About
synonyms: clgy750, smb750Et.
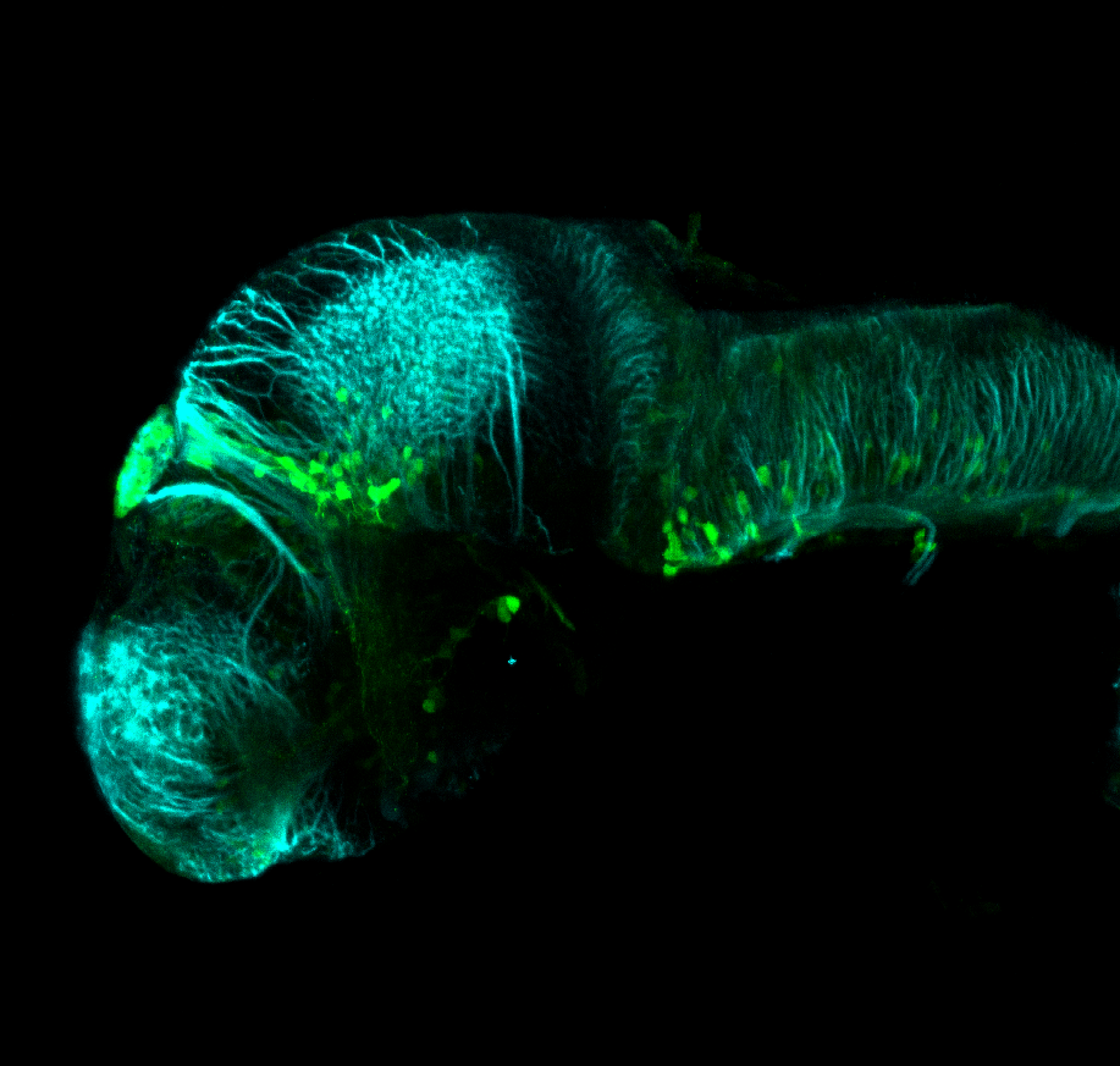
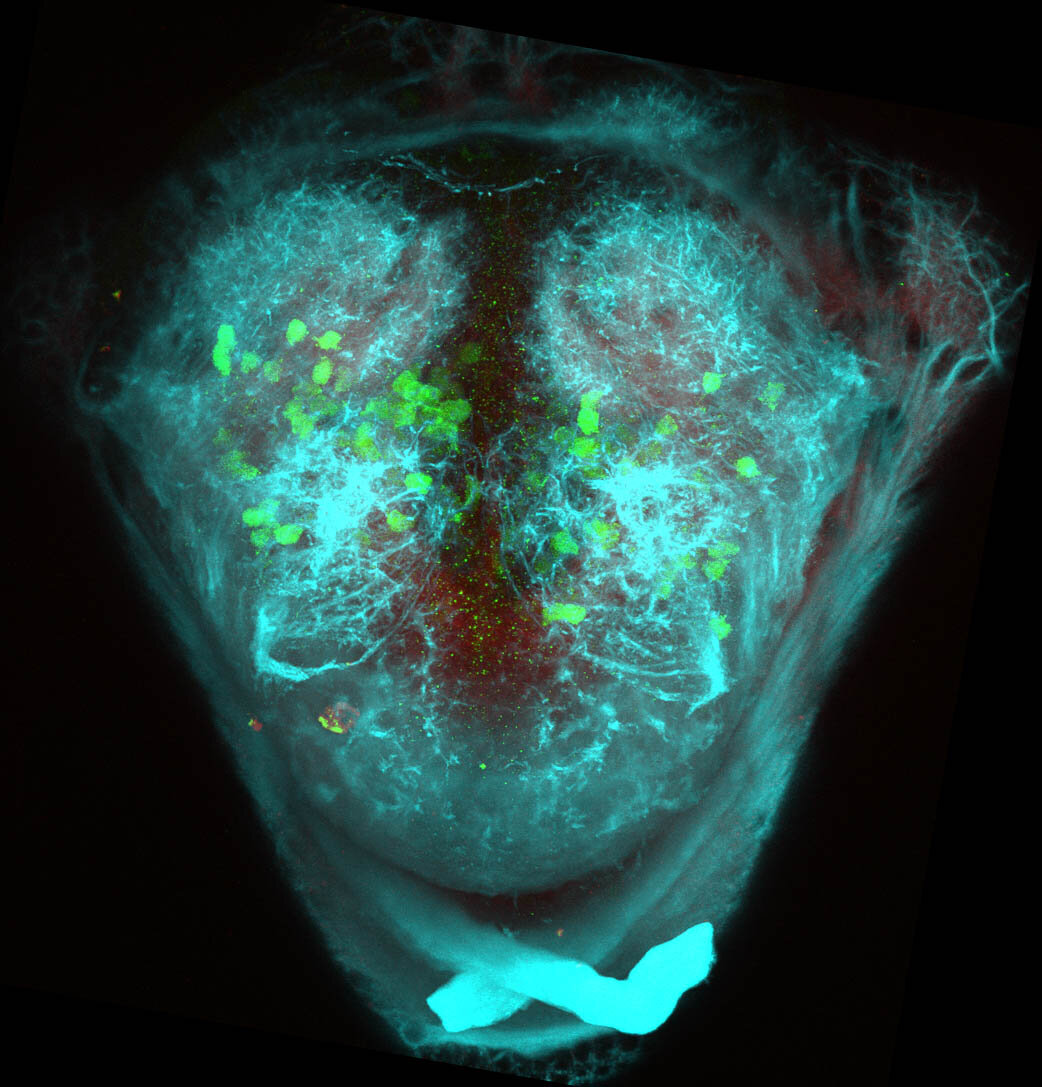
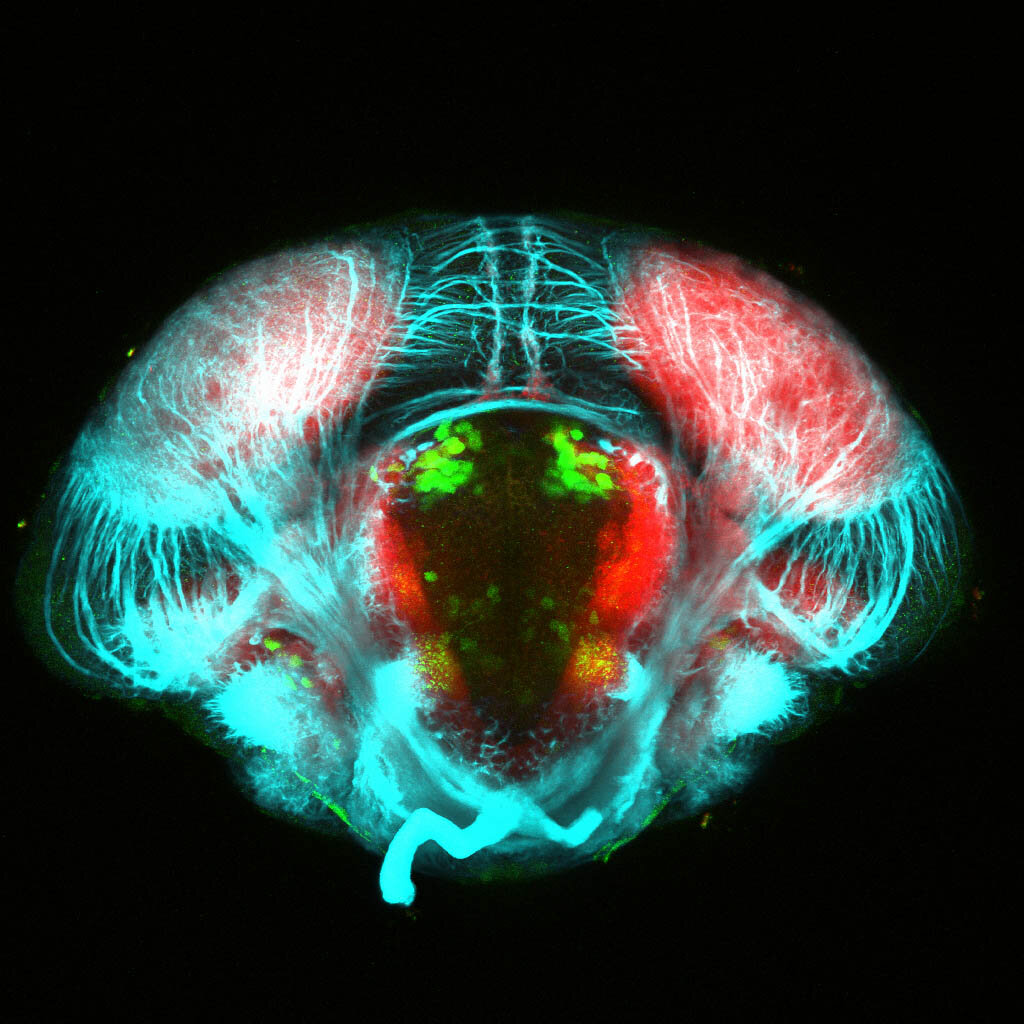
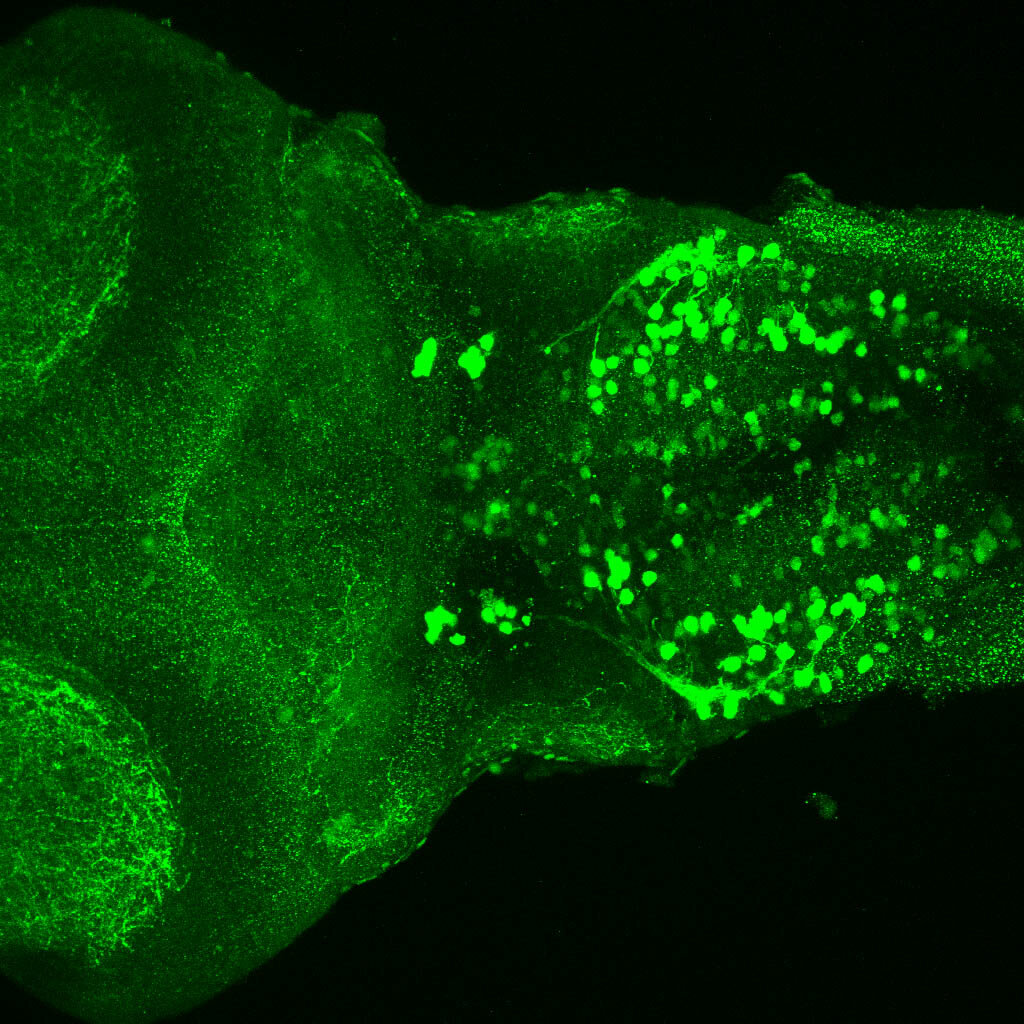
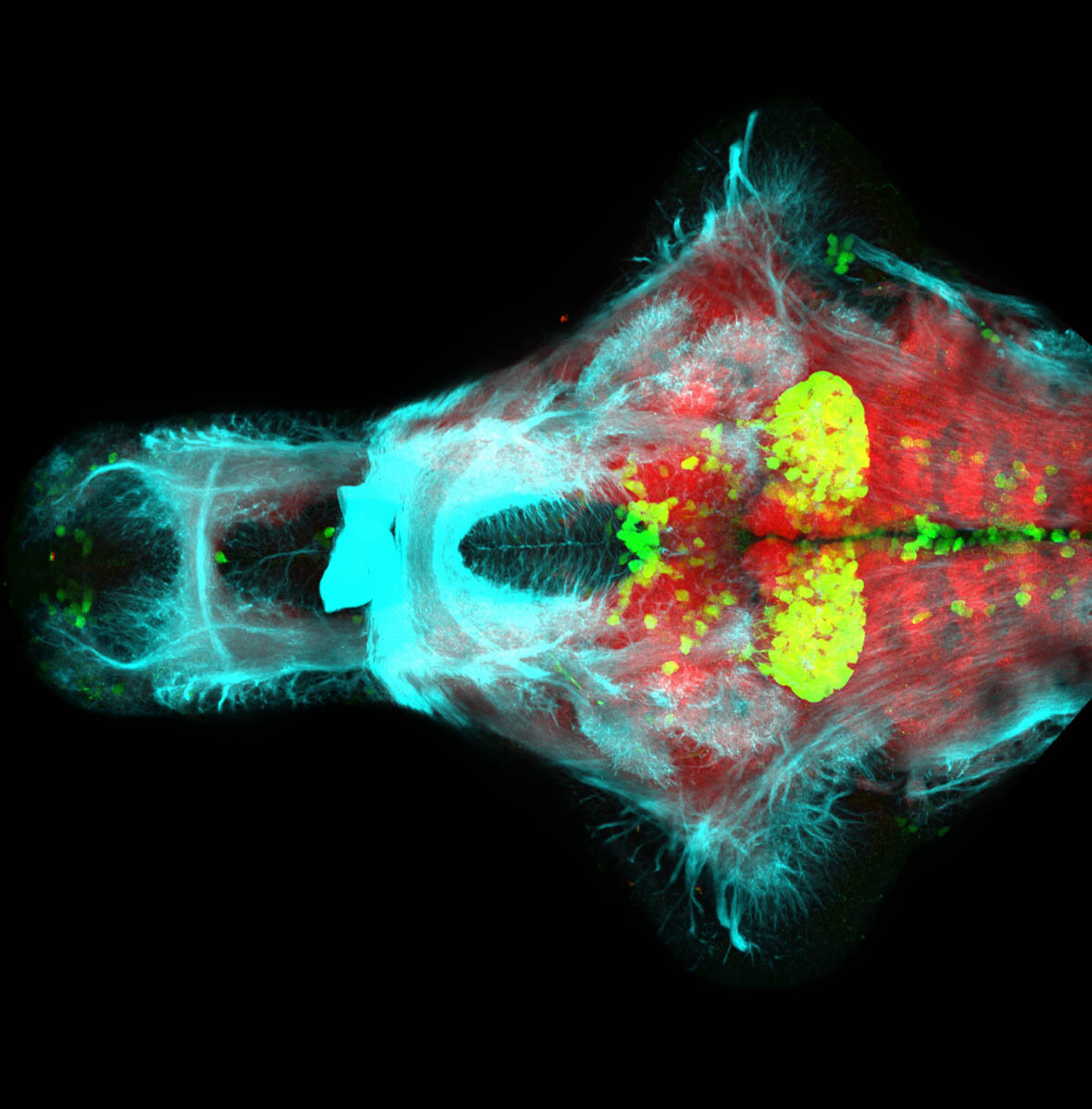
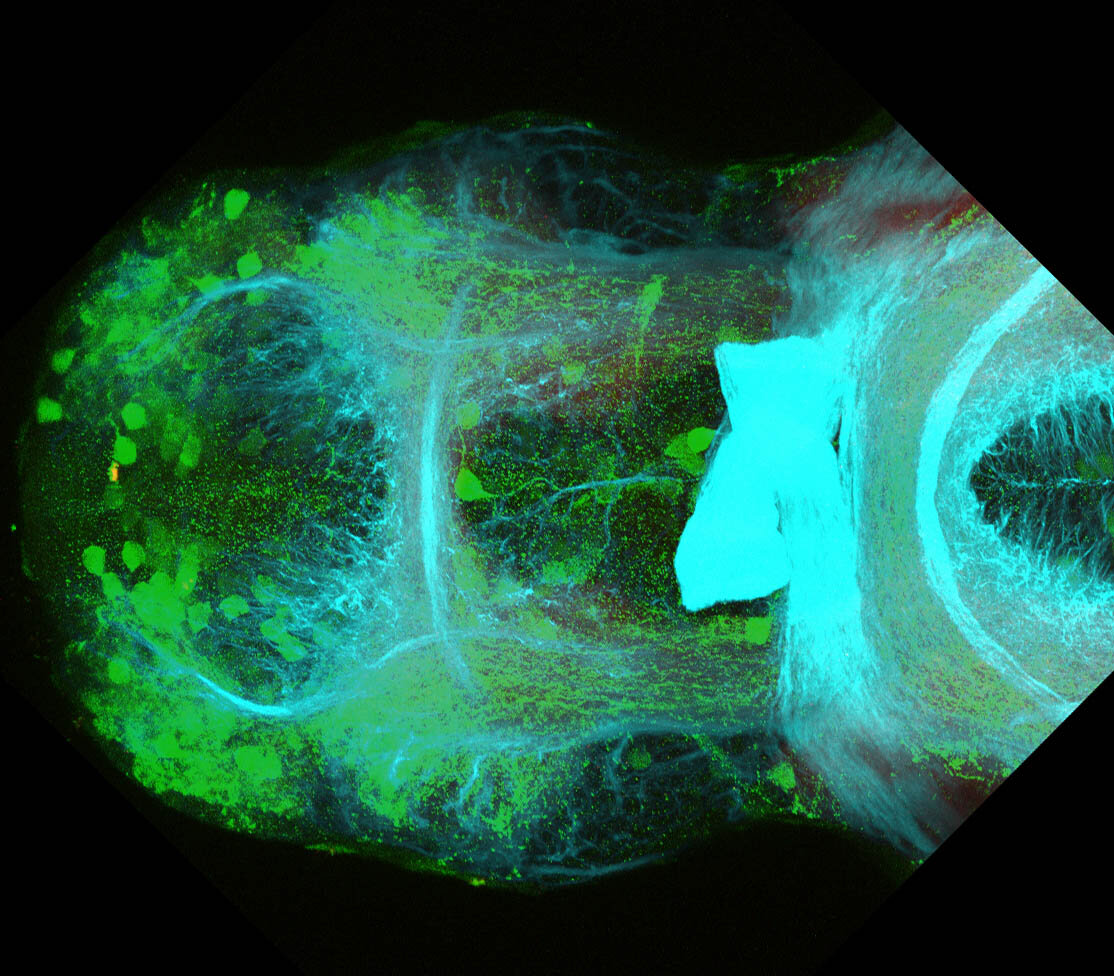
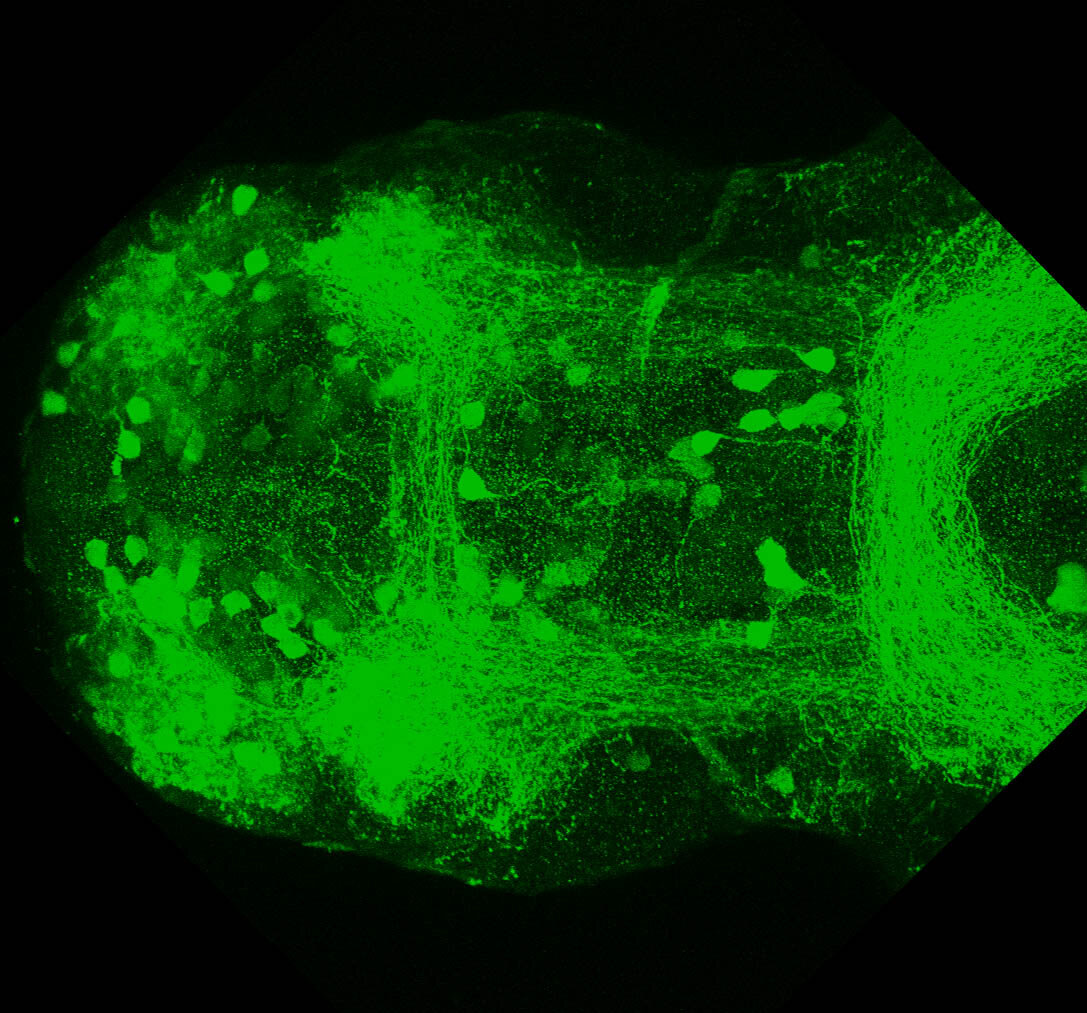
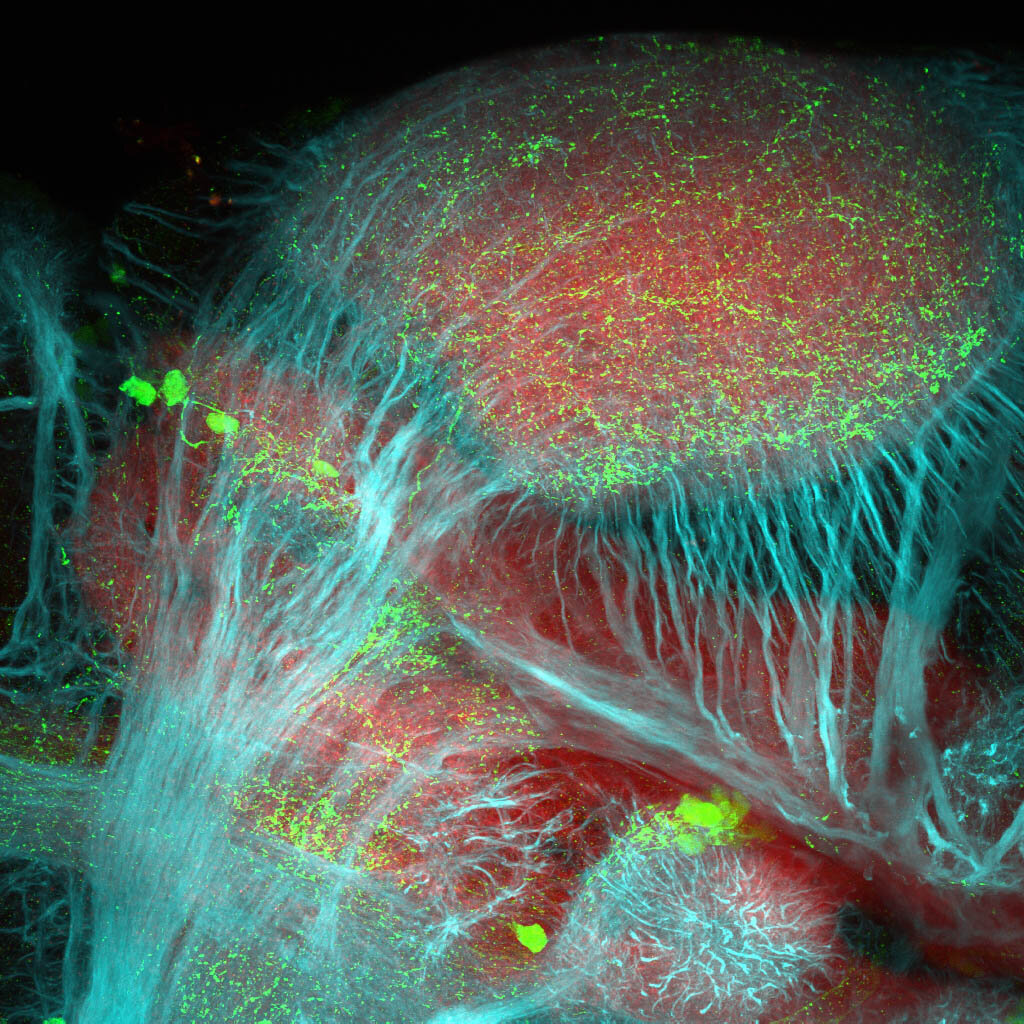
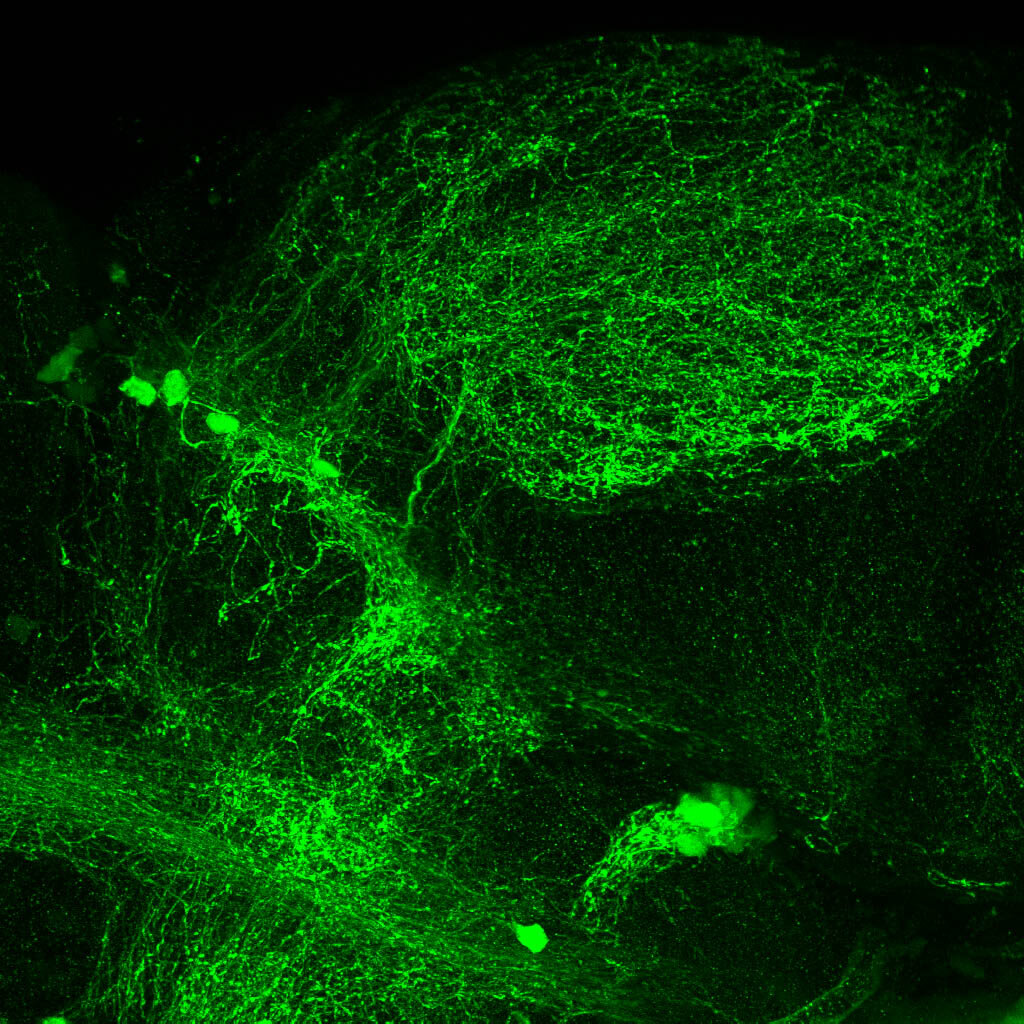
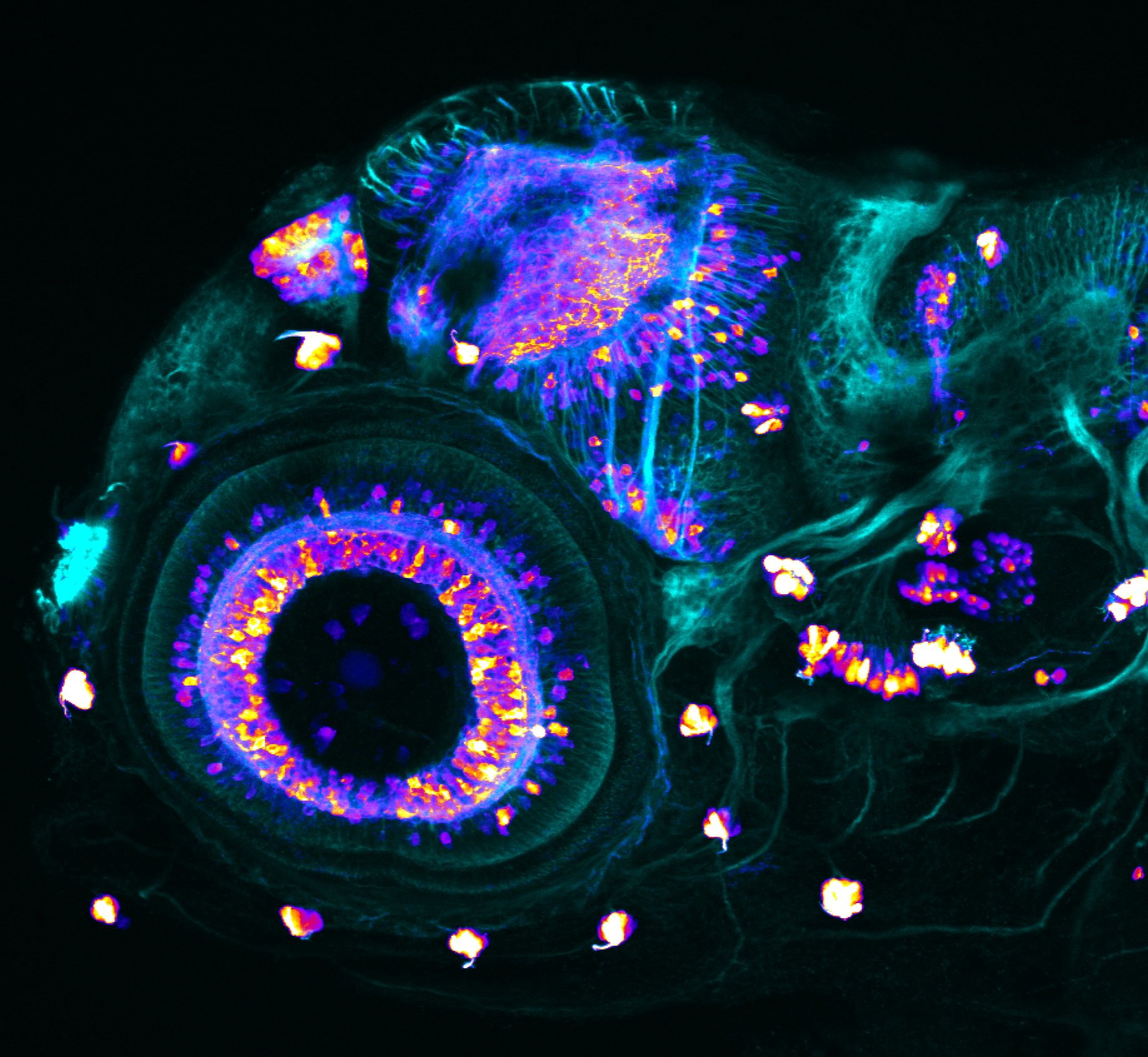
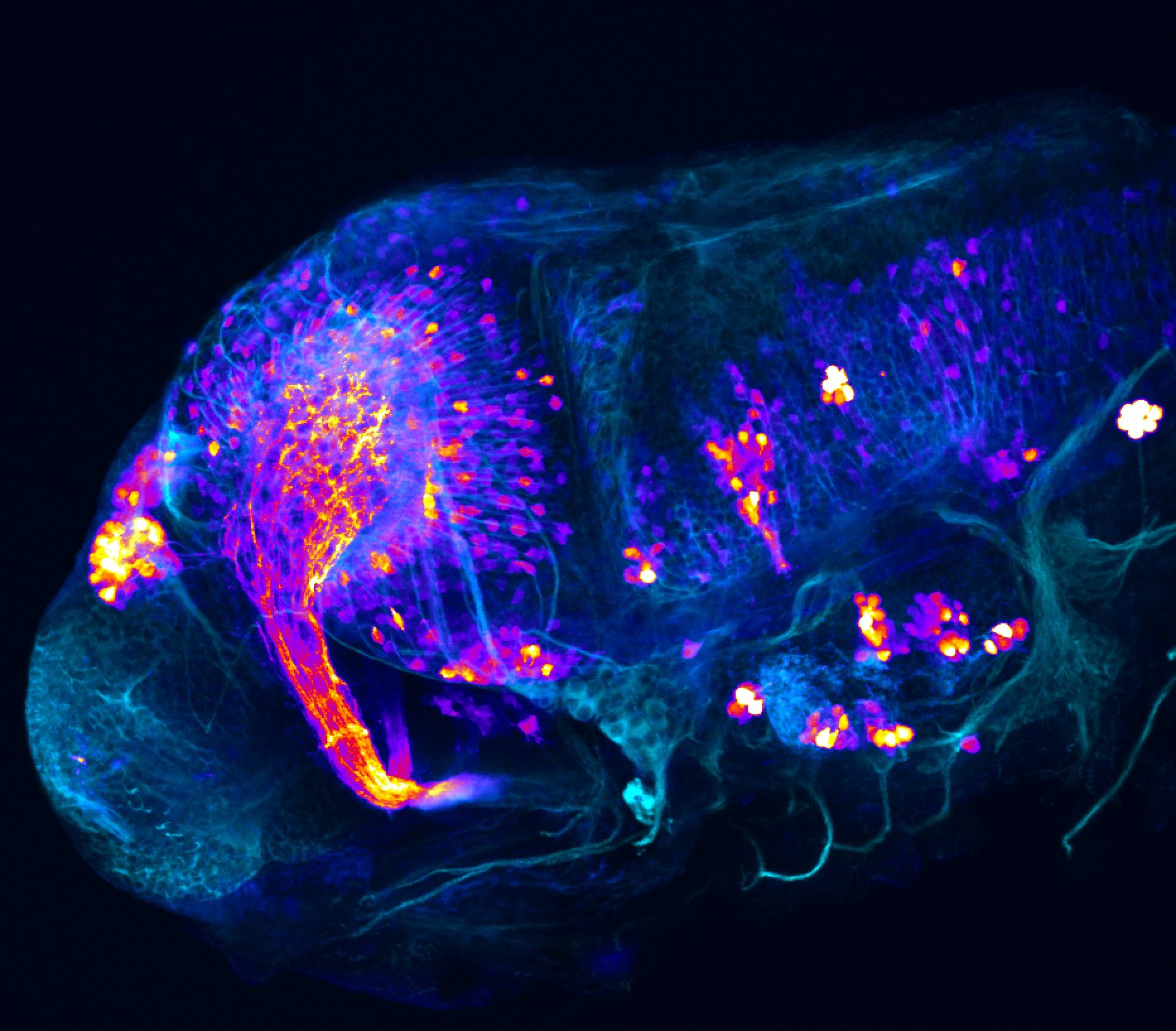
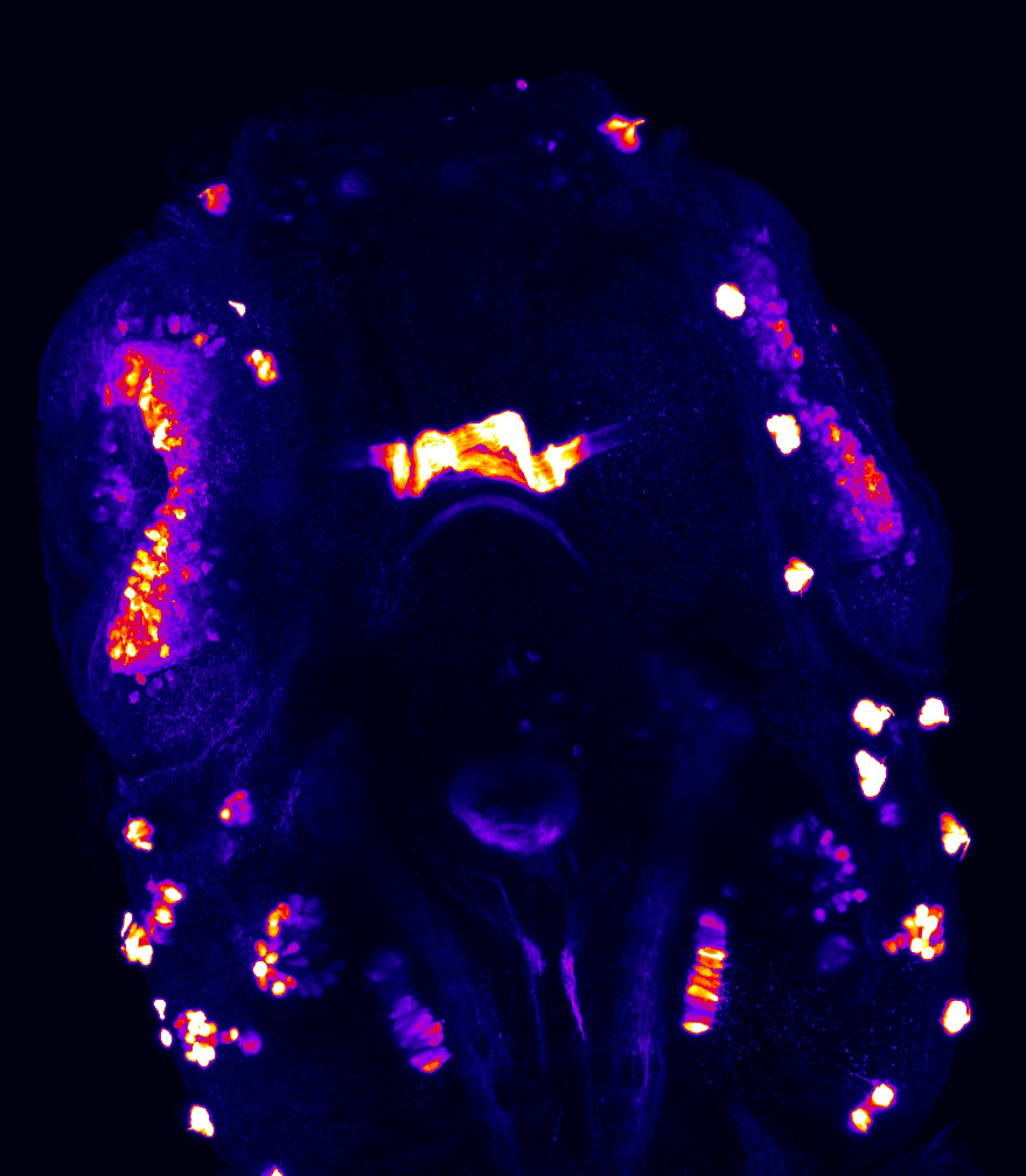
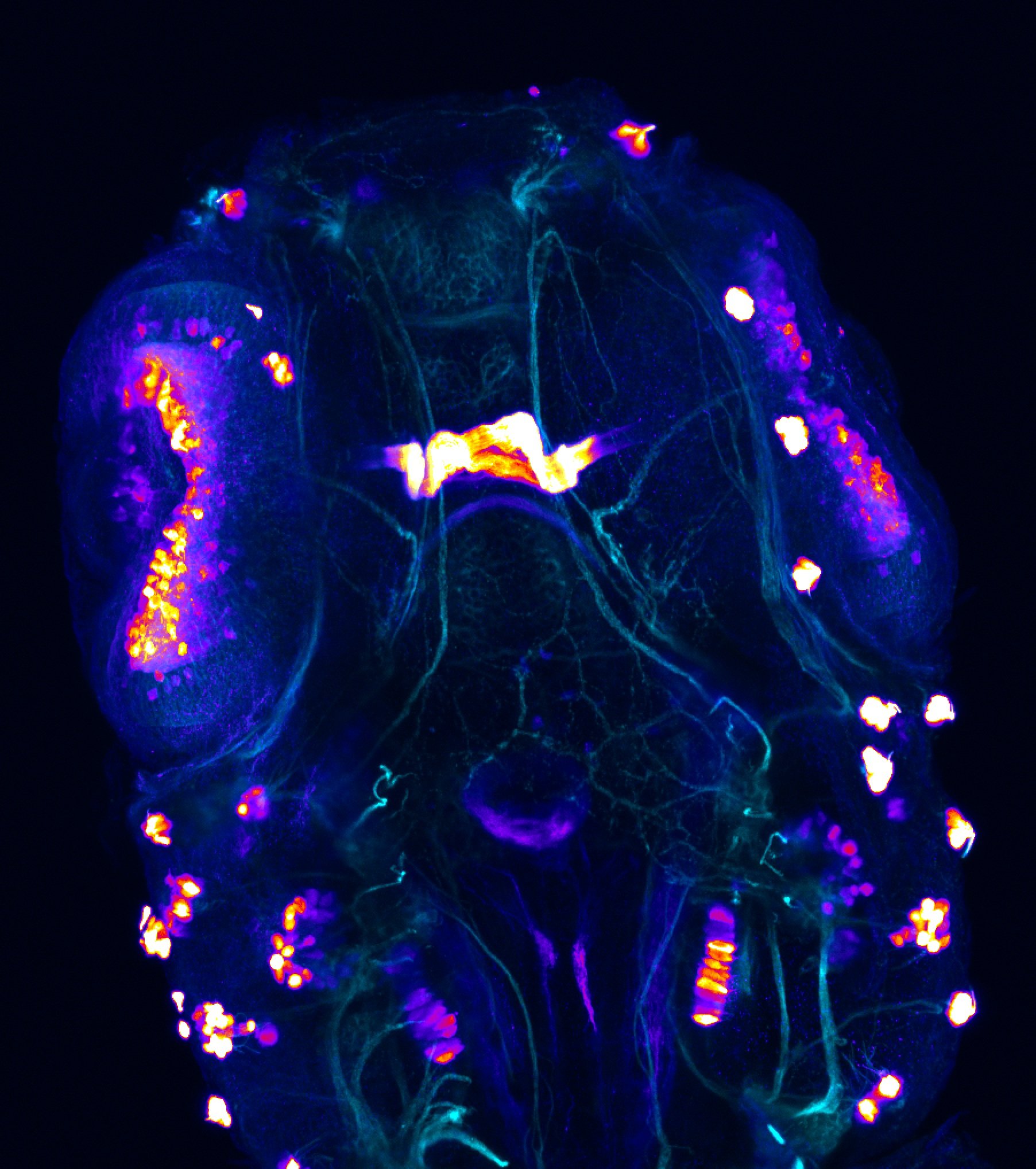
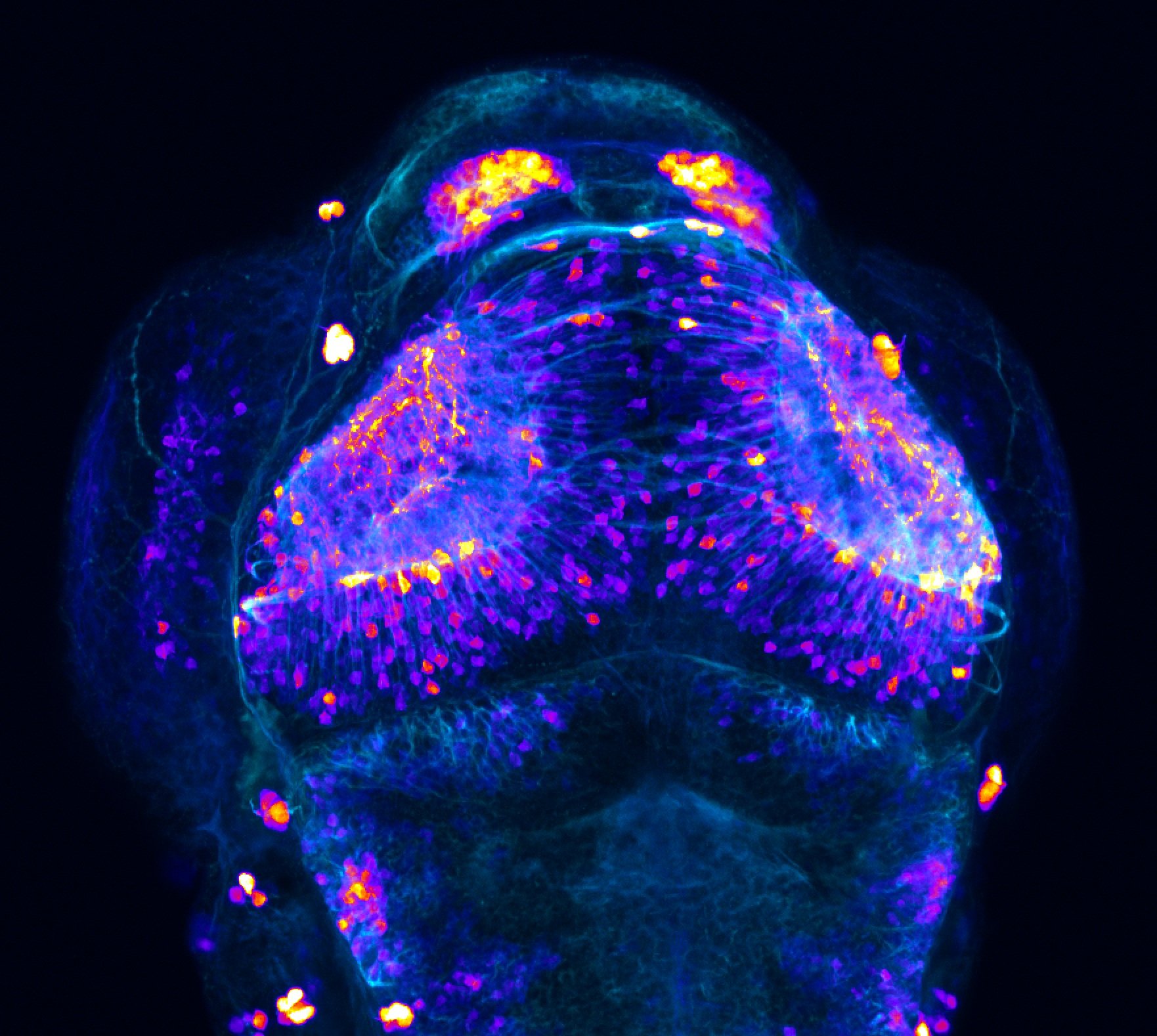
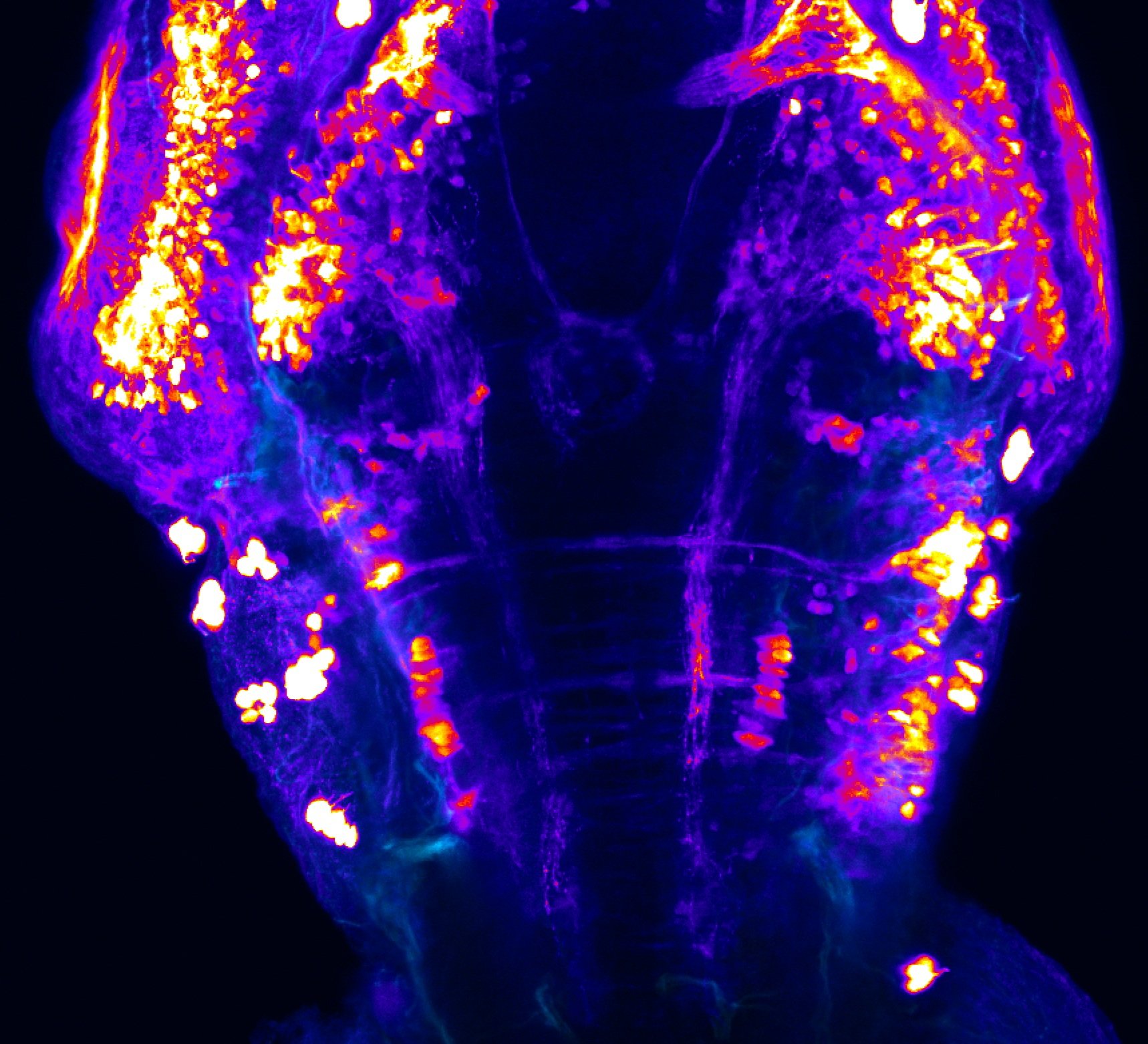
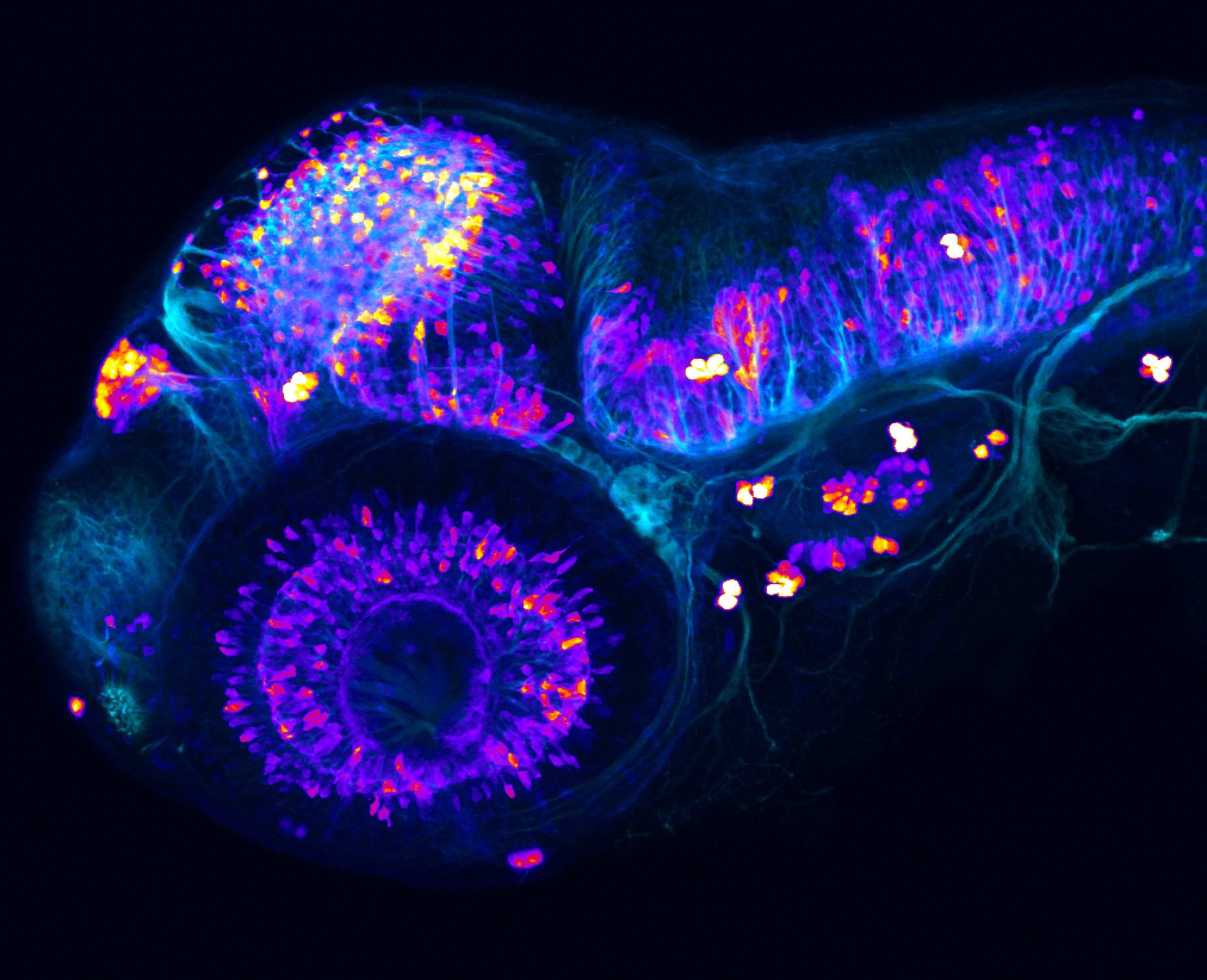
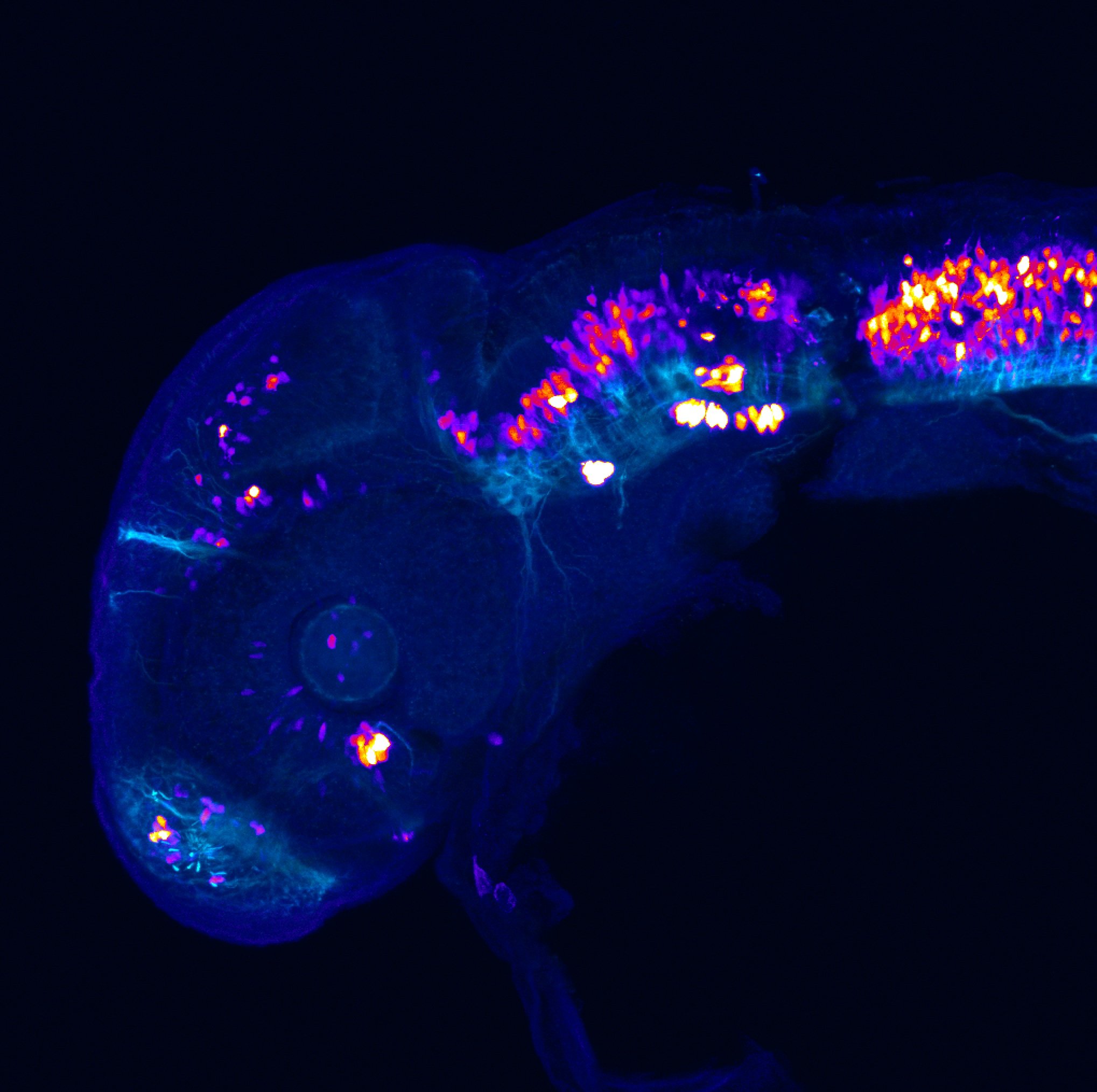
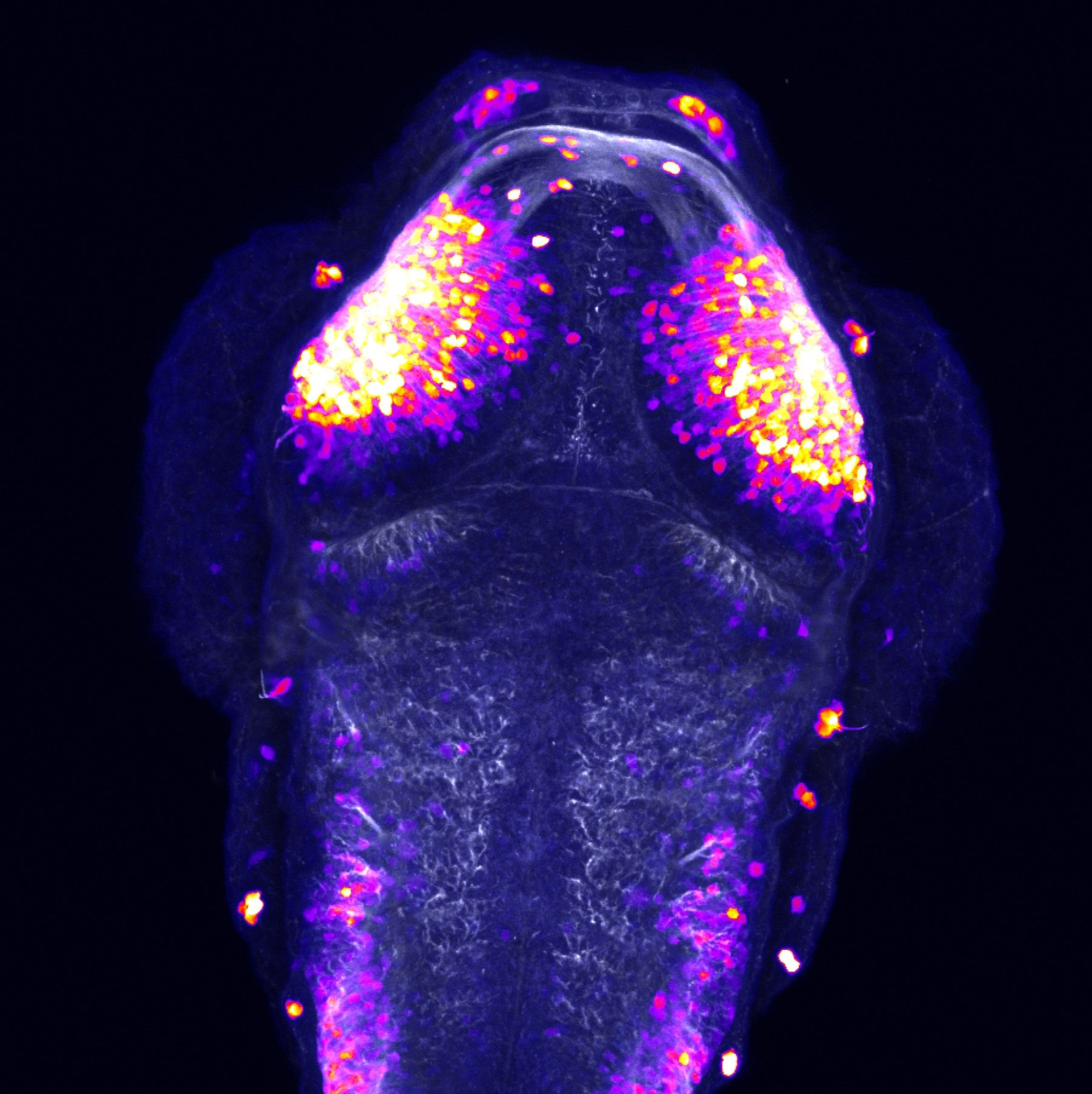
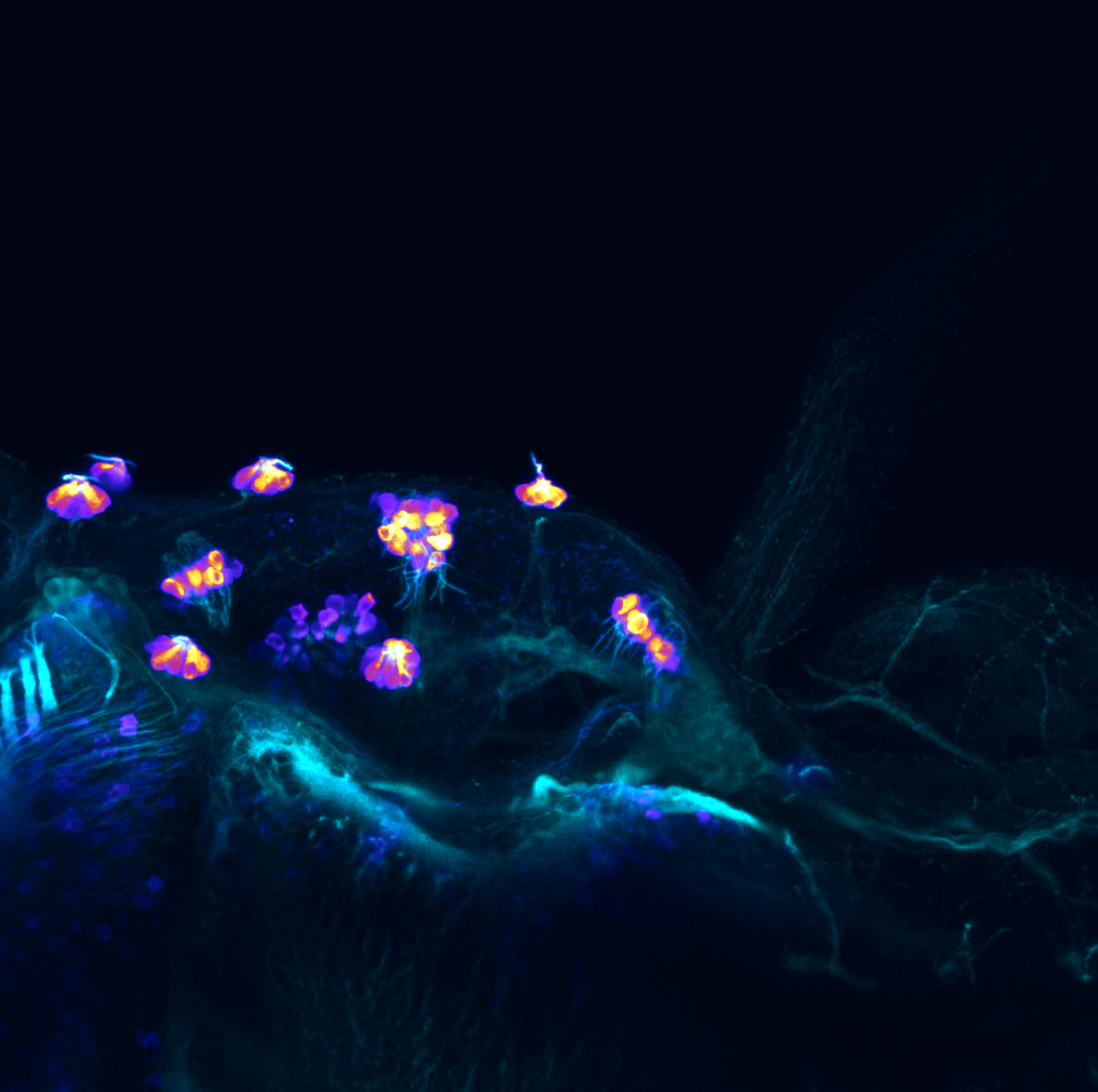
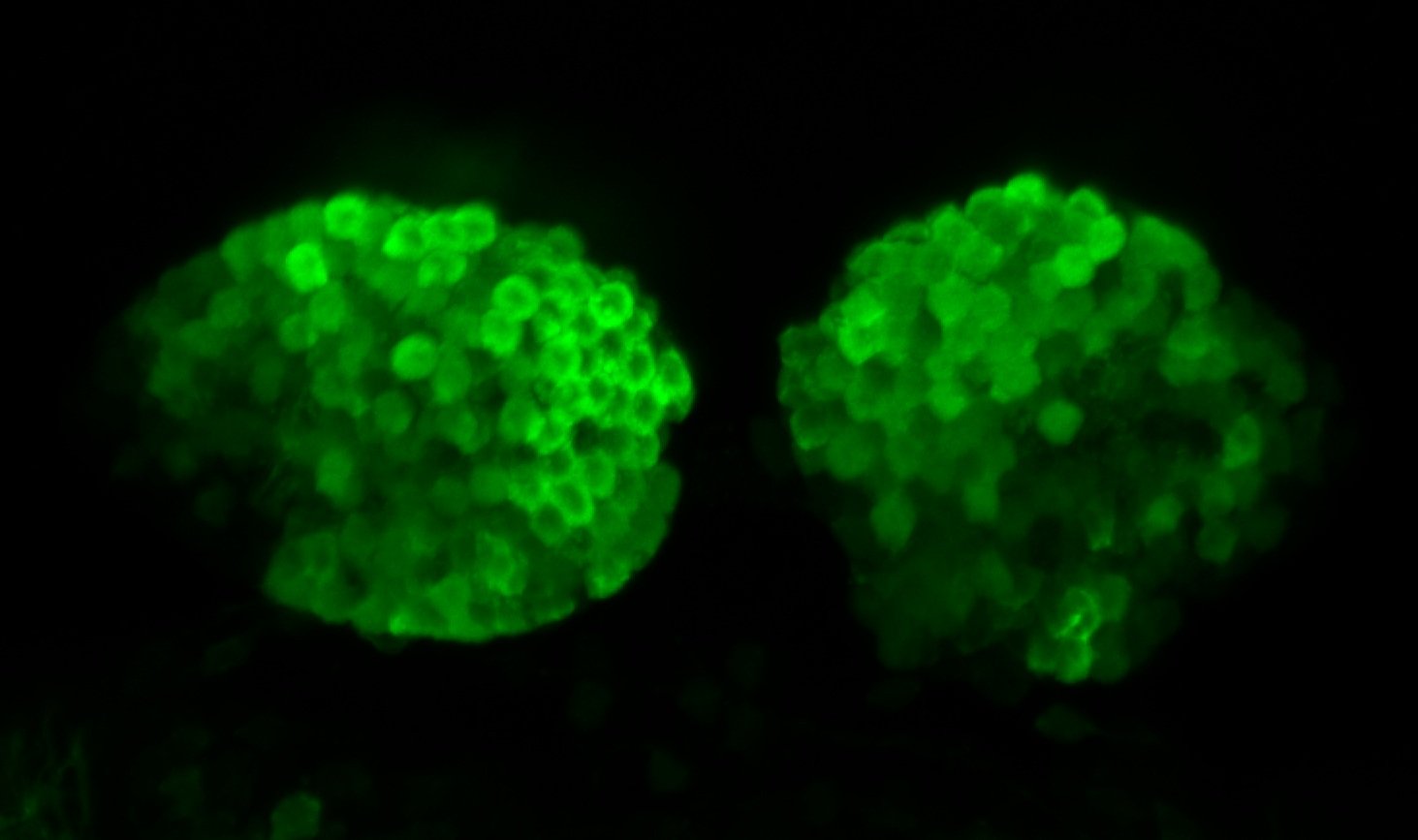
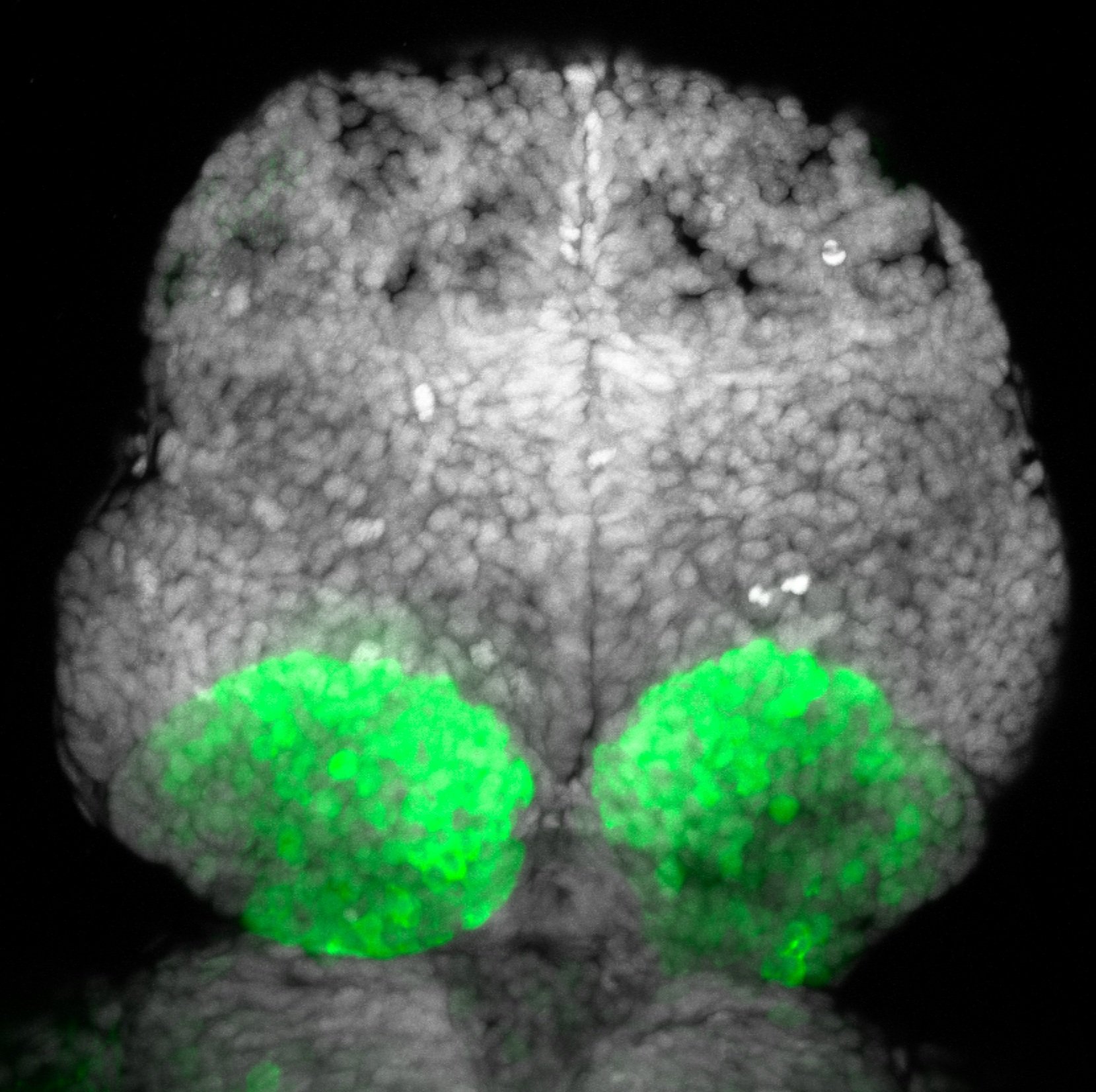
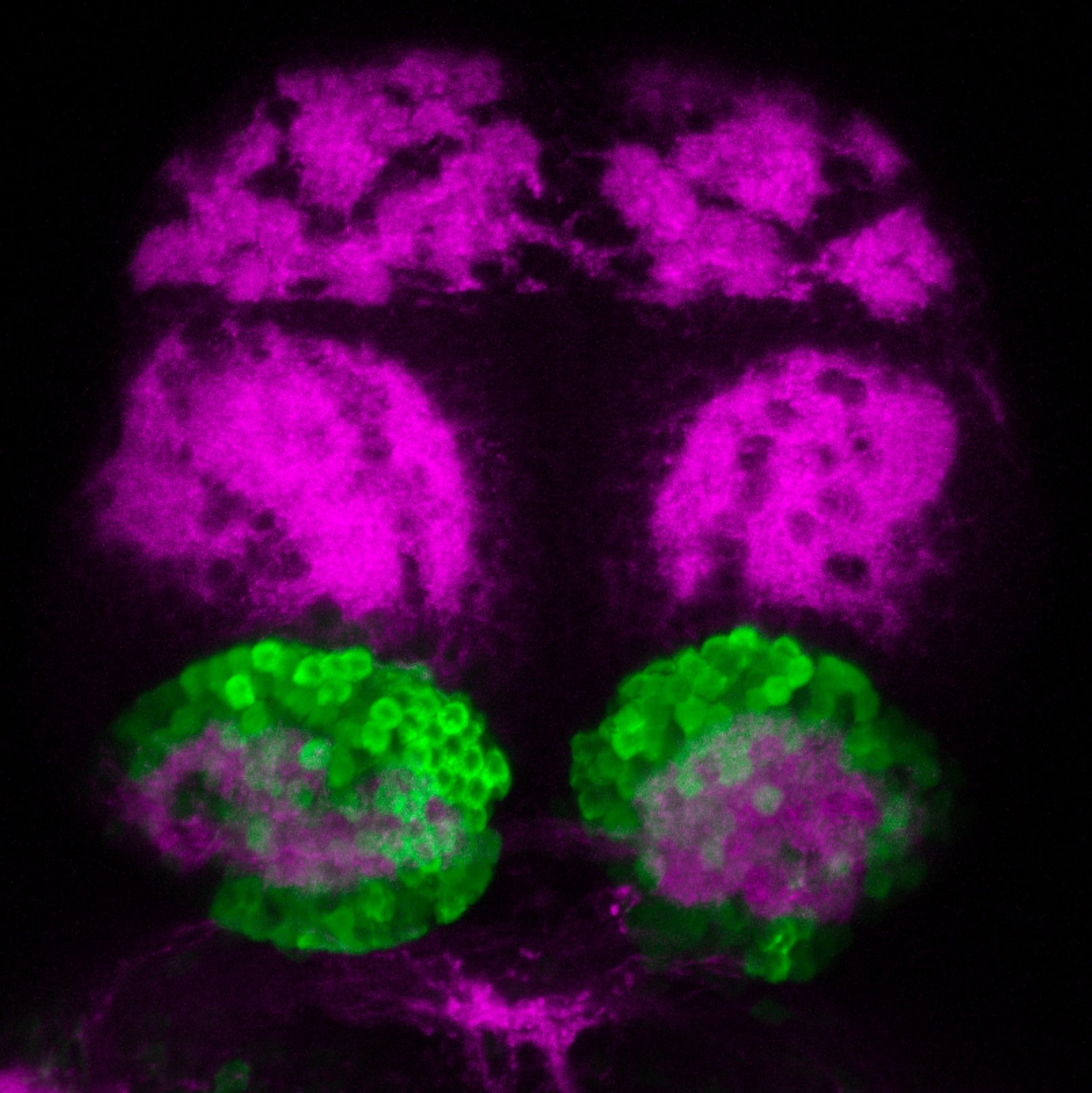
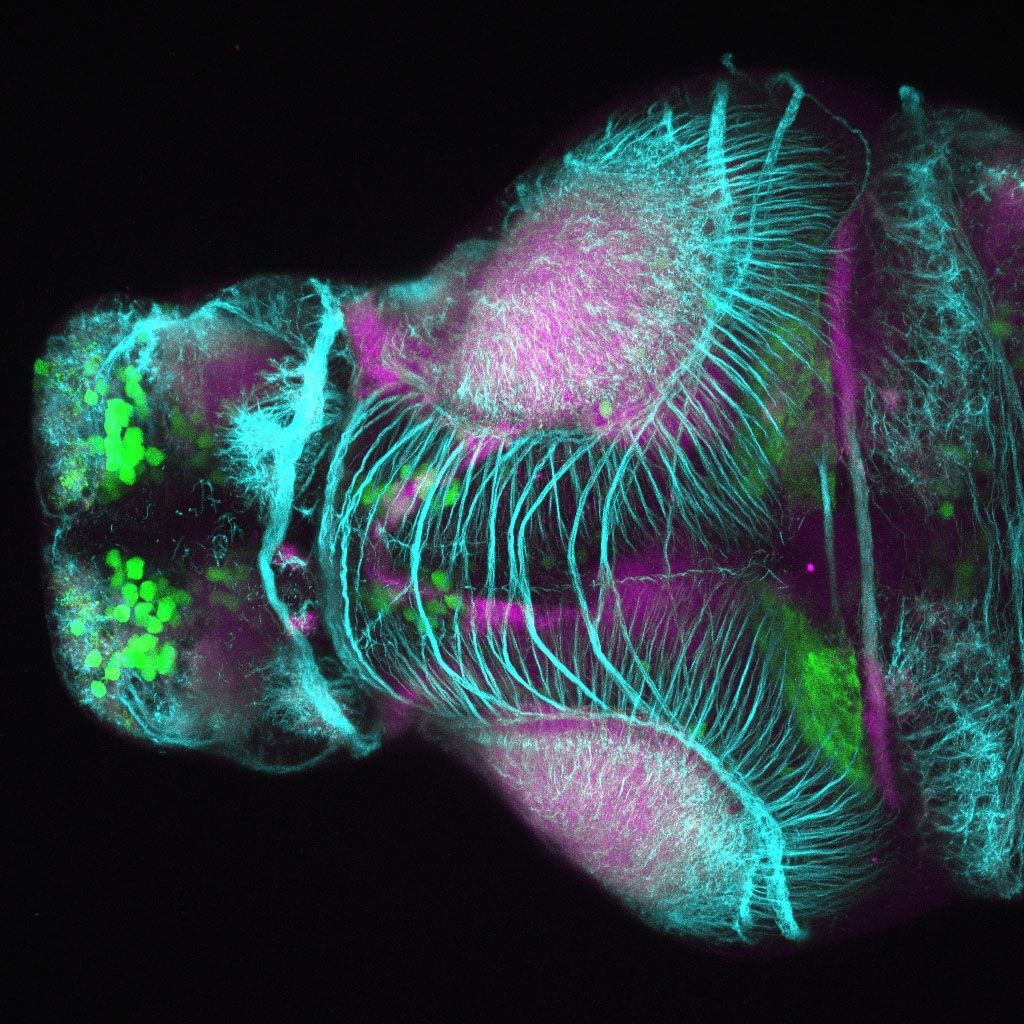
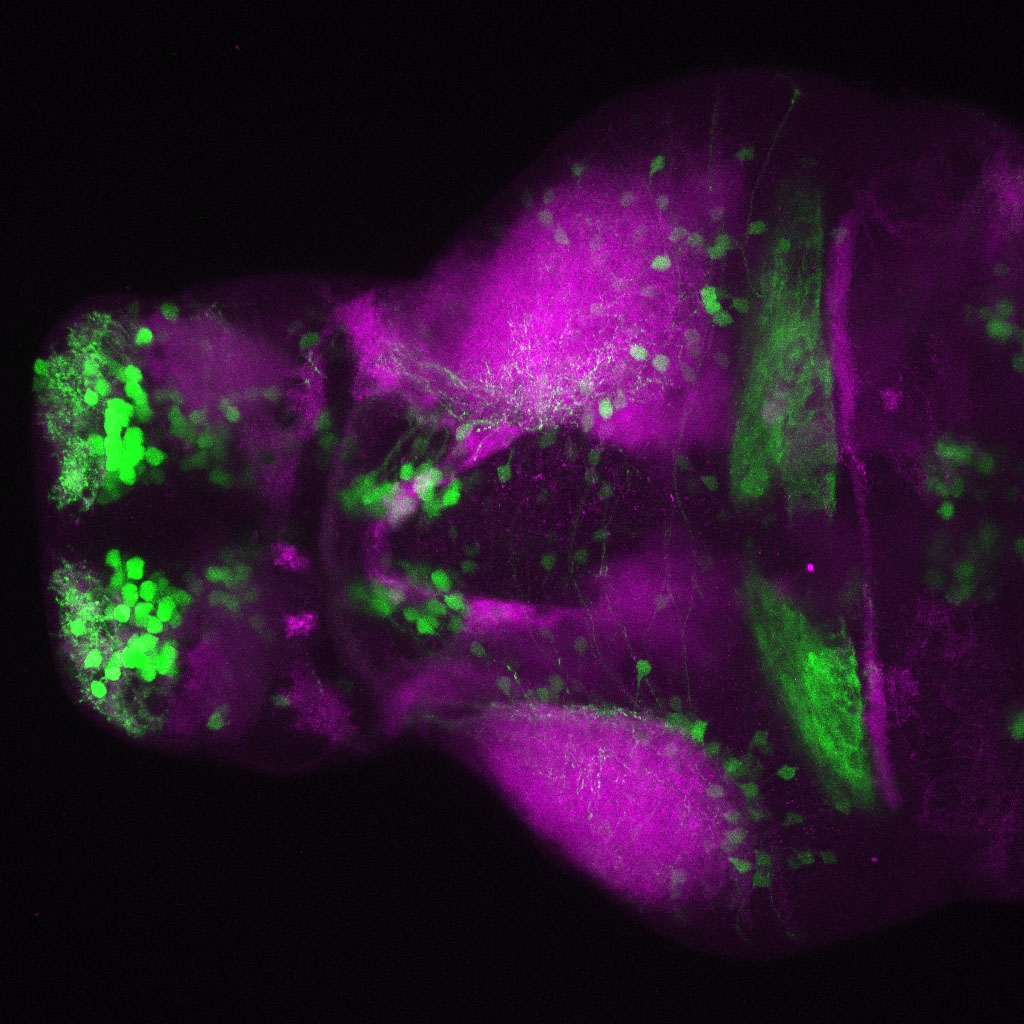
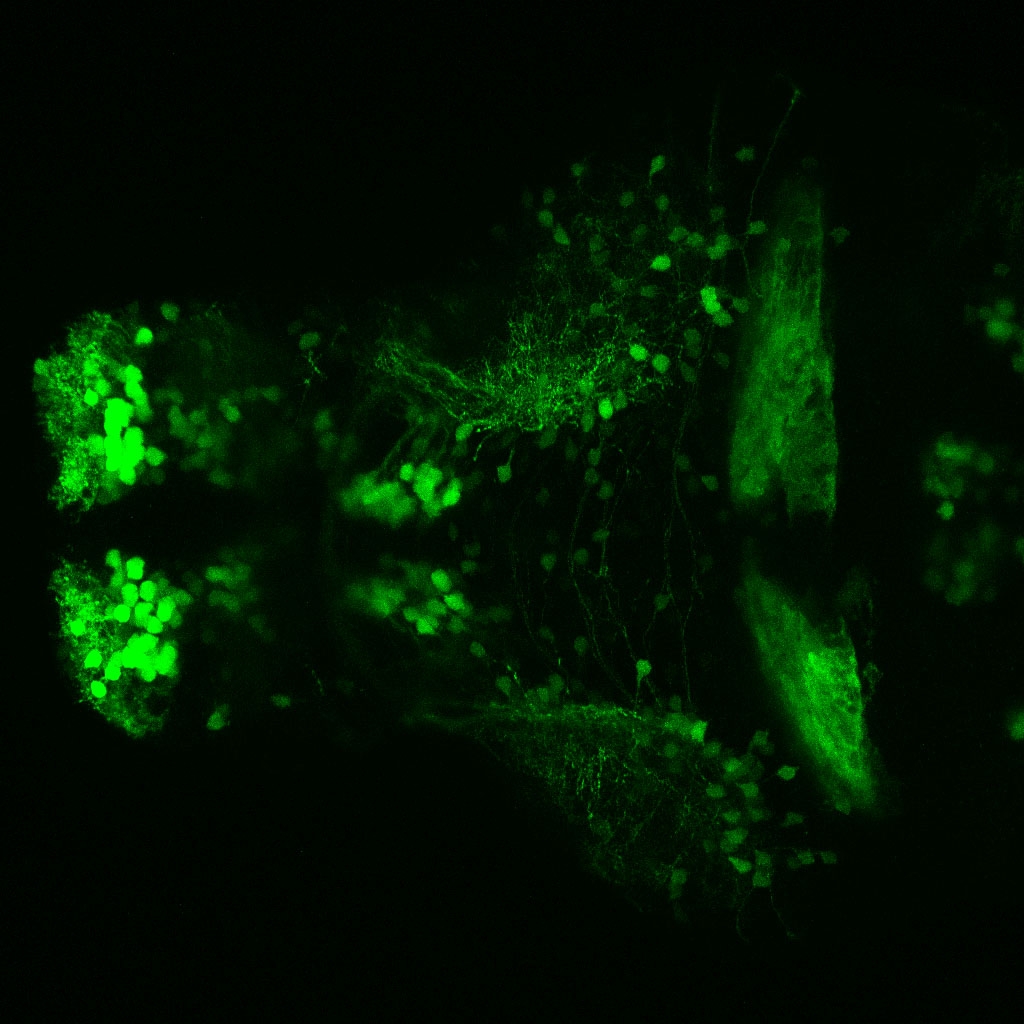
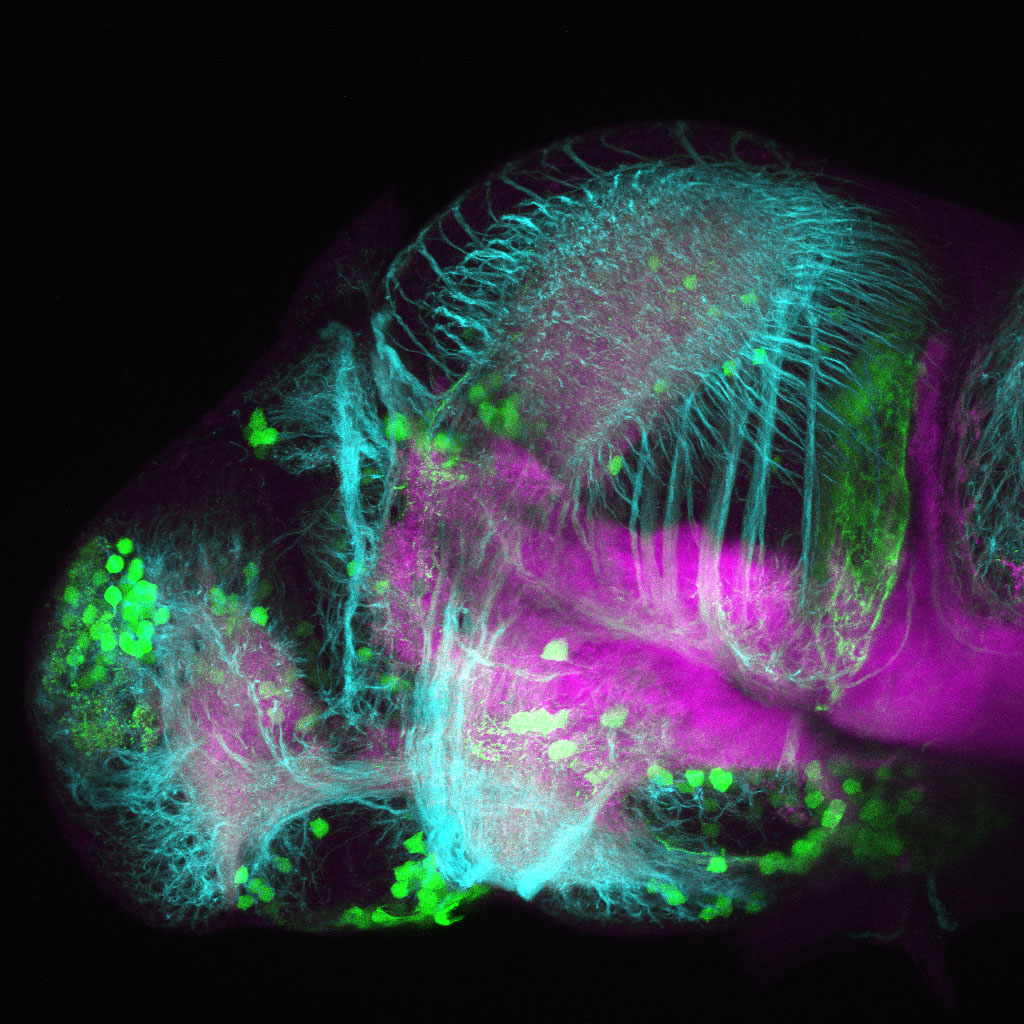
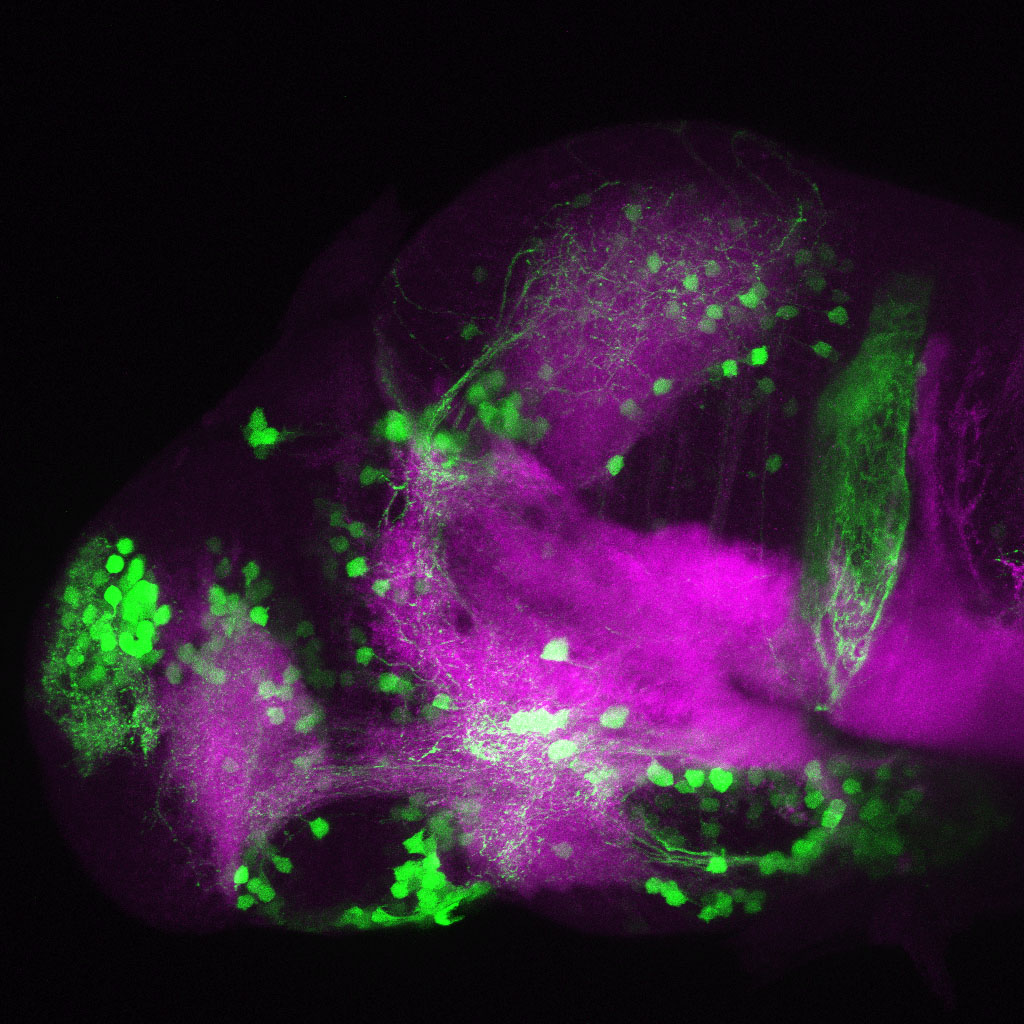
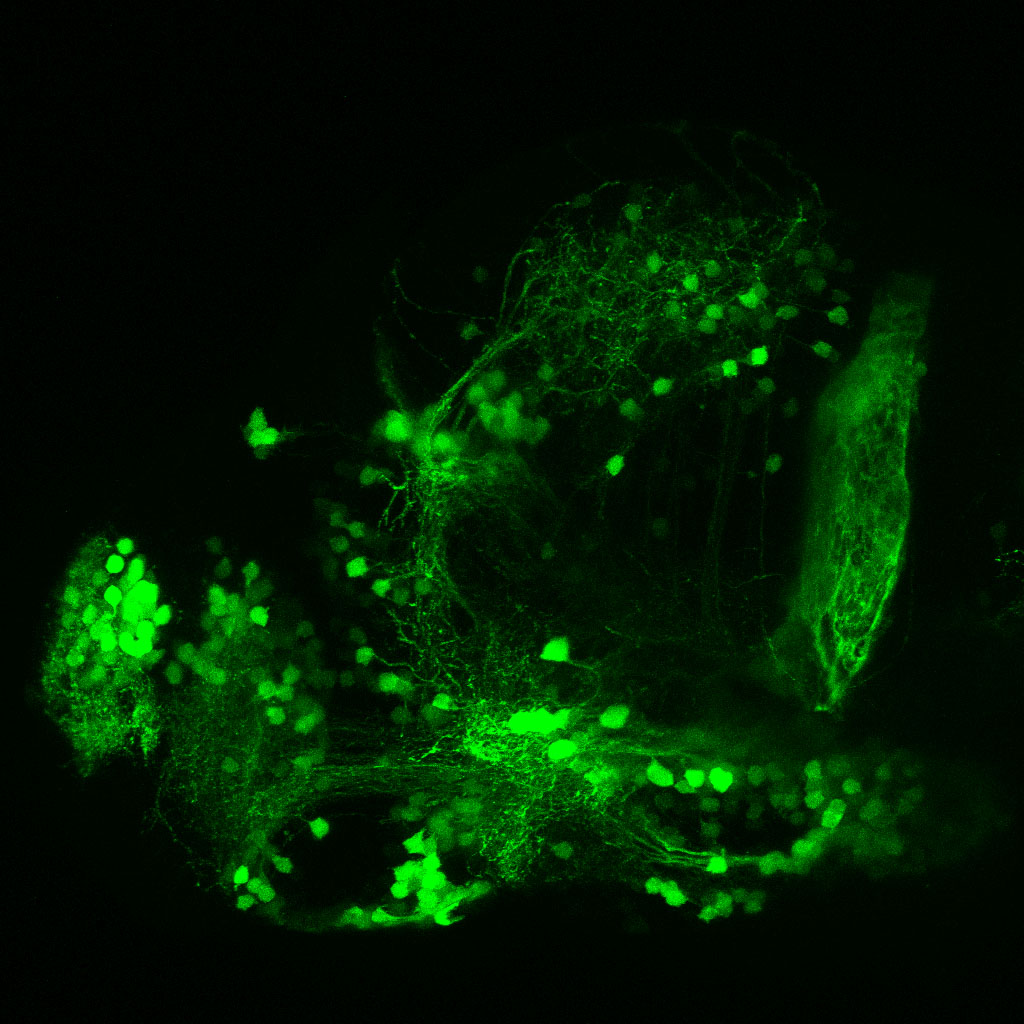
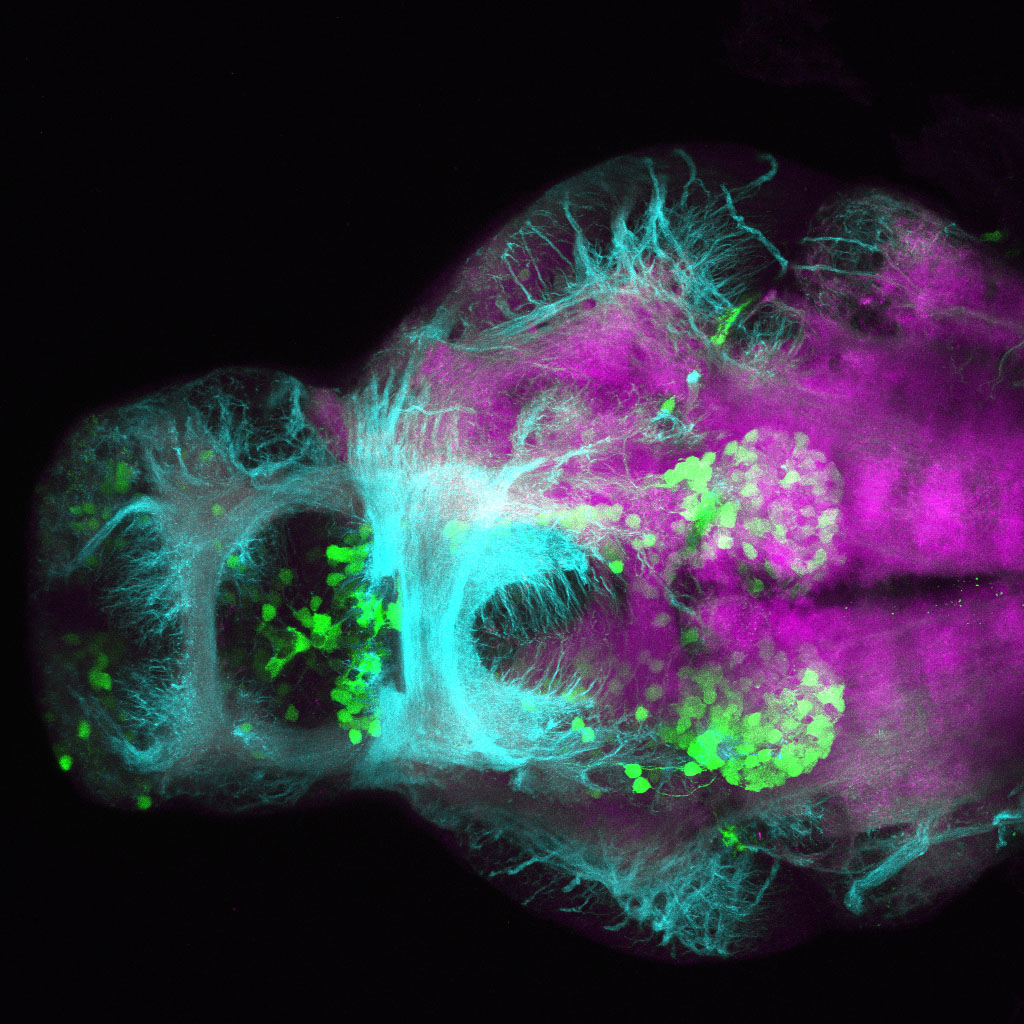
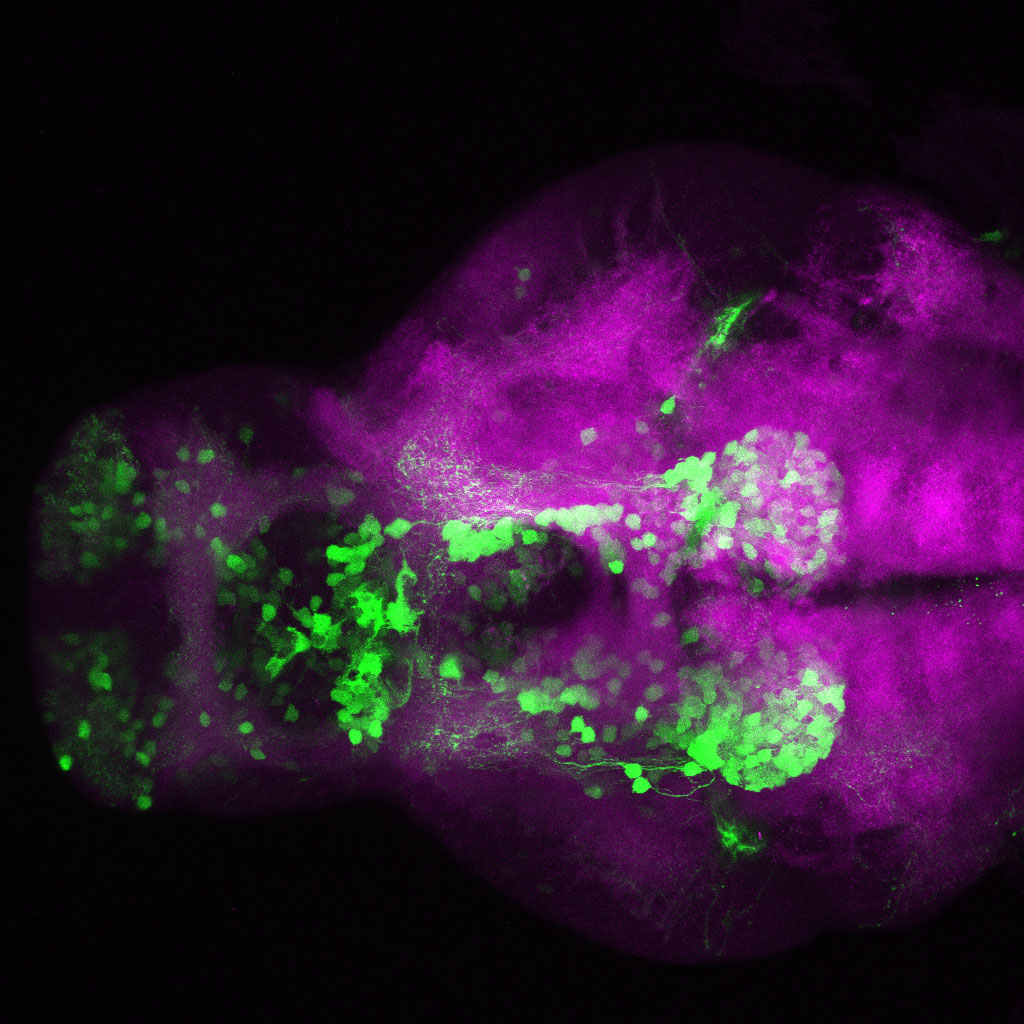
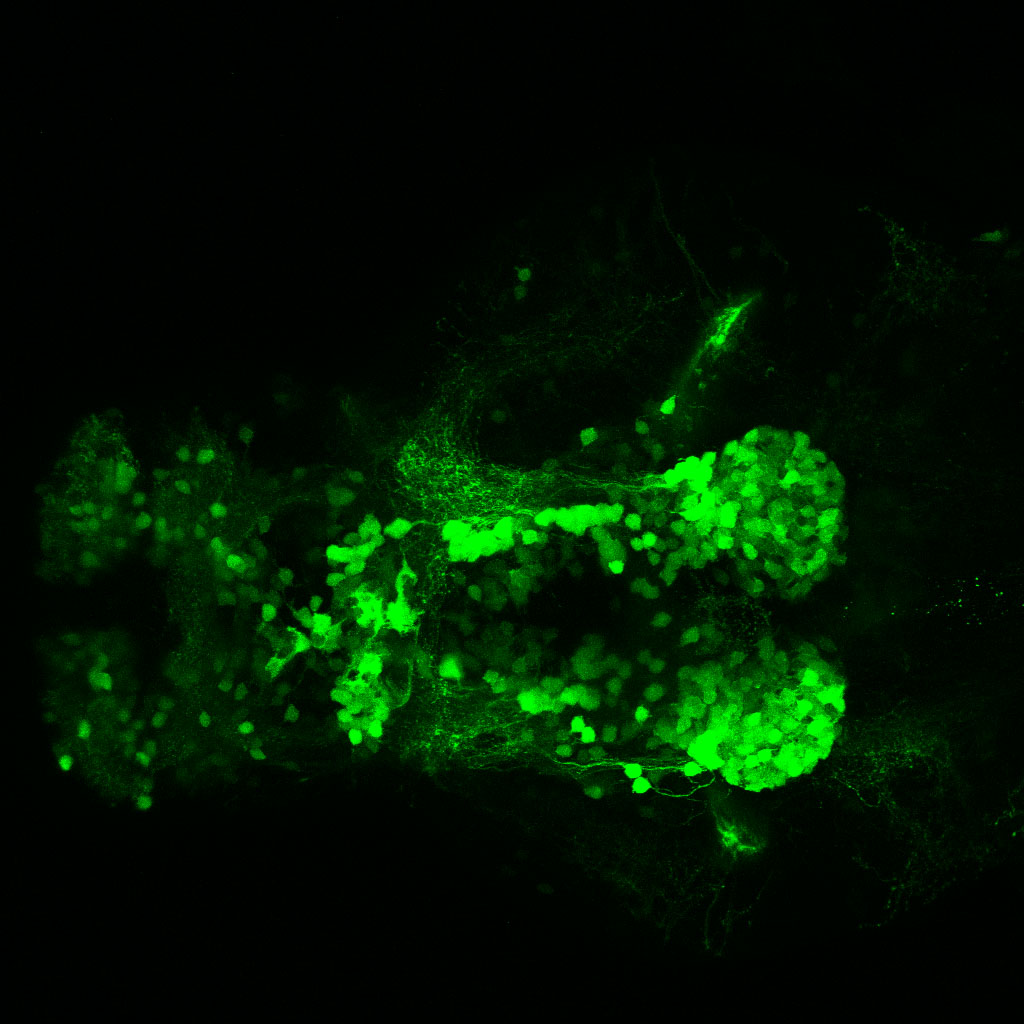
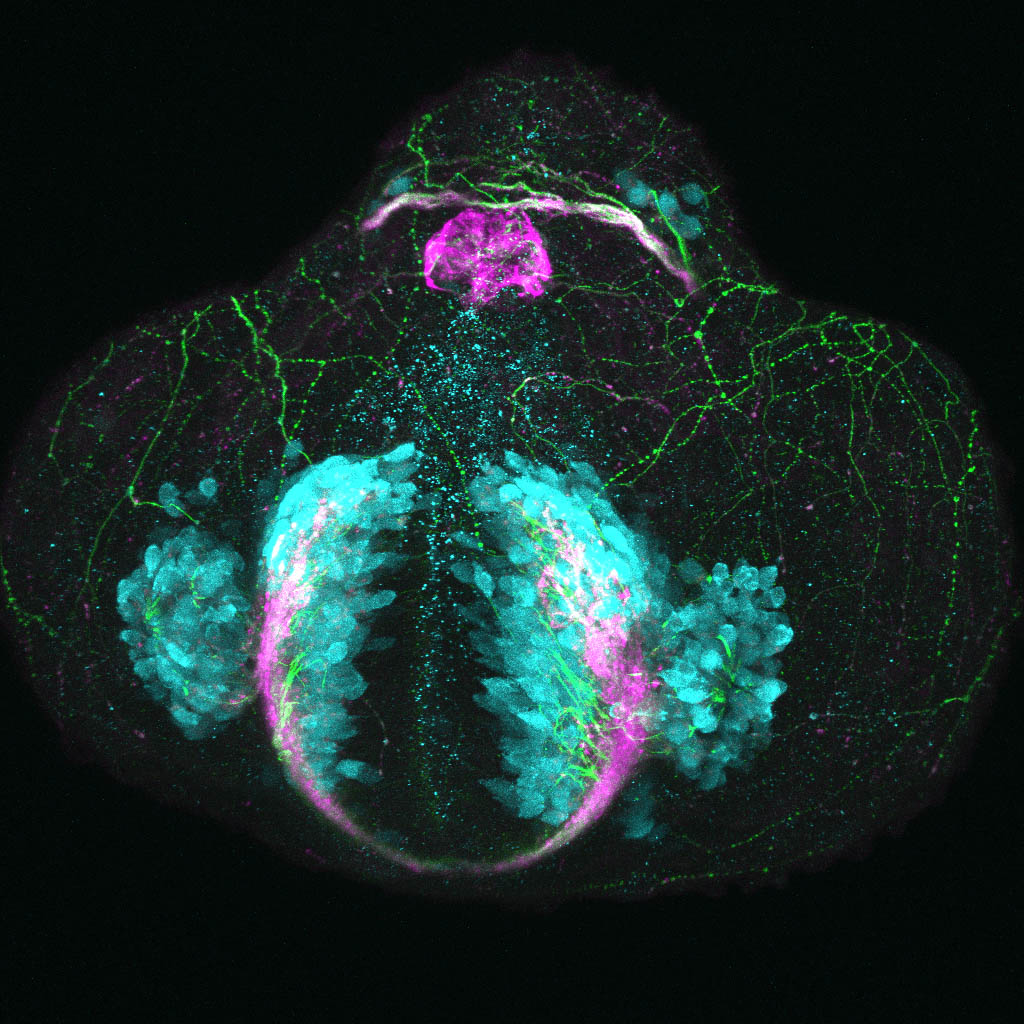
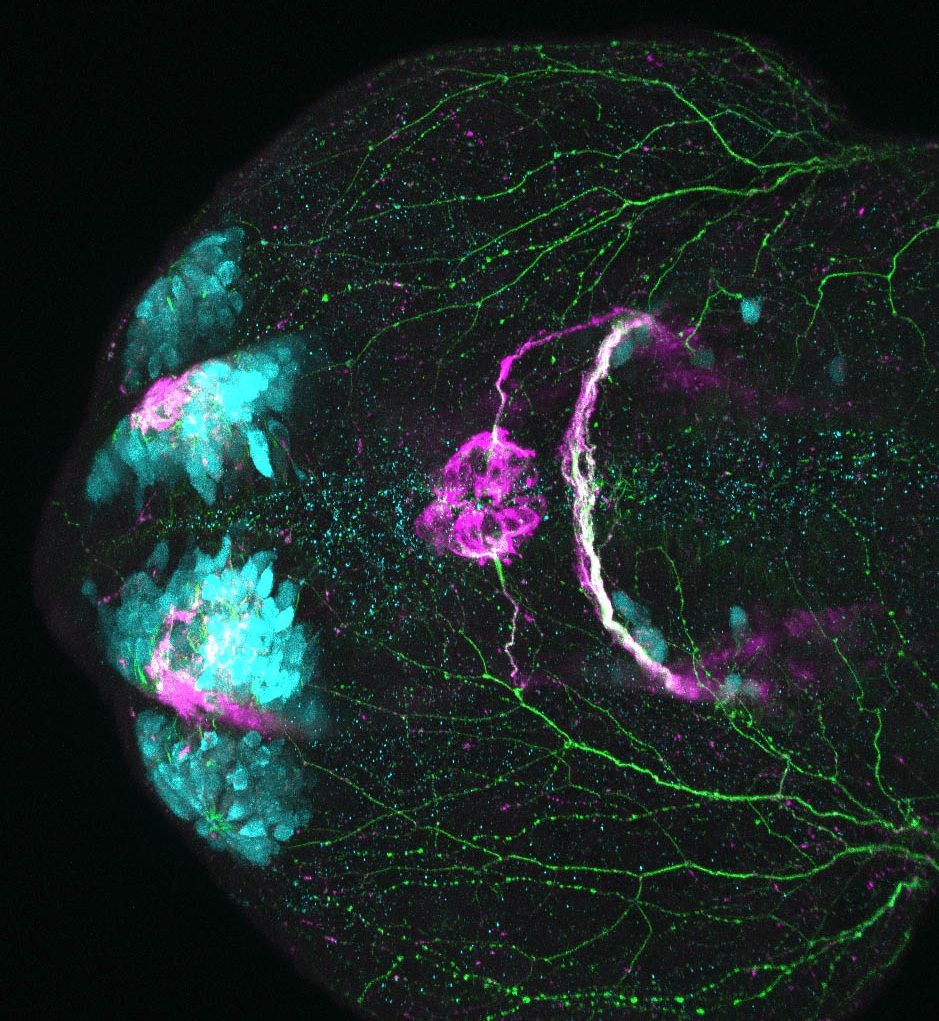
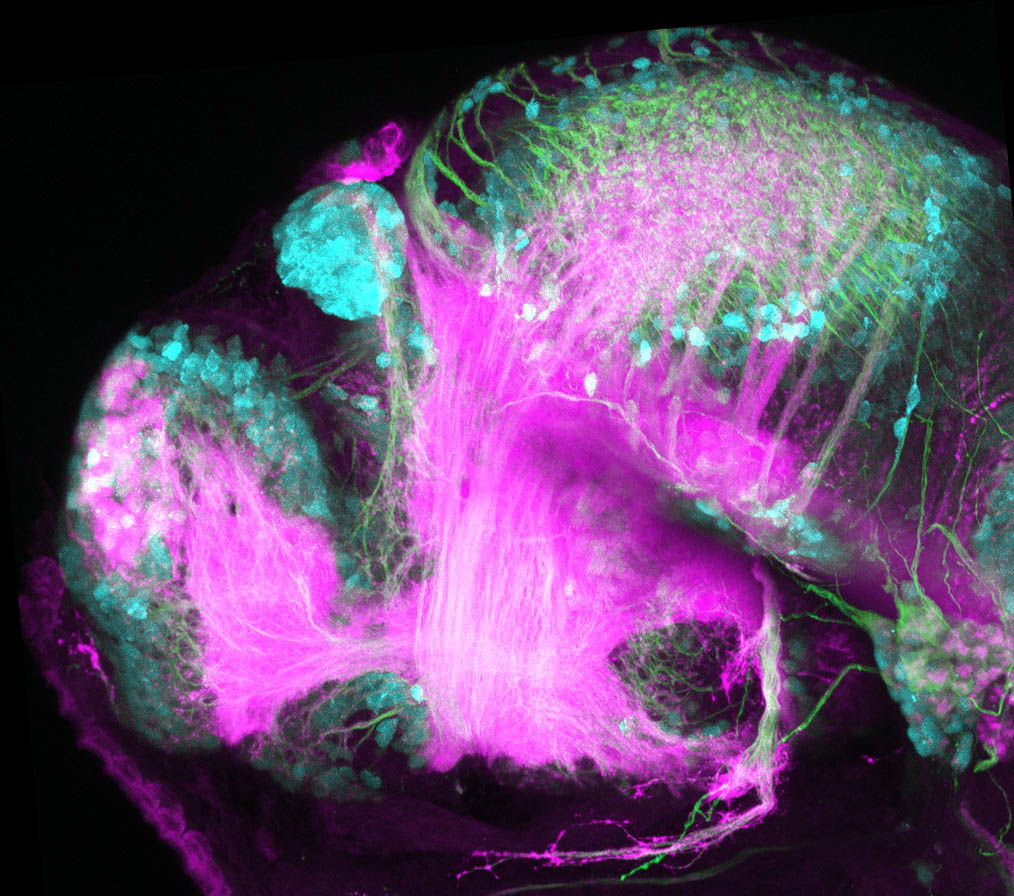
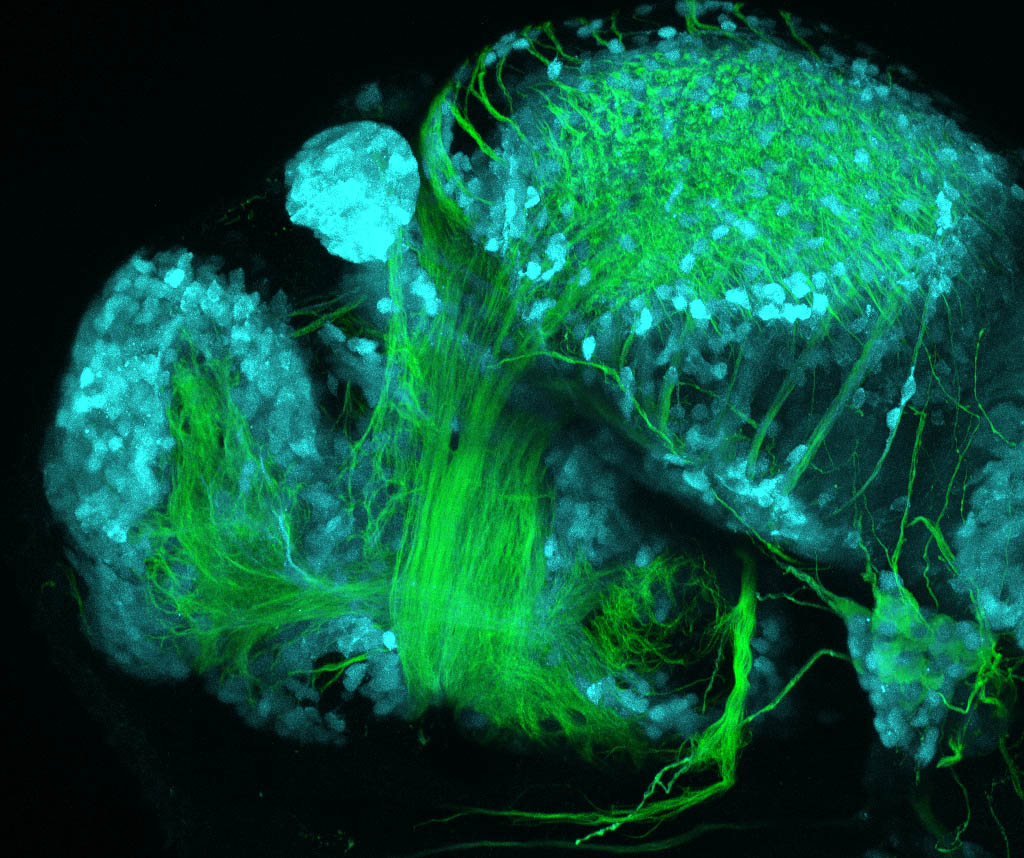
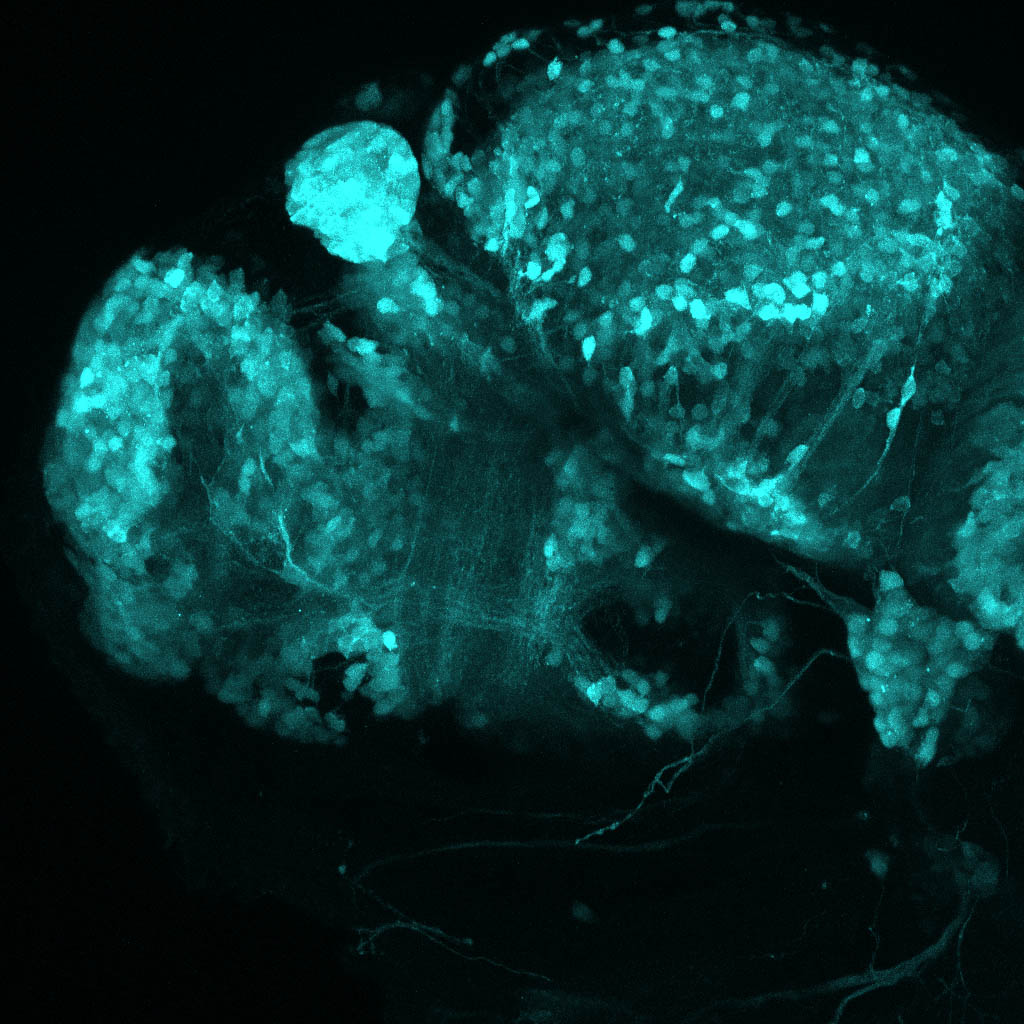
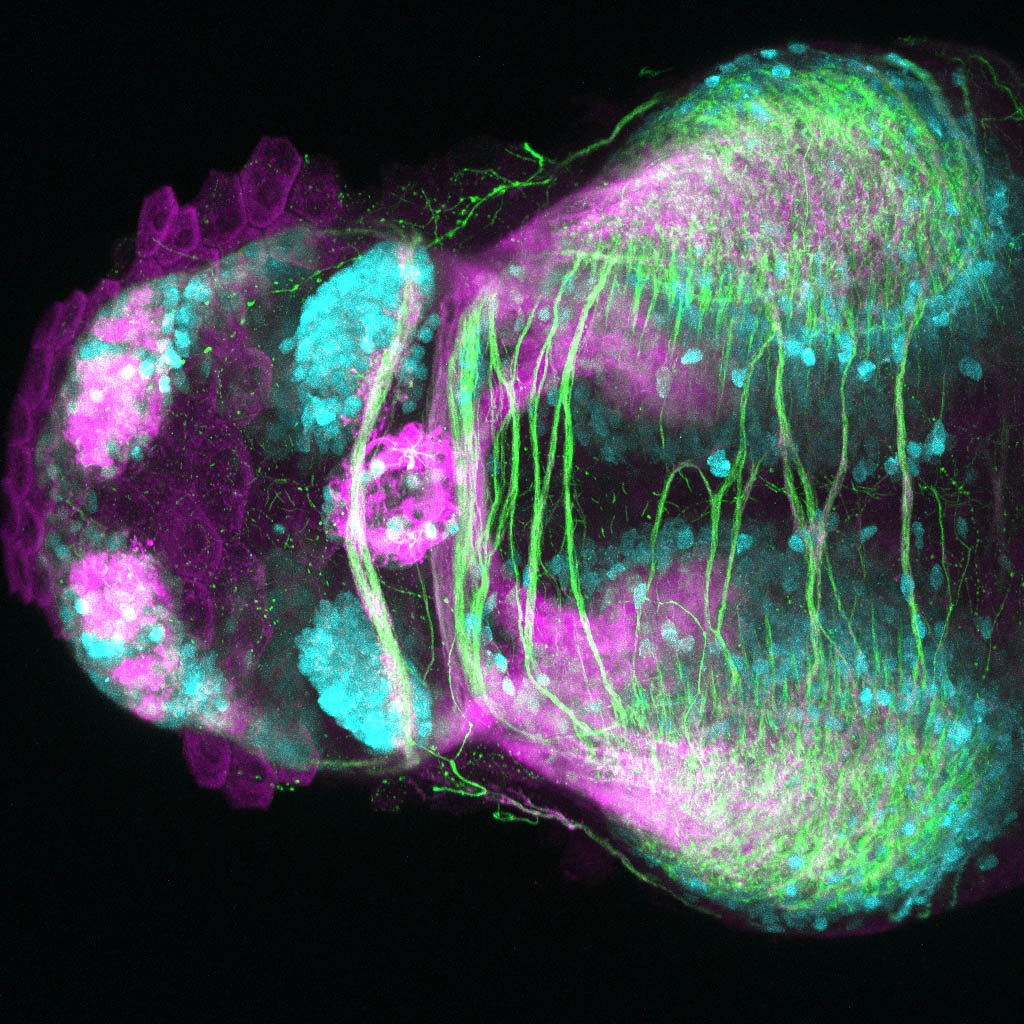
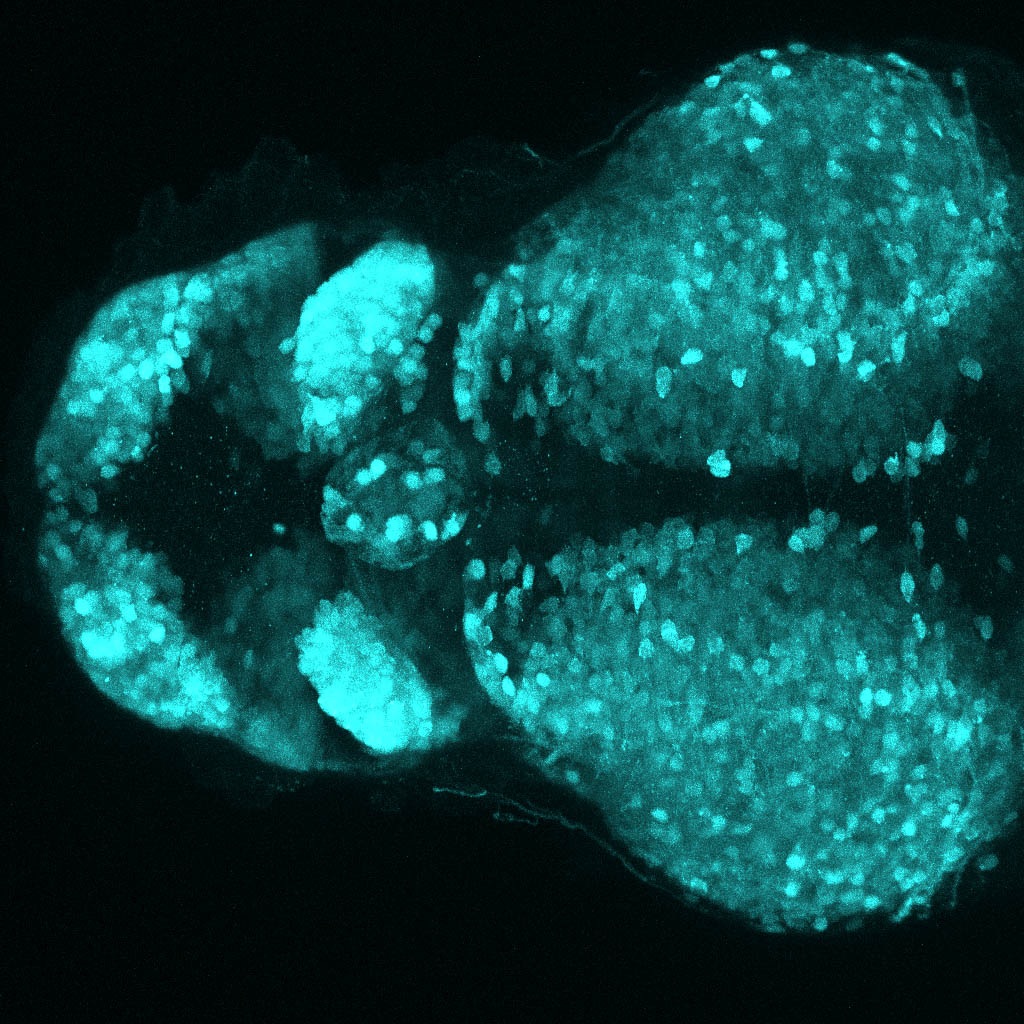
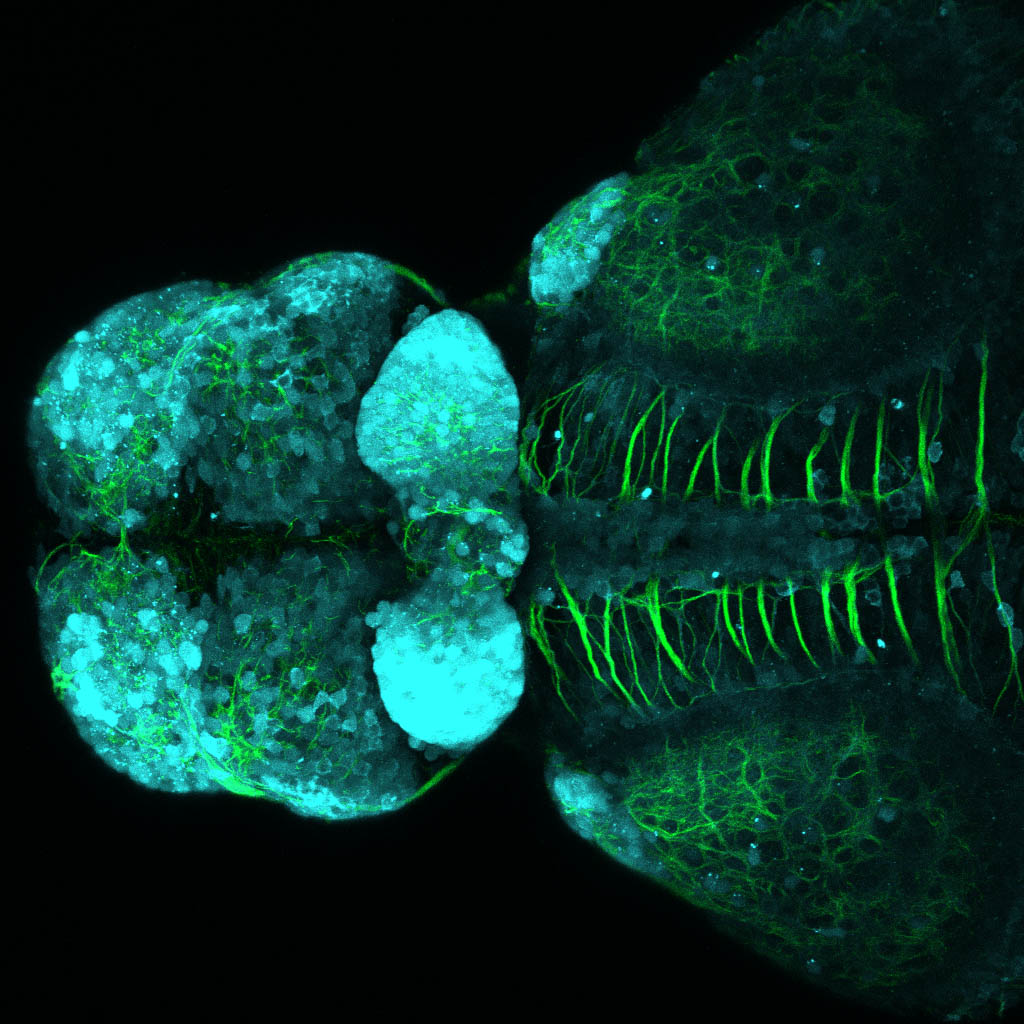
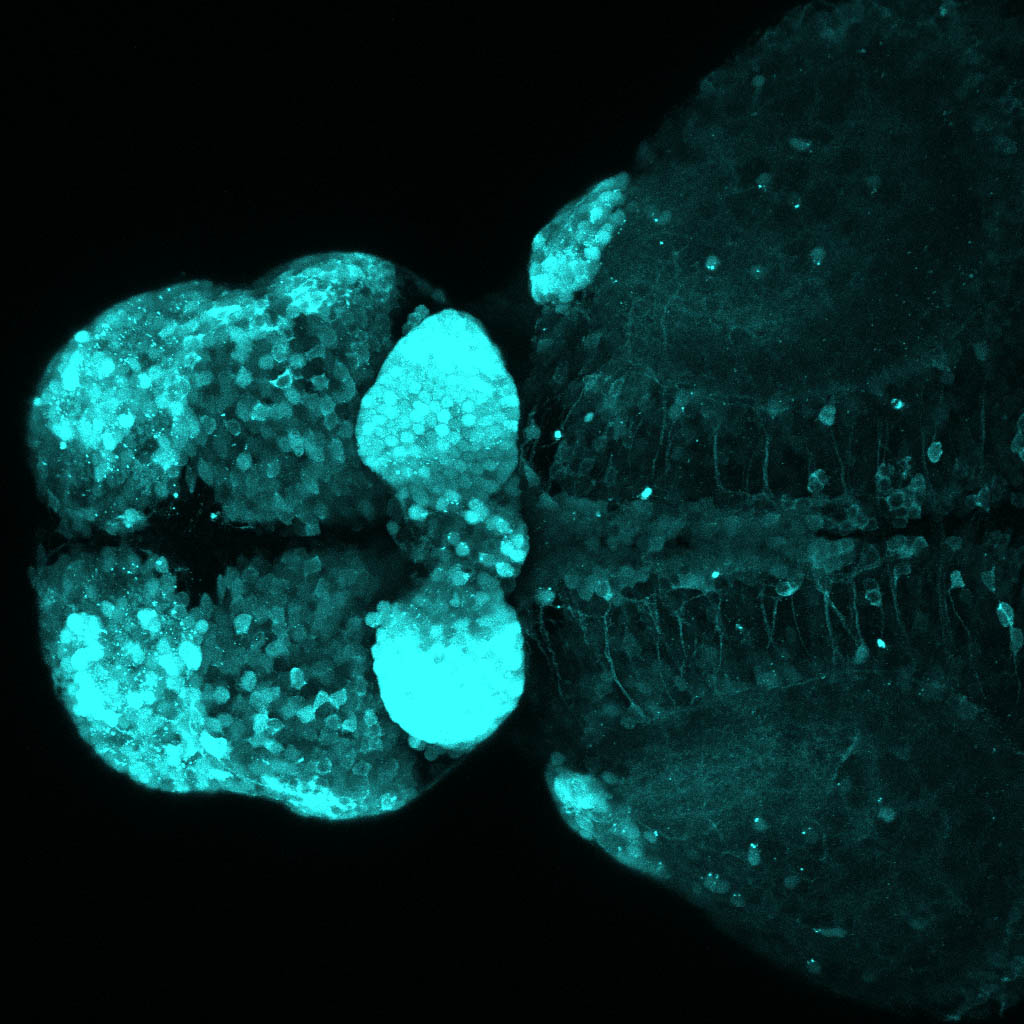
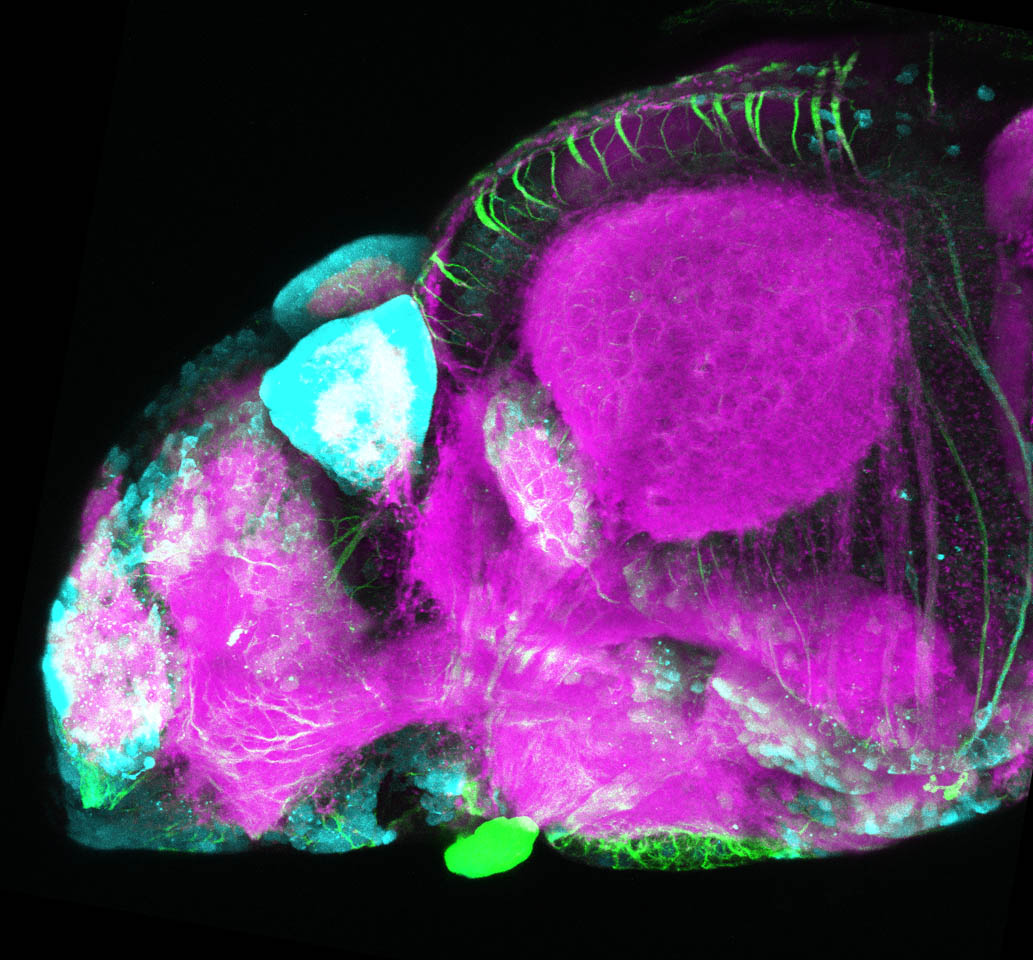
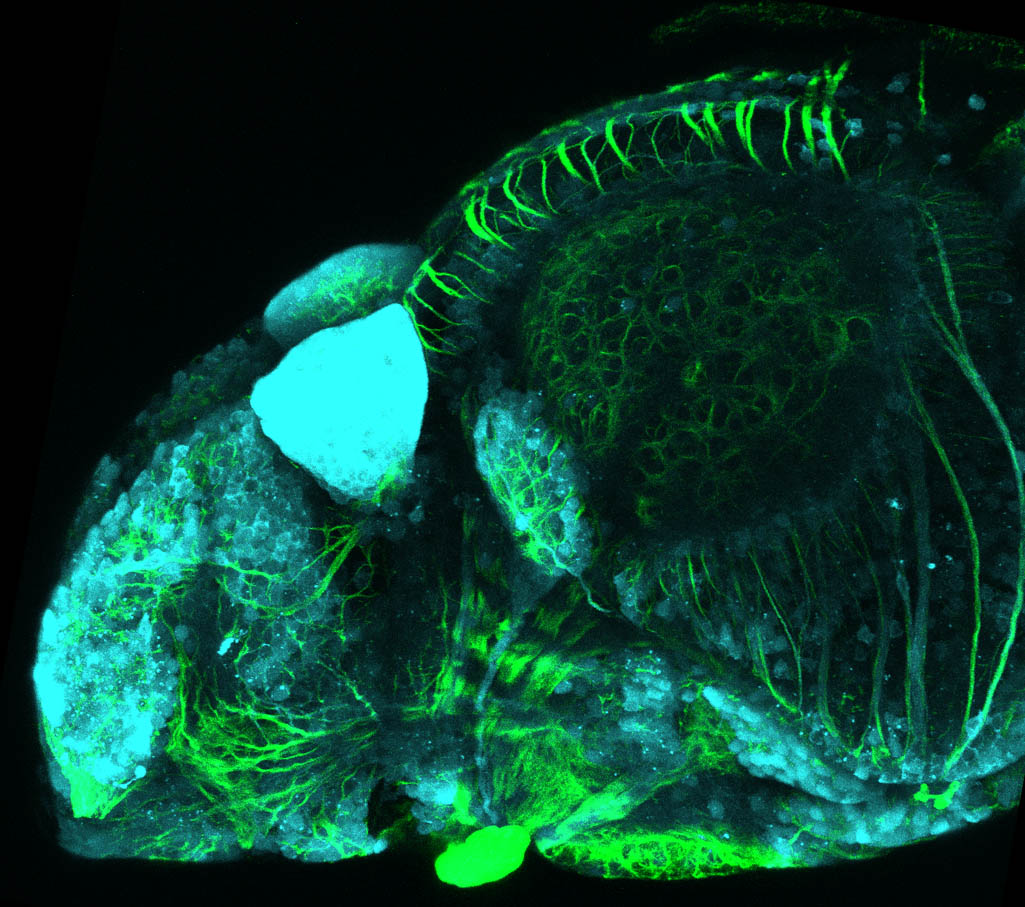
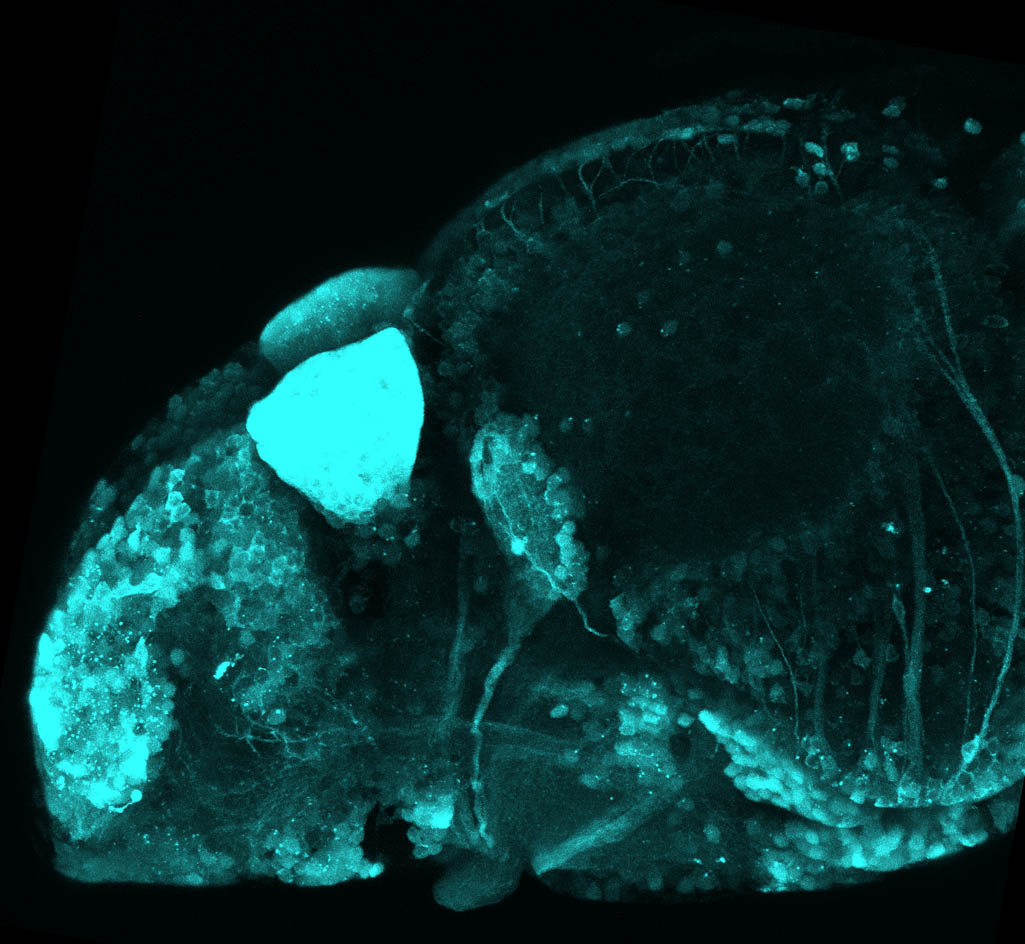
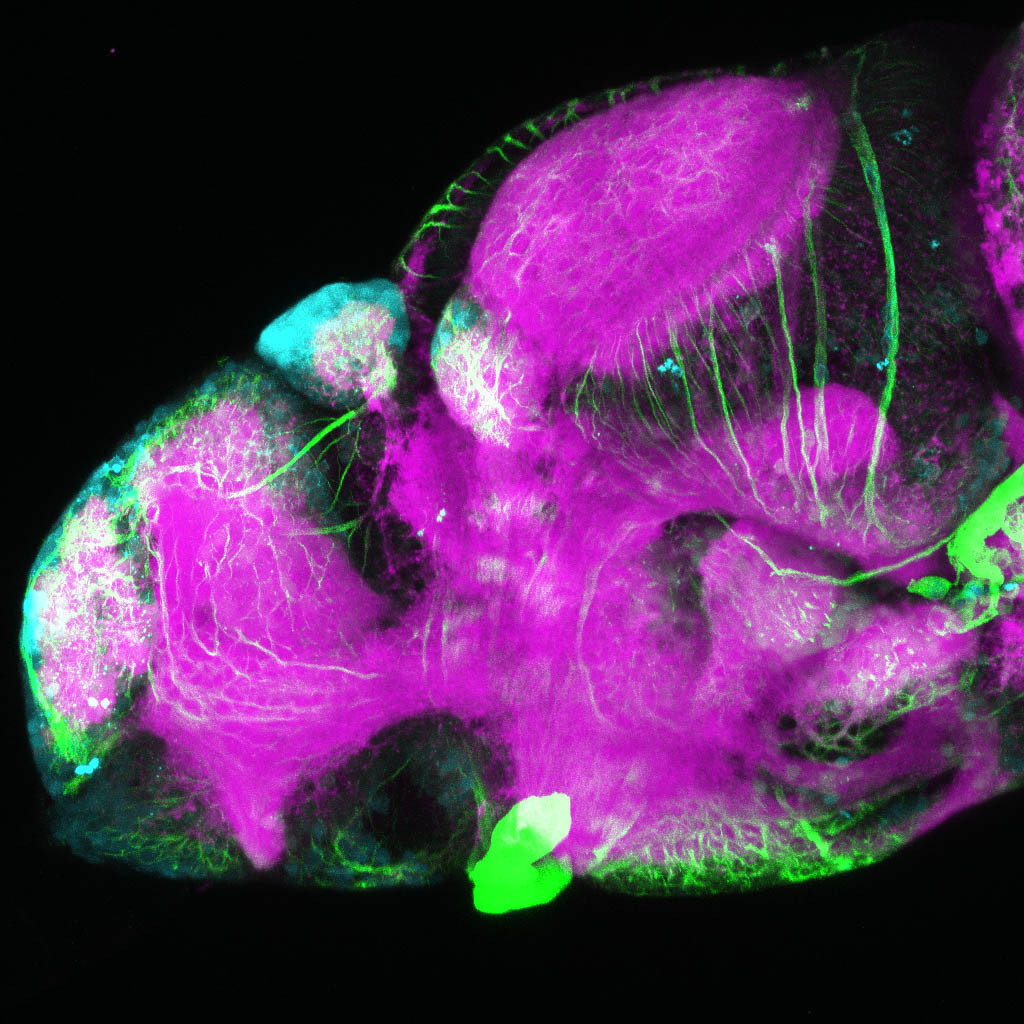
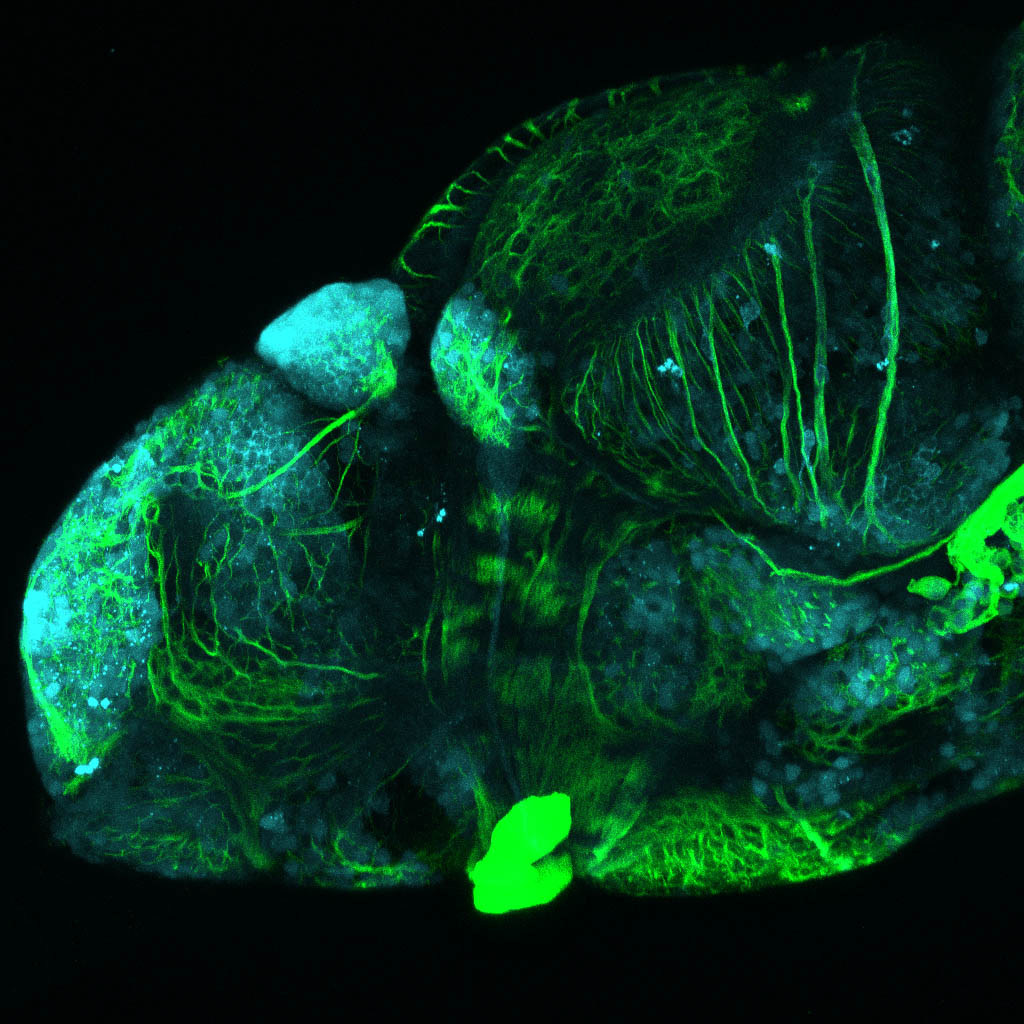
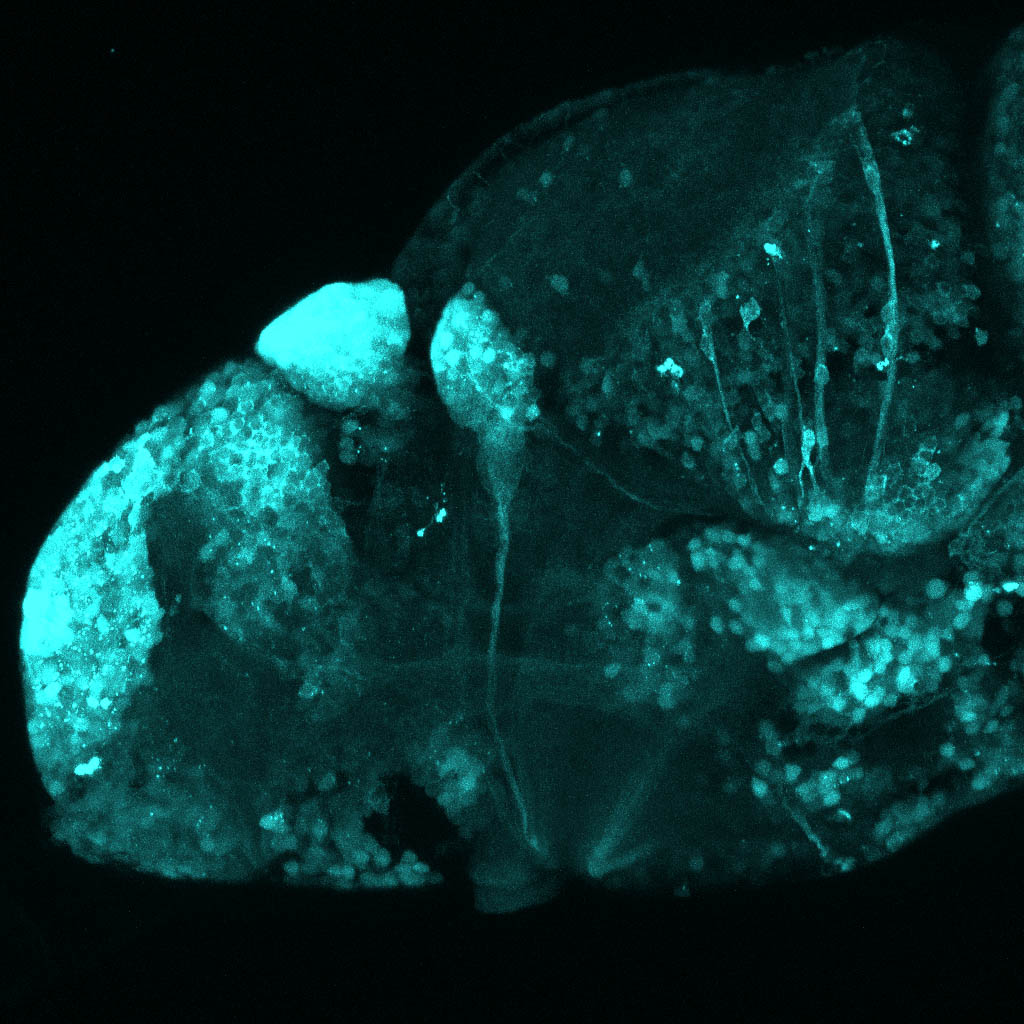
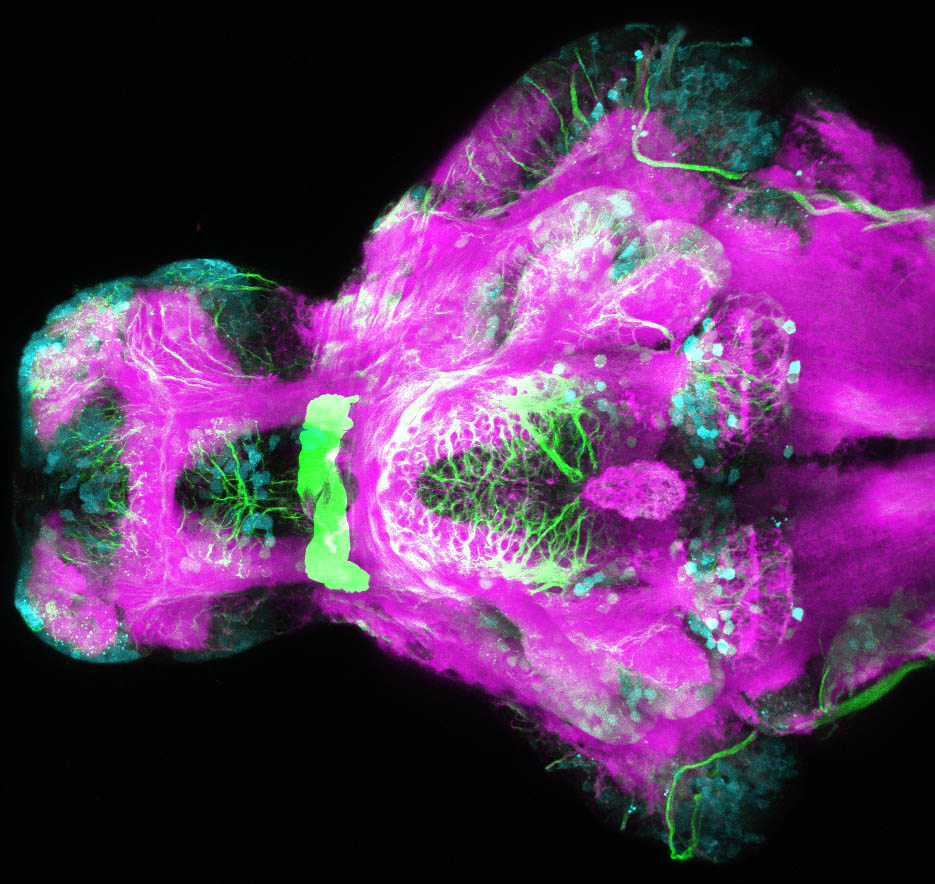
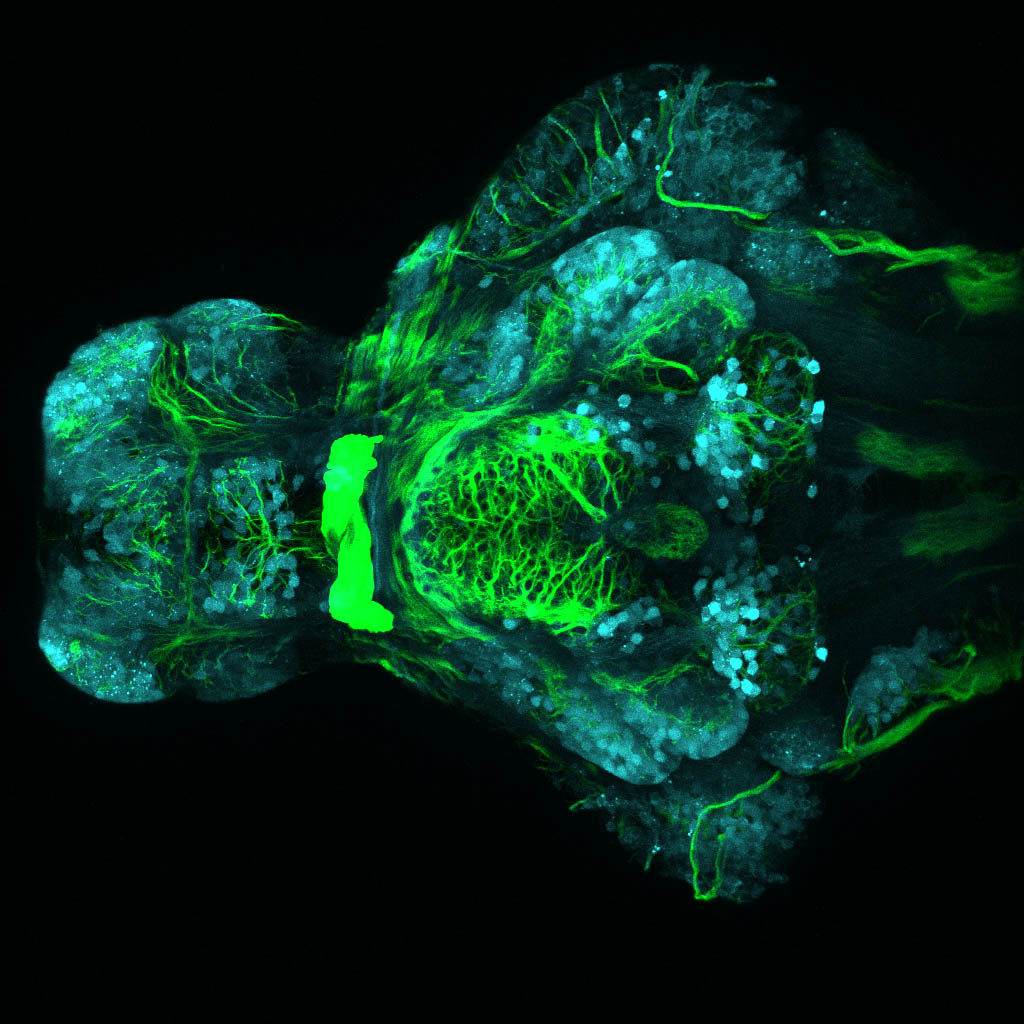
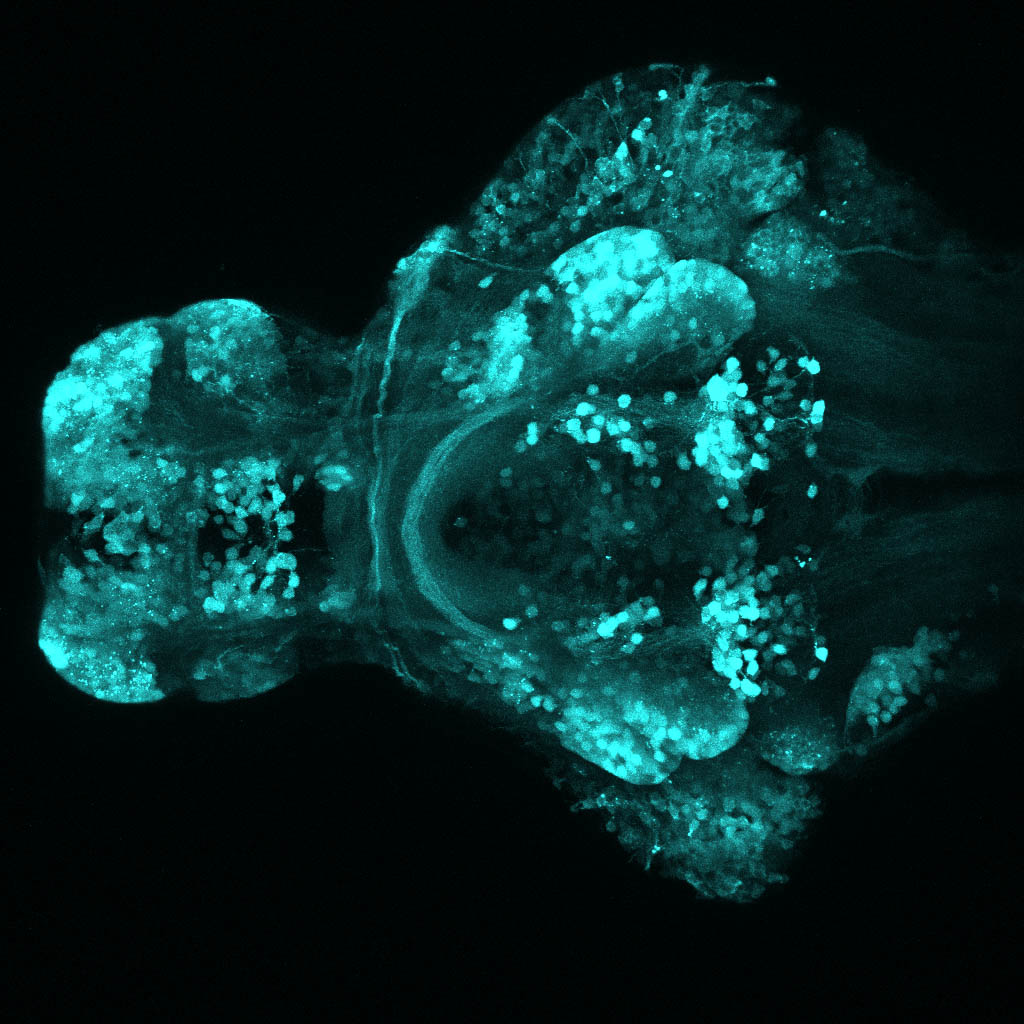
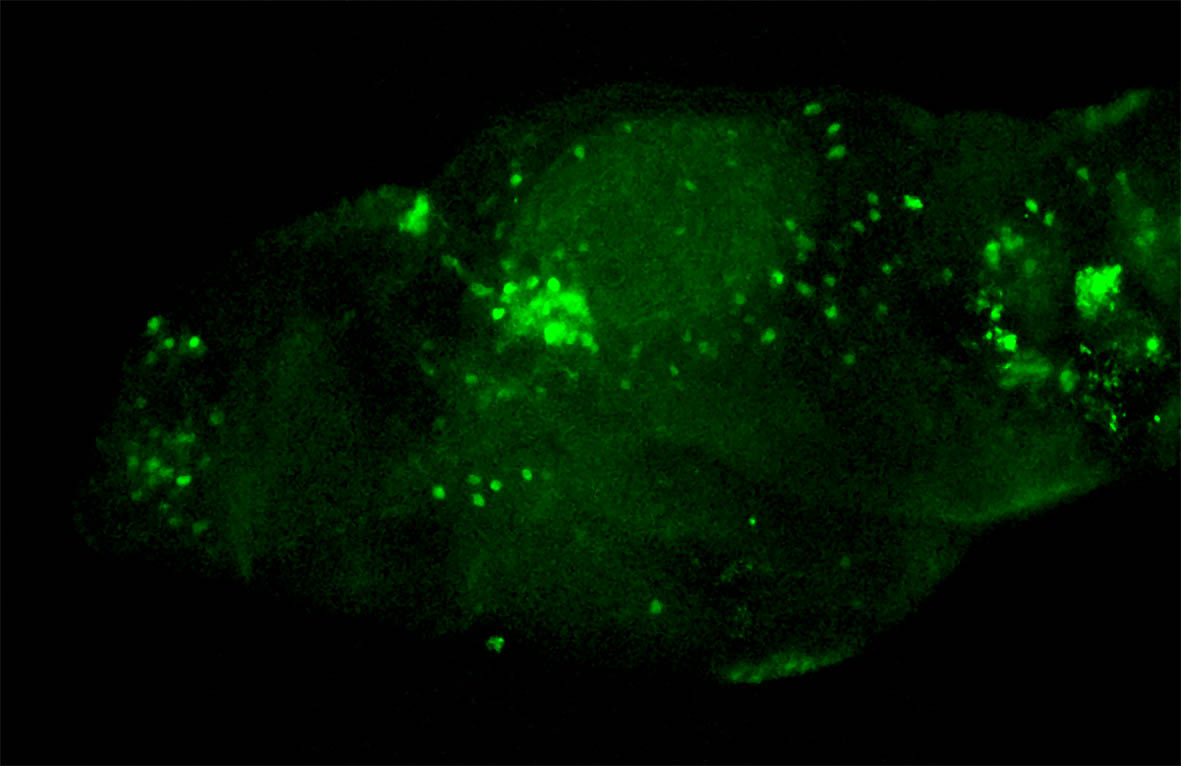
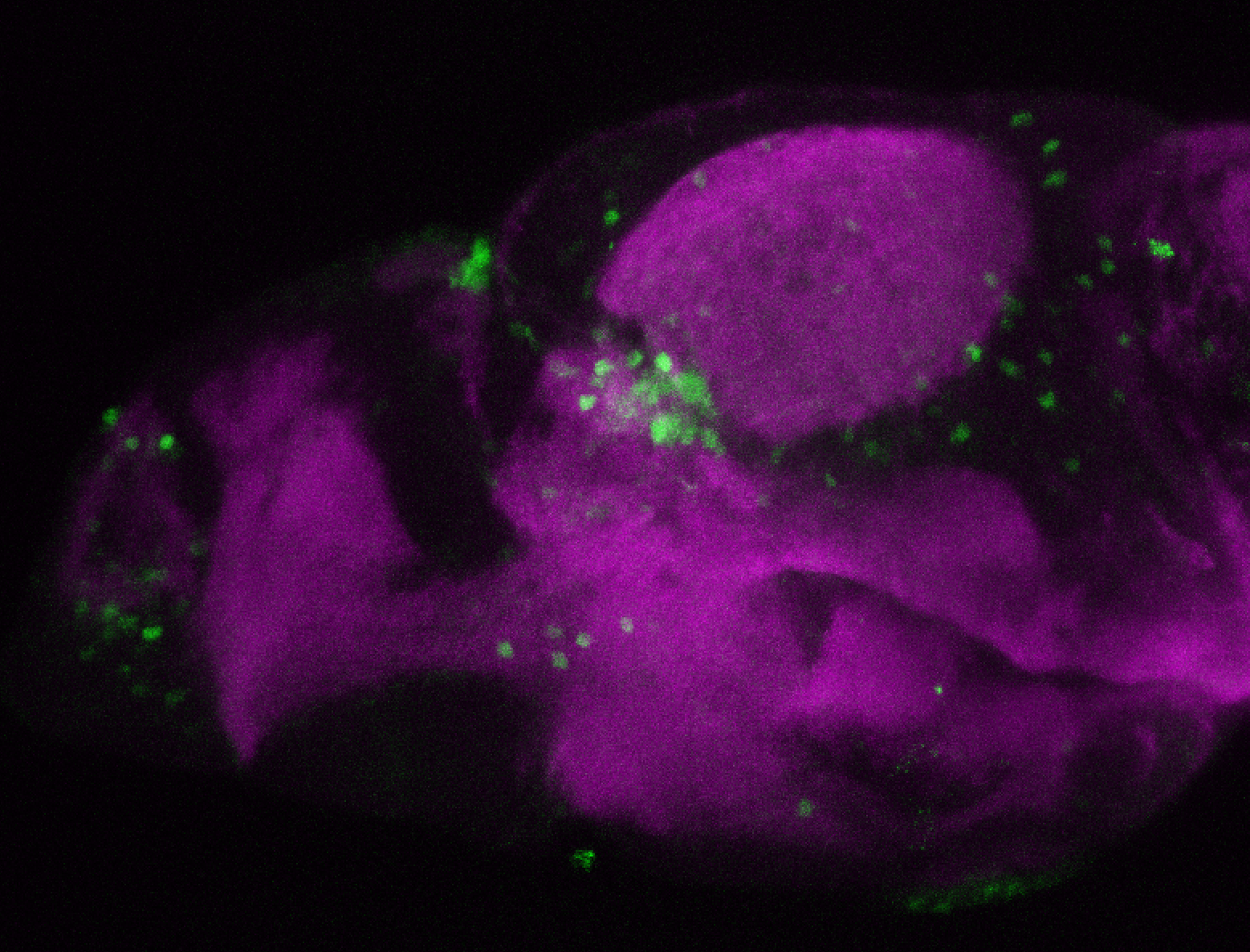
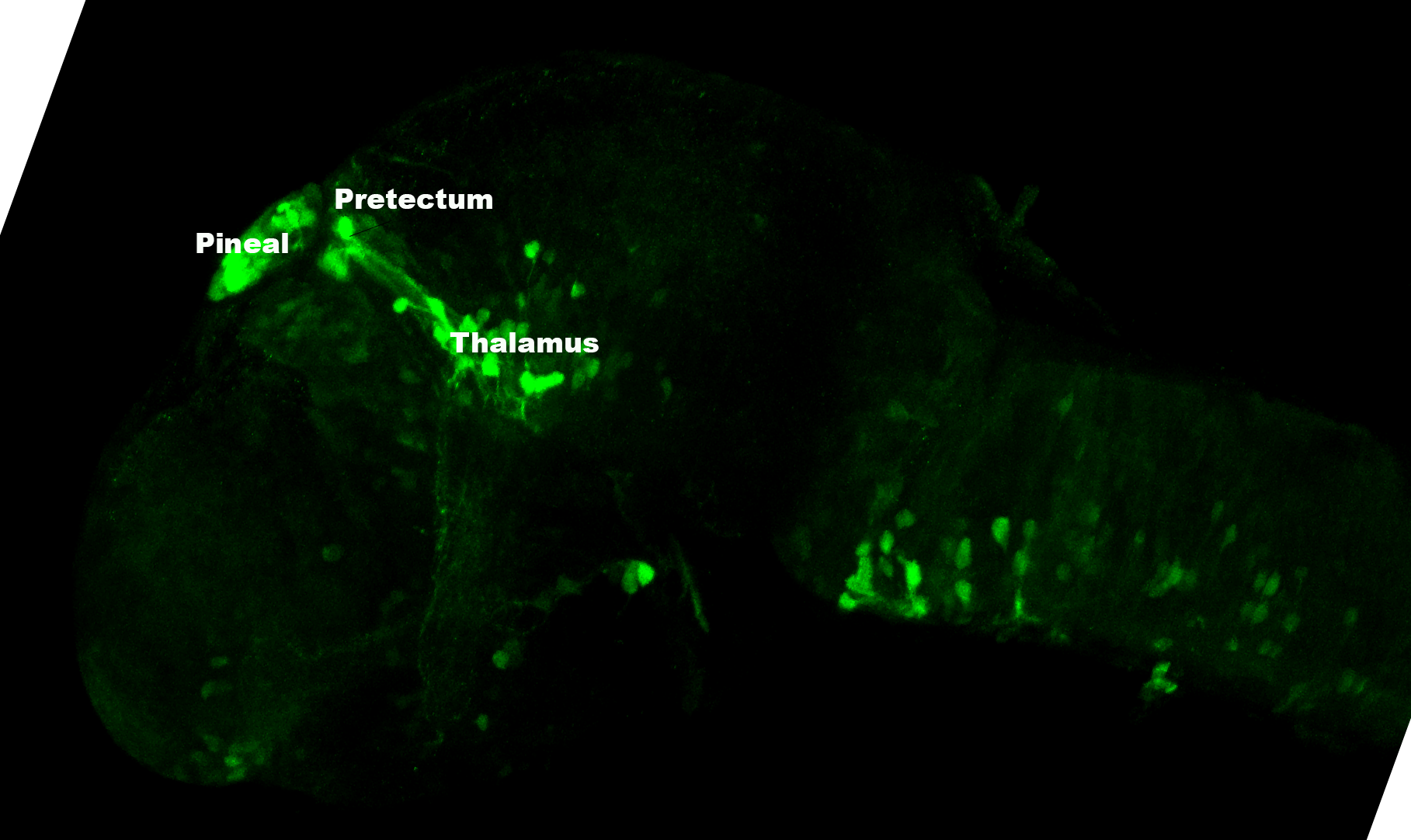
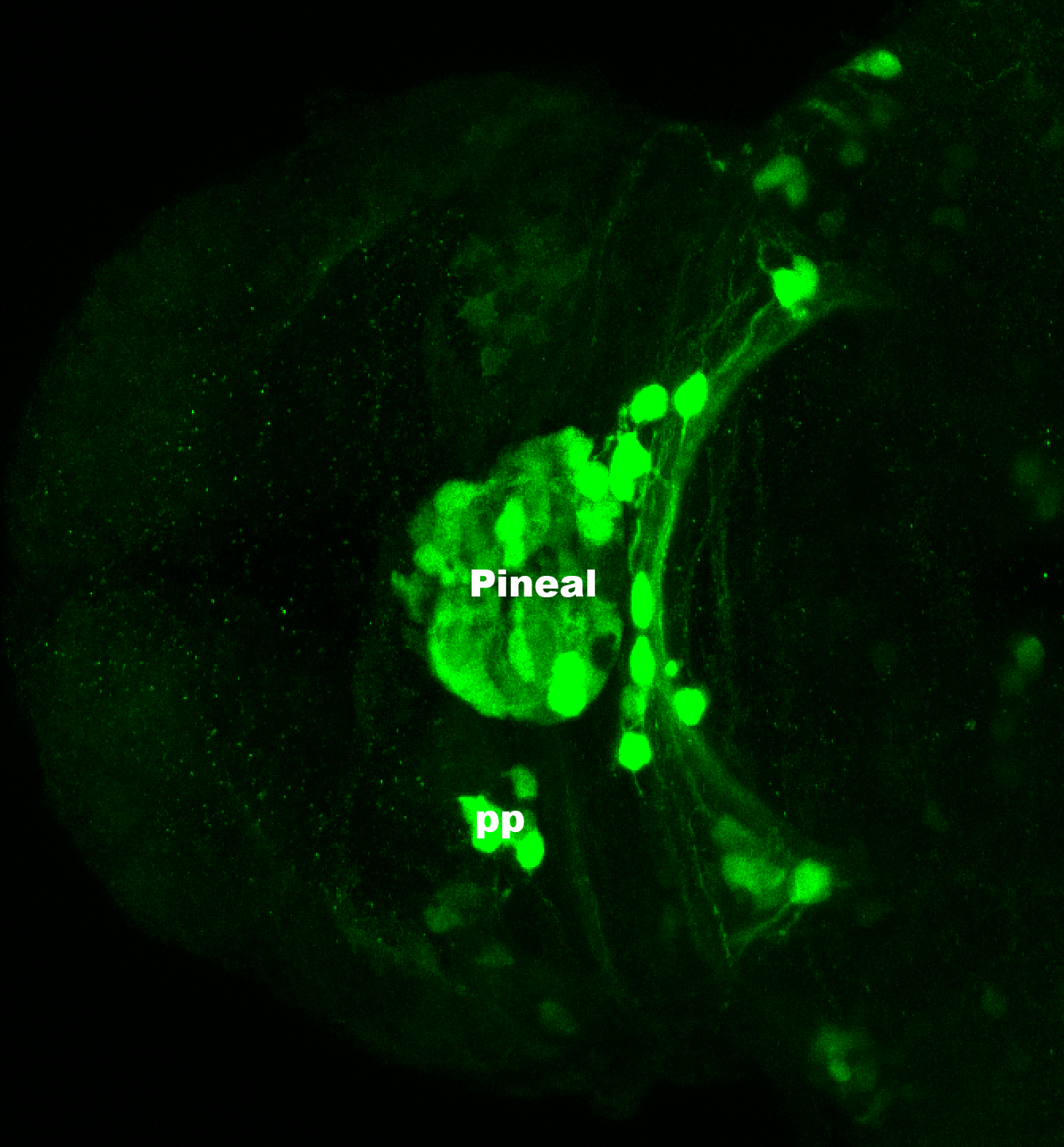
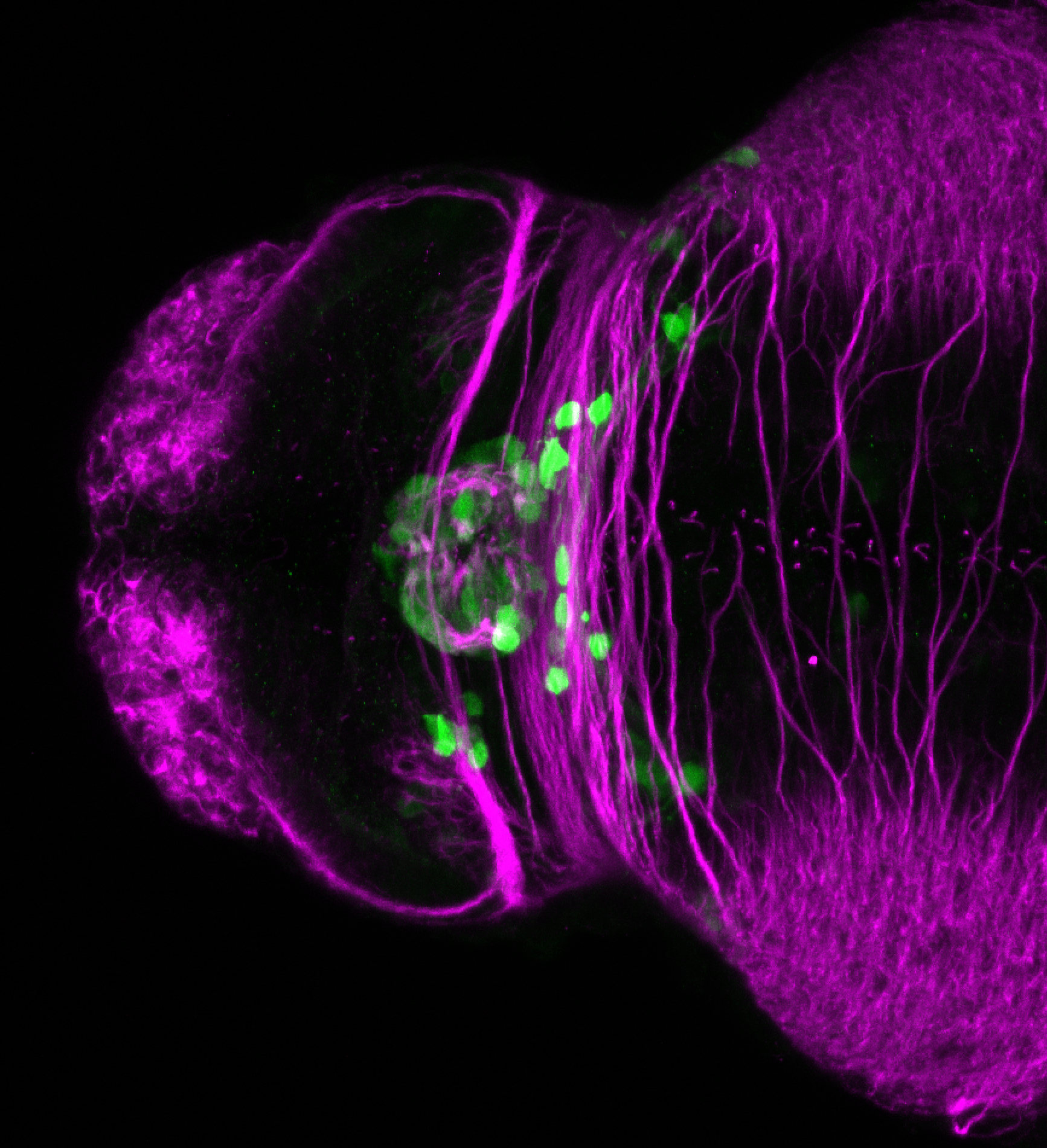
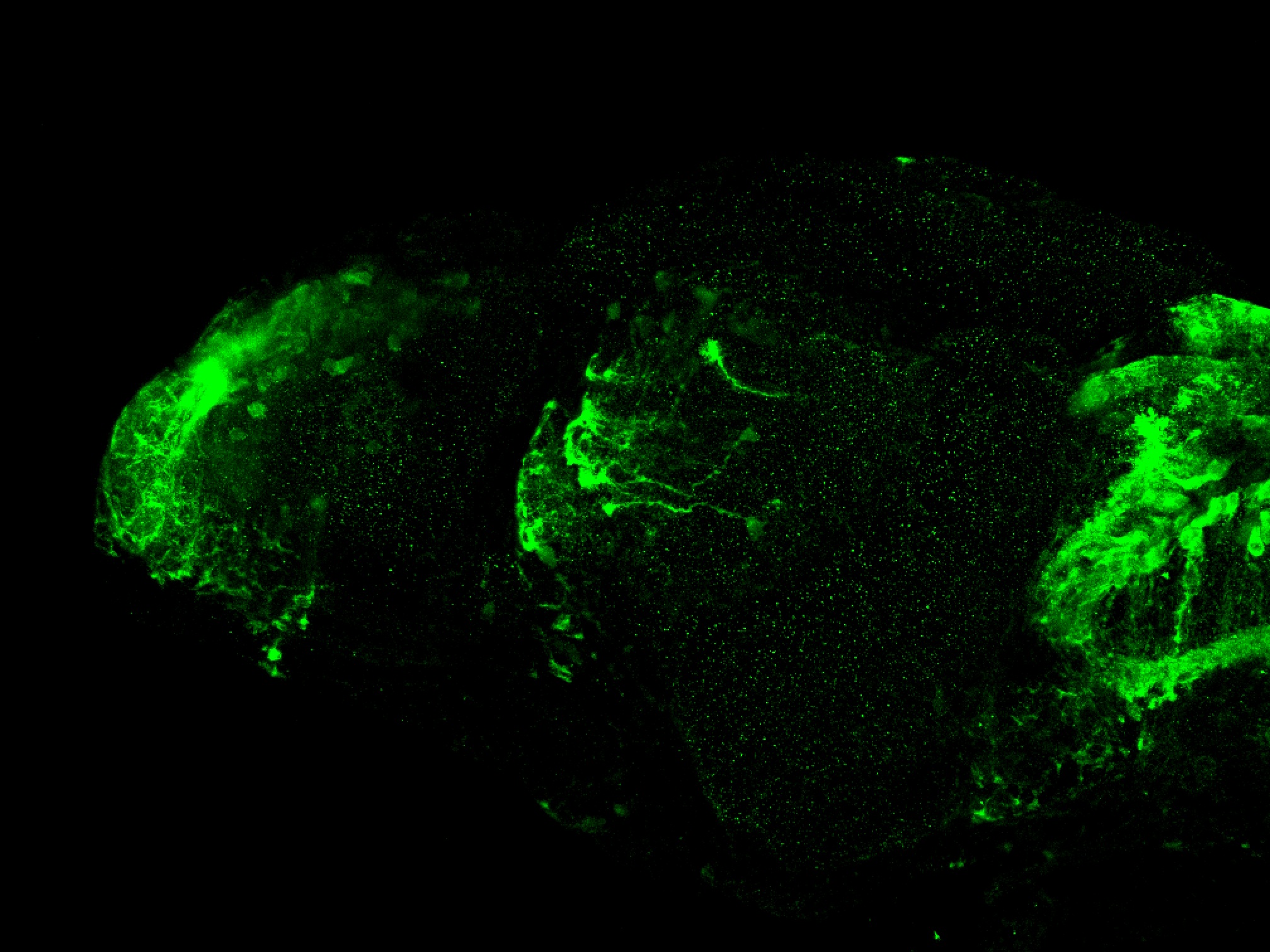
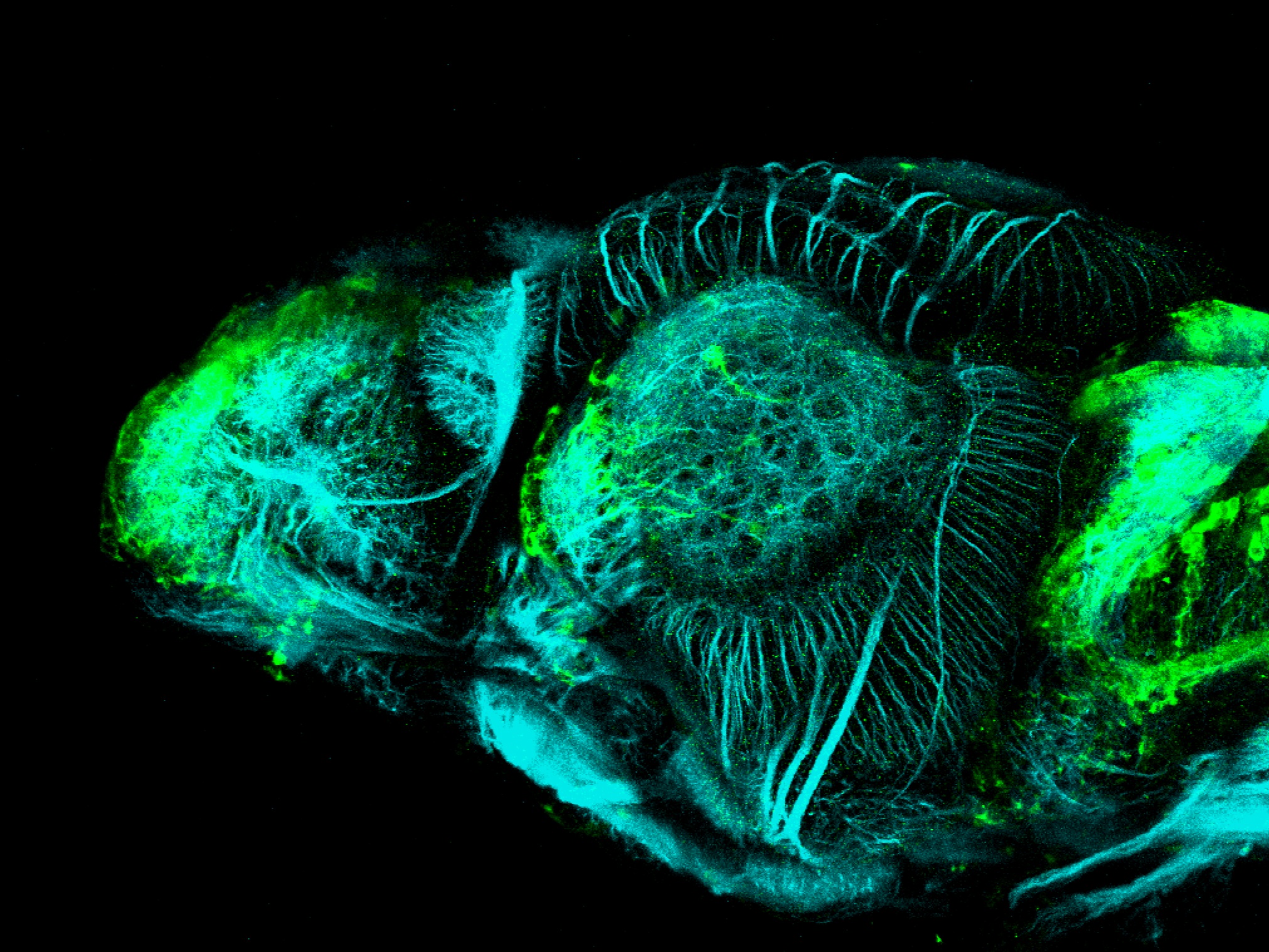
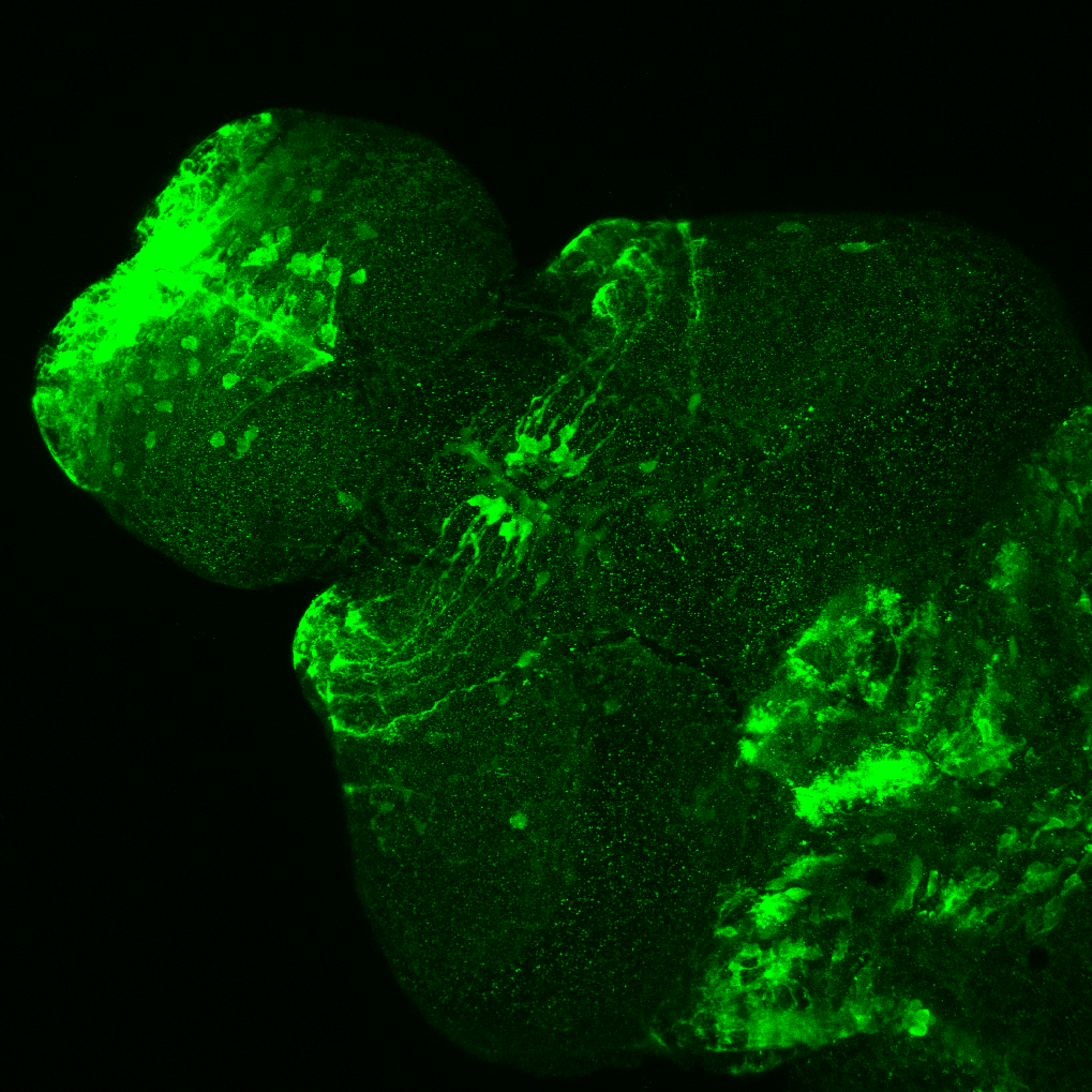
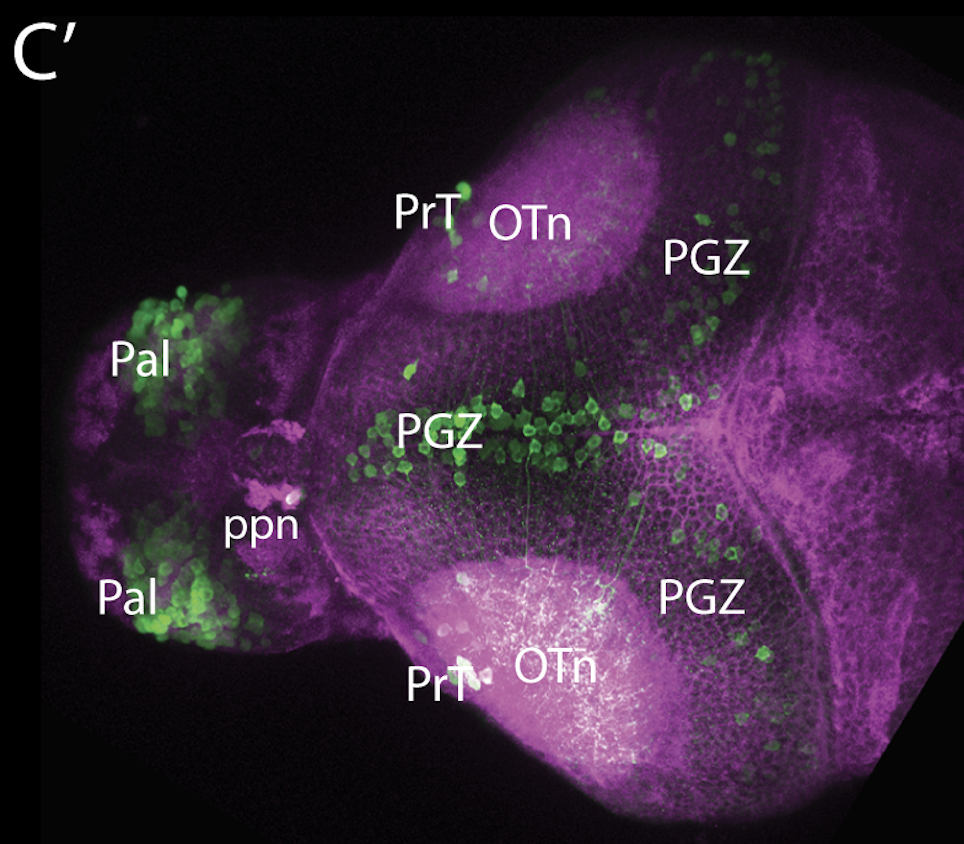
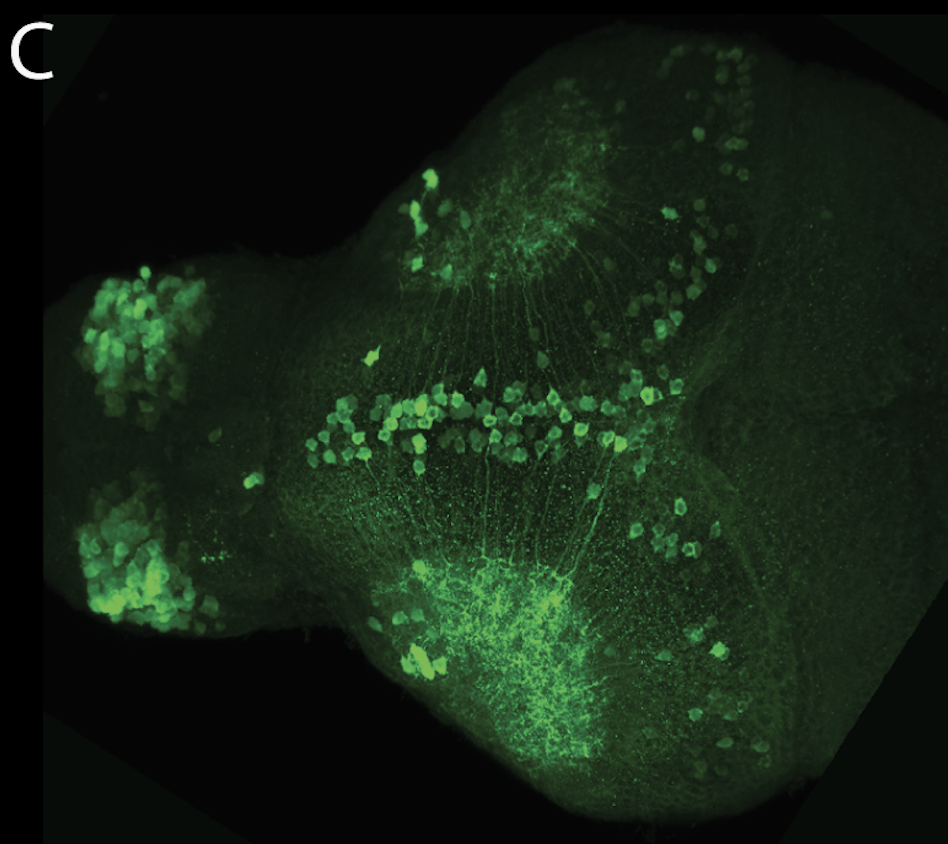
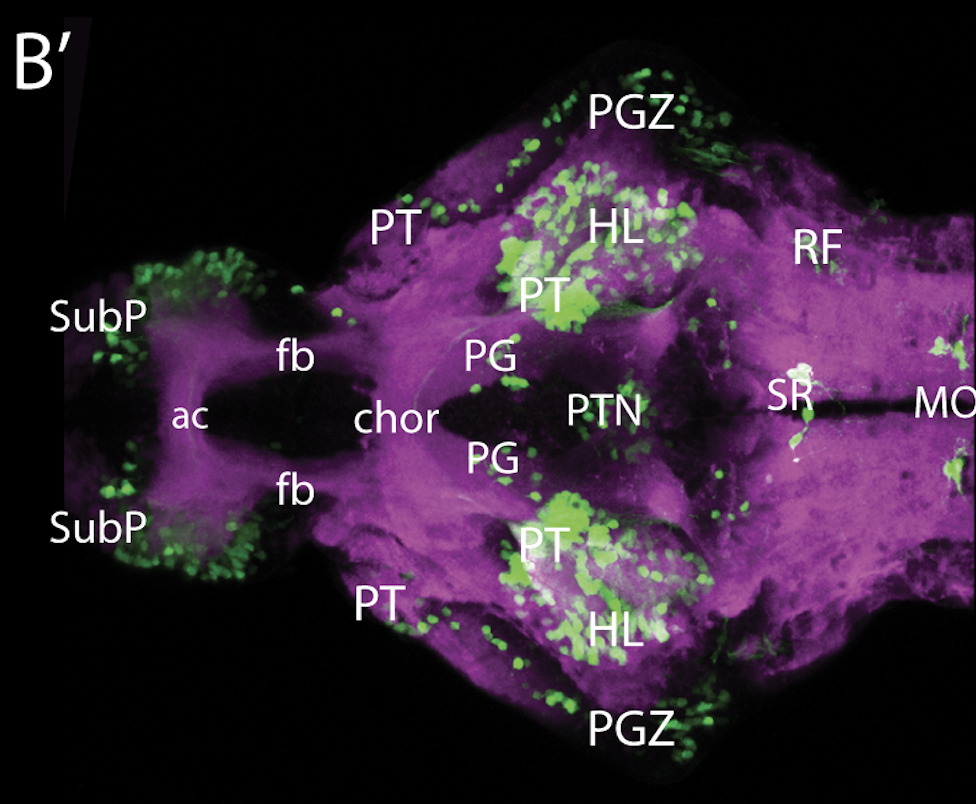
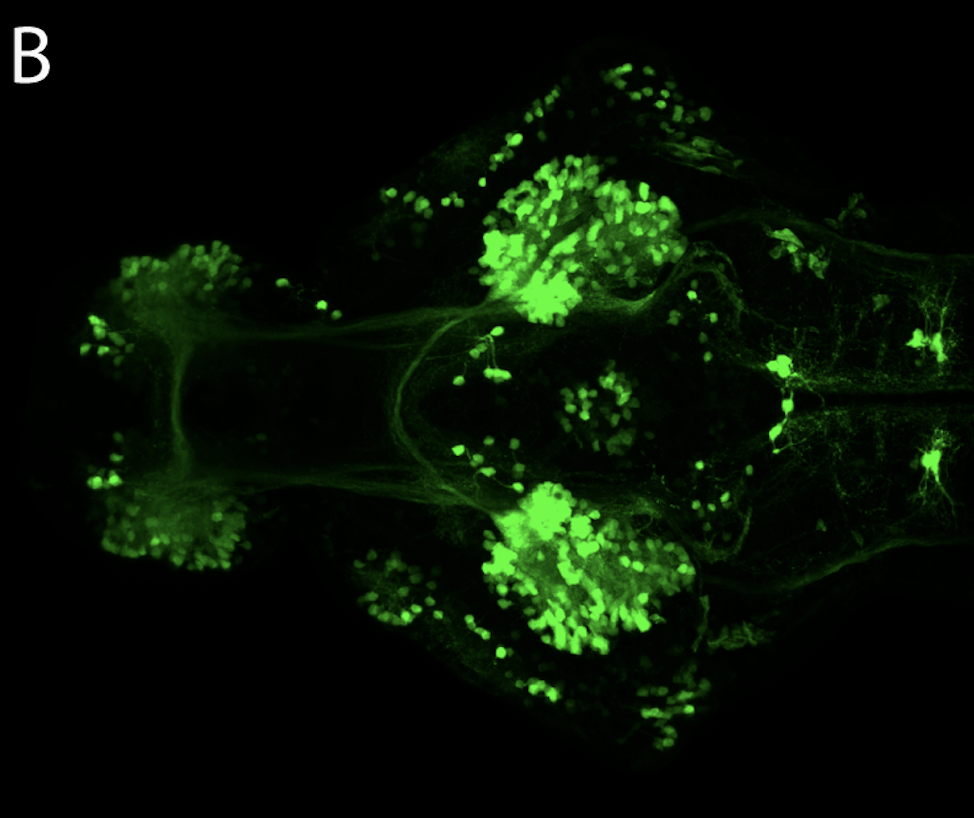
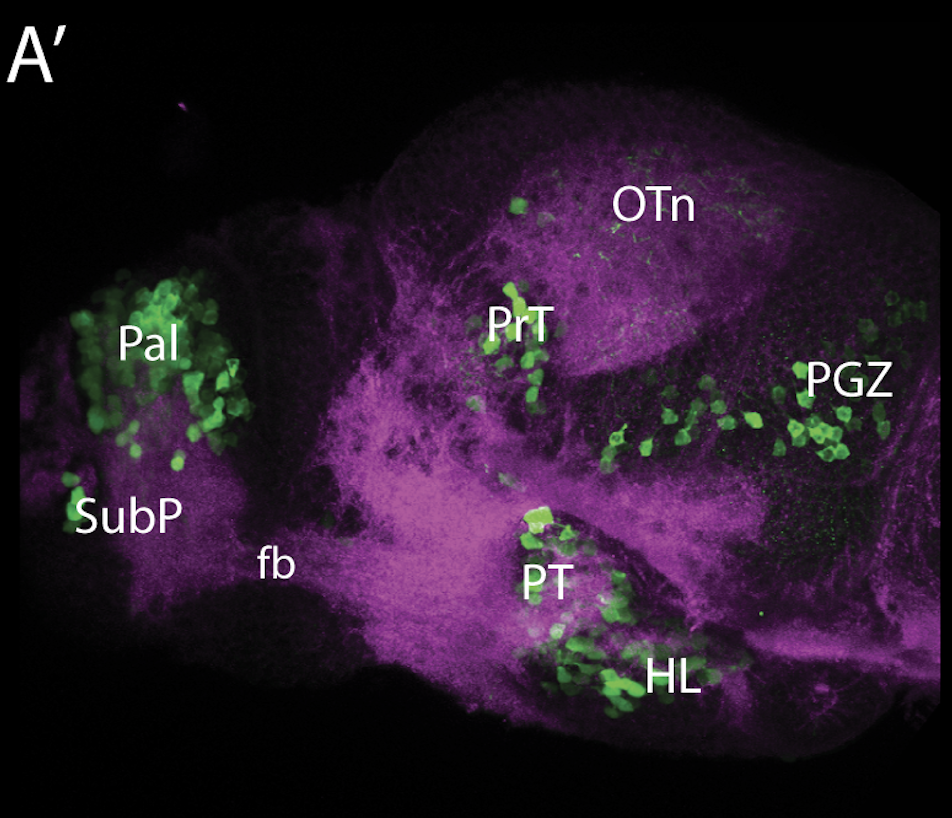
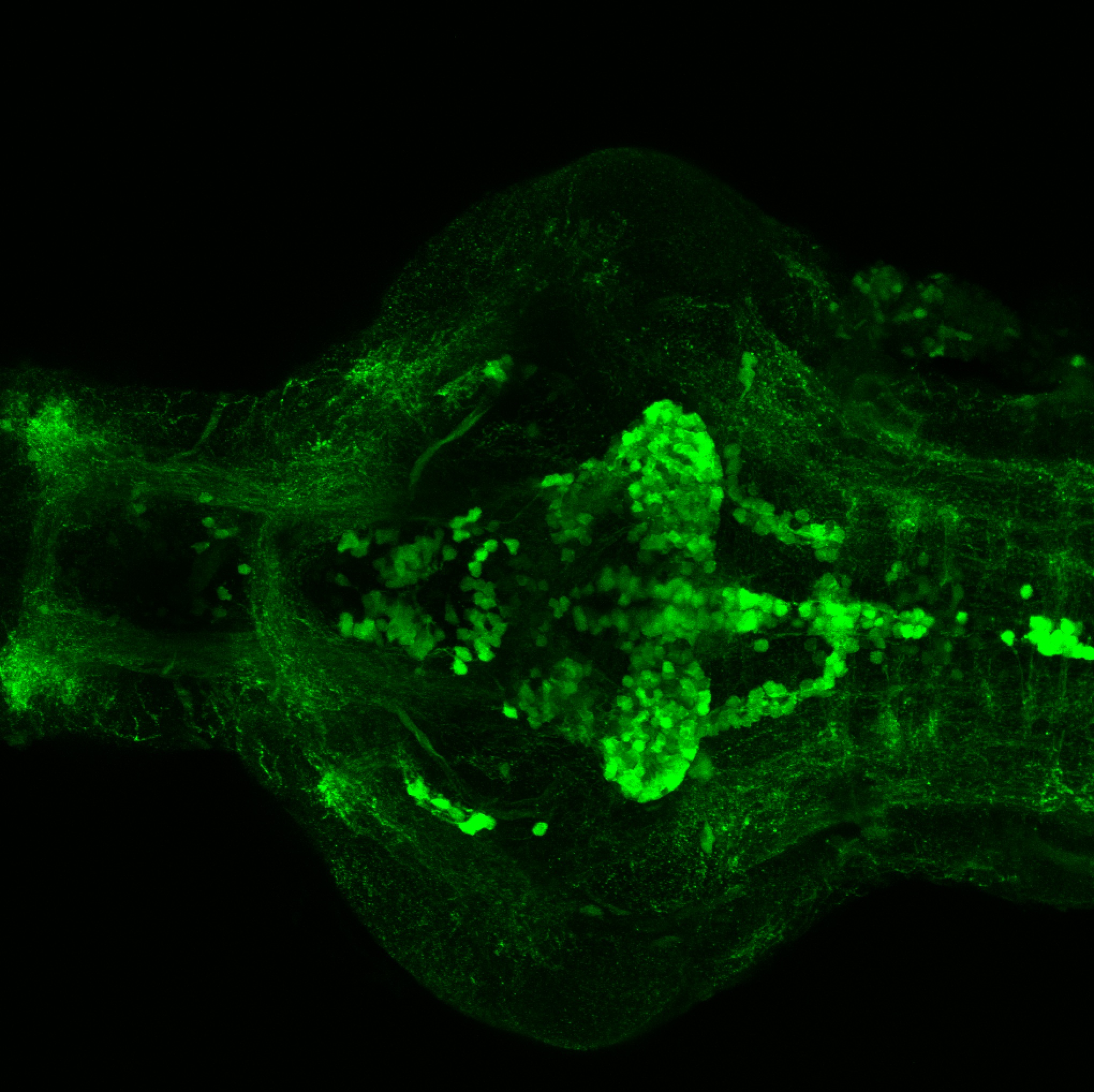
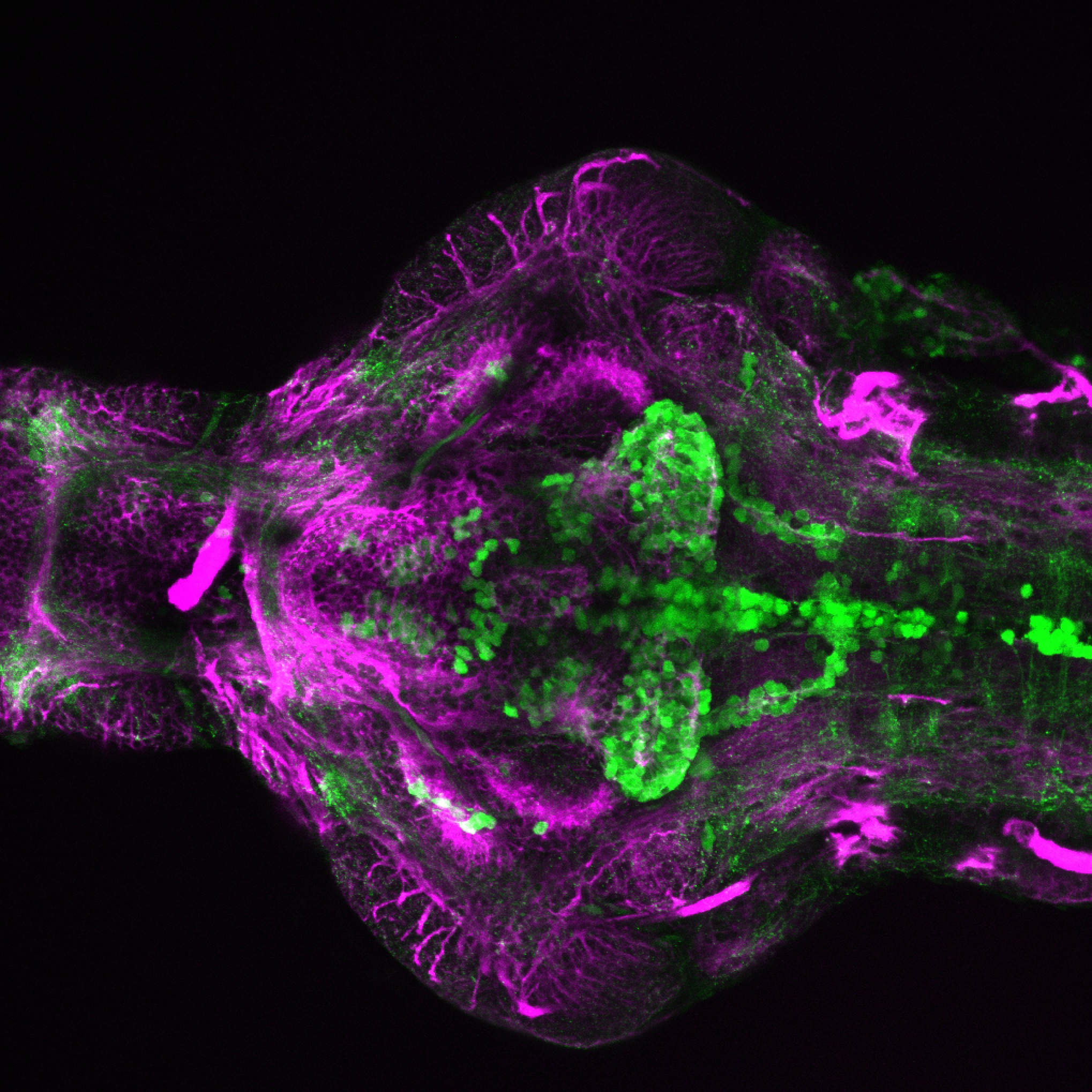
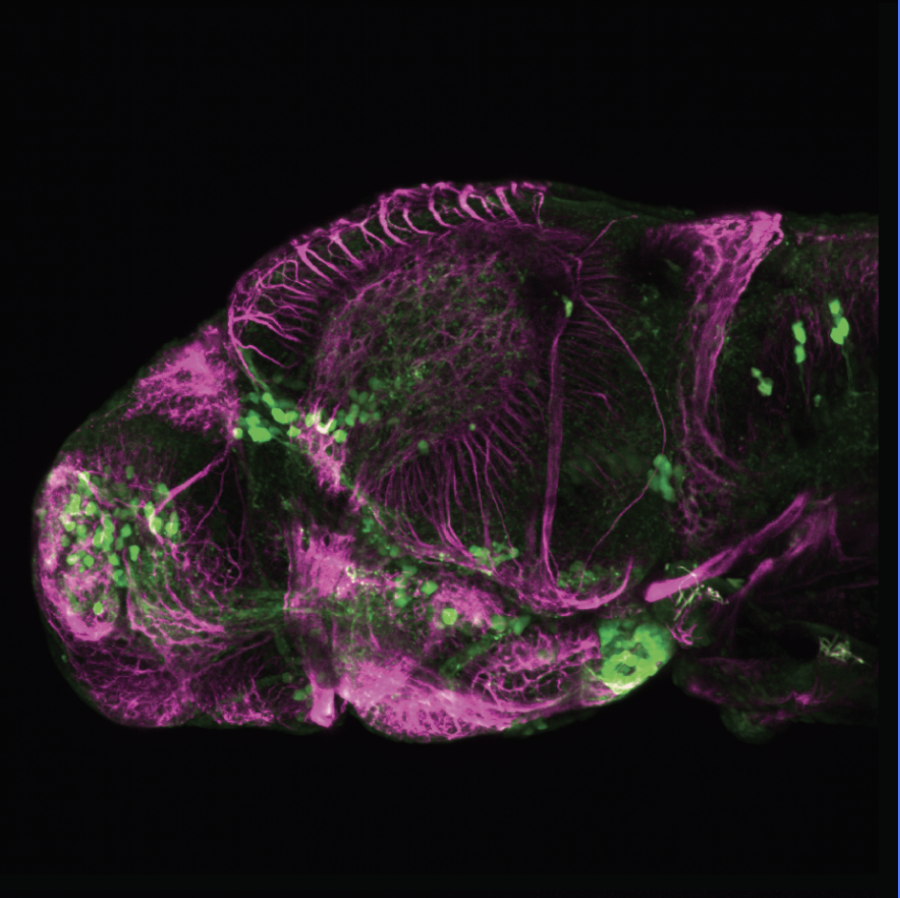
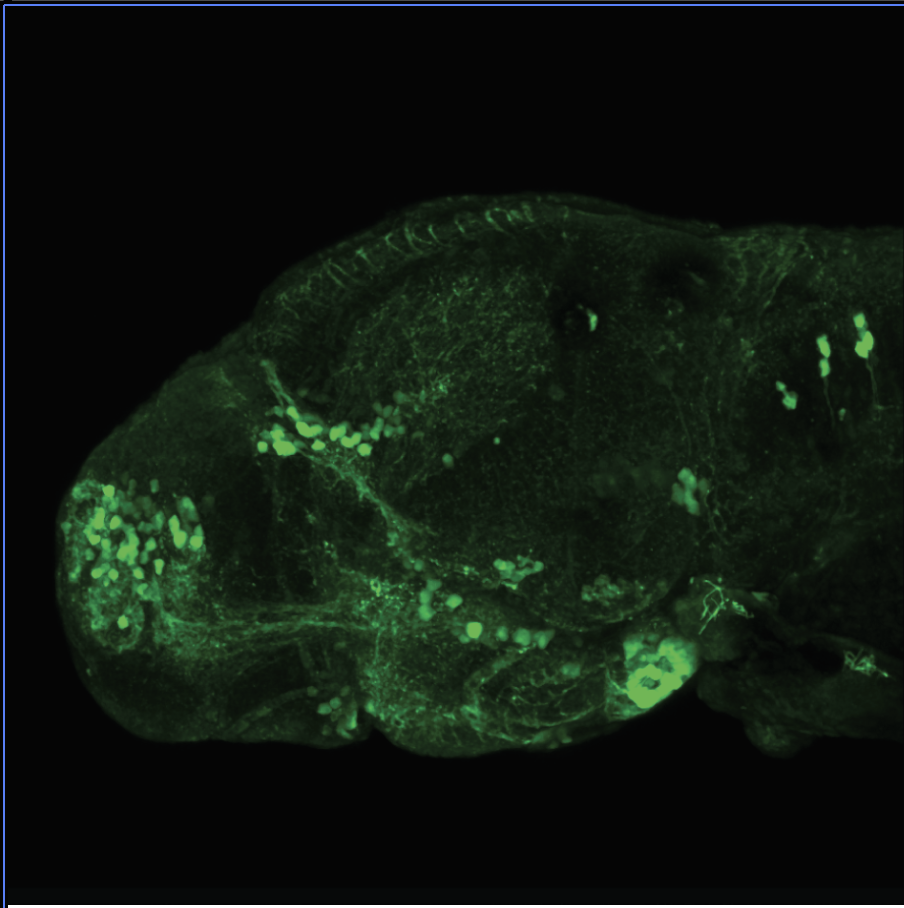
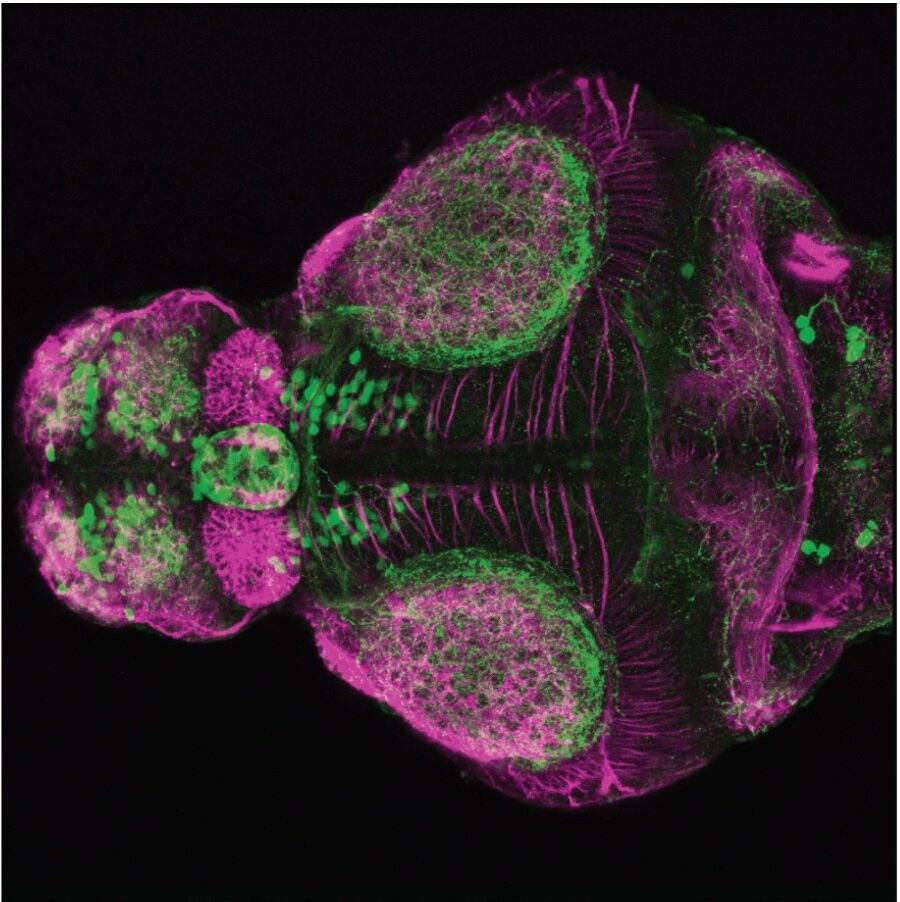
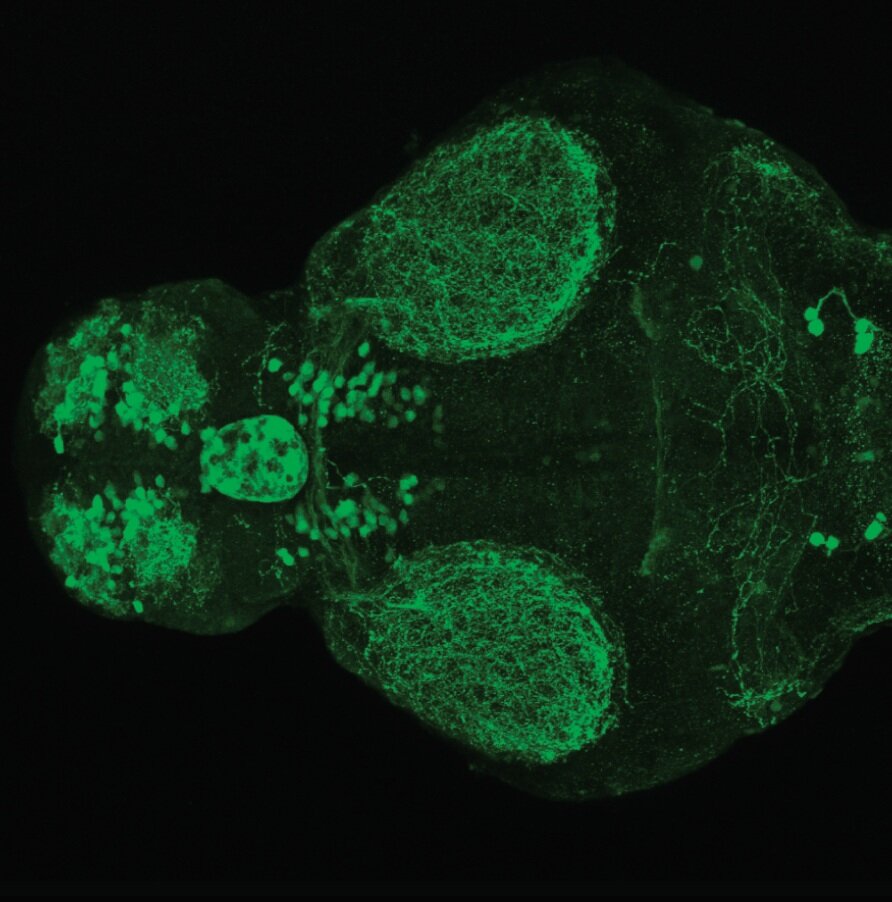
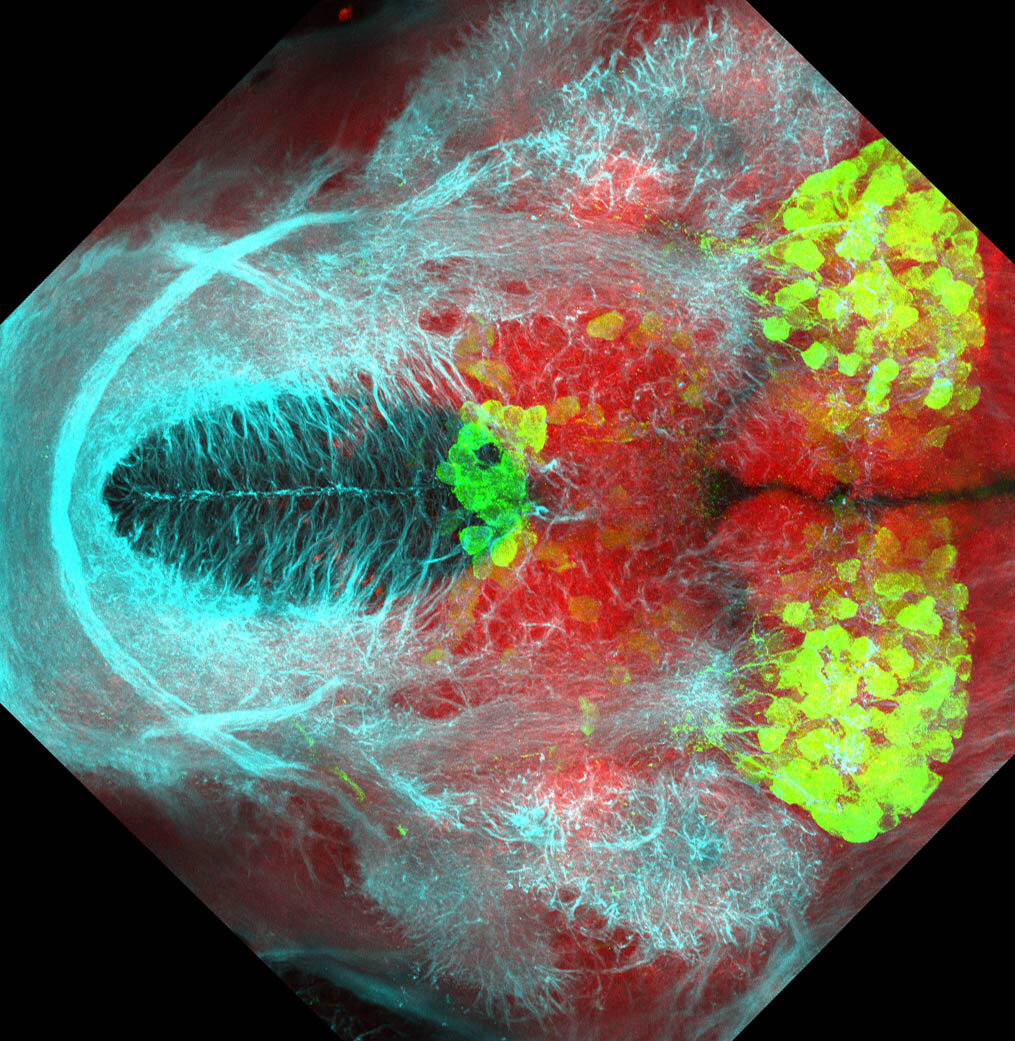
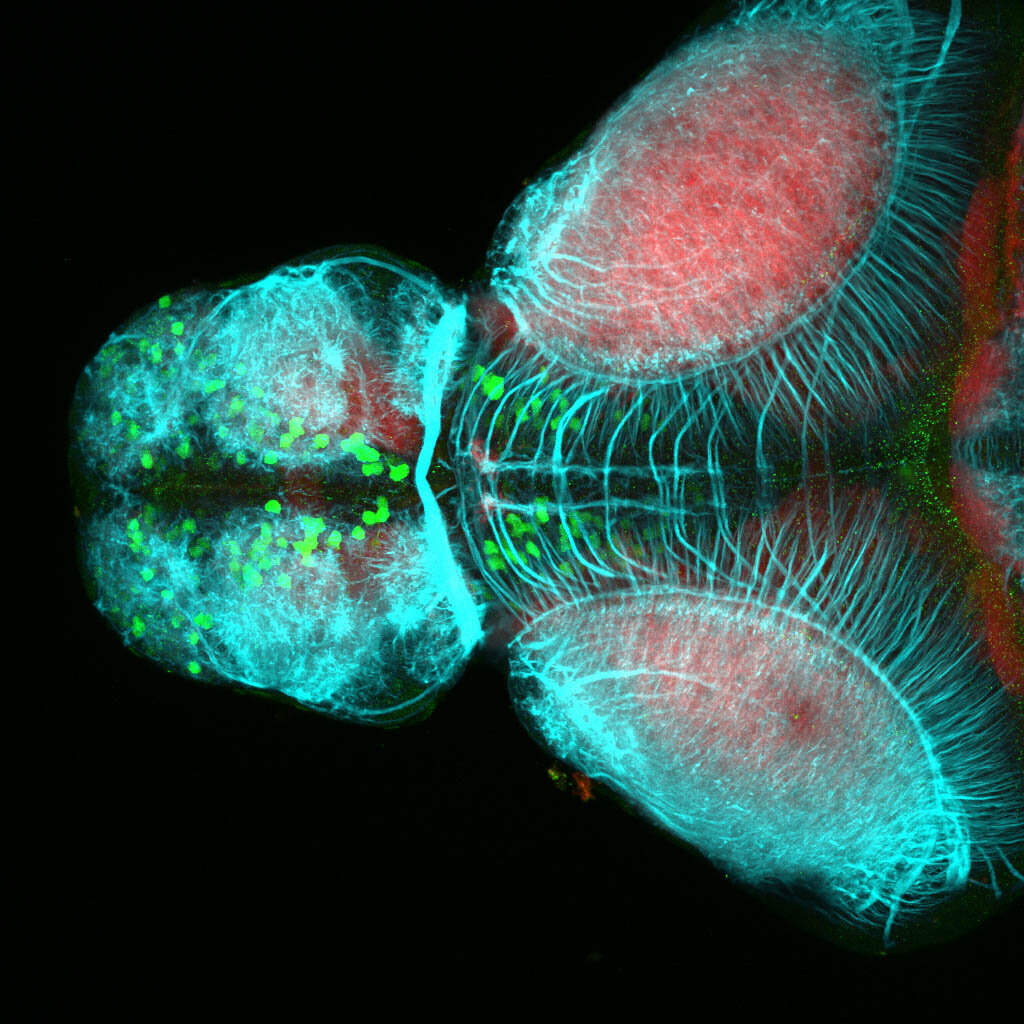
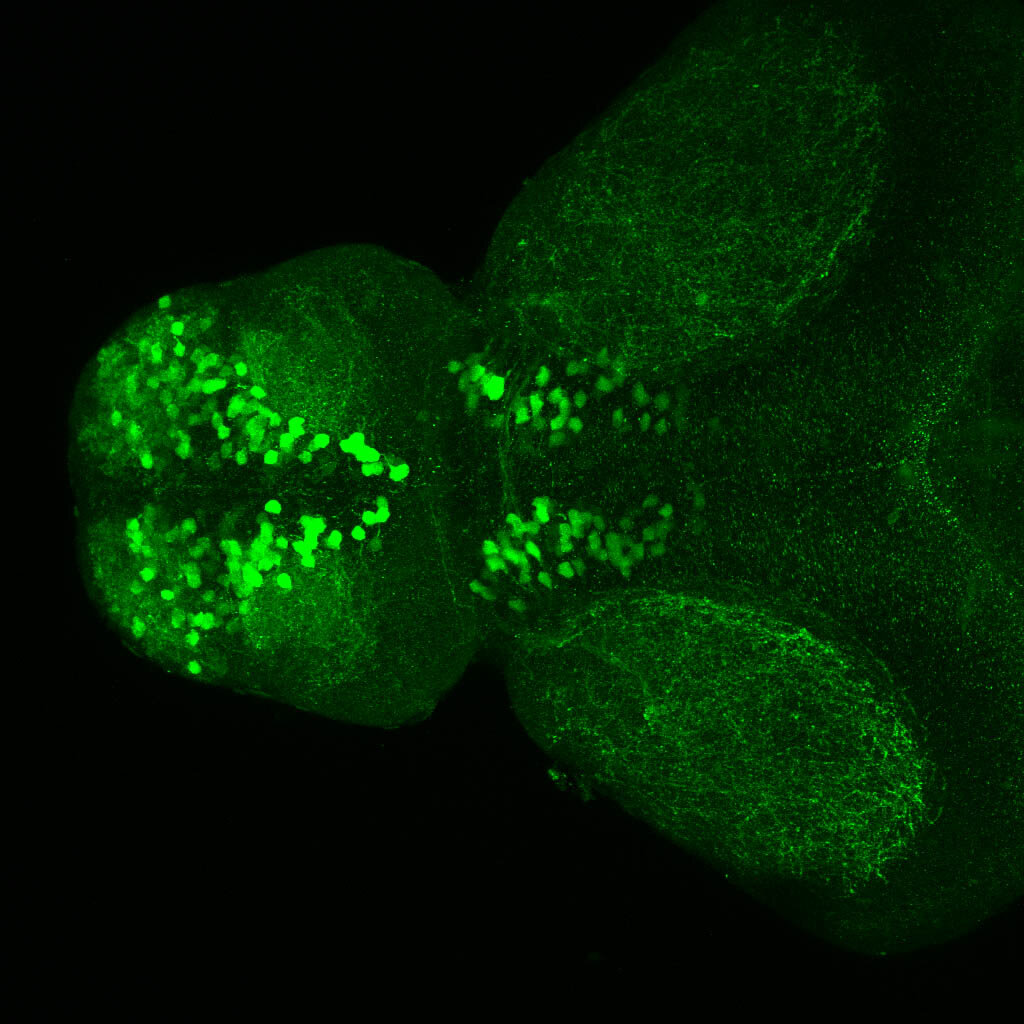
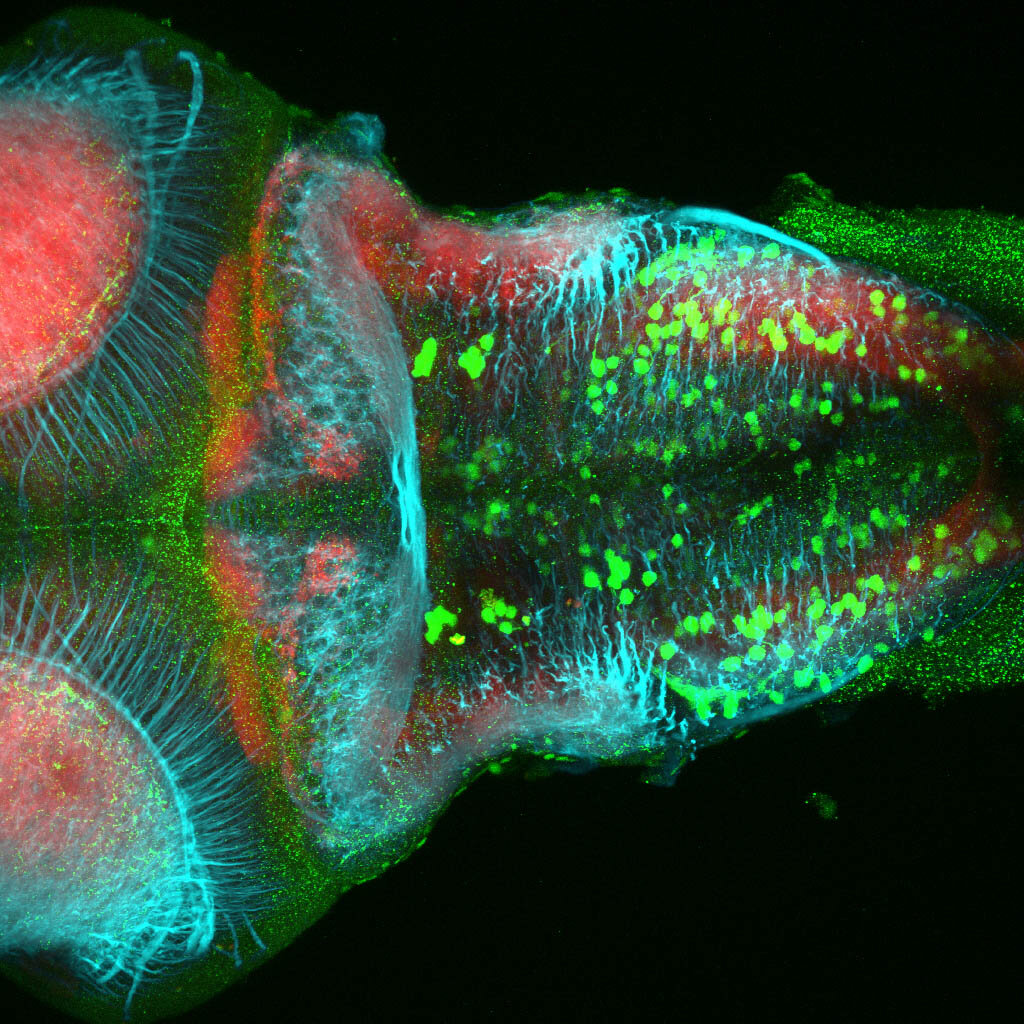
This enhancer trap line was generated as part of a large enhancer screen performed by the Becker Lab. This enhancer trap transgenic line shows expression of YFP in the olfactory bulb, telencephalon, pretectum, torus longitudinalis, cerebellum.
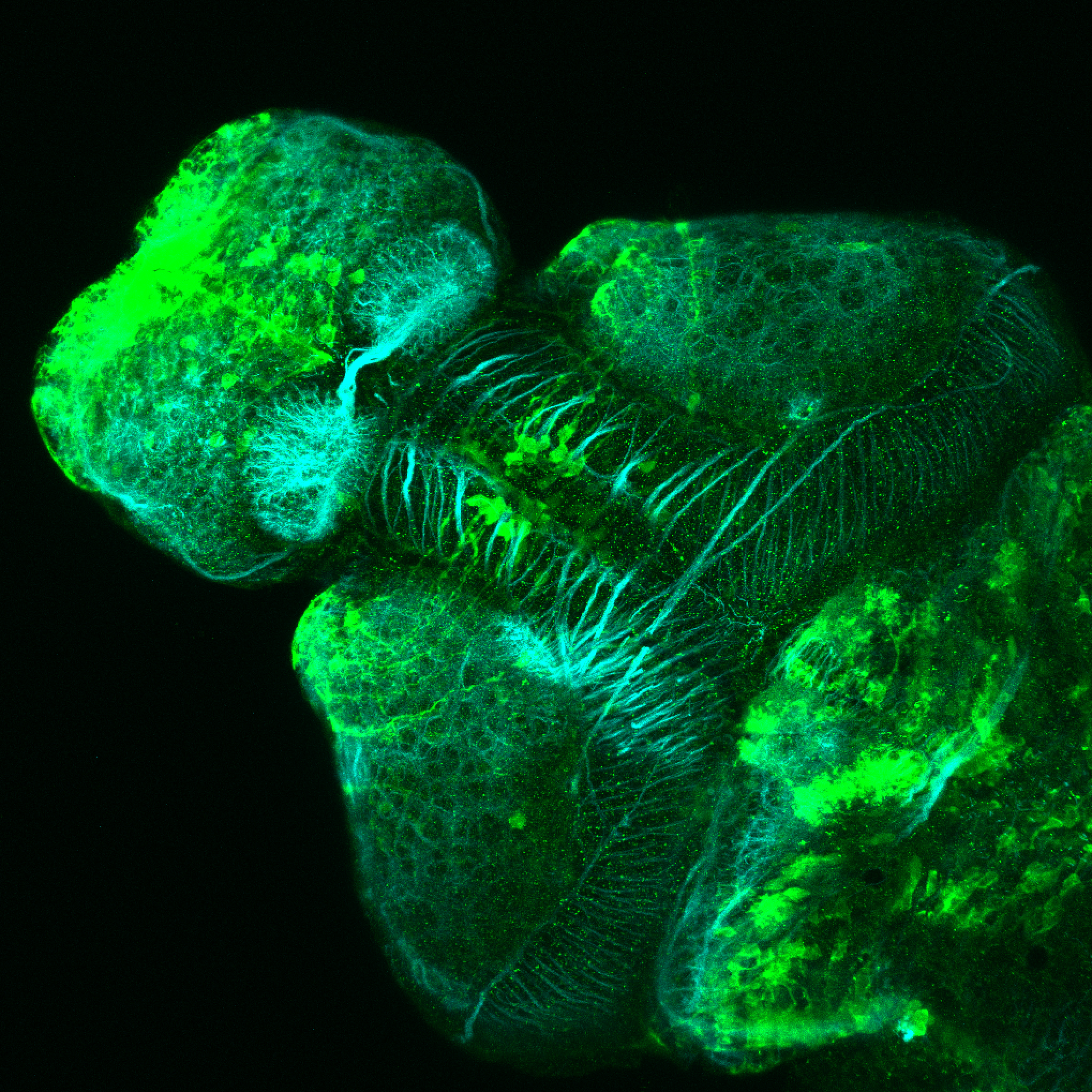
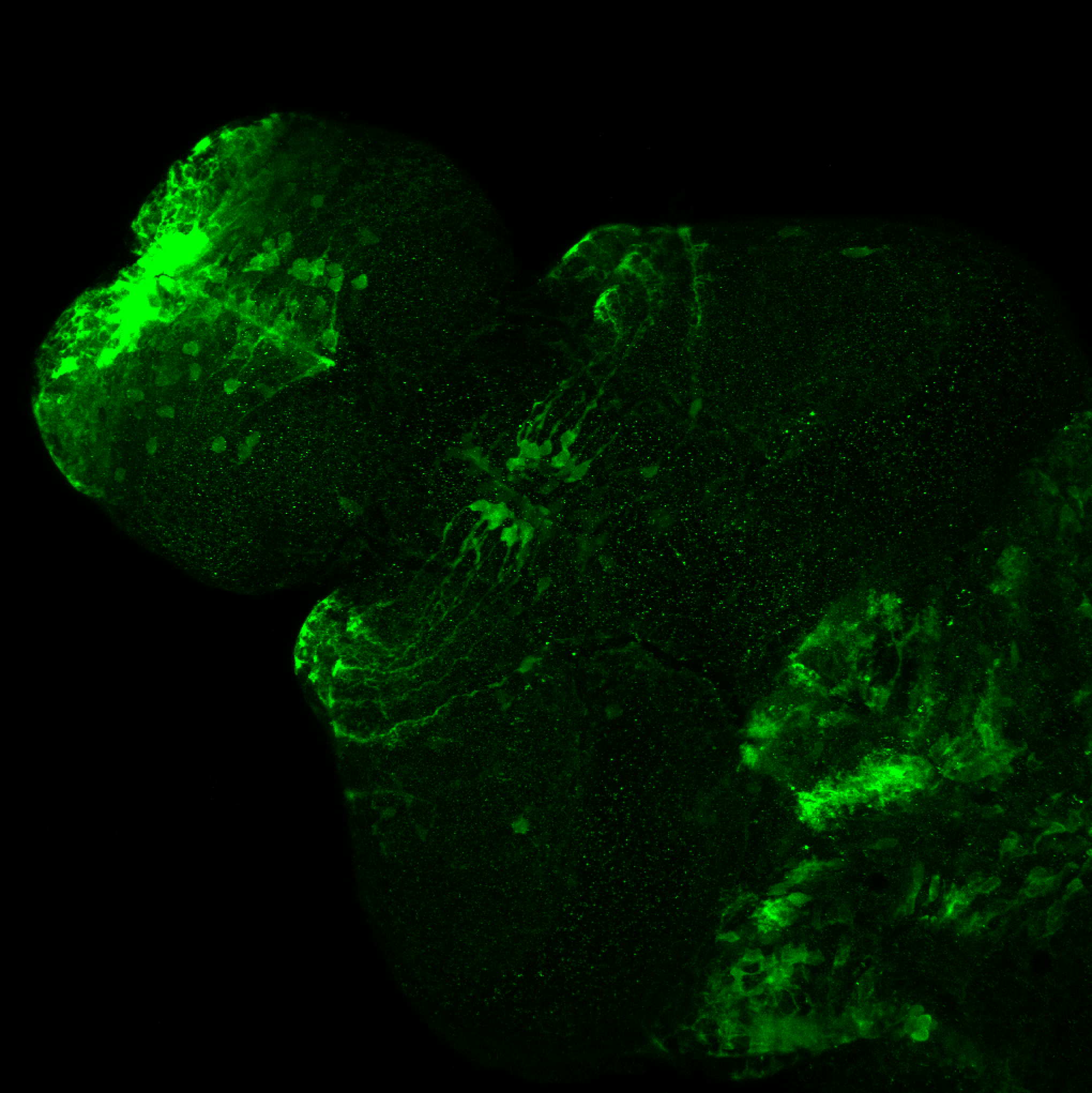
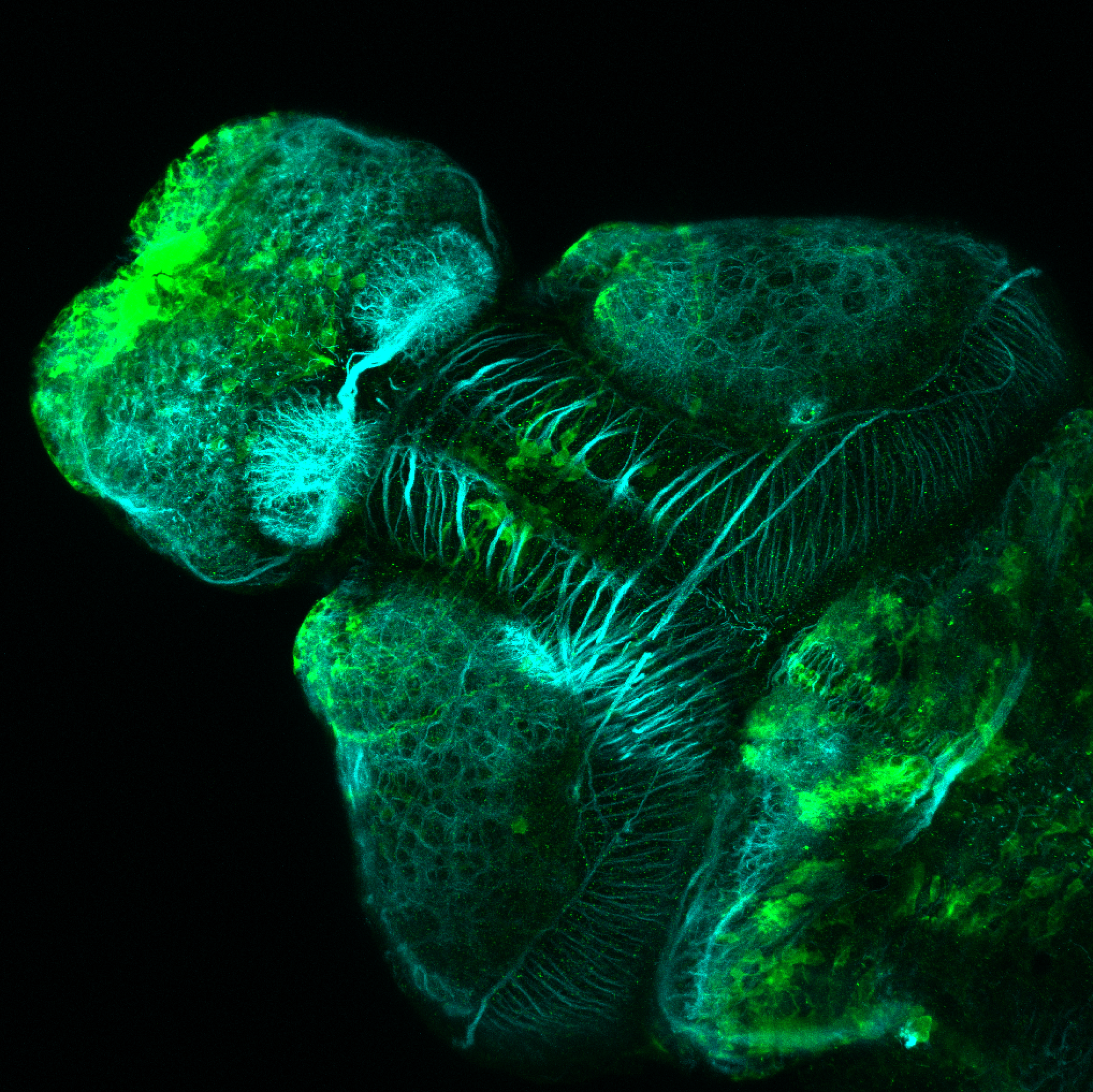
Expressed in:
olfactory bulb, telencephalon, pretectum, torus longitudinalis, cerebellum.
Key Publications
Kikuta, H., Laplante, M., Navratilova, P., Komisarczuk, A.Z., Engstrom, P.G., Fredman, D., Akalin, A., Caccamo, M., Sealy, I., Howe, K., Ghislain, J., Pezeron, G., Mourrain, P., Ellingsen, S., Oates, A.C., Thisse, C., Thisse, B., Foucher, I., Adolf, B., Geling, A., Lenhard, B., and Becker, T.S. (2007)
Genomic regulatory blocks encompass multiple neighboring genes and maintain conserved synteny in vertebrates.
Genome research. 17(5):545-555.




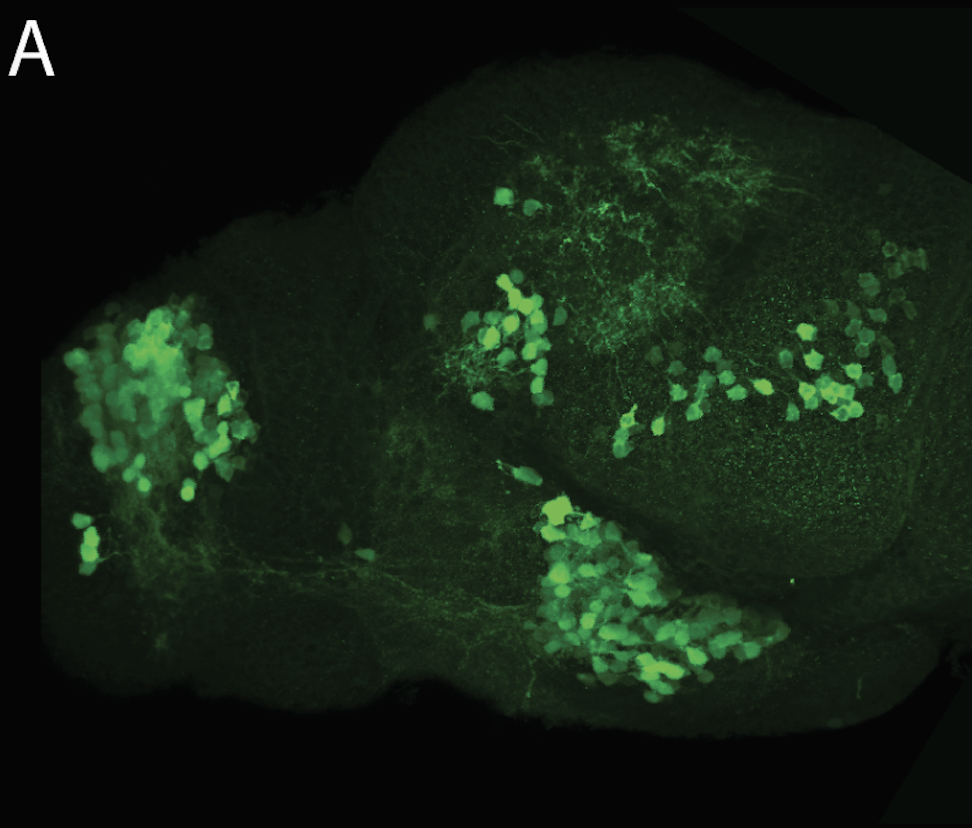


![[Improvision Data]ImageName=TimeStampMicroSeconds=3319455431398154TimeStamp=14:57:11.398 on 09 Mar 2009ChannelName=ChannelNo=1TimepointName=1TimepointNo=1ZPlane=1BlackPoint=0WhitePoint=255WhiteColour=255,255,255XCalibrationMicrons=1YCalibrationMicro](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/58065fb61b631b37ff3ce66a/1568631946526-34AZDYGG28NB7Q4A9WXX/Snapshot+of+Series008+%28vmat_tub_sv2_5d%29_10.jpg)
![[Improvision Data]ImageName=TimeStampMicroSeconds=3319455437197463TimeStamp=14:57:17.197 on 09 Mar 2009ChannelName=ChannelNo=1TimepointName=1TimepointNo=1ZPlane=1BlackPoint=0WhitePoint=255WhiteColour=255,255,255XCalibrationMicrons=1YCalibrationMicro](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/58065fb61b631b37ff3ce66a/1568631420219-DNOWMW8T30HIN5ZAE238/Snapshot+of+Series008+%28vmat_tub_sv2_5d%29_11.jpg)