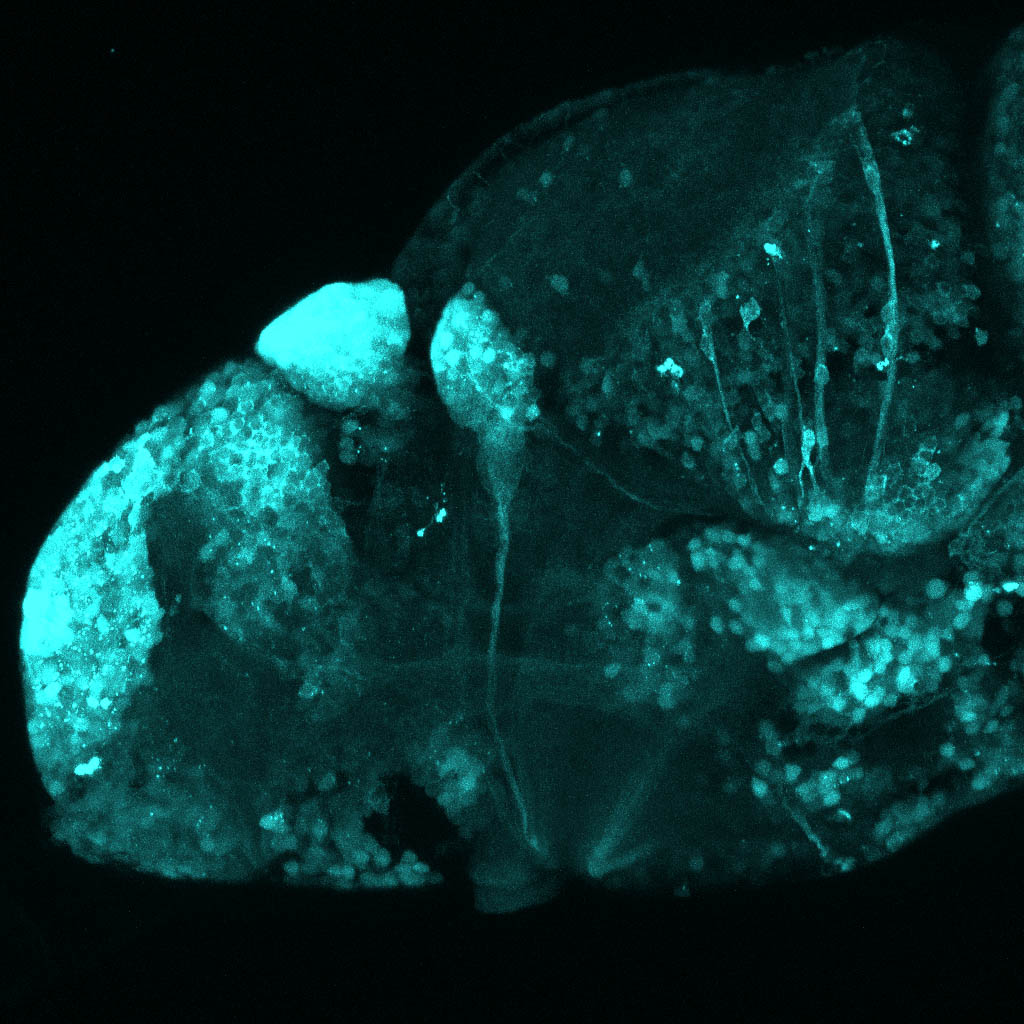
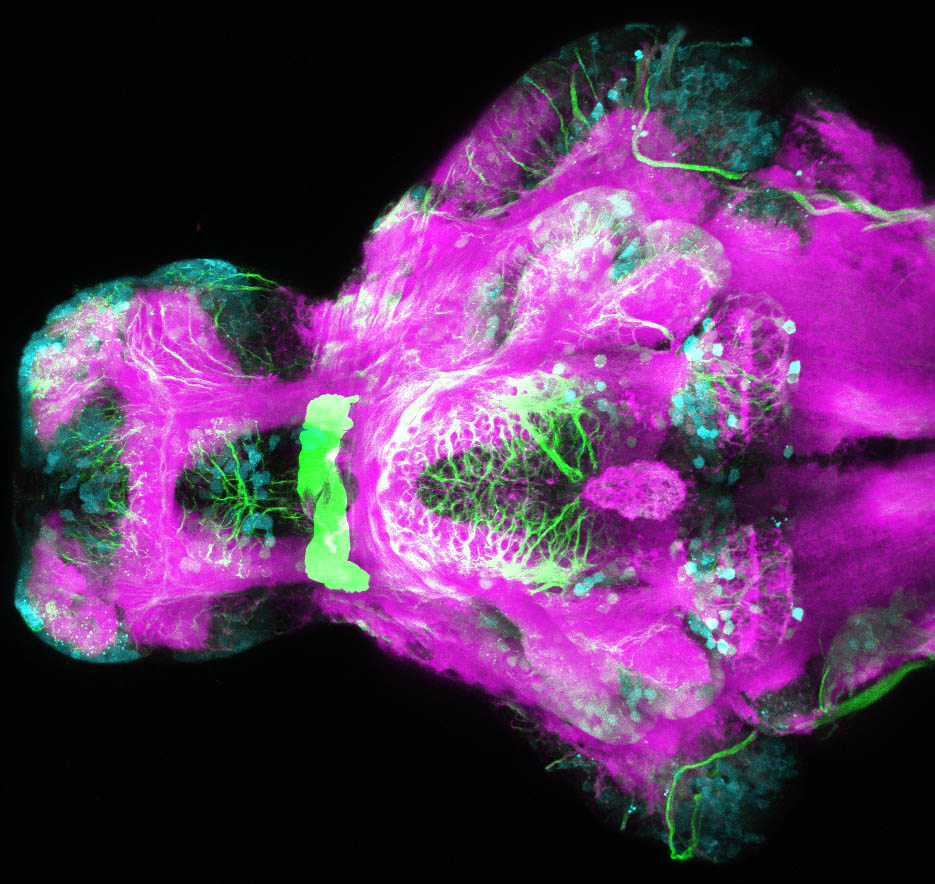
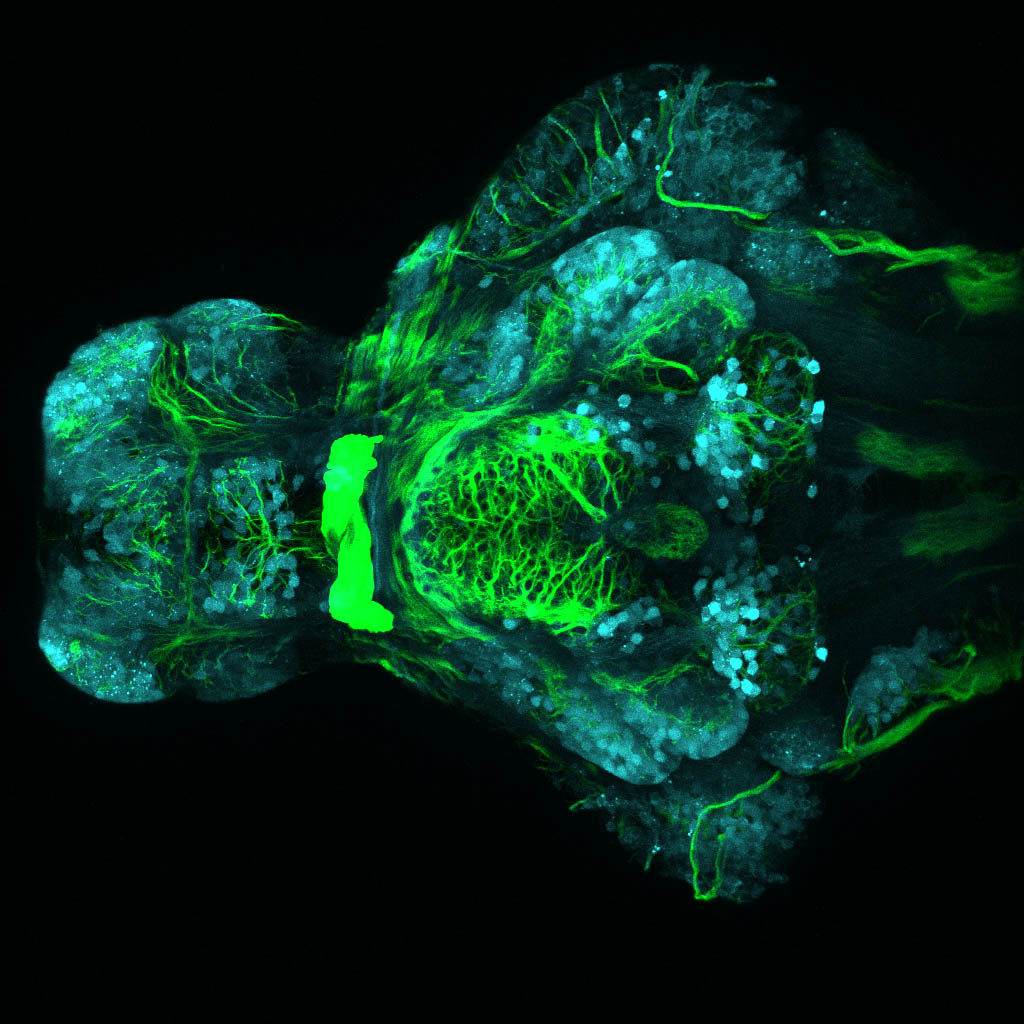
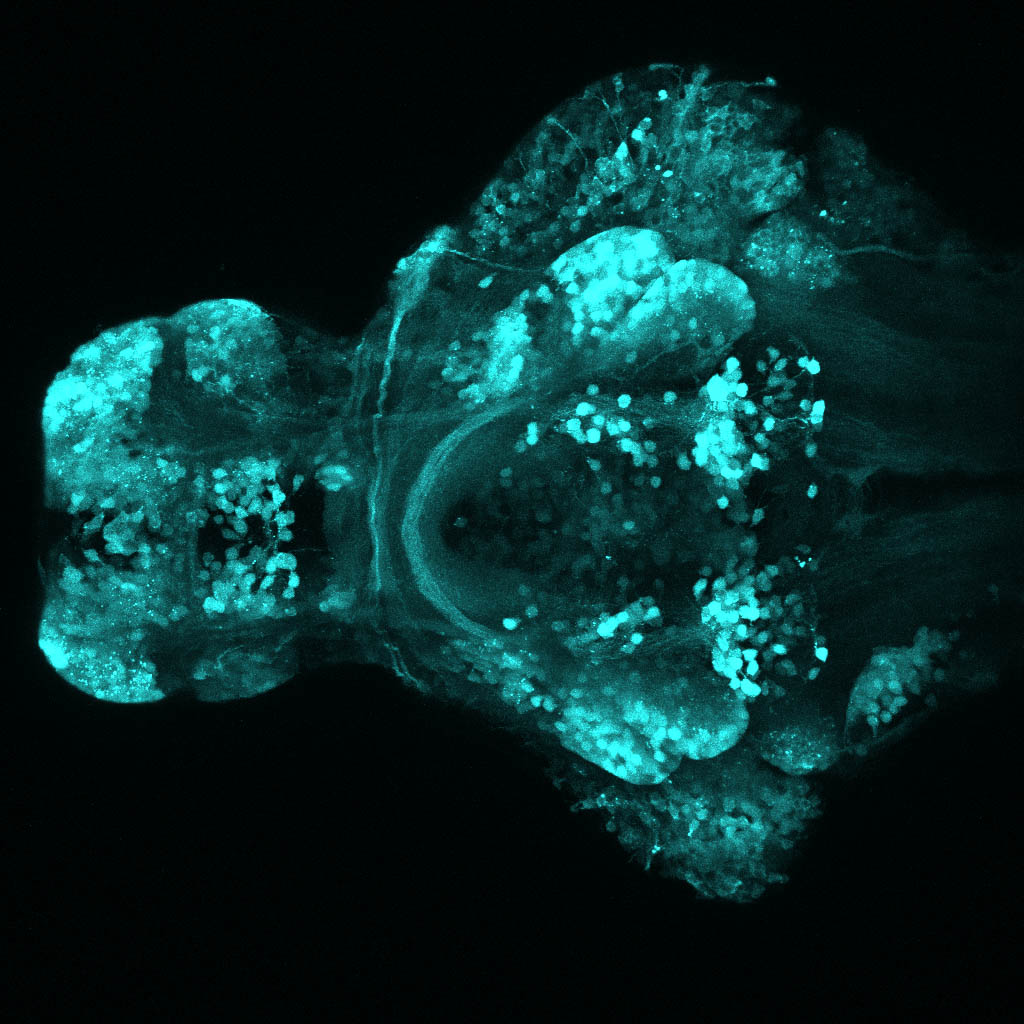
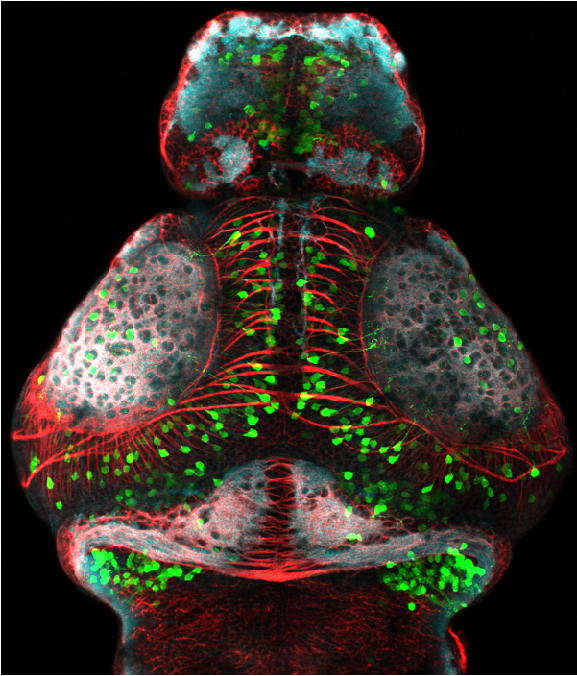
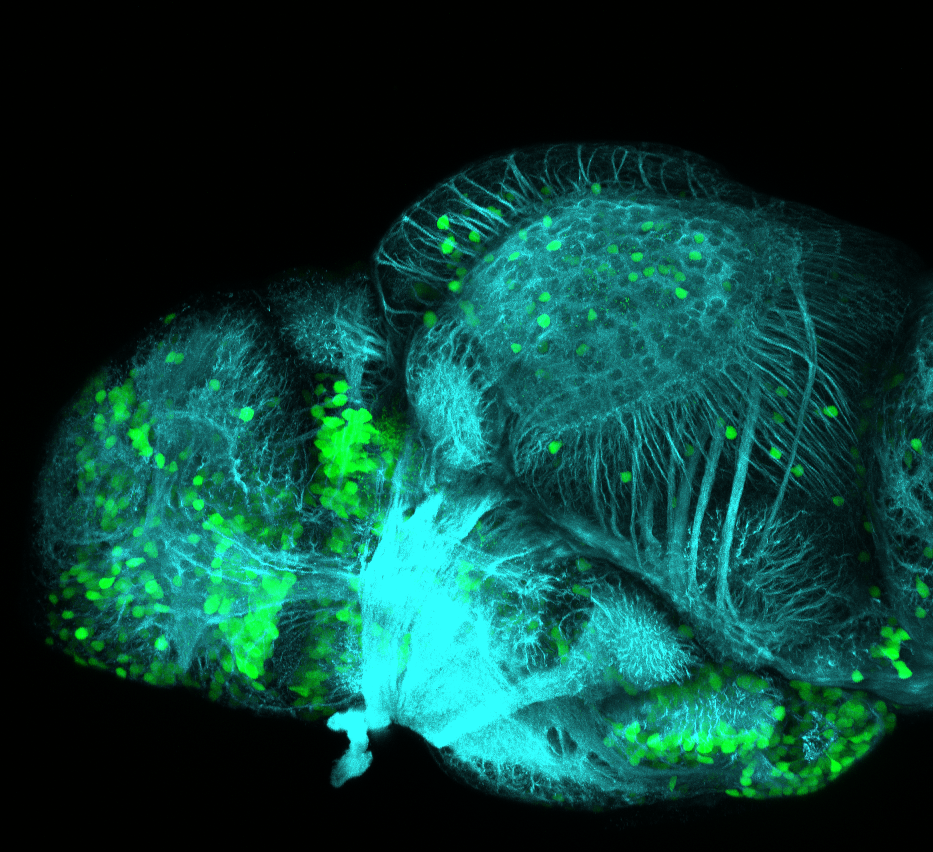
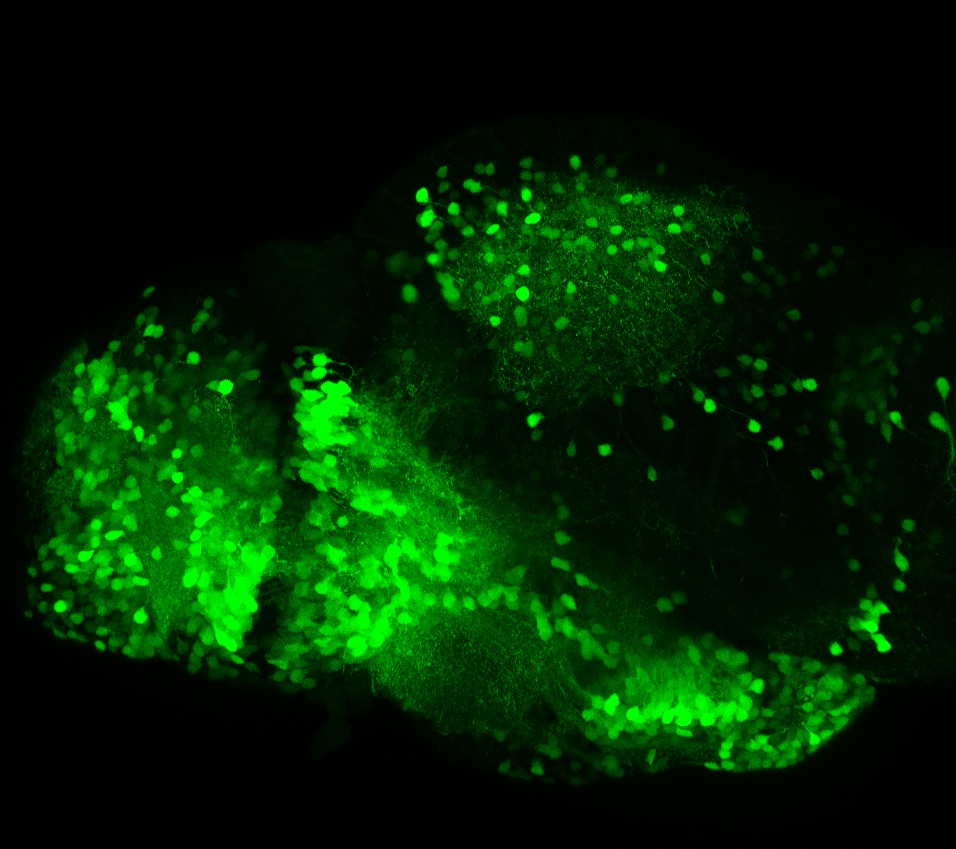
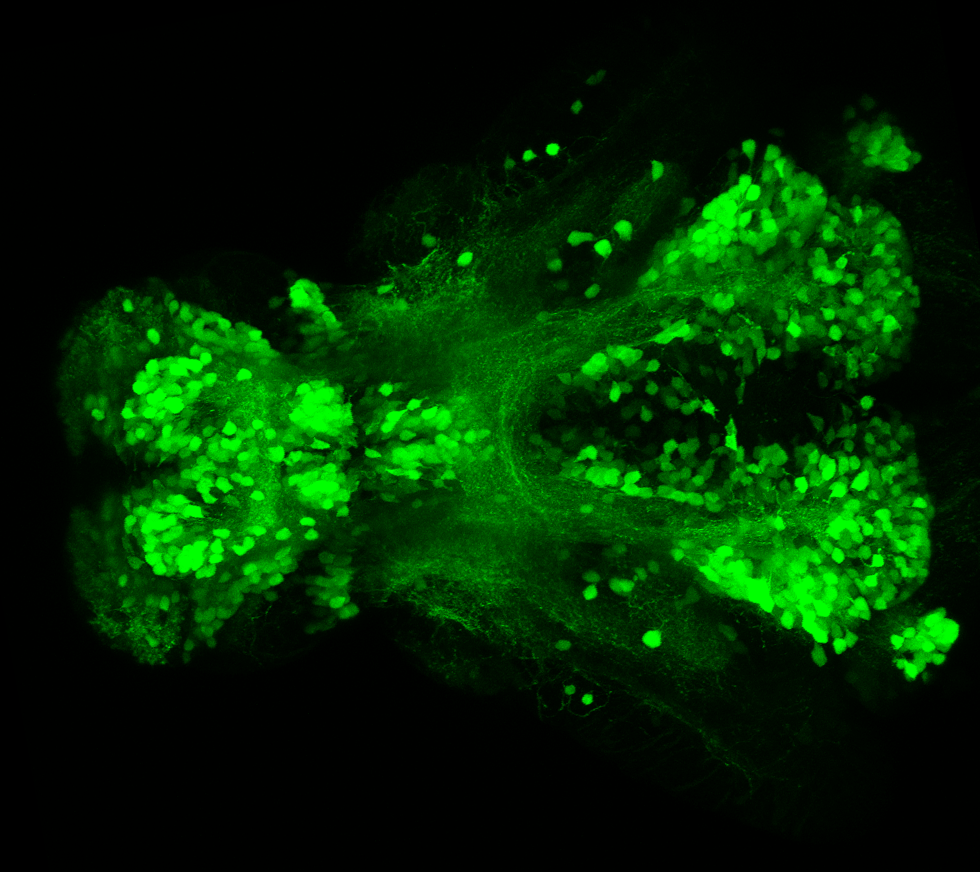
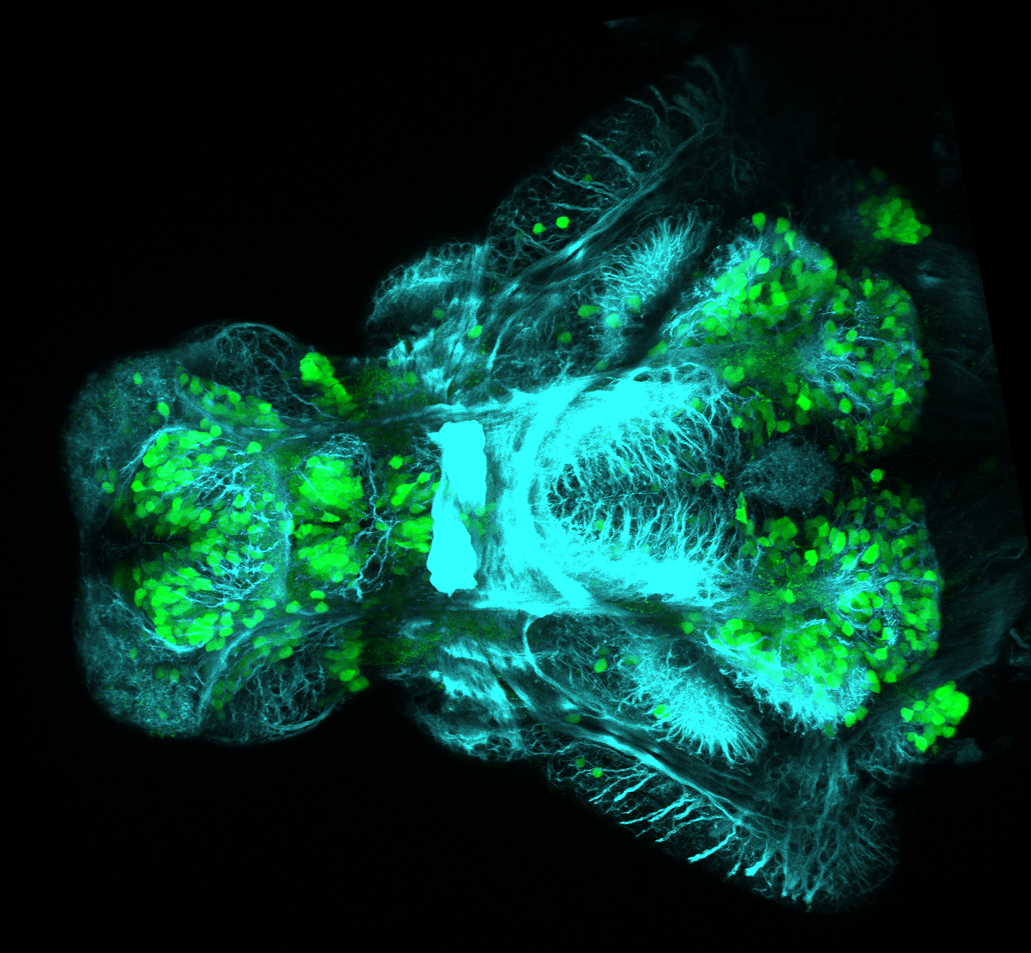
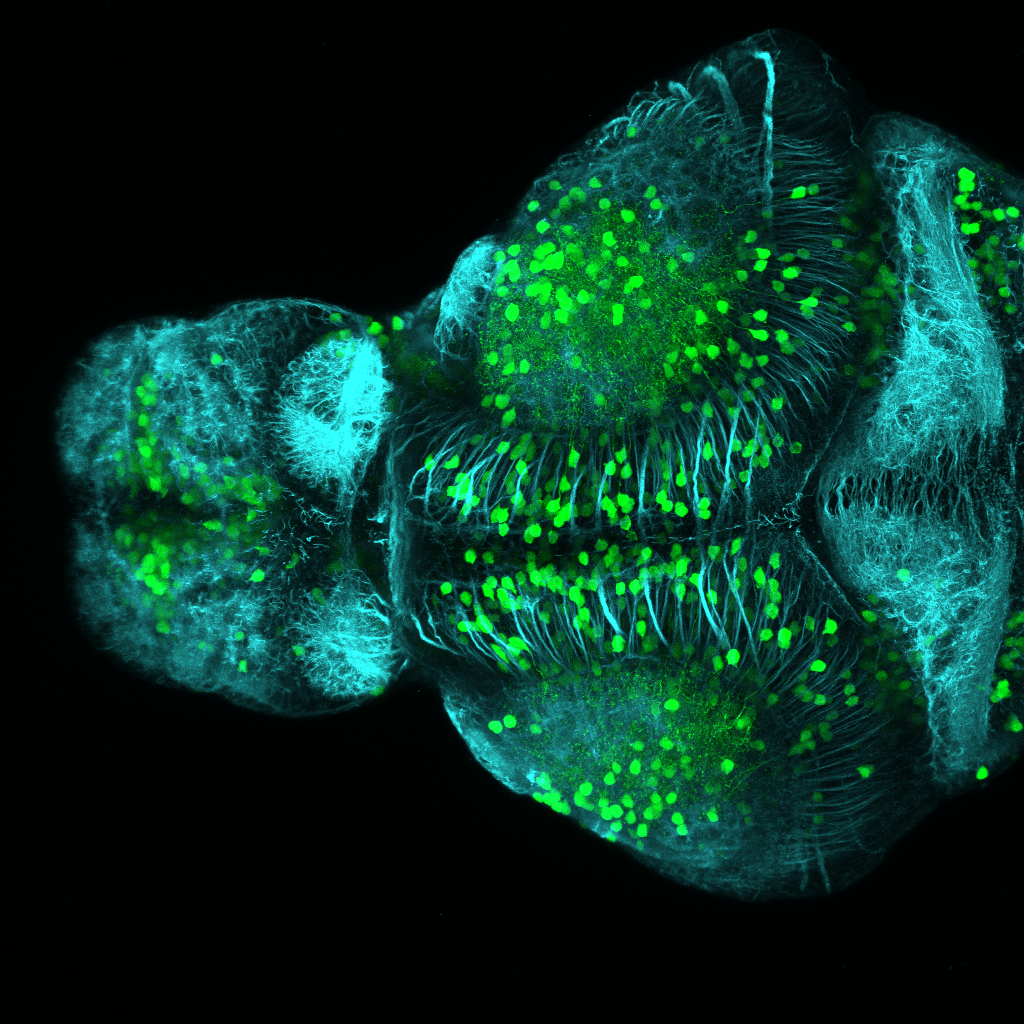
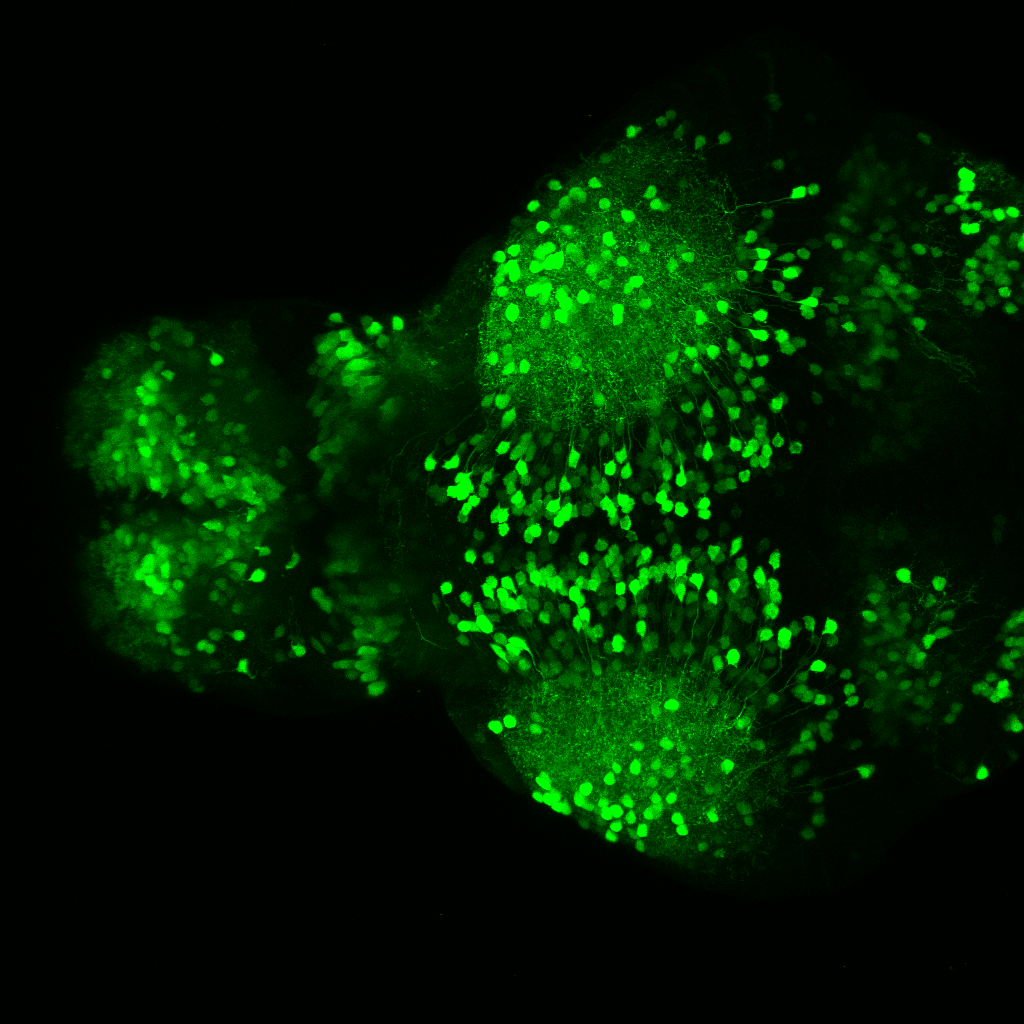
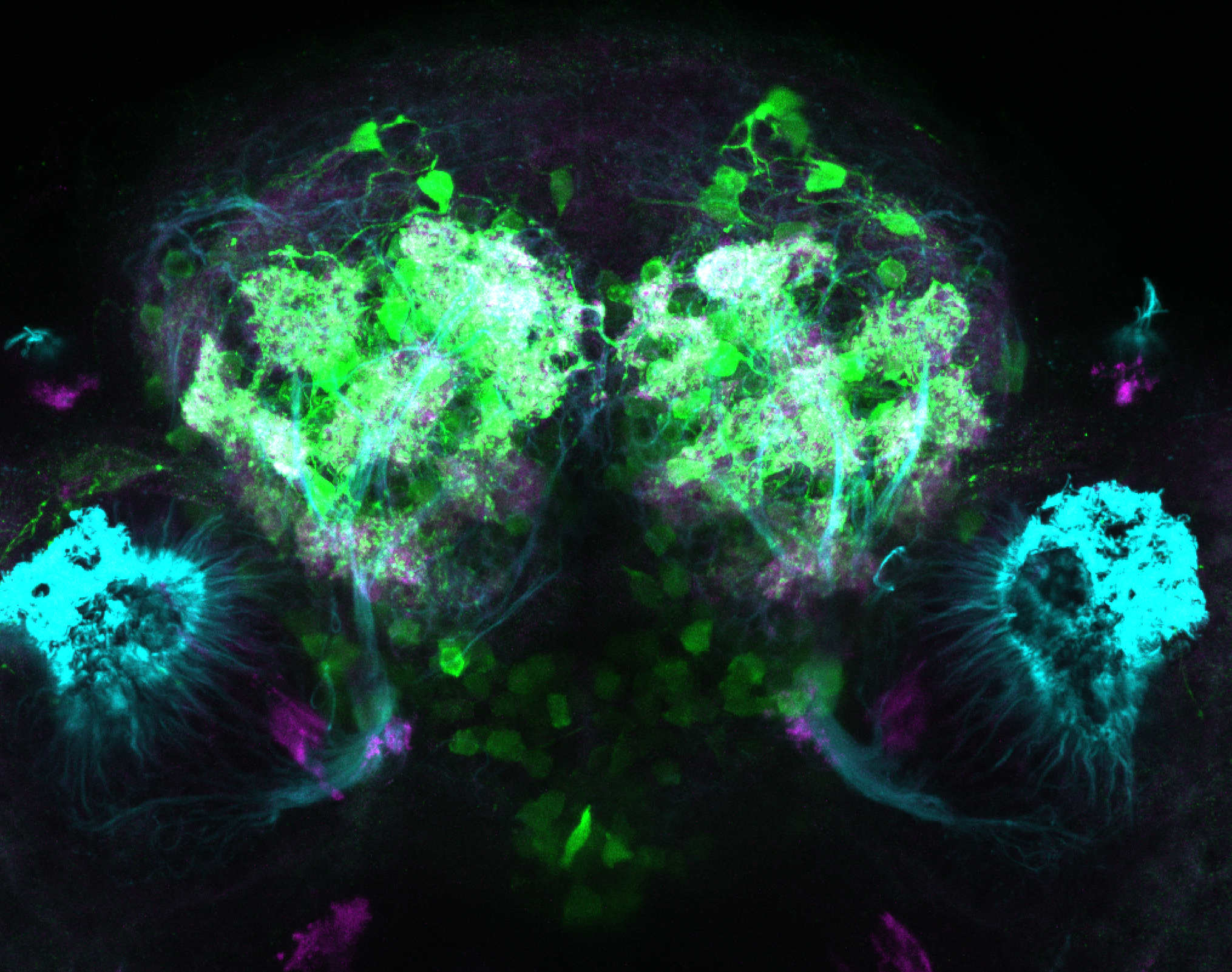
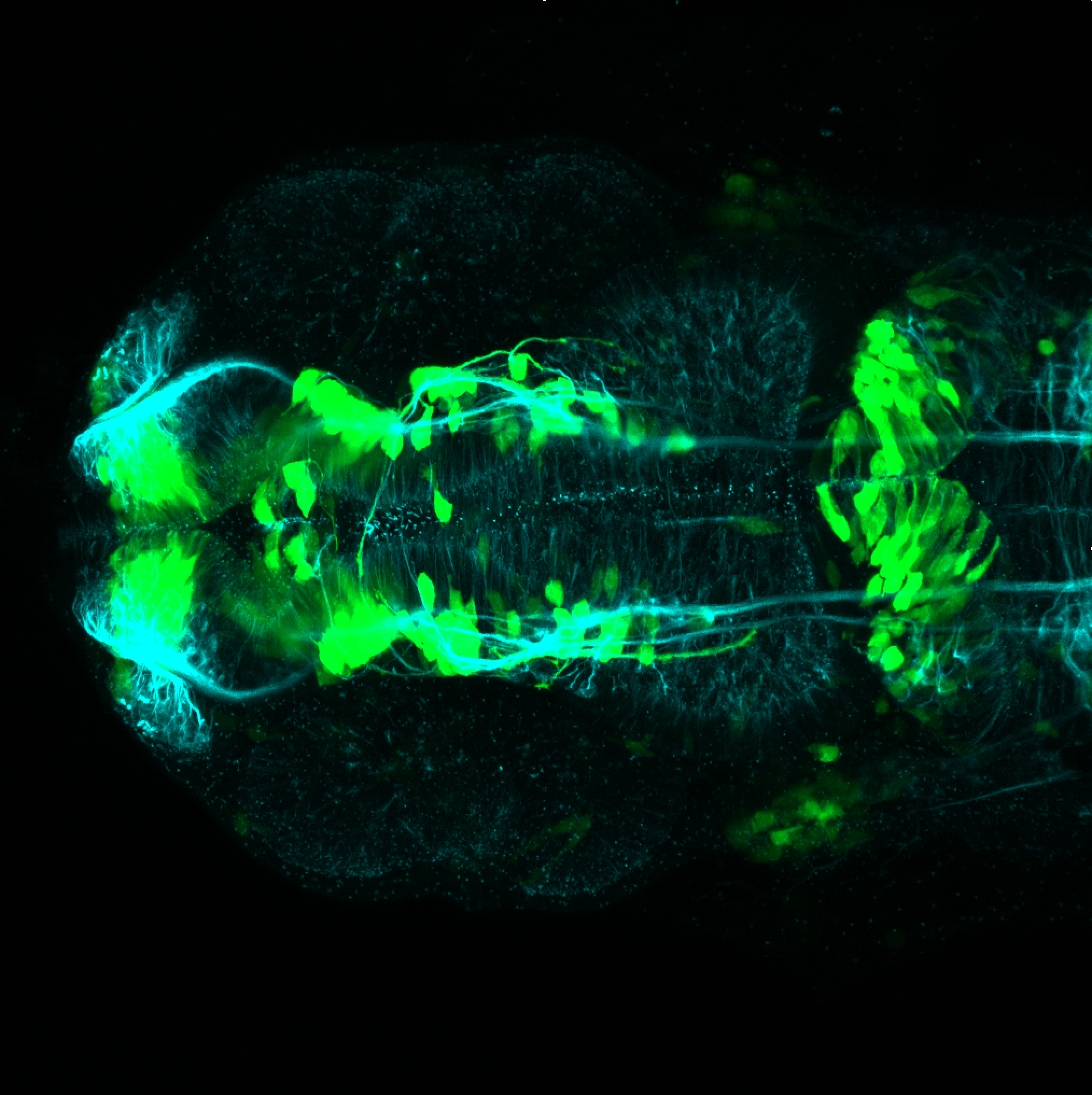
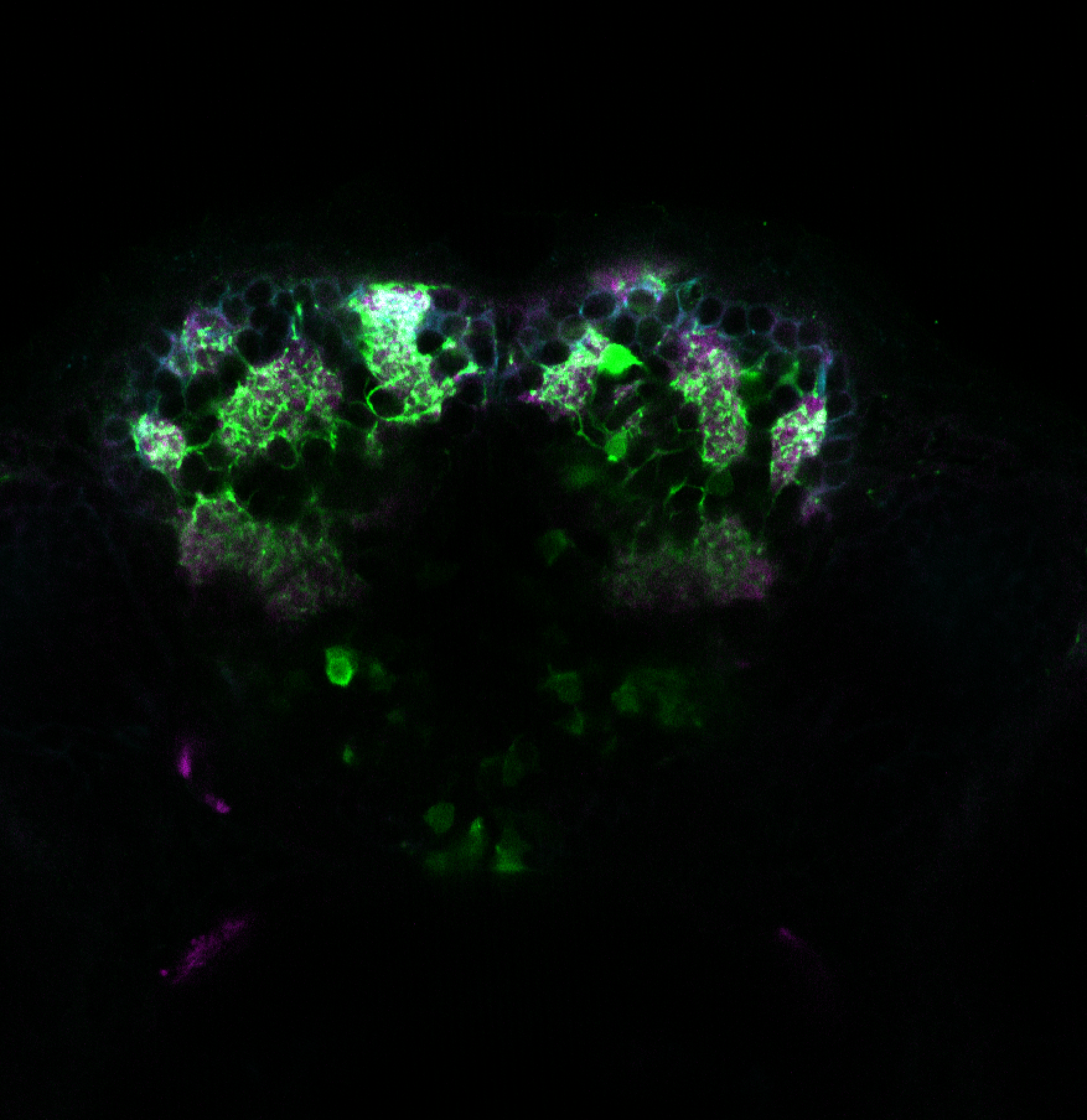
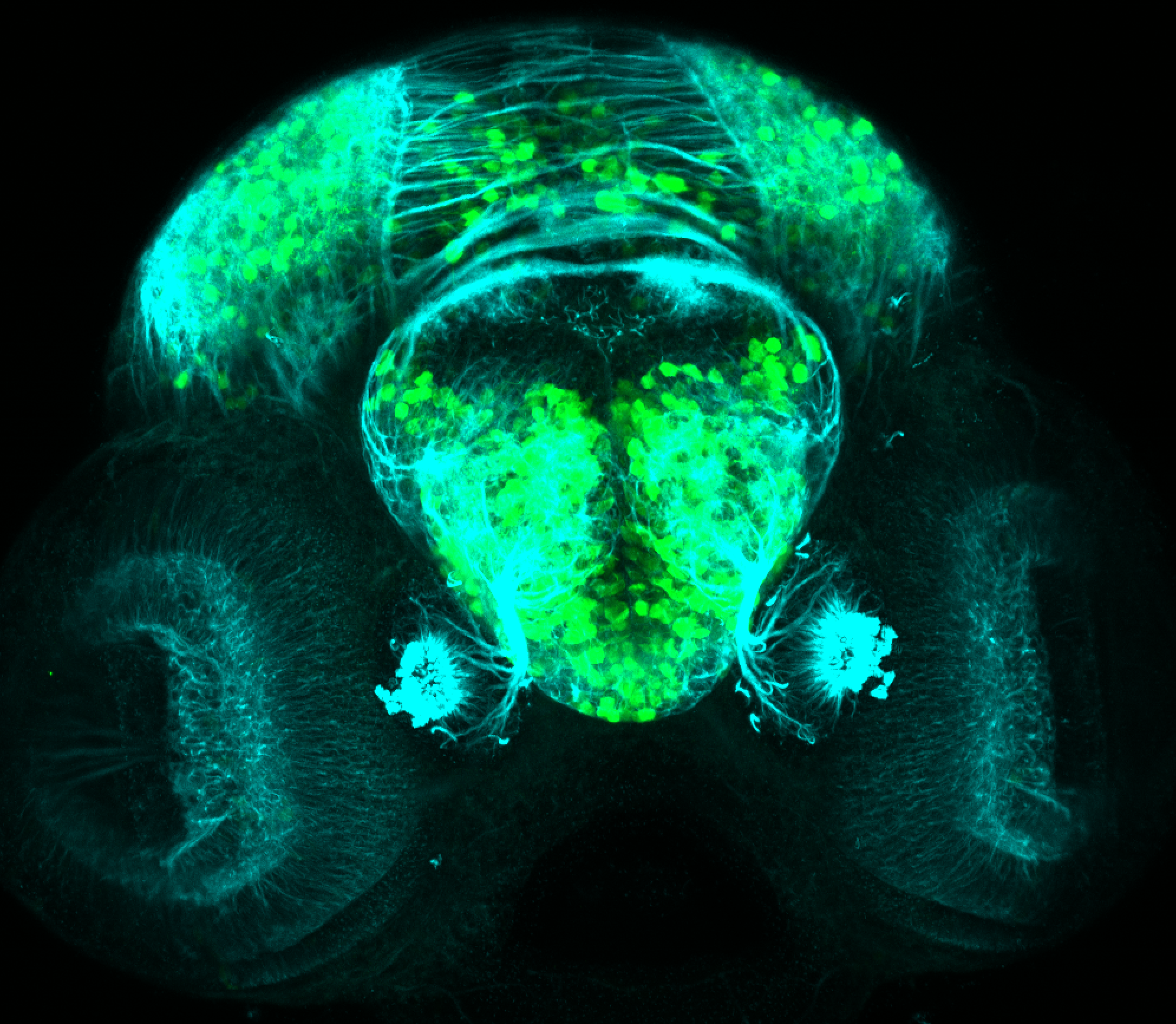
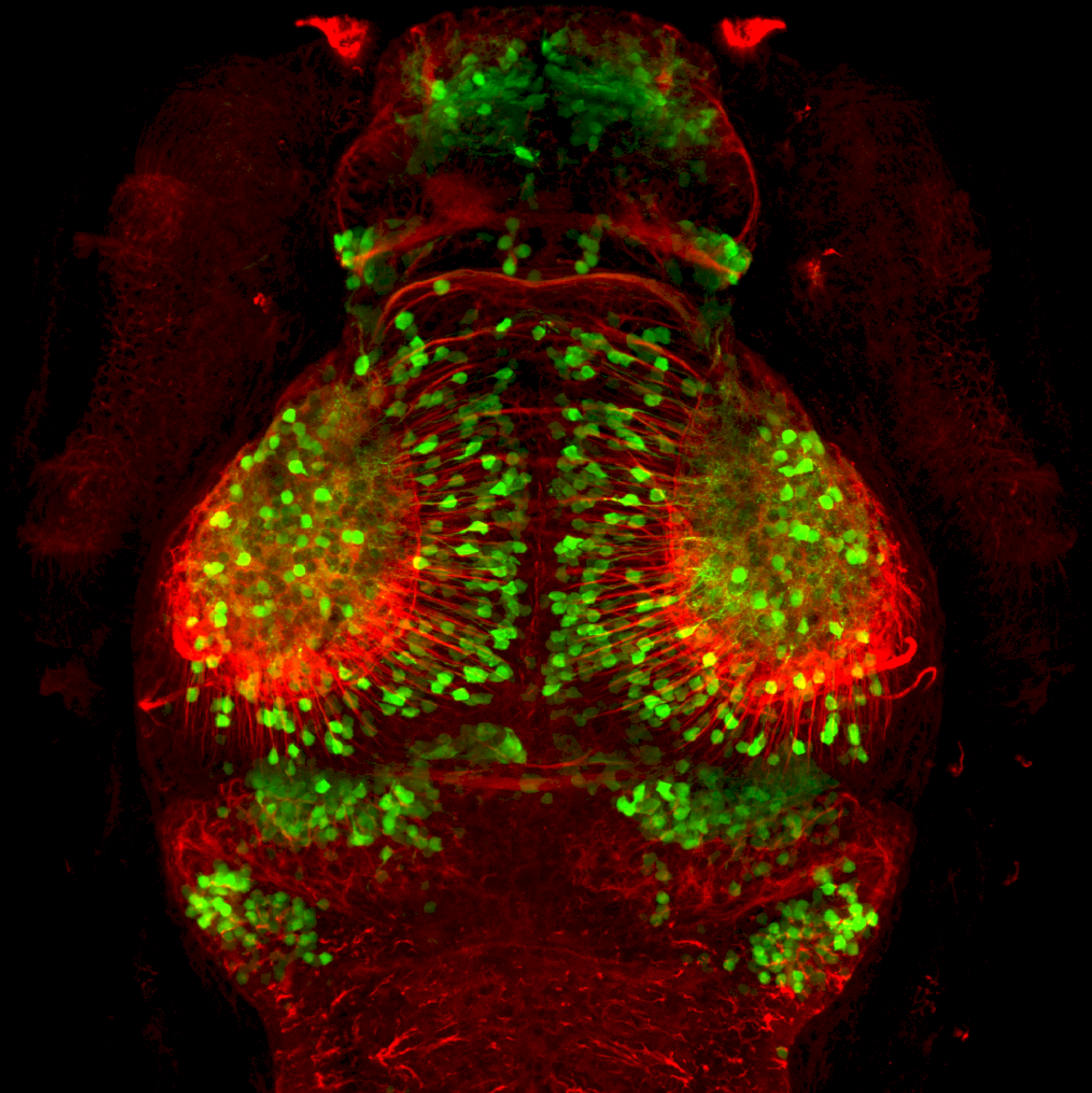
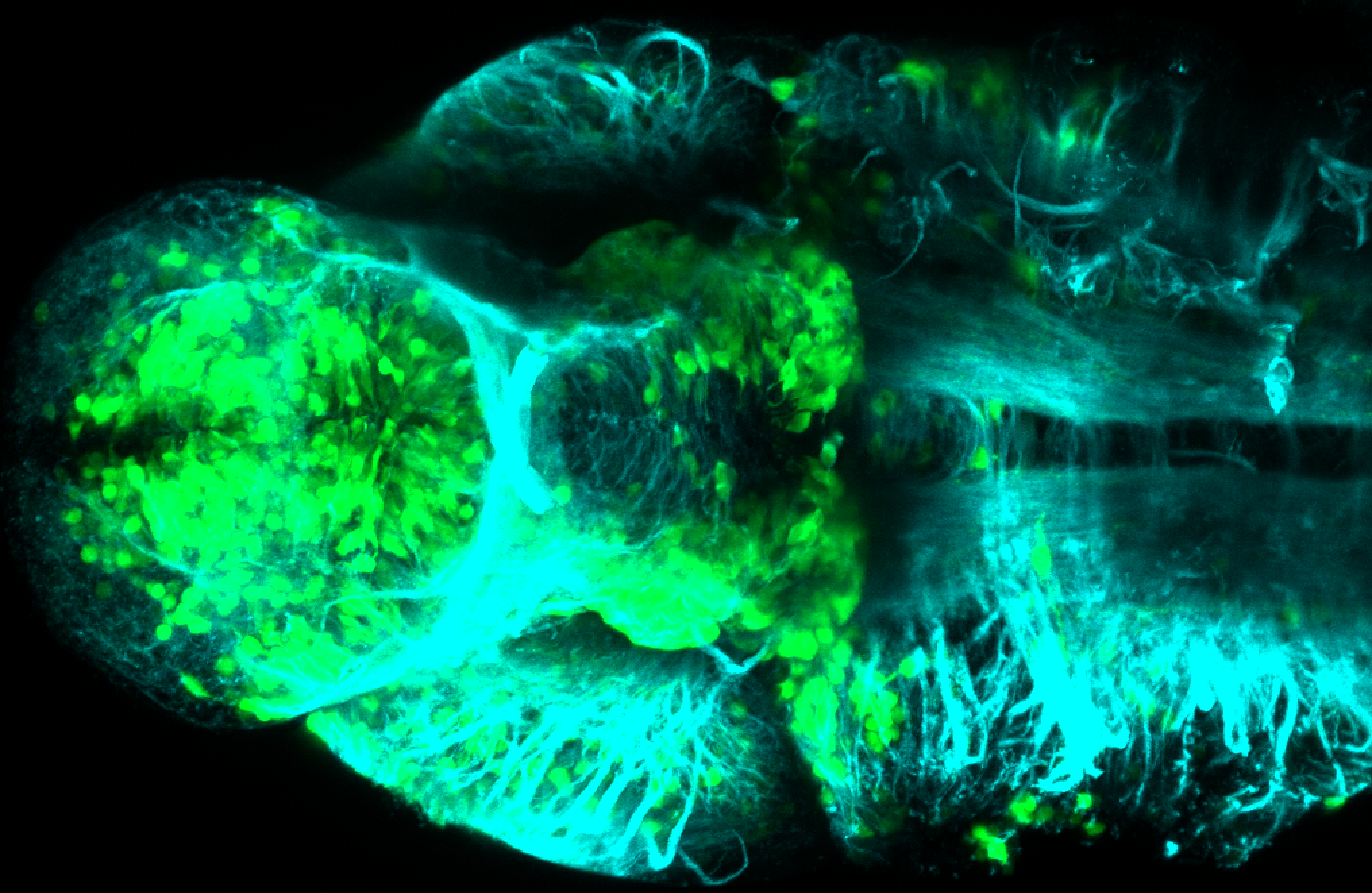
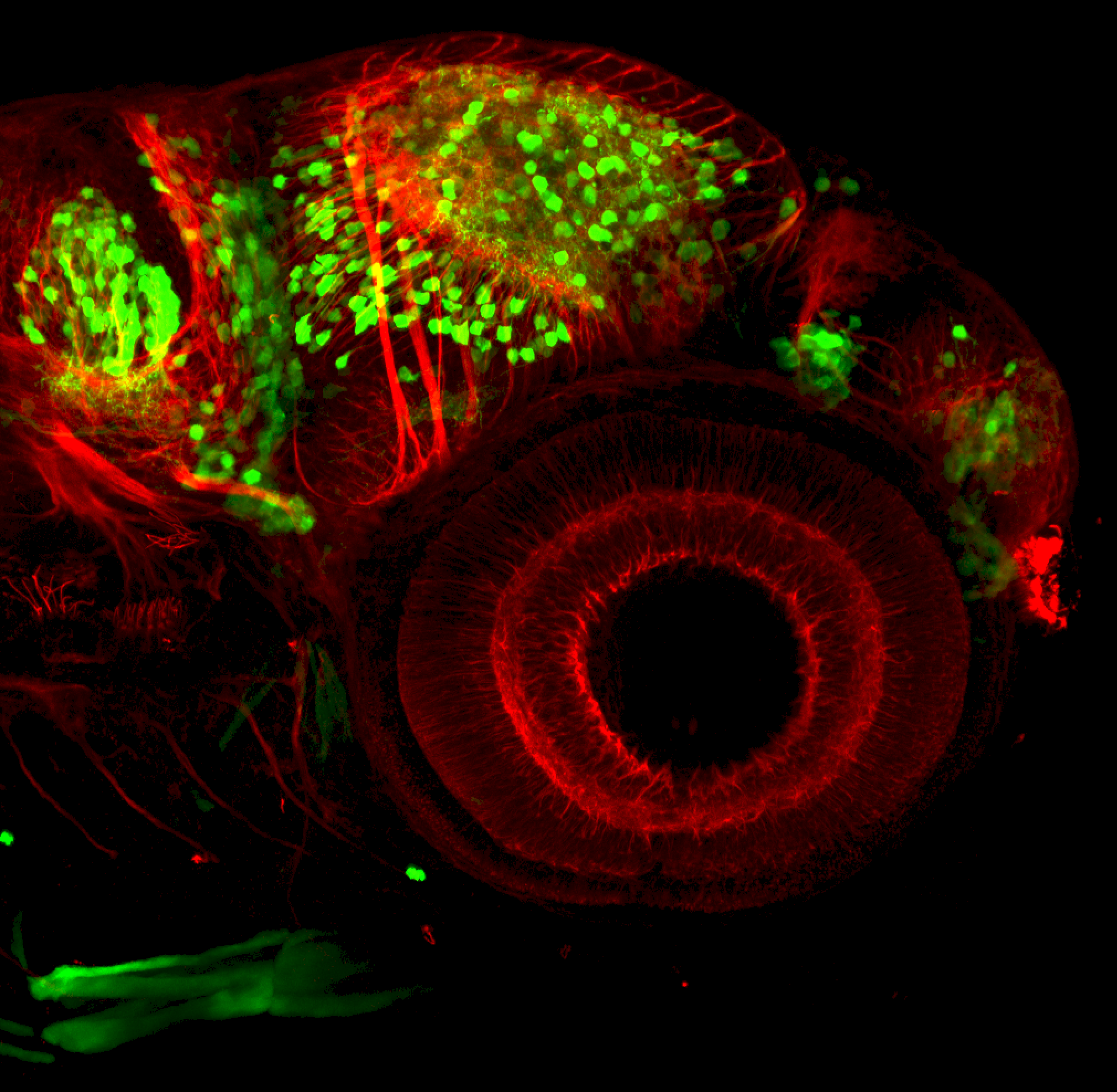
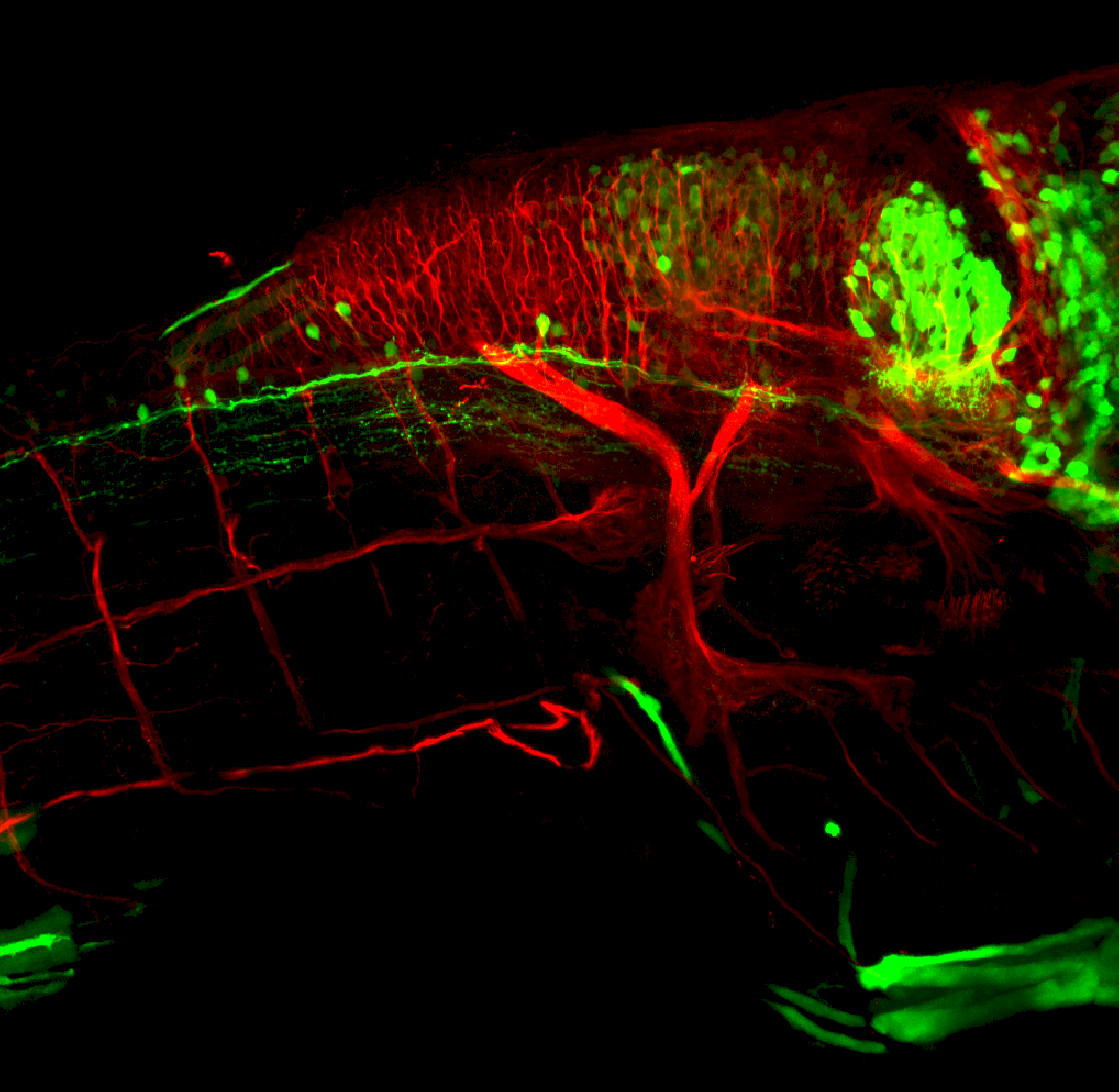
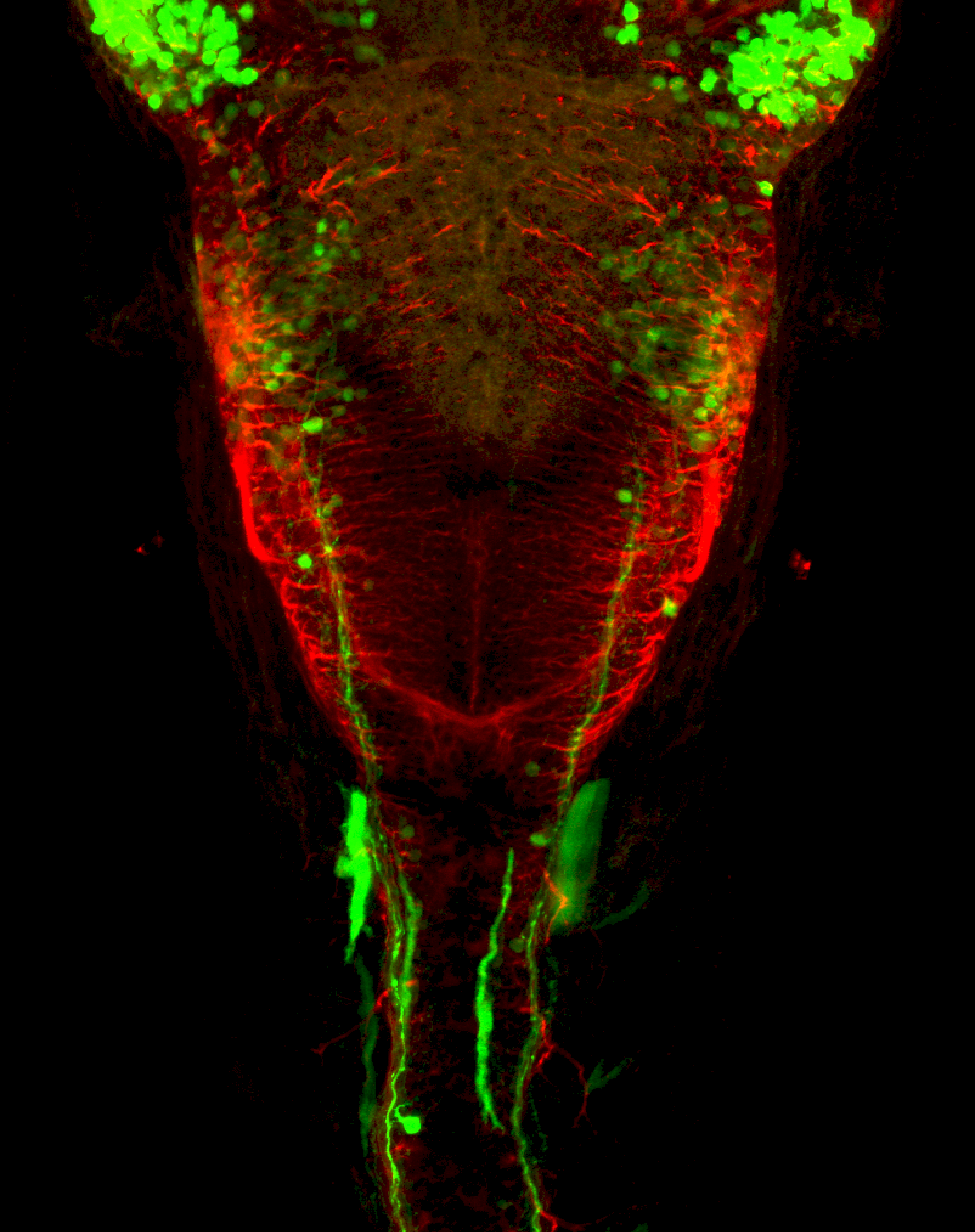
Tg(1.4dlx5a-dlx6a:GFP)ot1 larvae express GFP in subpallial neurons γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-expressing neurons. Several other brain regions also show GFP expression in this transgenic line such as the optic tectum and cerebellum.
Dlx homeobox genes play essential roles in the differentiation, migration and survival of subpallial precursor cells that will later give rise to diverse subtypes of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-expressing neurons. They also participate in the regulation of the Gad genes encoding the enzymes necessary for GABA synthesis (Yu et al., 2011).
Mouse over the different areas of GFP expression in the interactive images below to see the name of the brain area.
More images
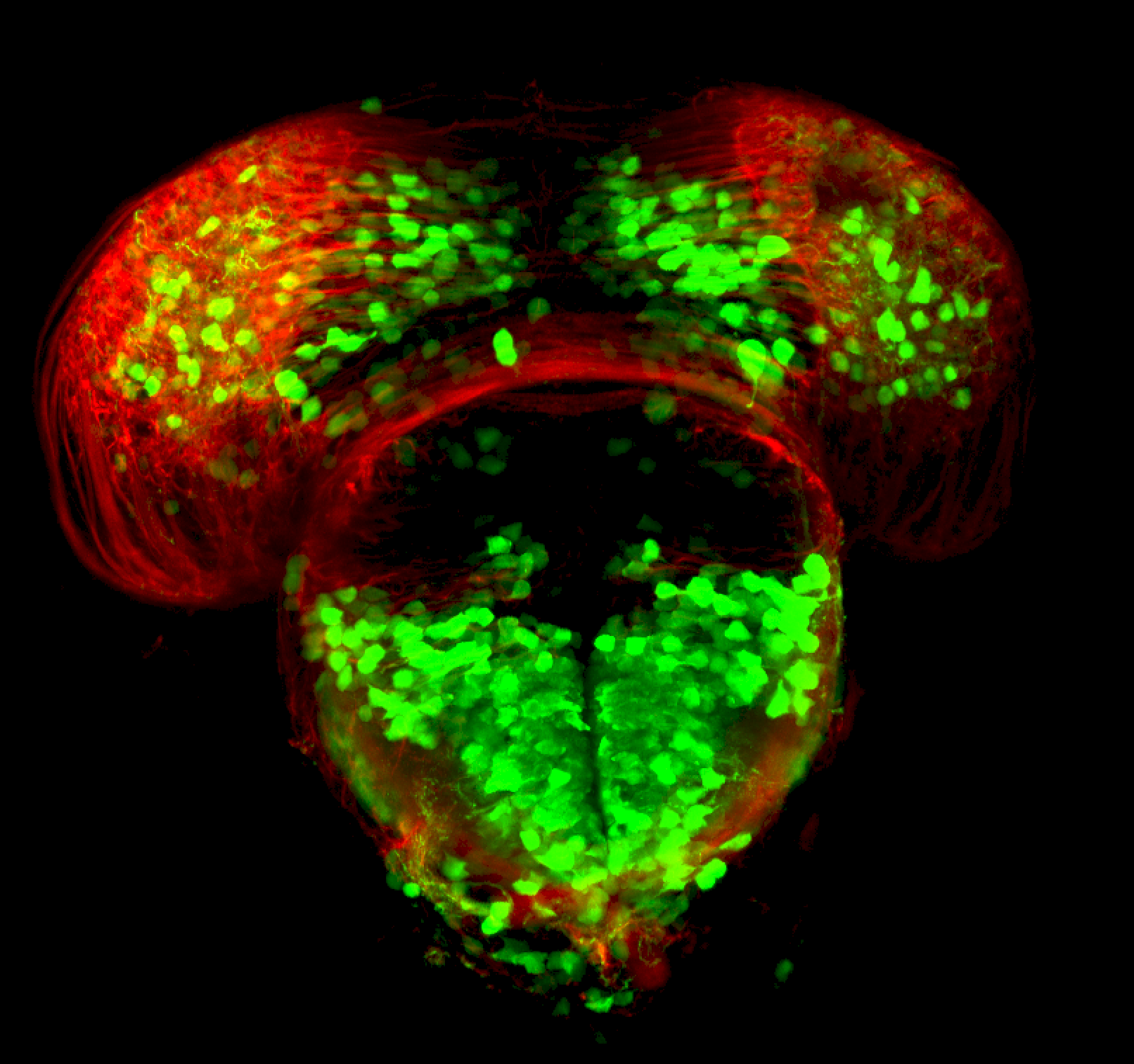
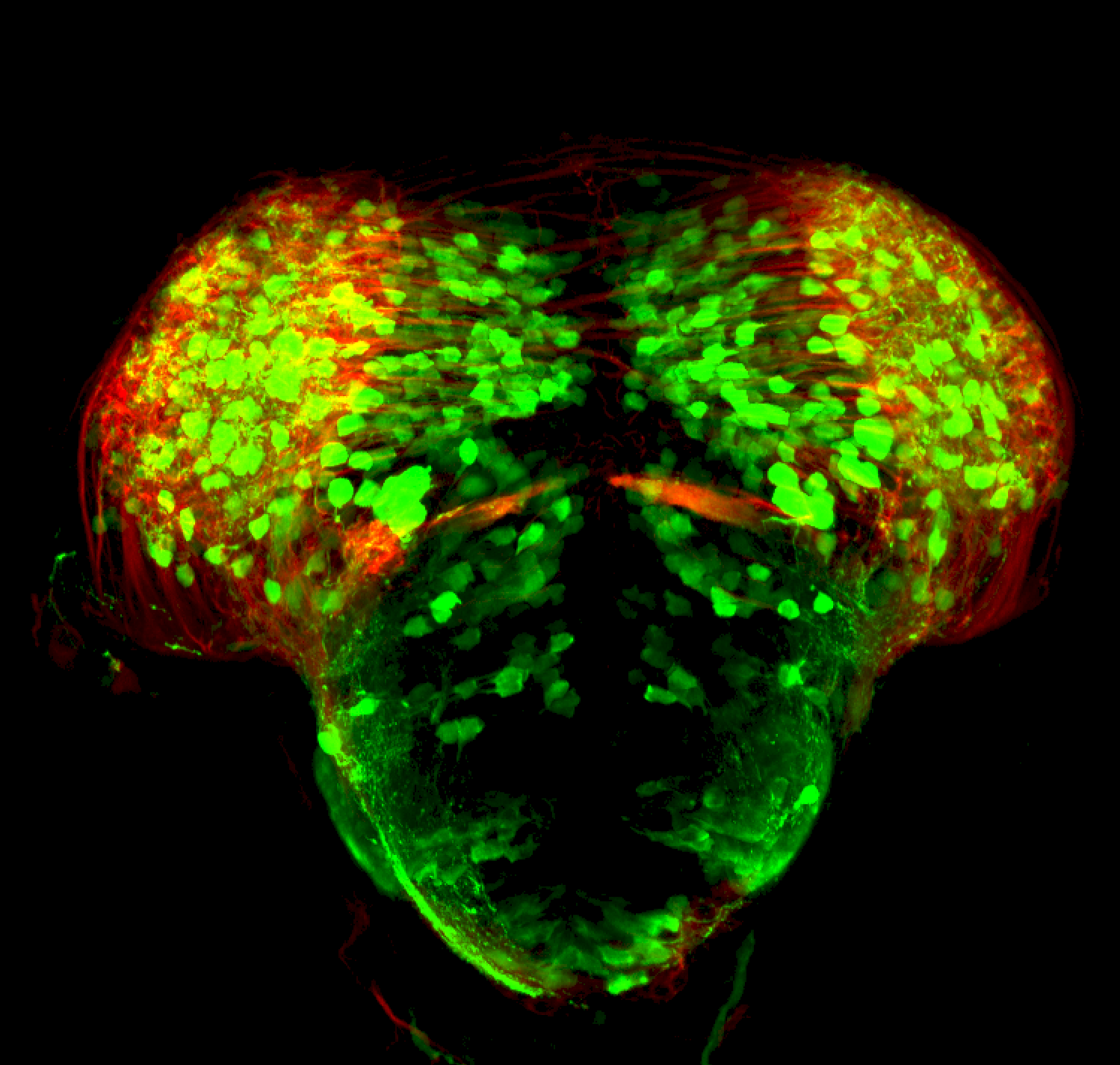
Expressed in:
olfactory bulb, subpallium, pallium, preoptic area, prethalamus, posterior tuberculum, hypothalamus, optic tectum, cerebellum.
Key Publications
Zerucha, T., Stuhmer, T., Hatch, G., Park, B.K., Long, Q., Yu, G., Gambarotta, A., Schultz, J.R., Rubenstein, J.L., and Ekker, M. (2000)
A highly conserved enhancer in the Dlx5/Dlx6 intergenic region is the site of cross-regulatory interactions between dlx genes in the embryonic forebrain.
The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience. 20(2):709-721.
Yu, M., Xi, Y., Pollack, J., Debiais-Thibaud, M., Macdonald, R.B., and Ekker, M. (2011)
Activity of dlx5a/dlx6a regulatory elements during zebrafish GABAergic neuron development.
Int. J. Dev. Neurosci.. 29(7):681-91.