About
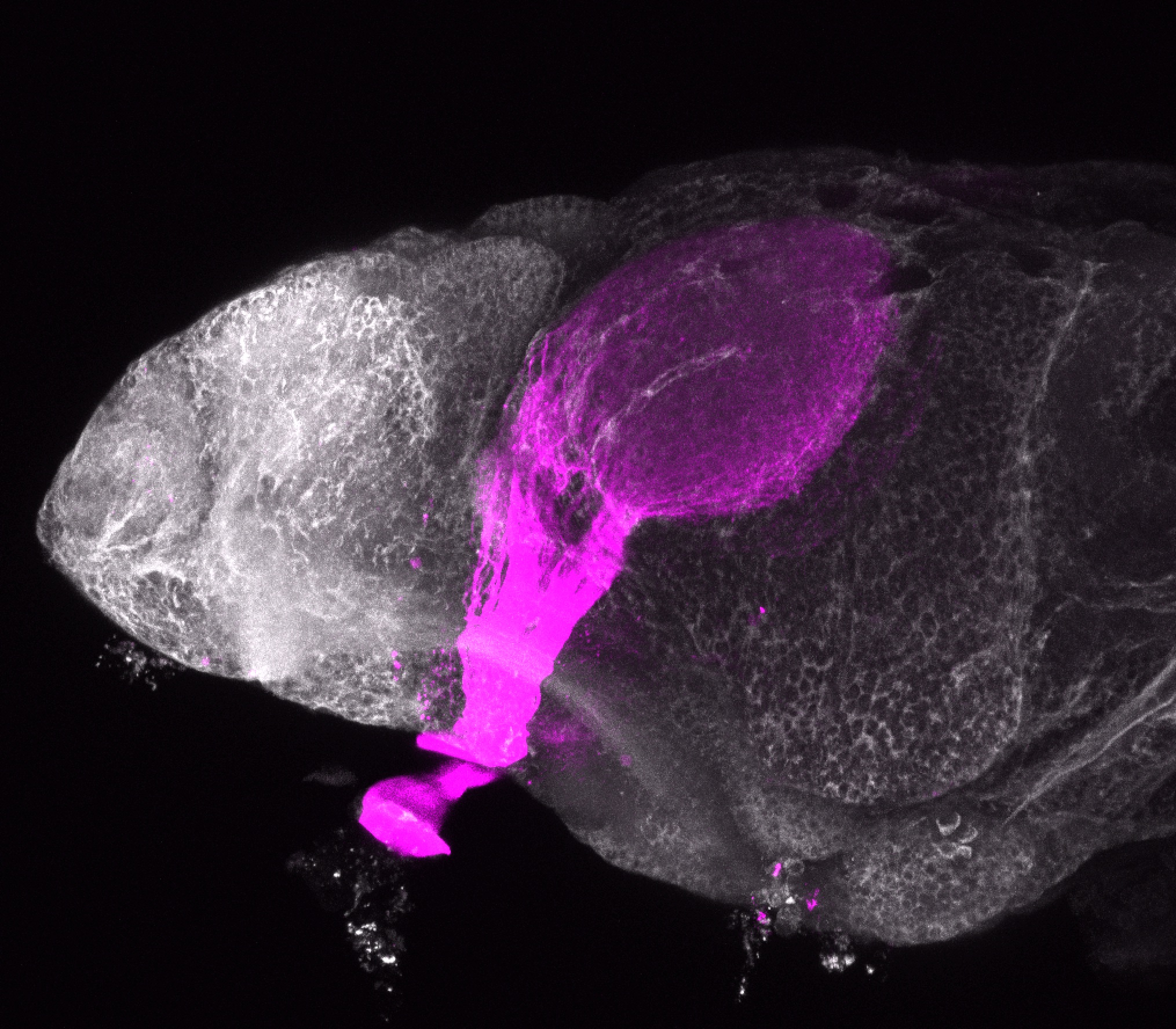
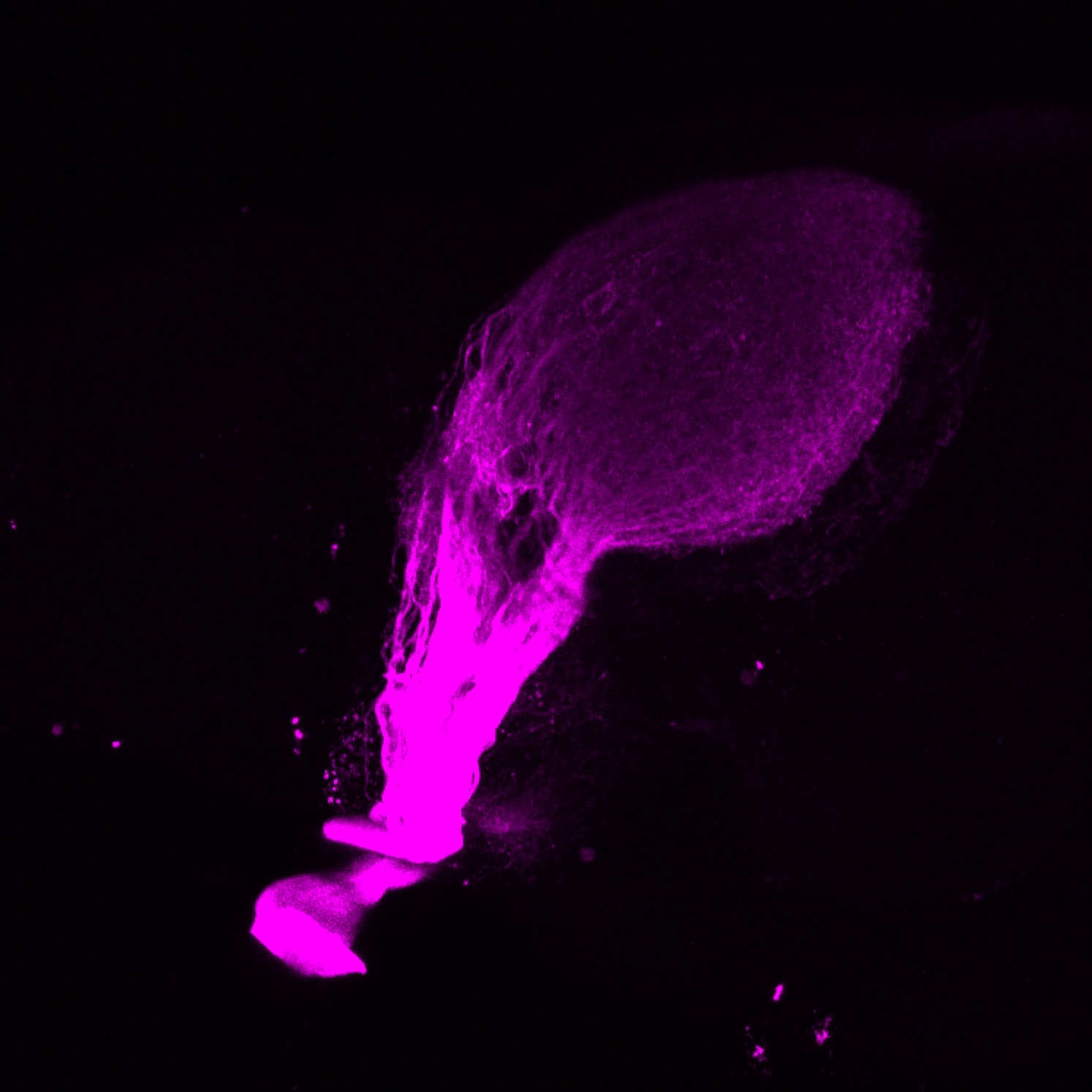
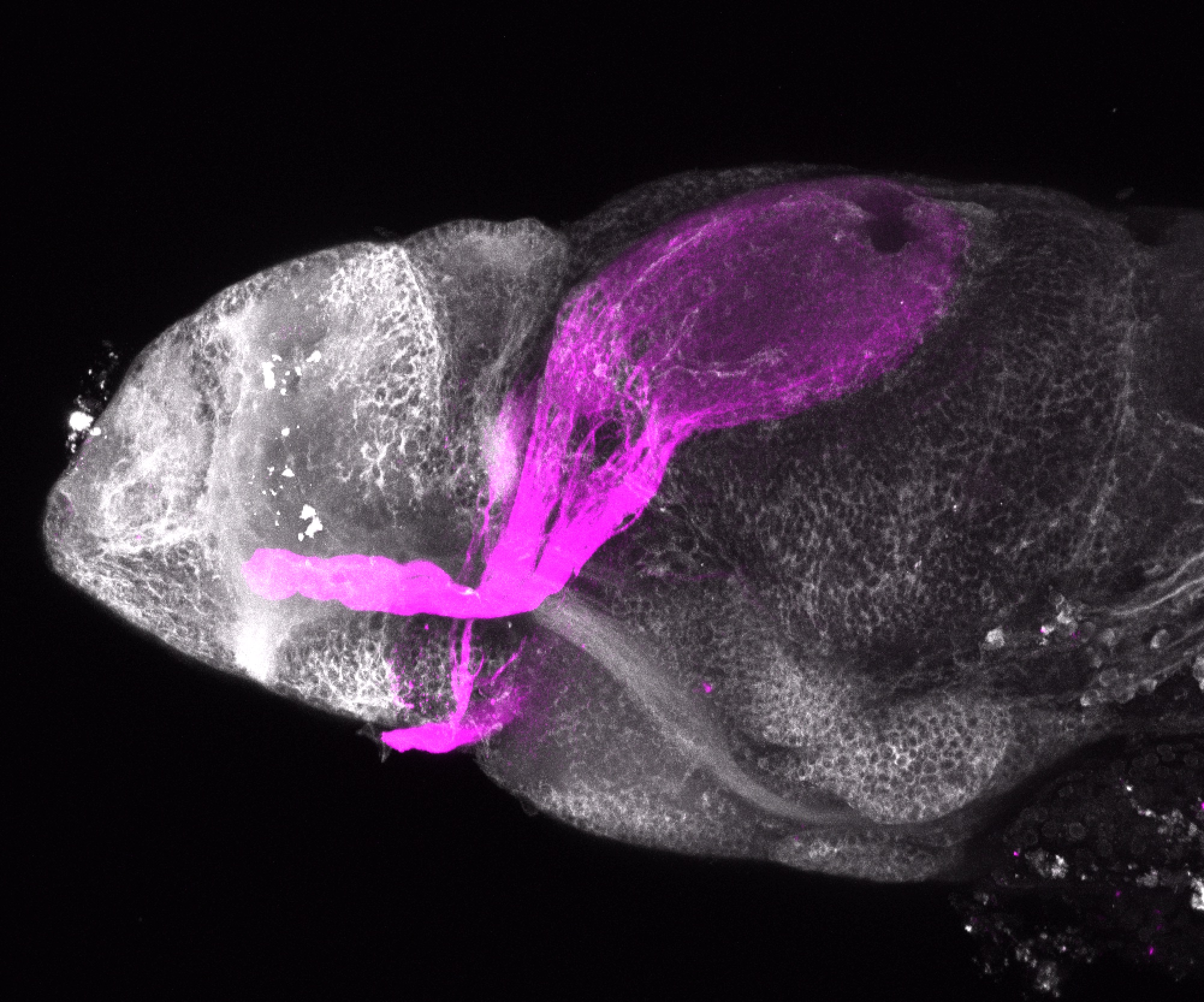
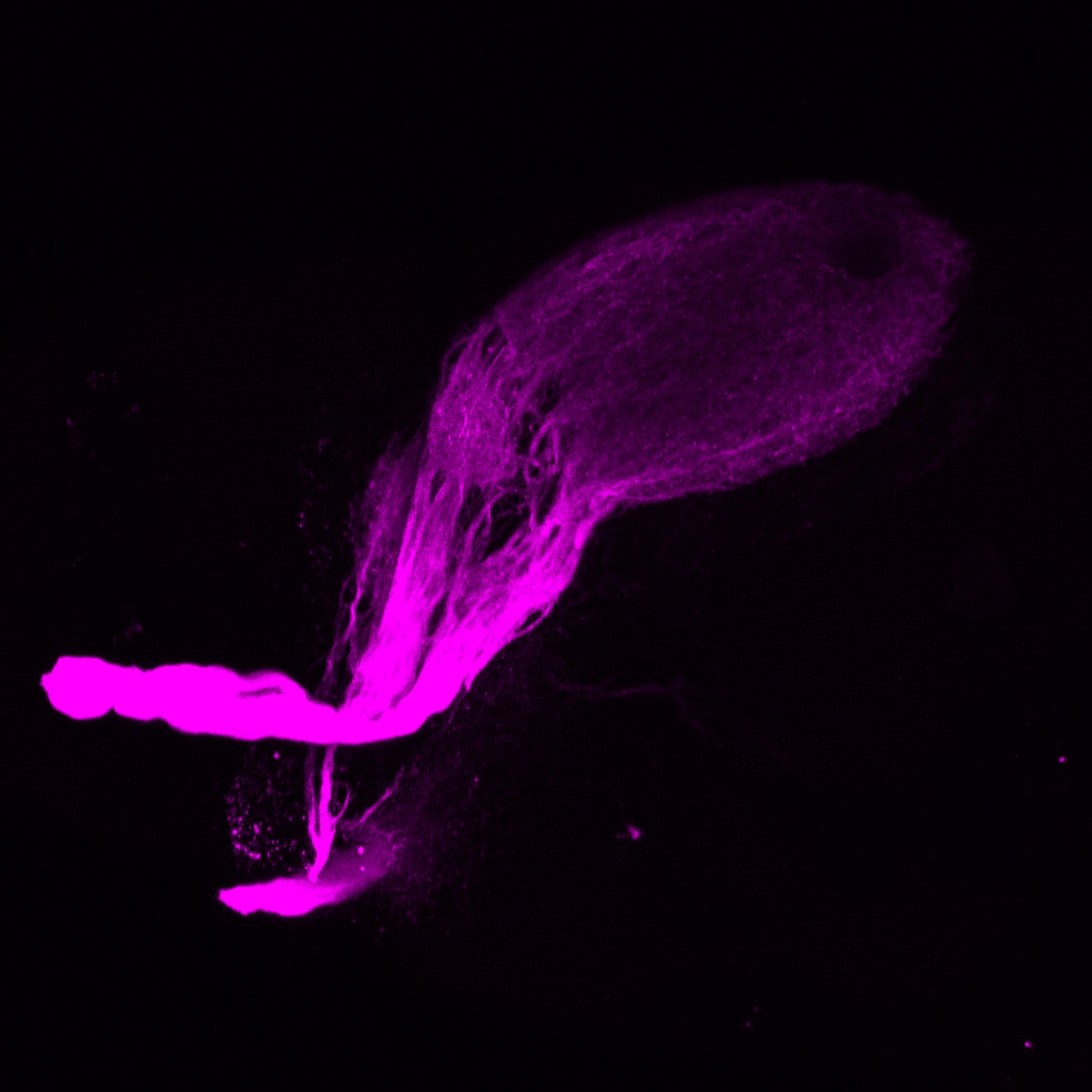
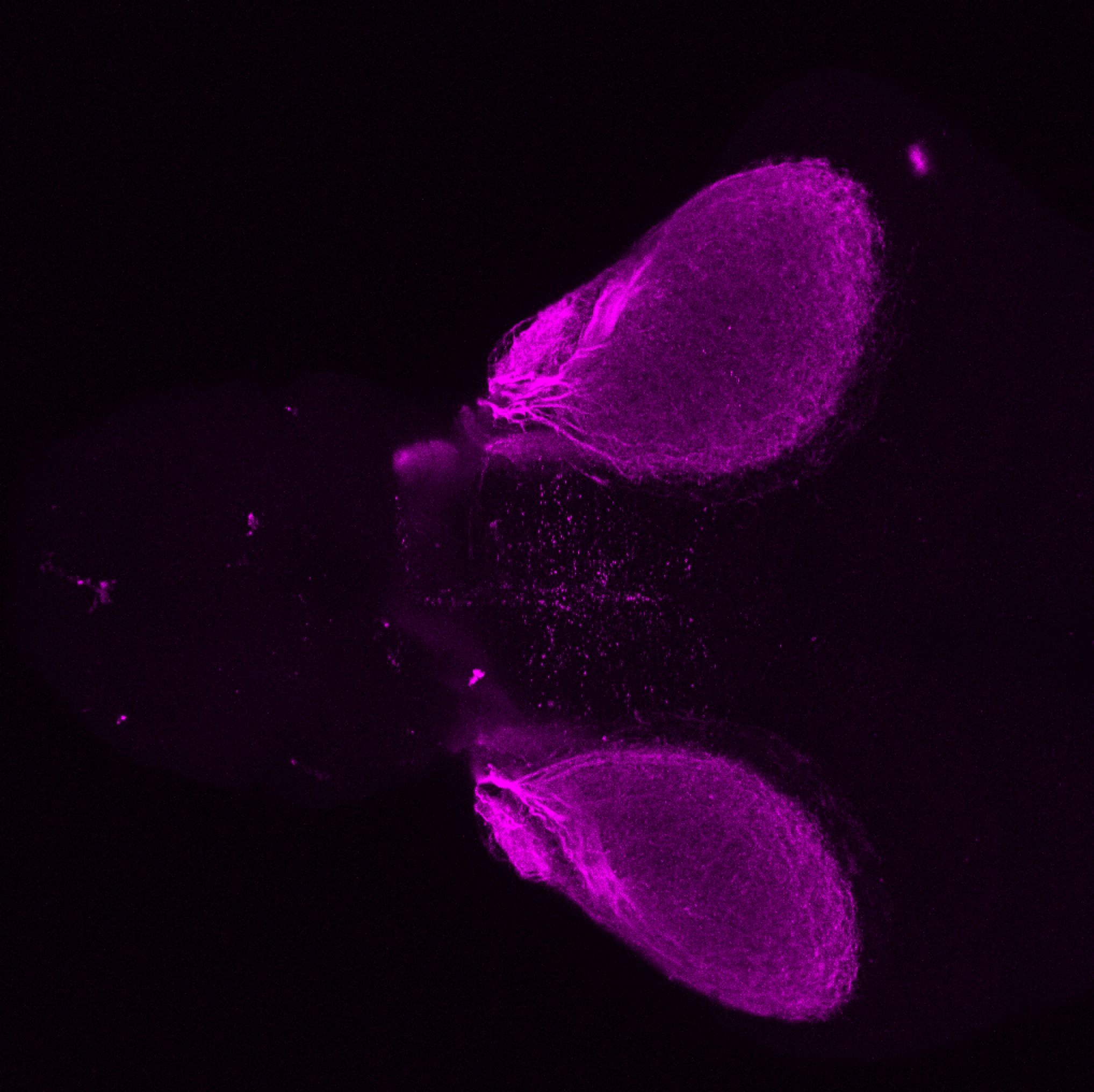
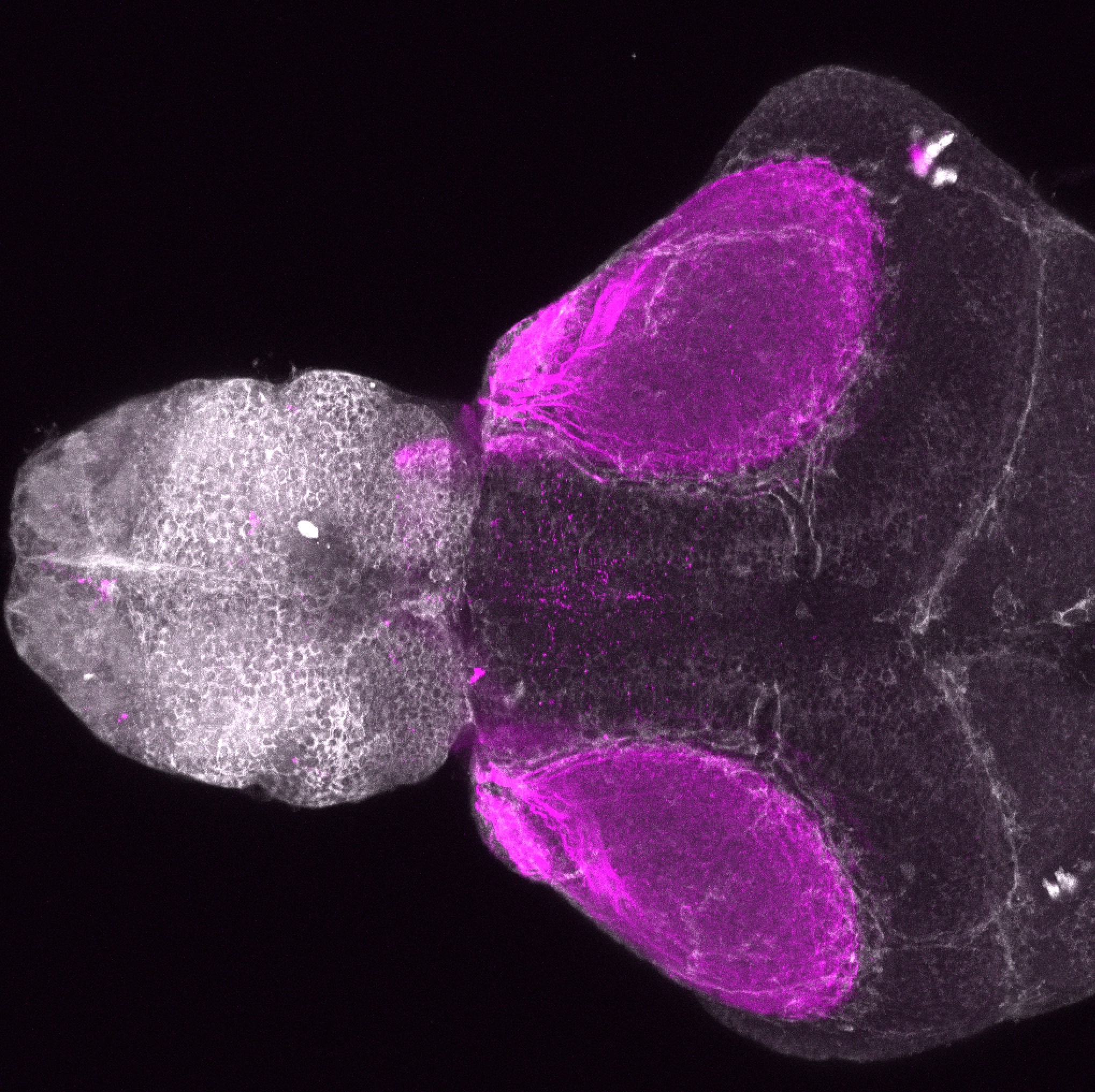
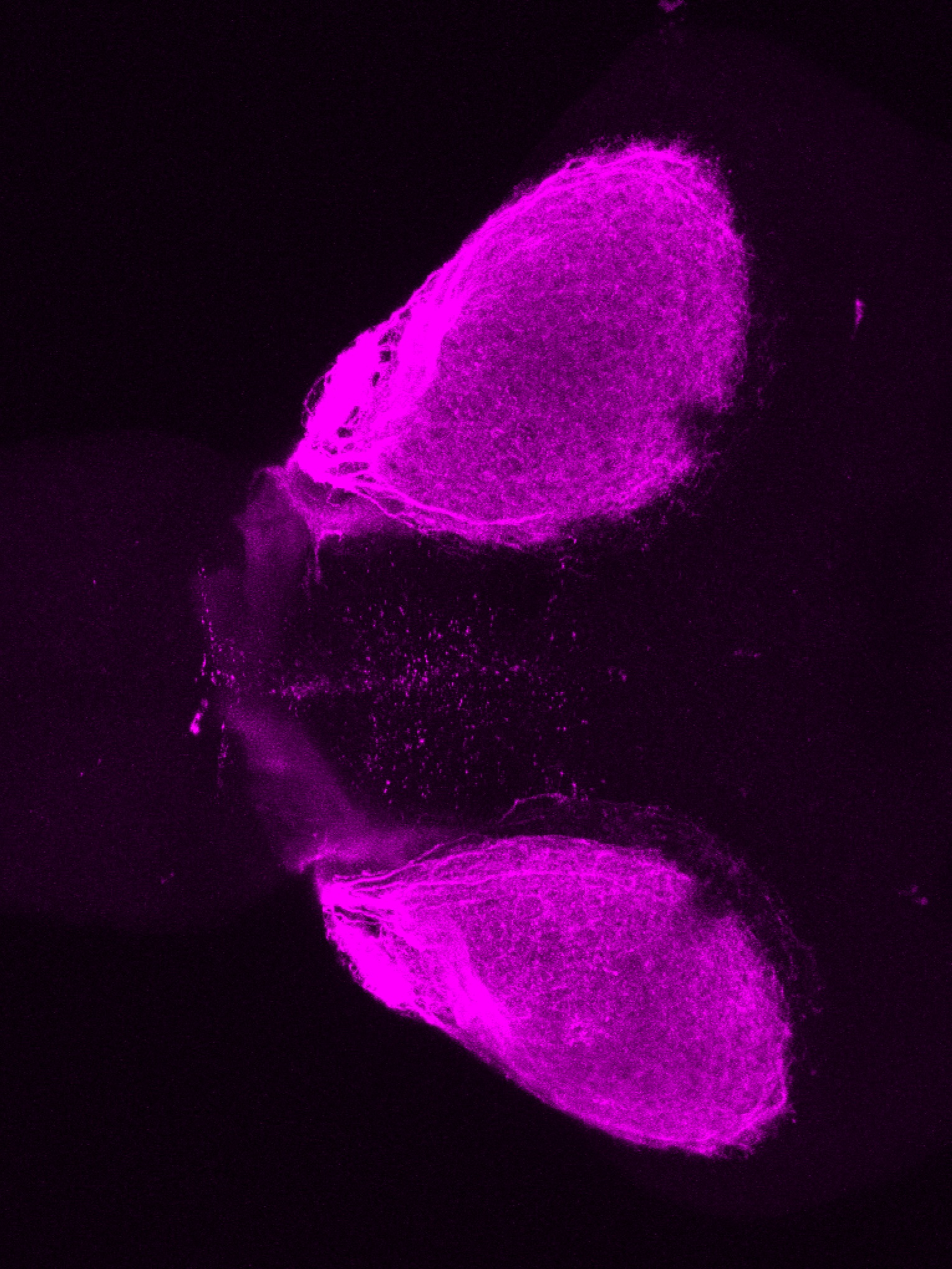
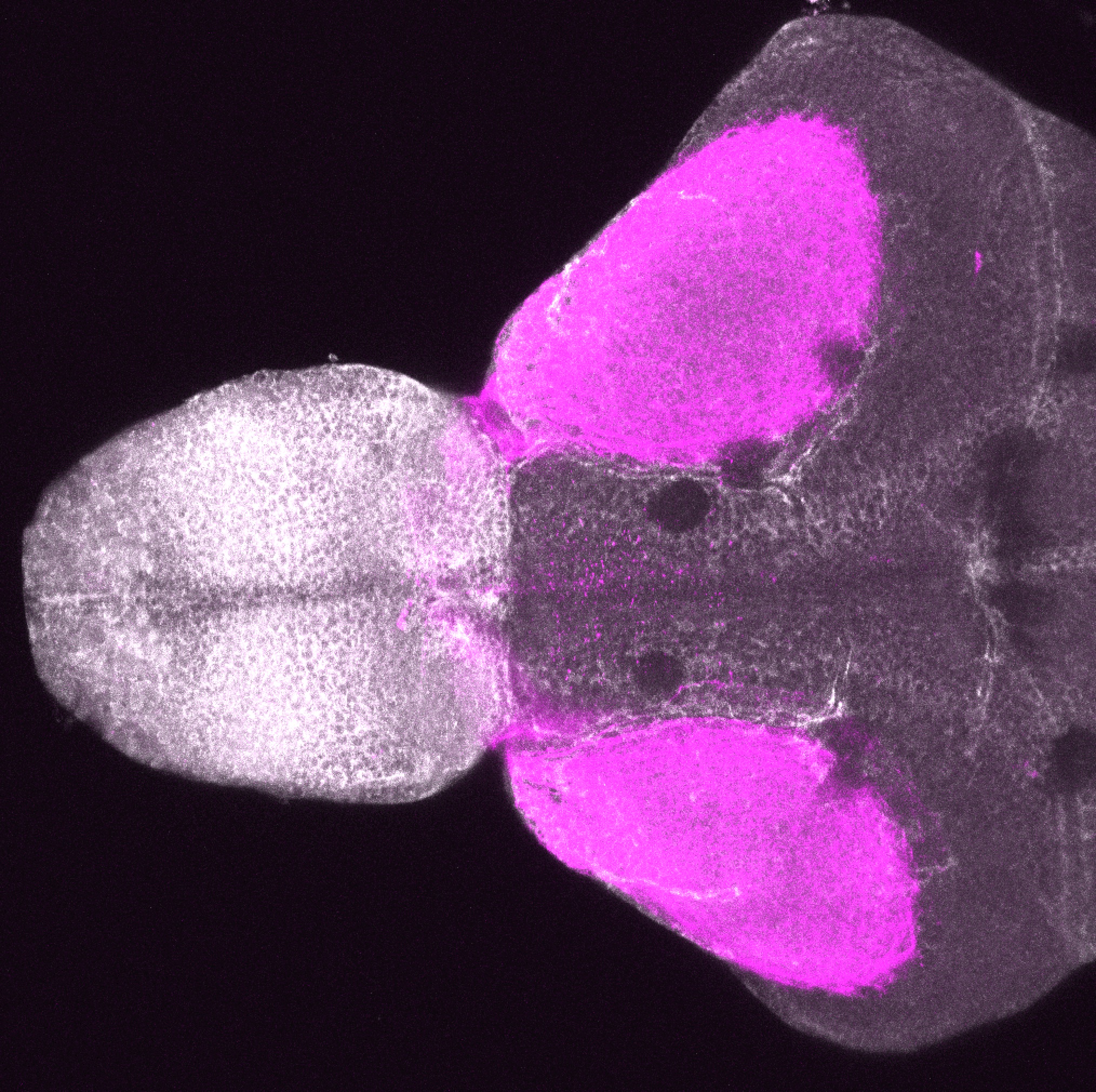
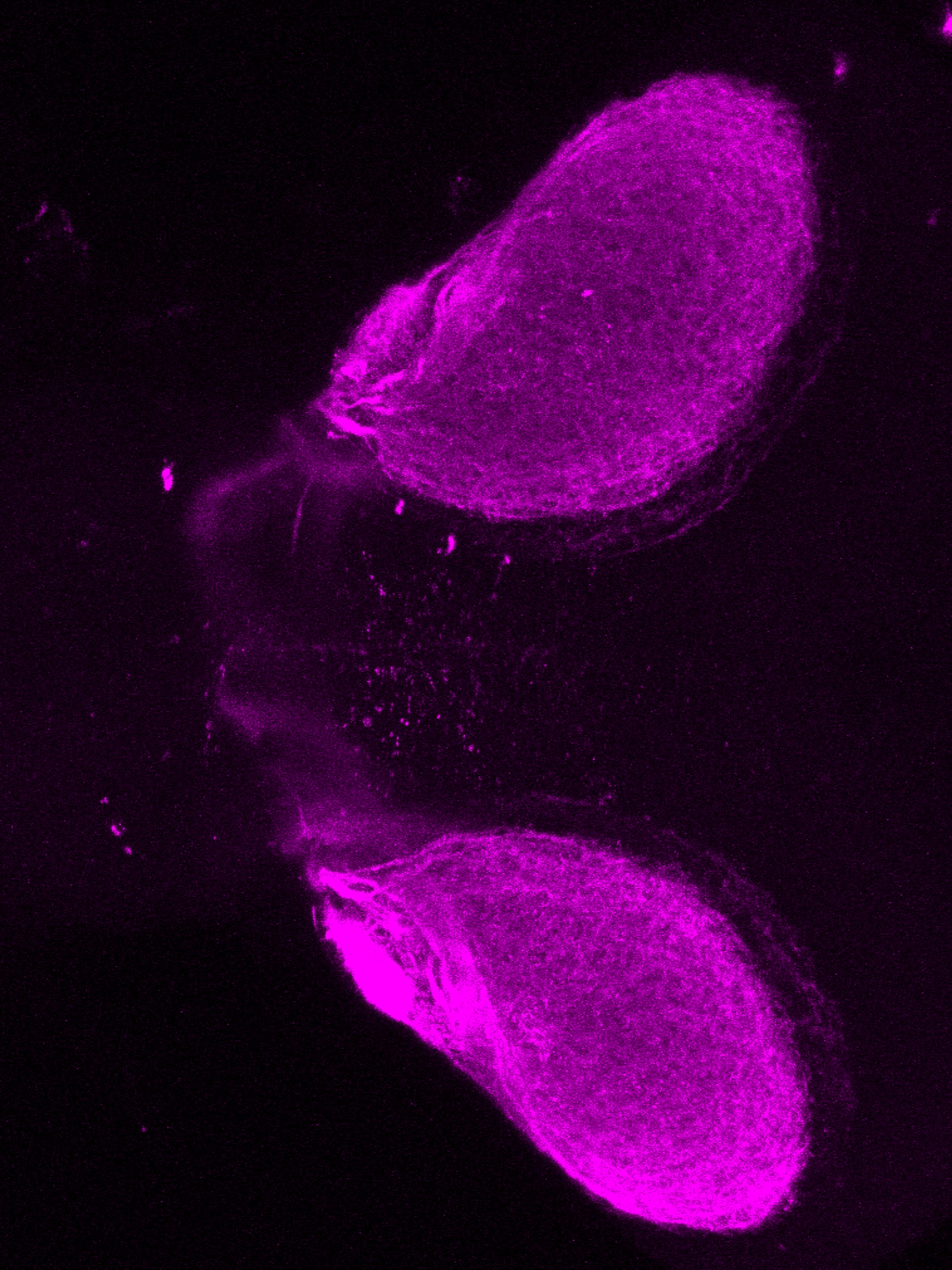
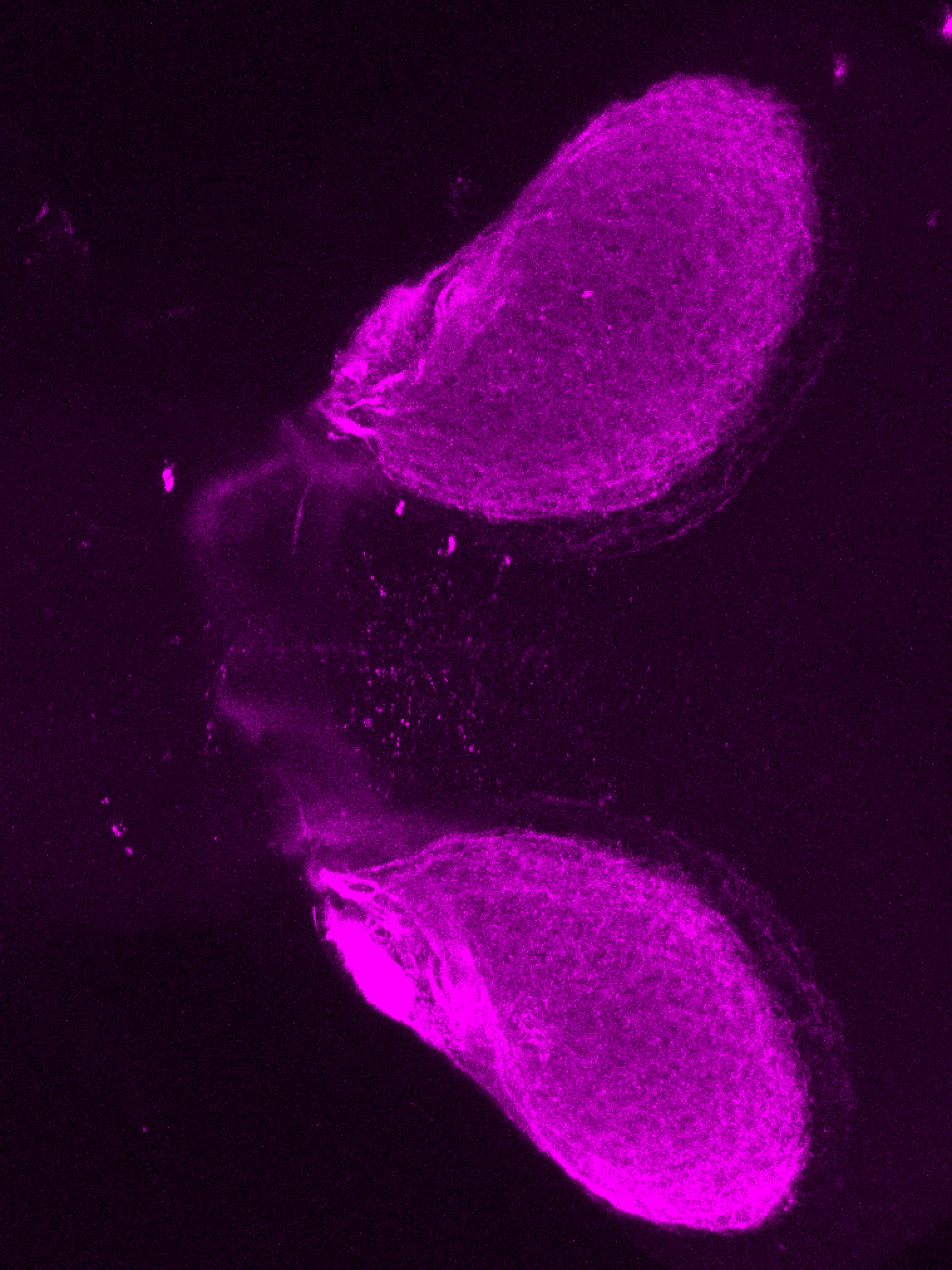
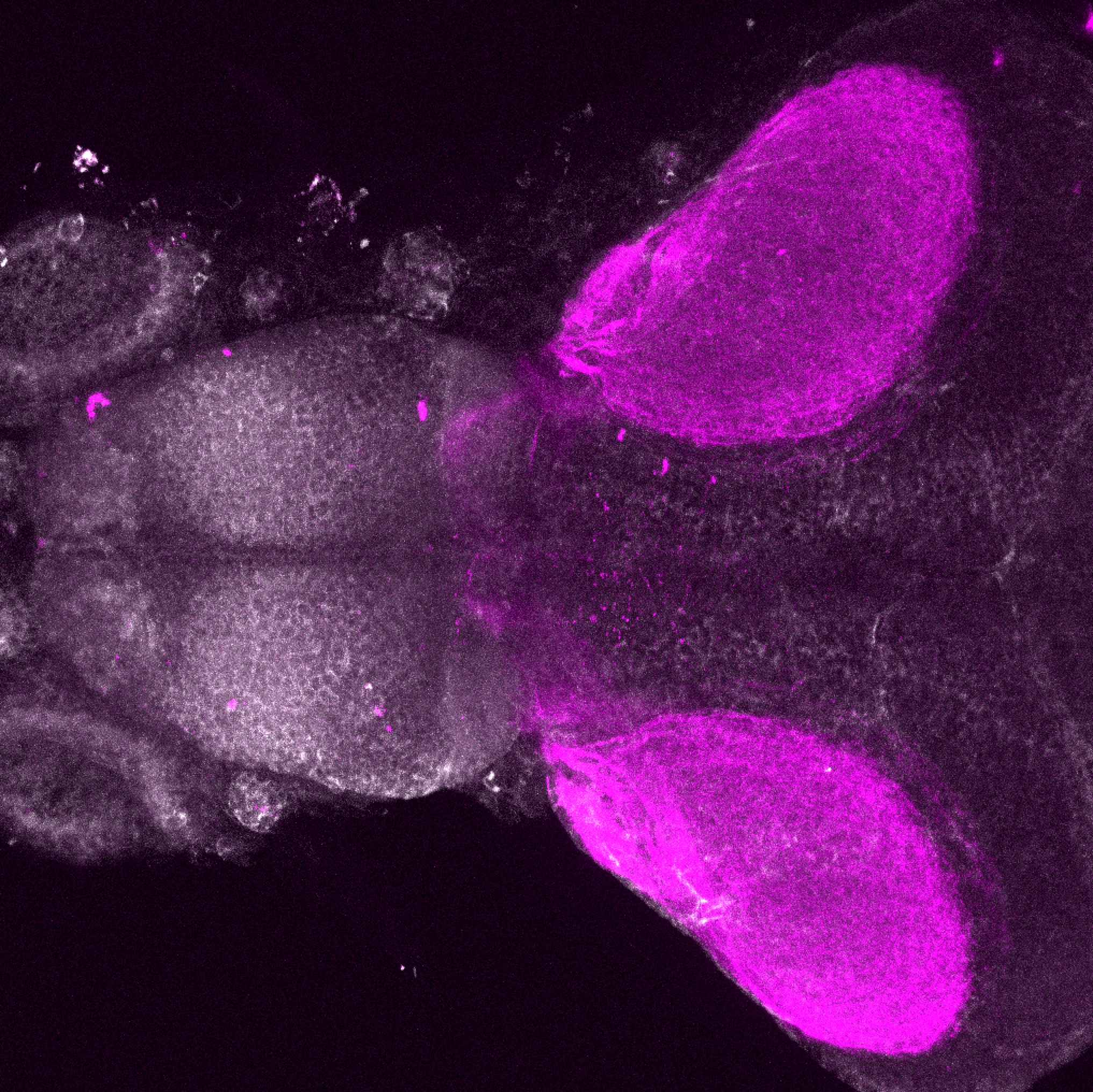
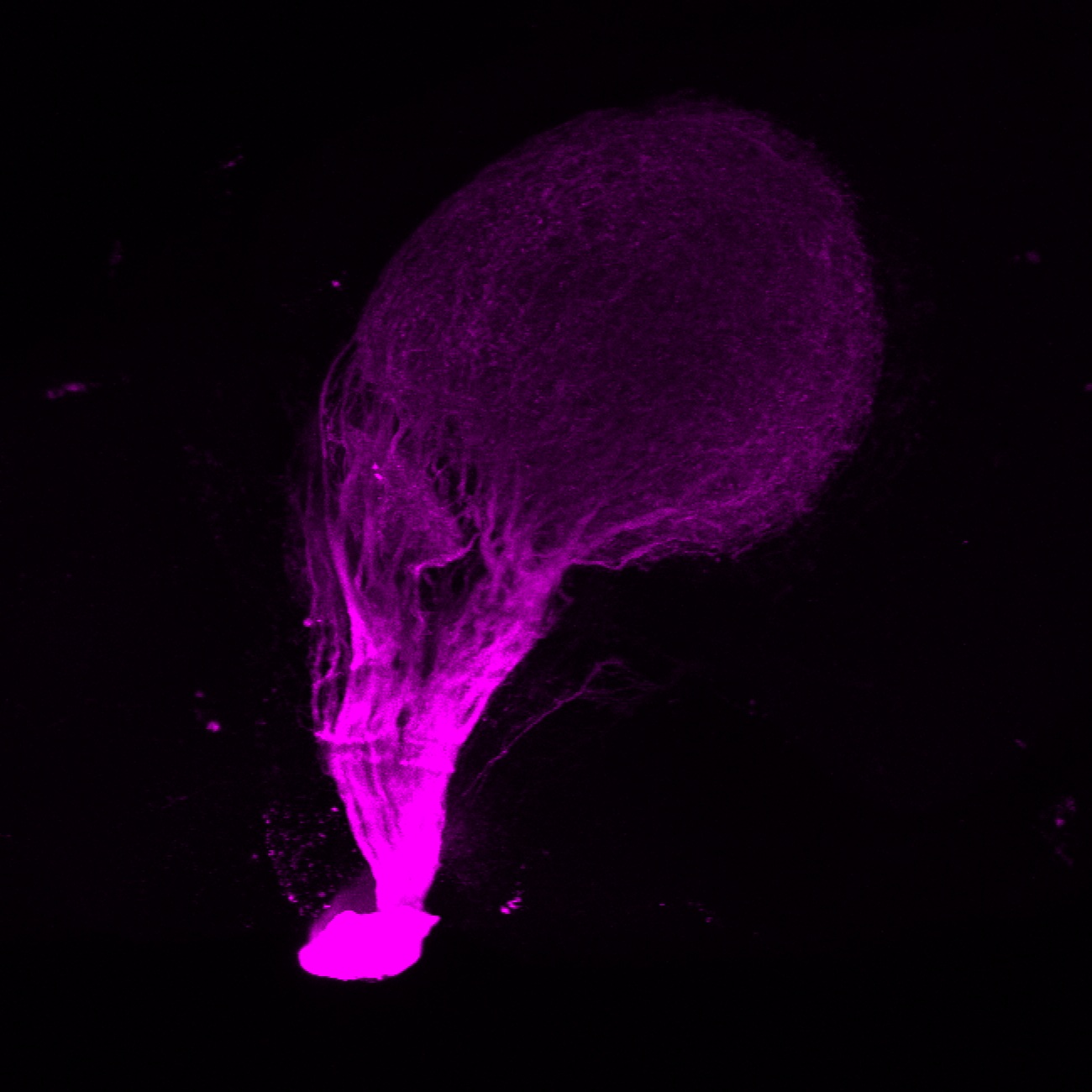
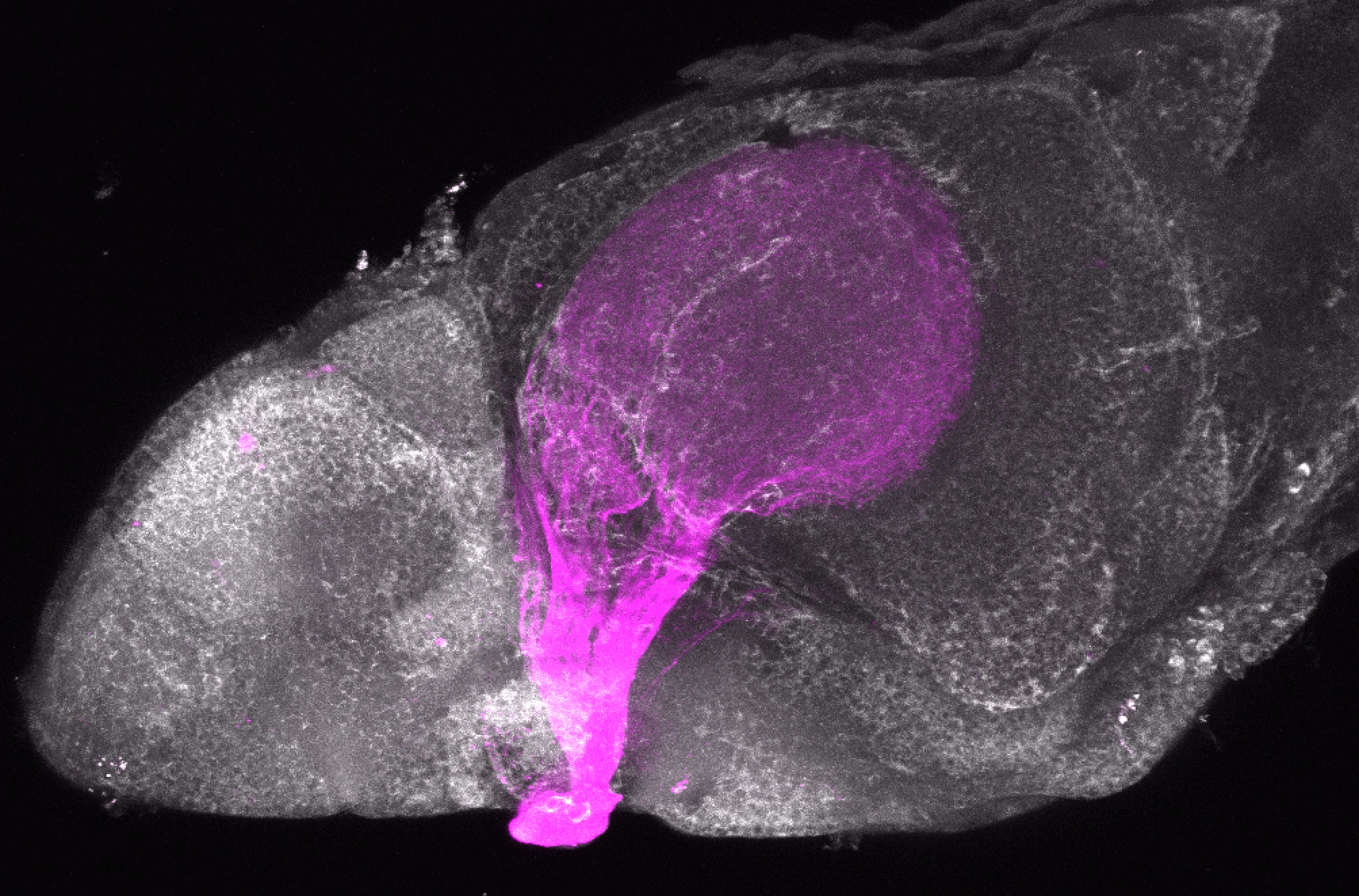
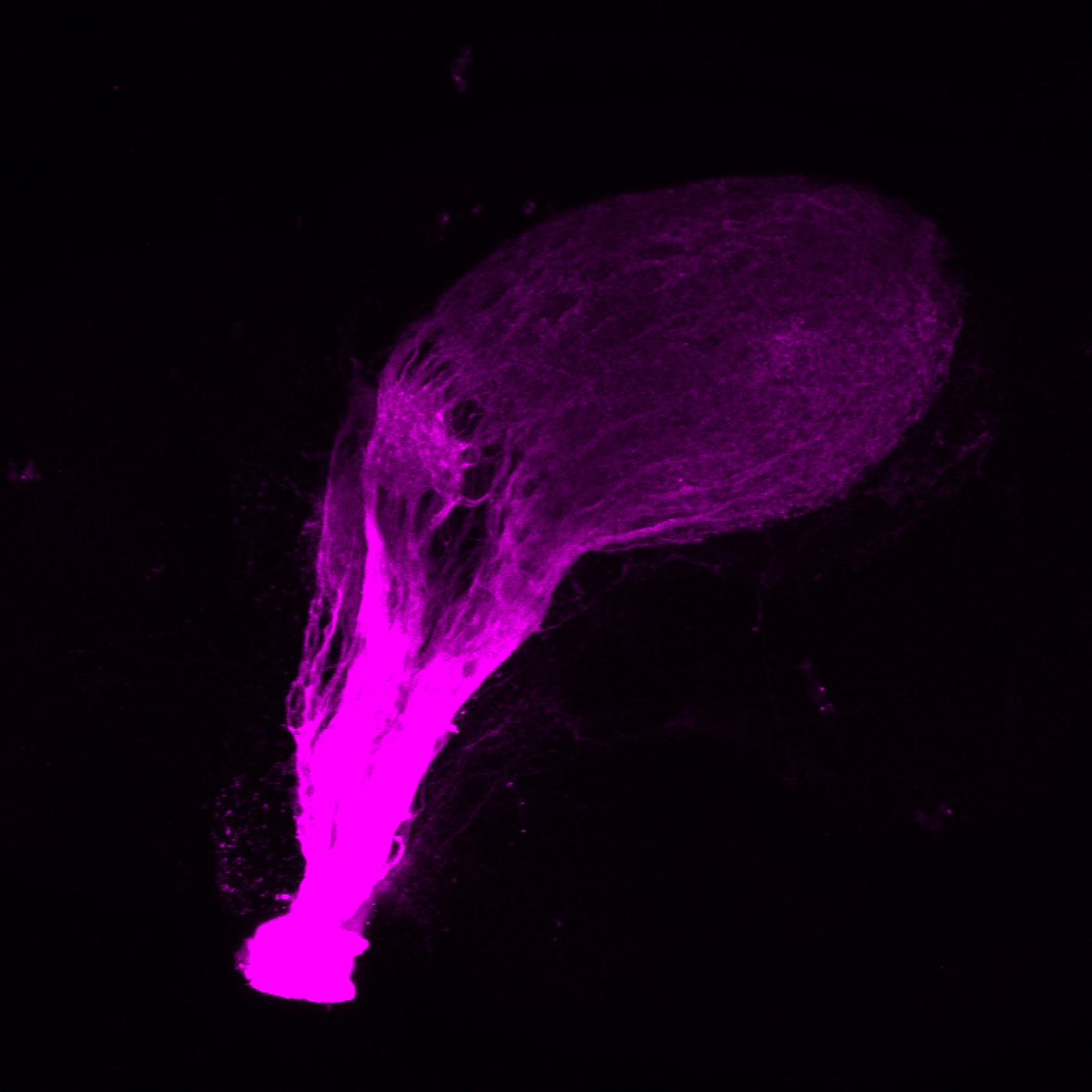
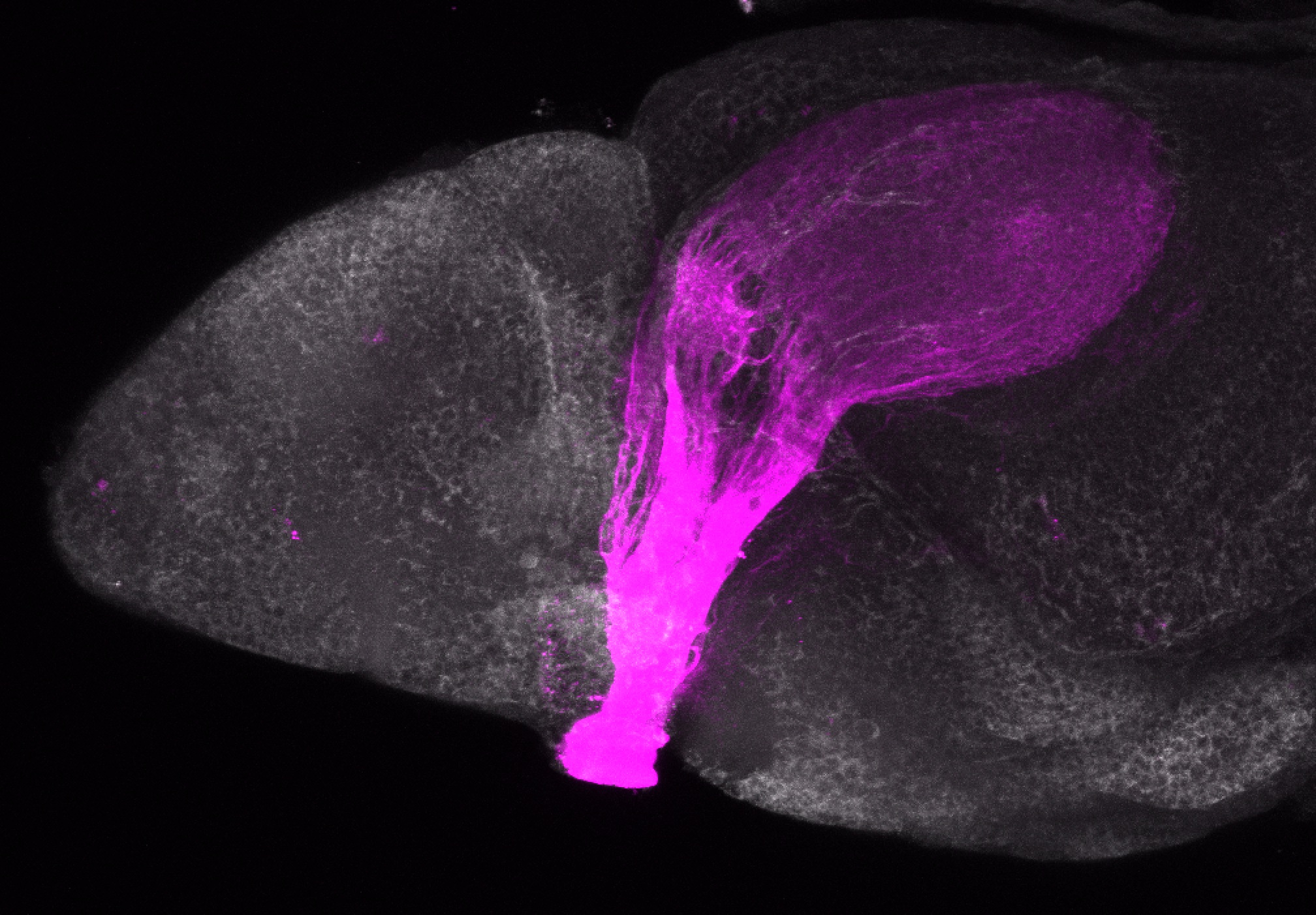
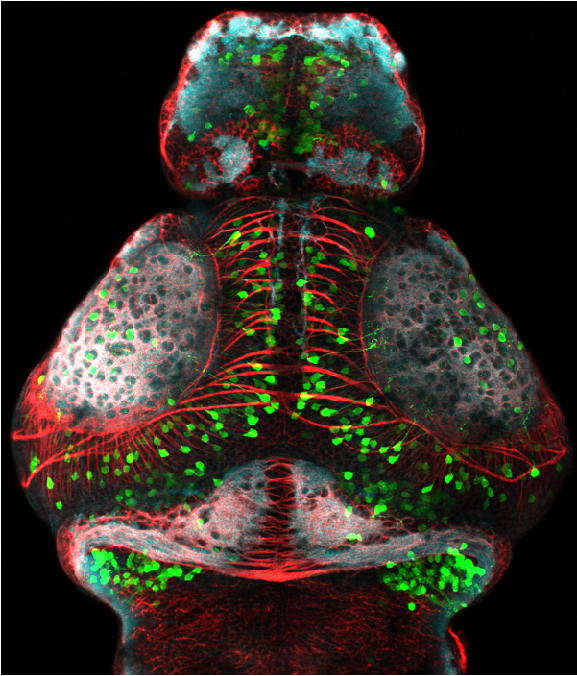
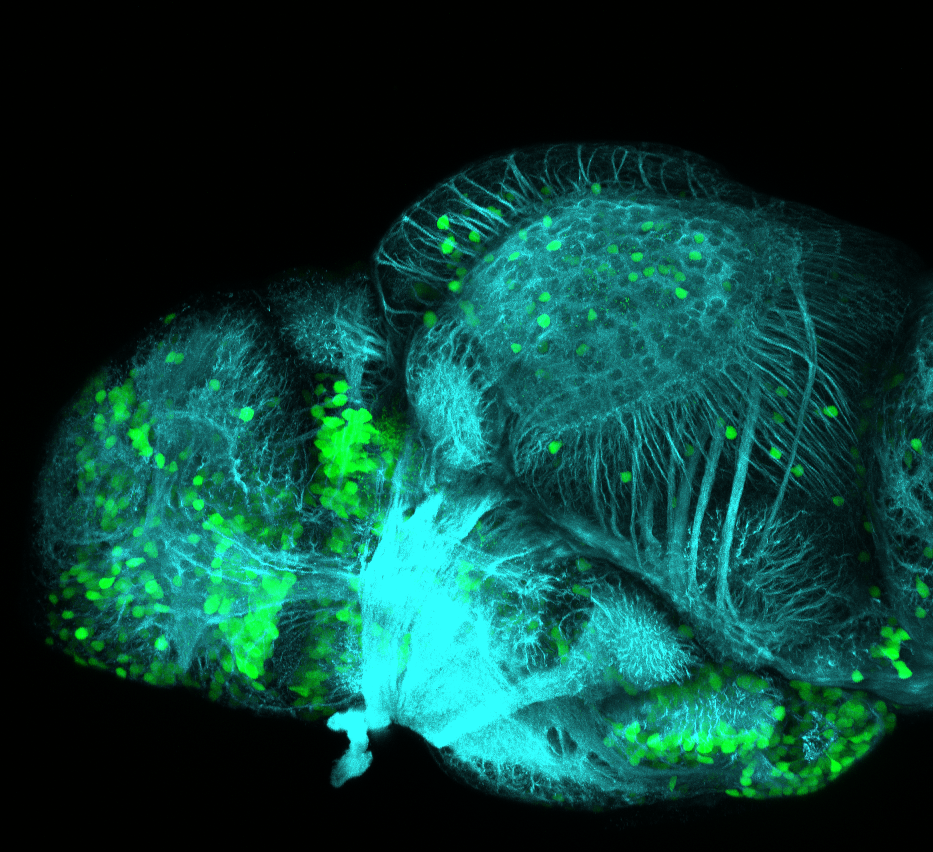
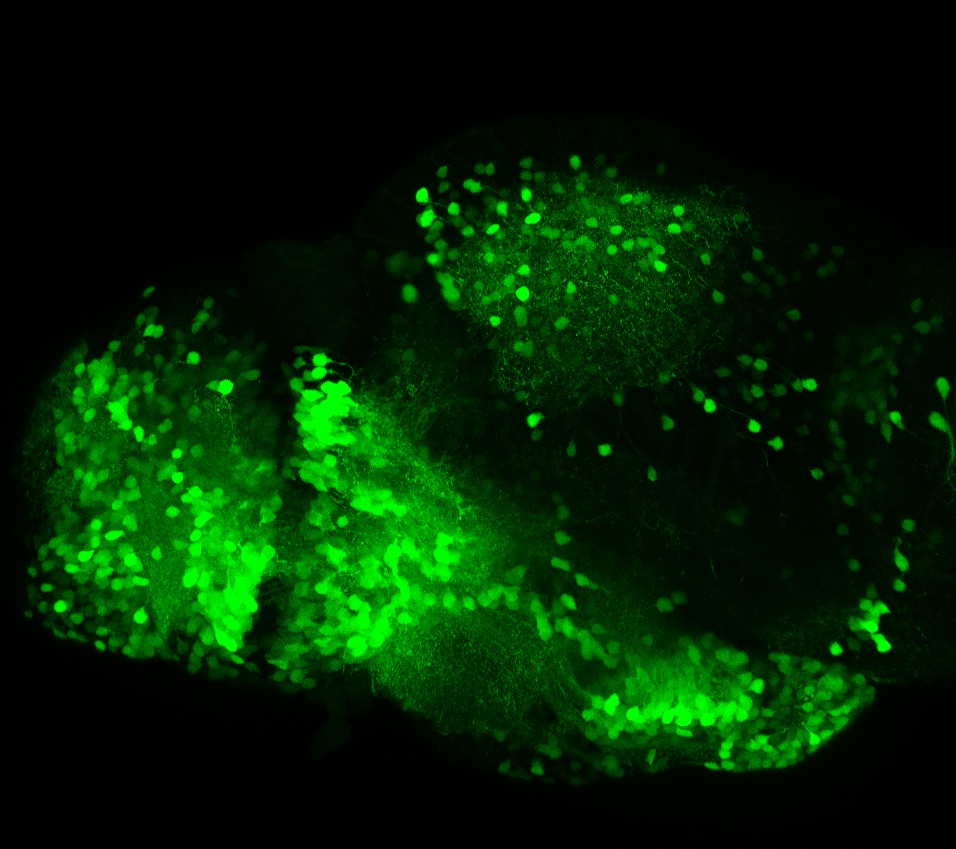
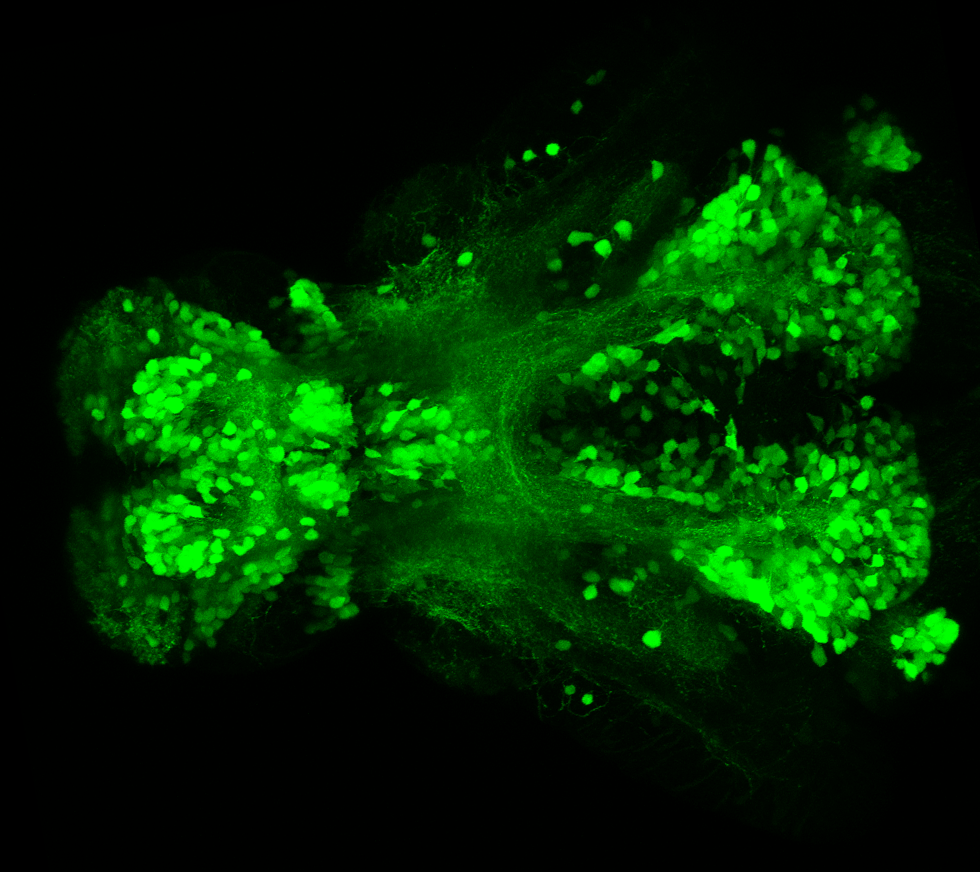
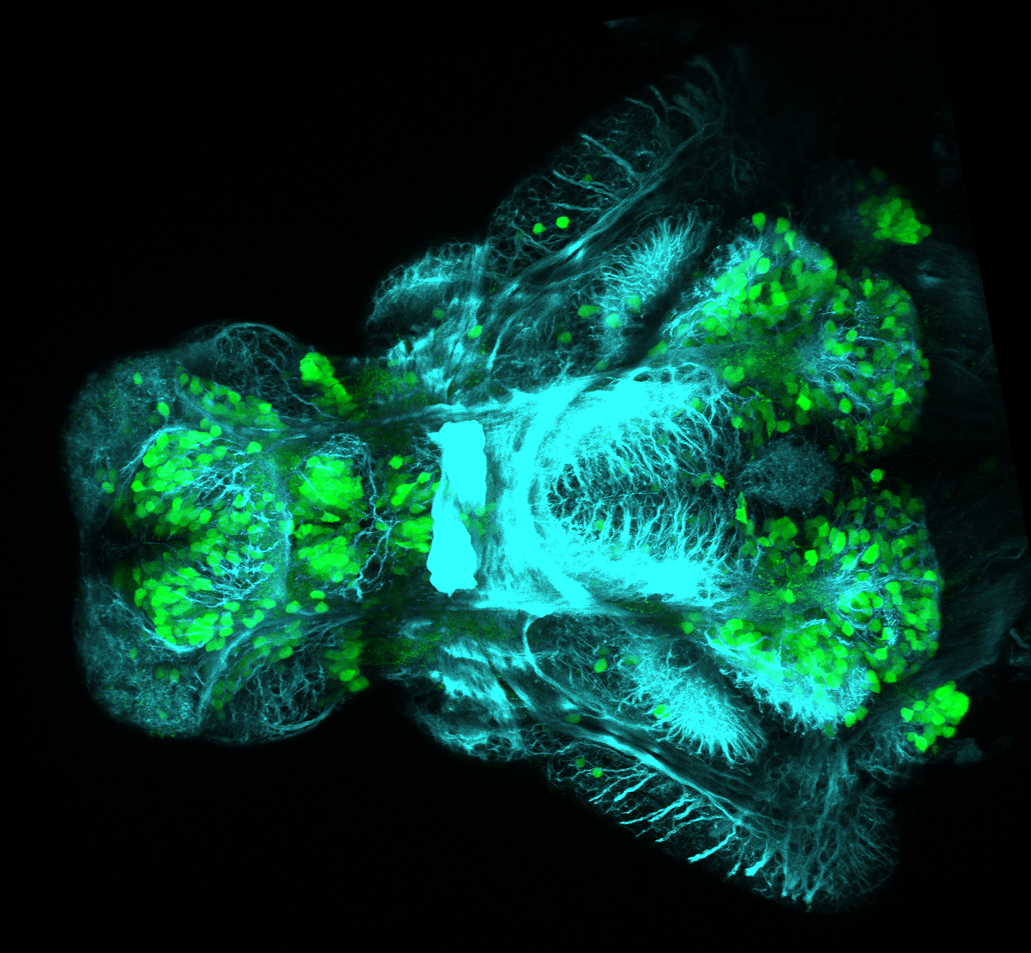
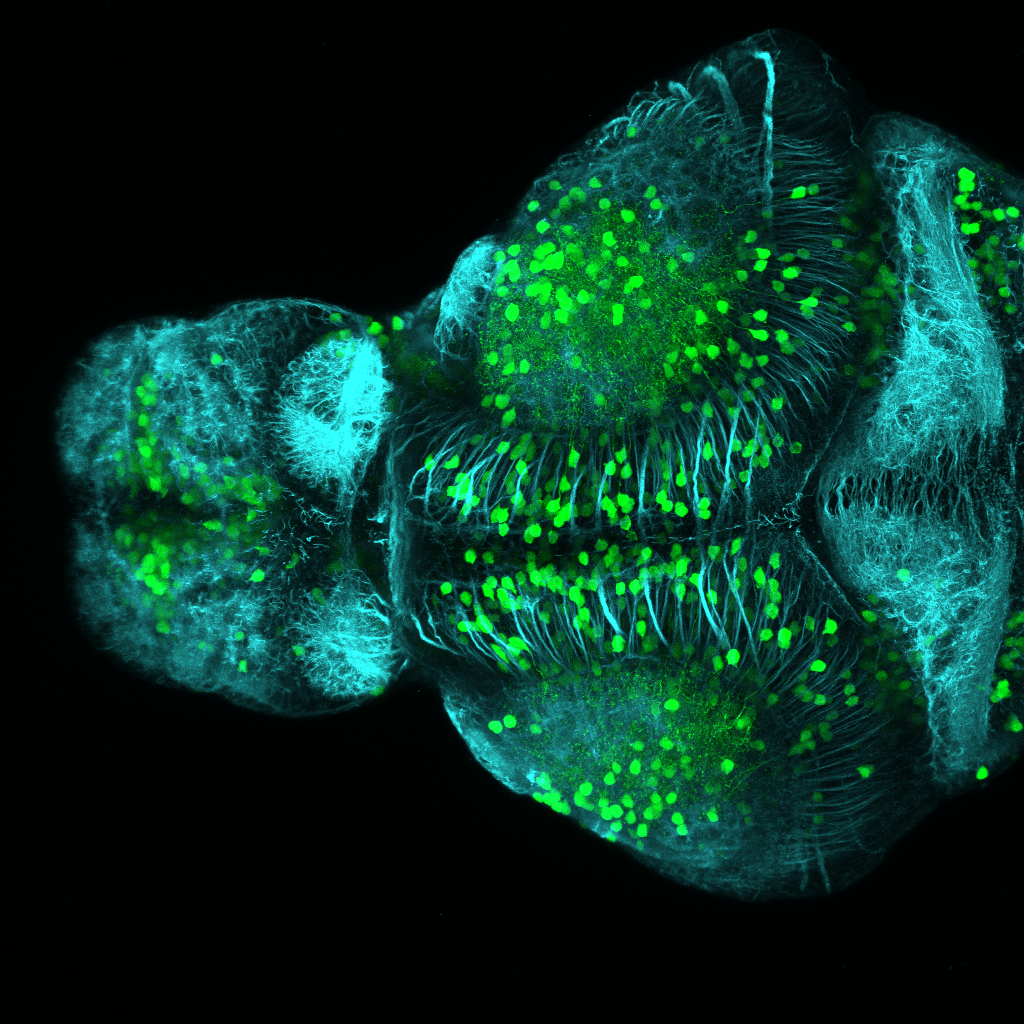
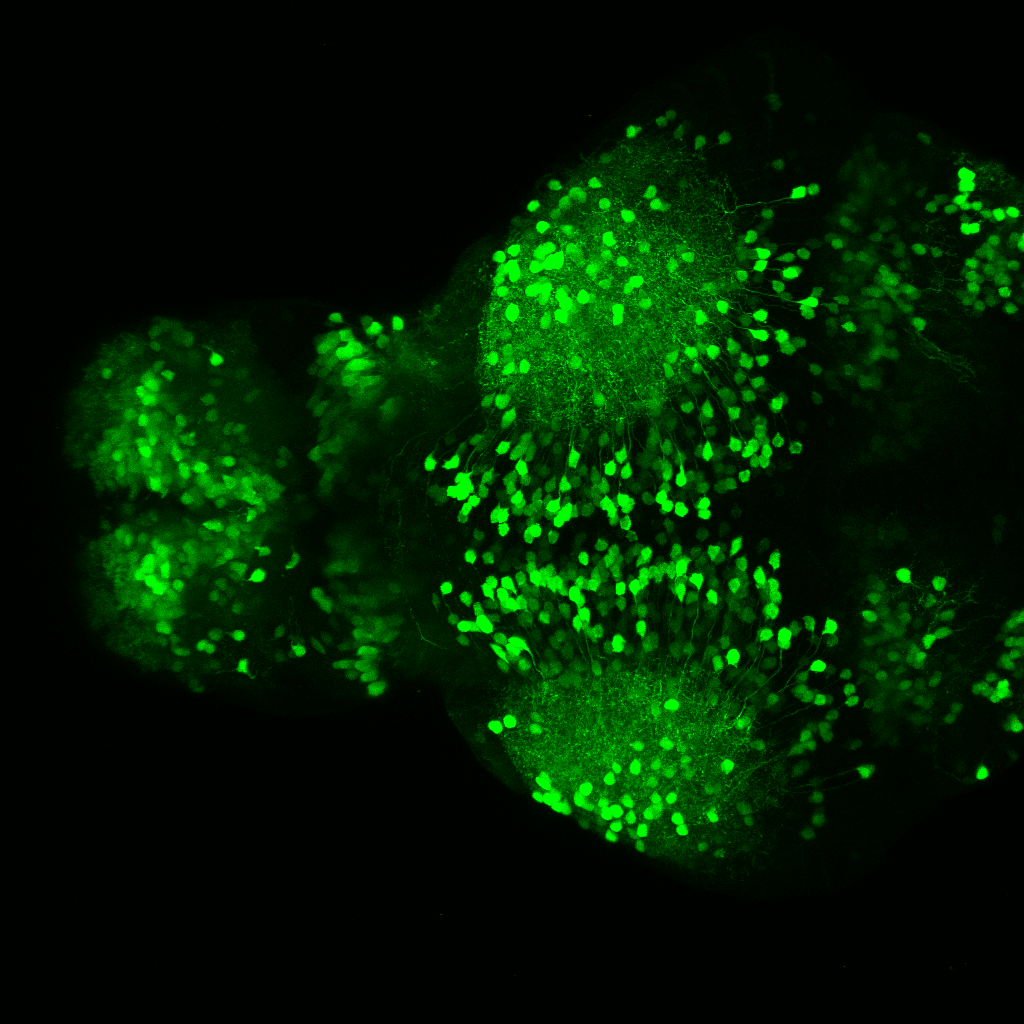
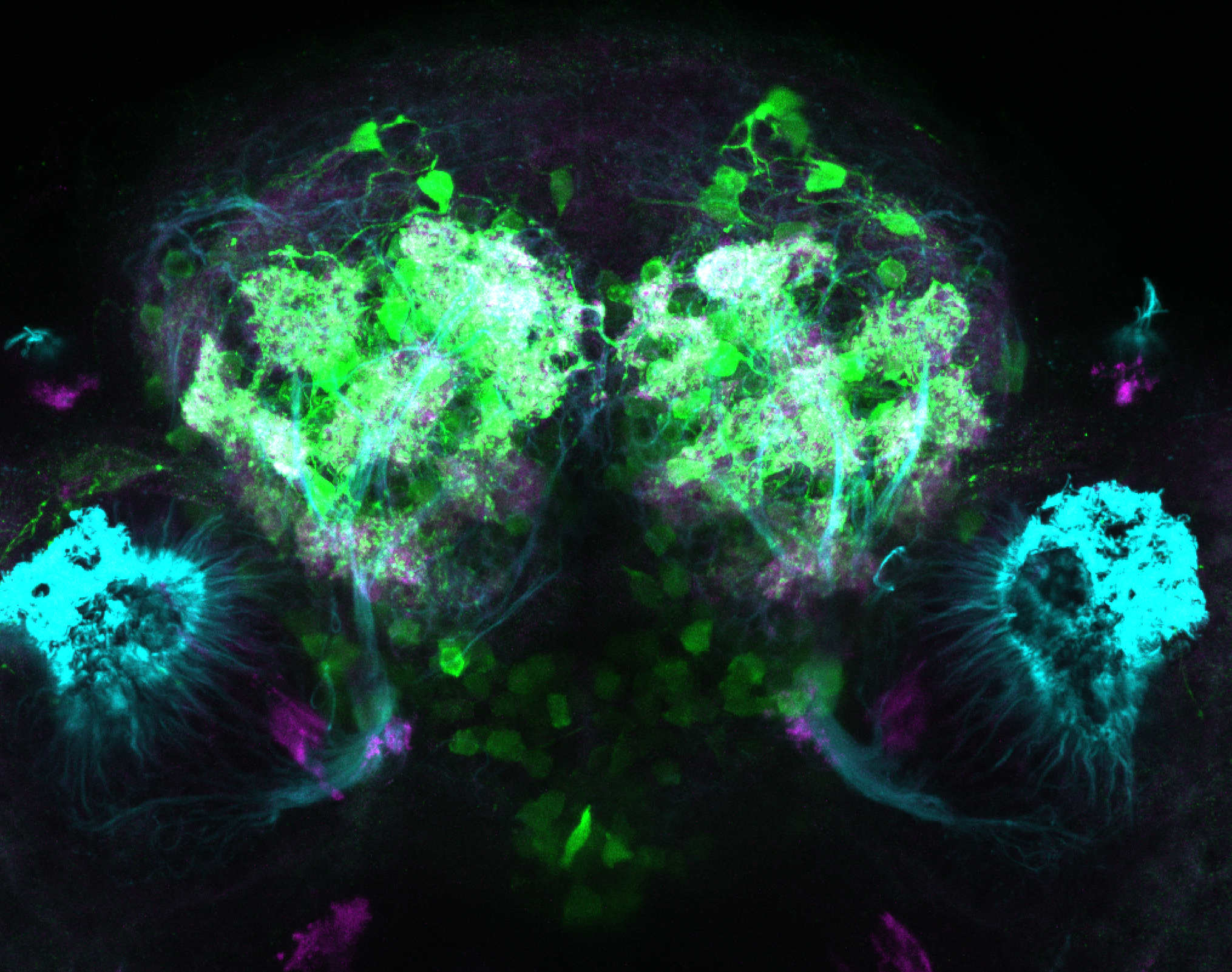
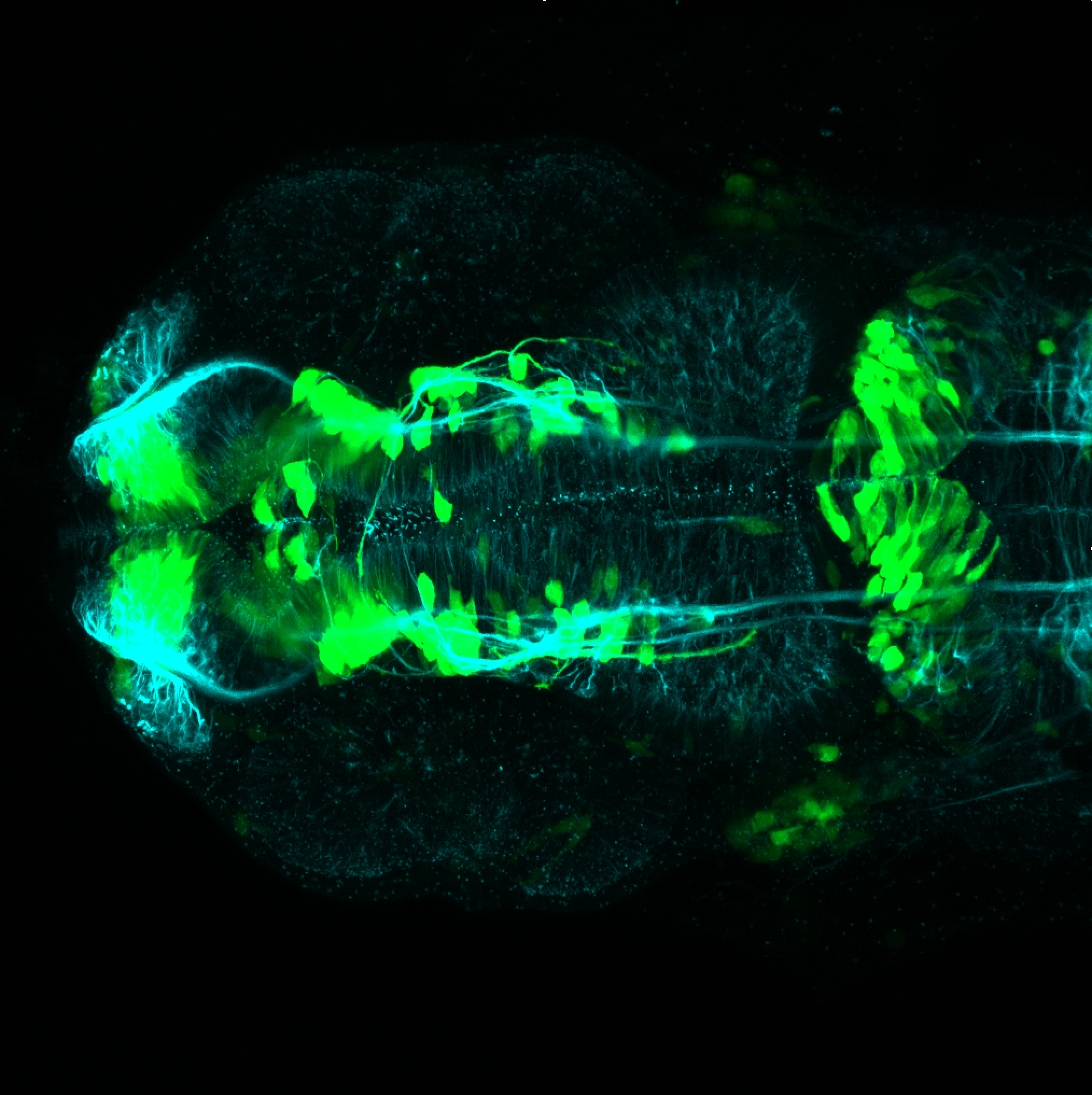
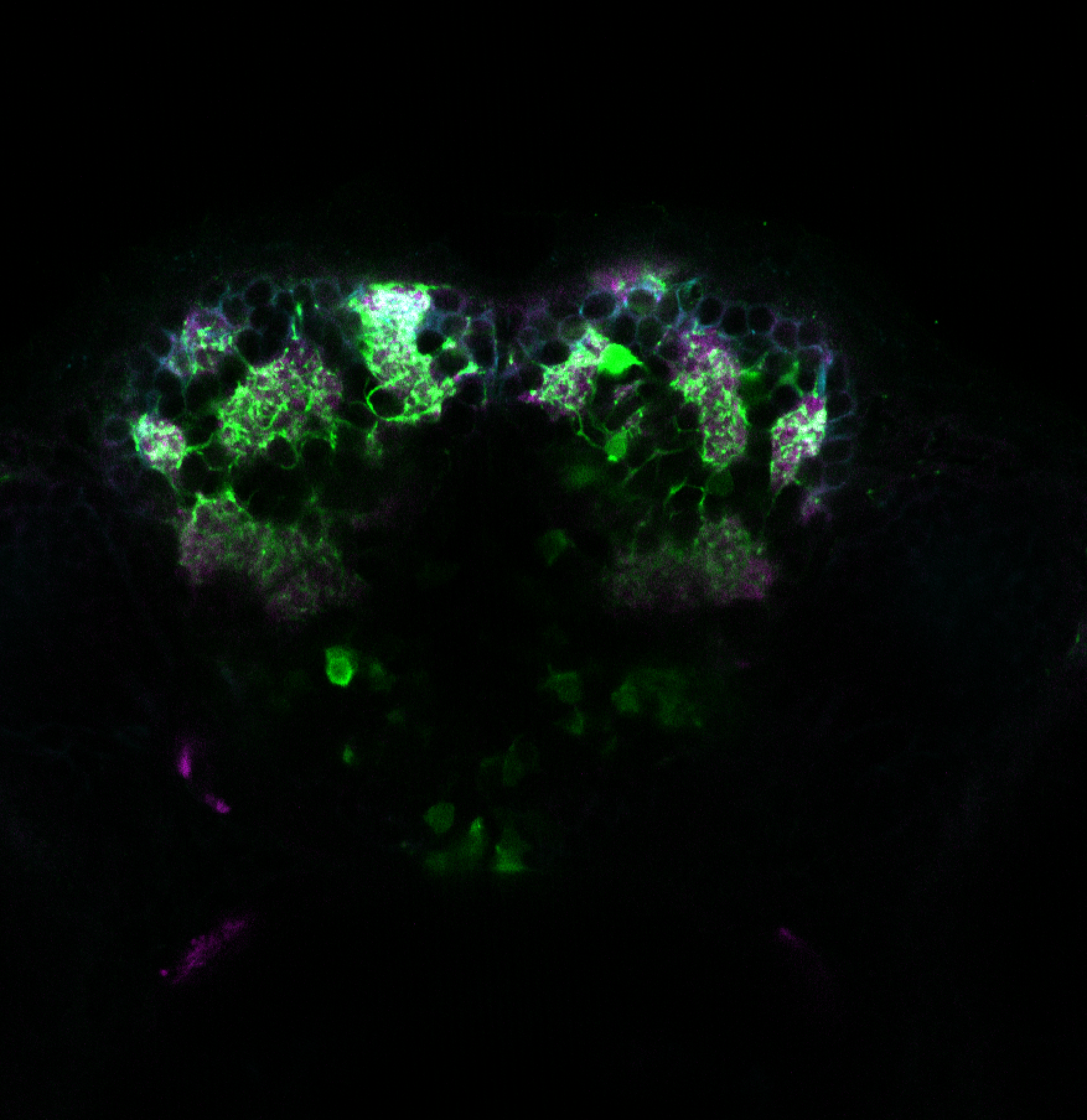
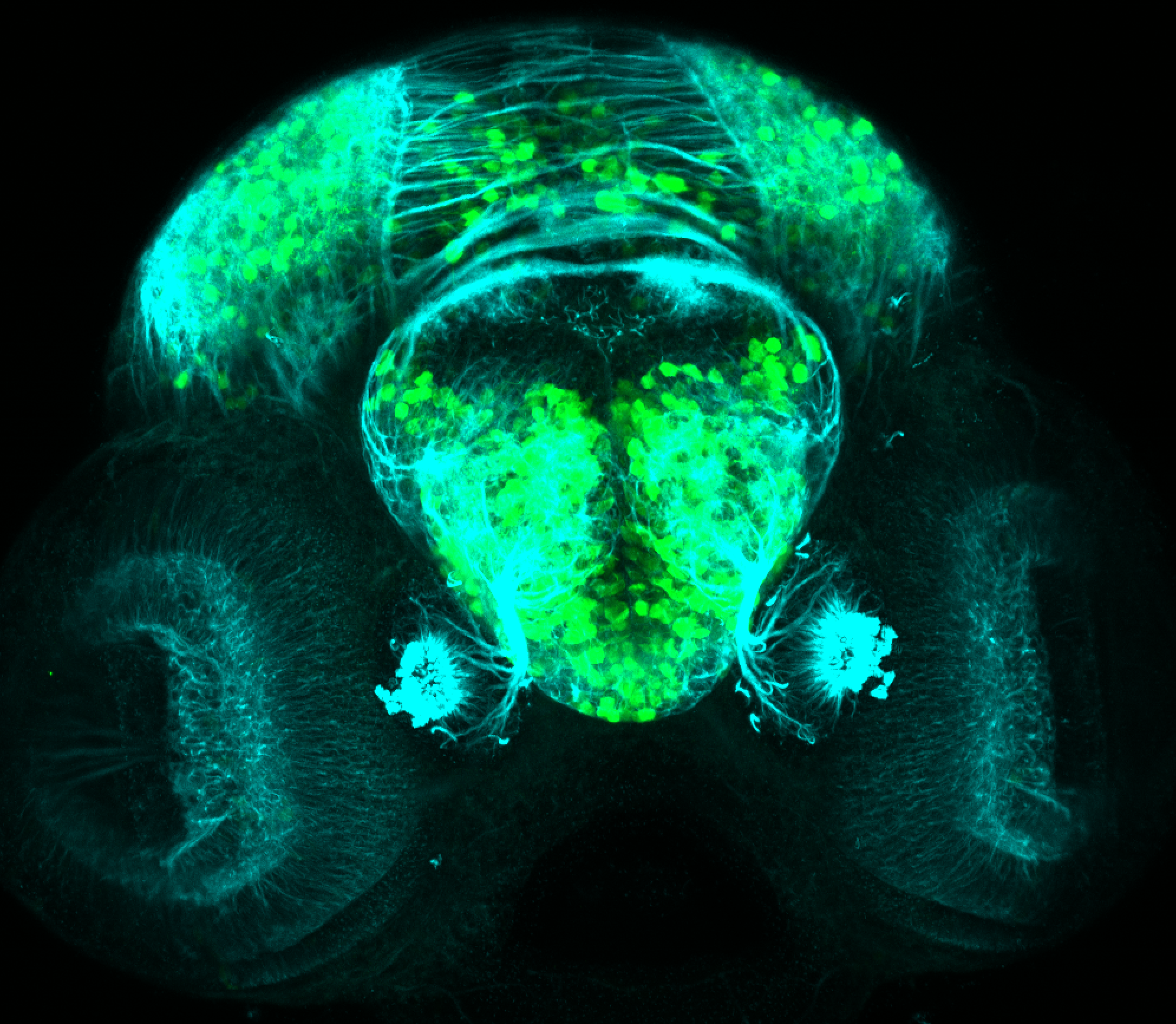
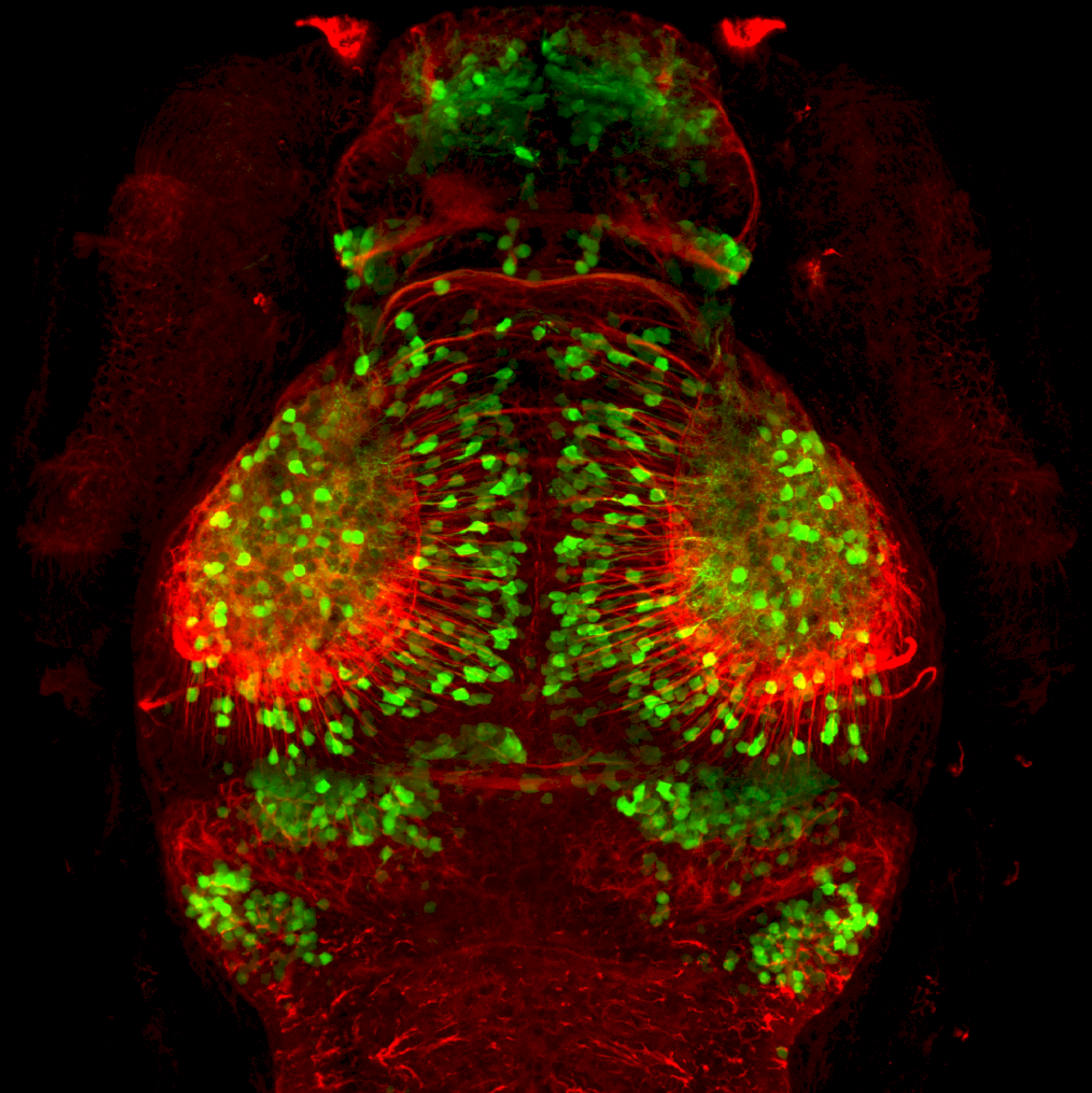
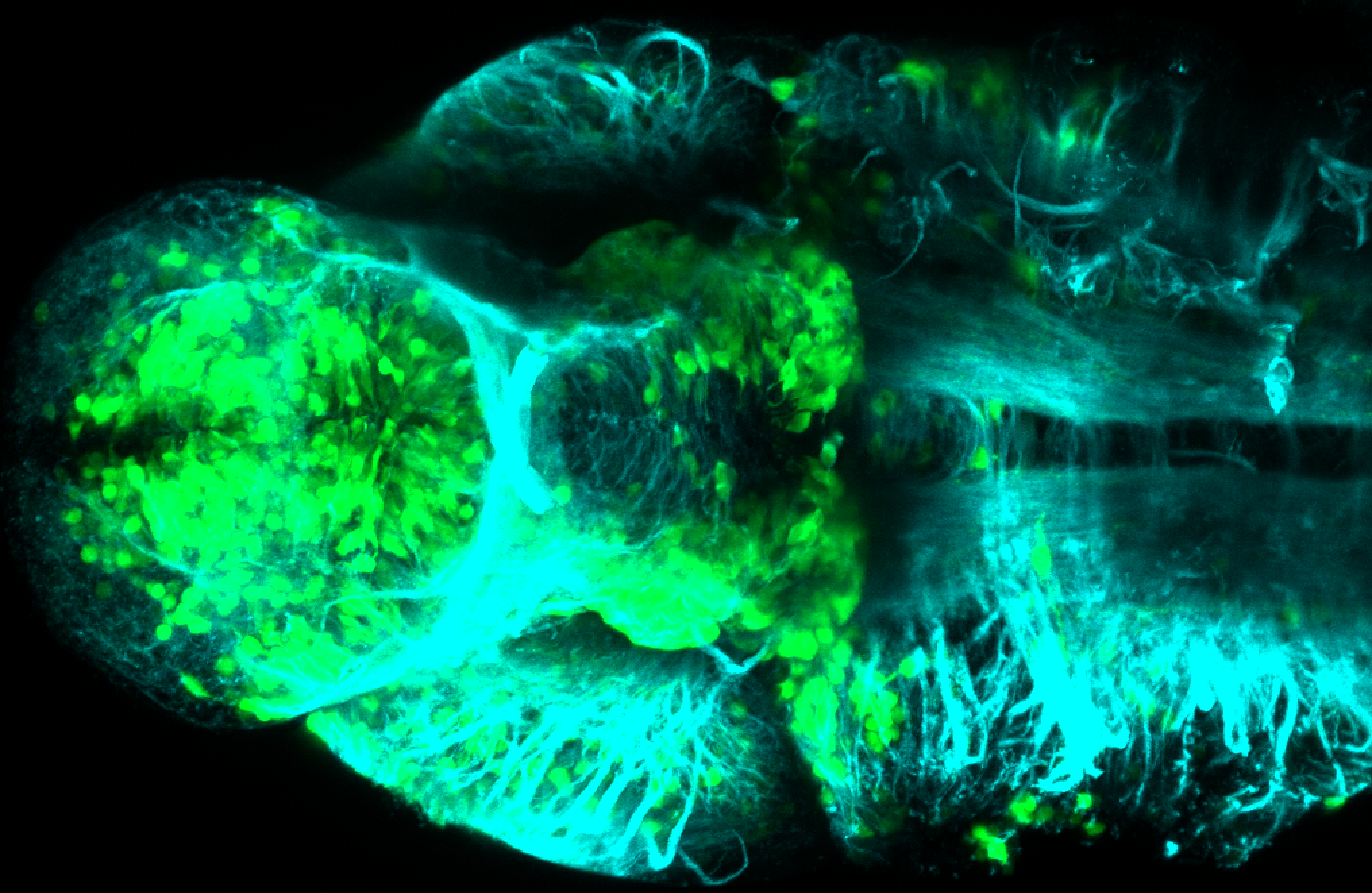
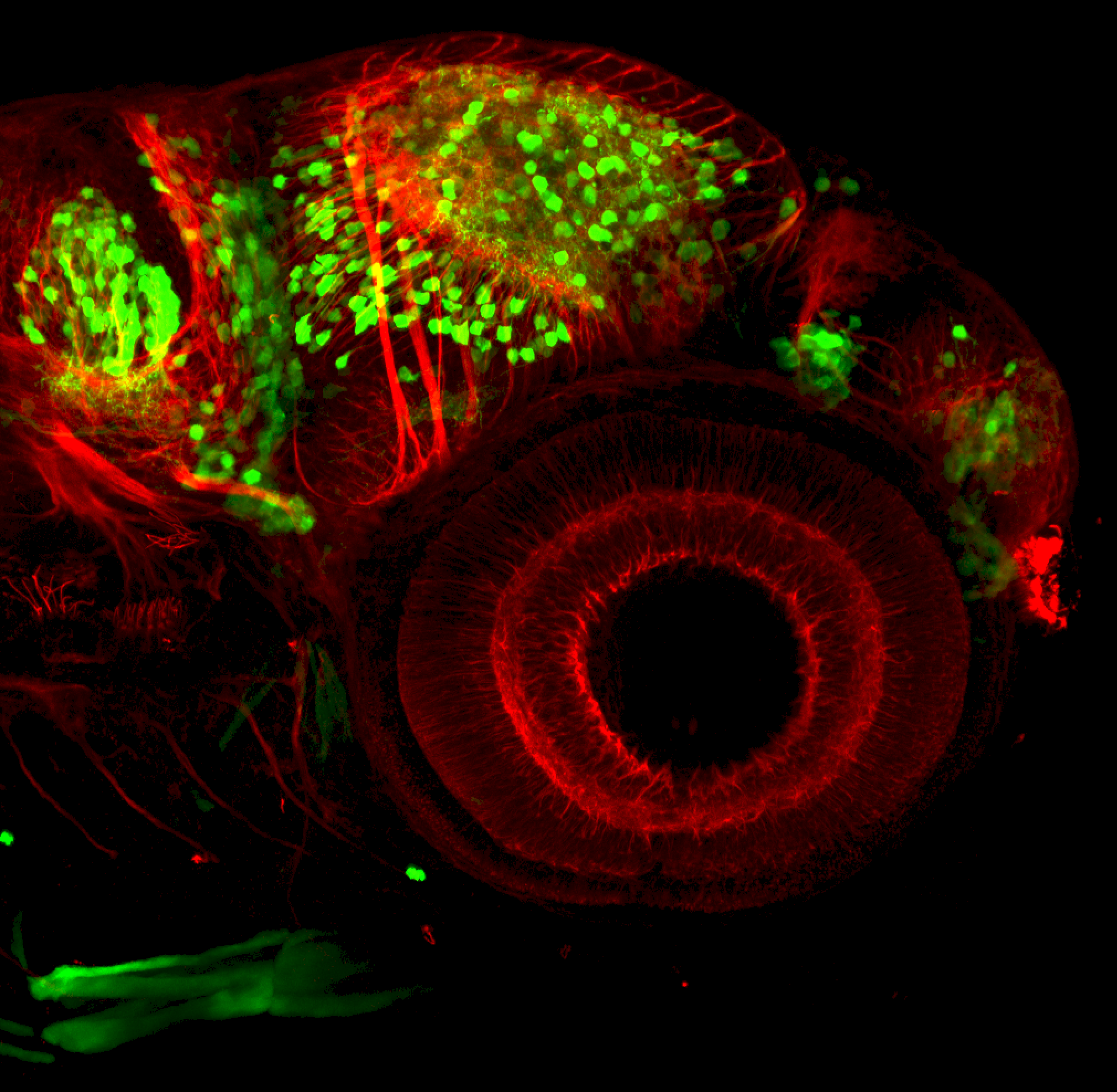
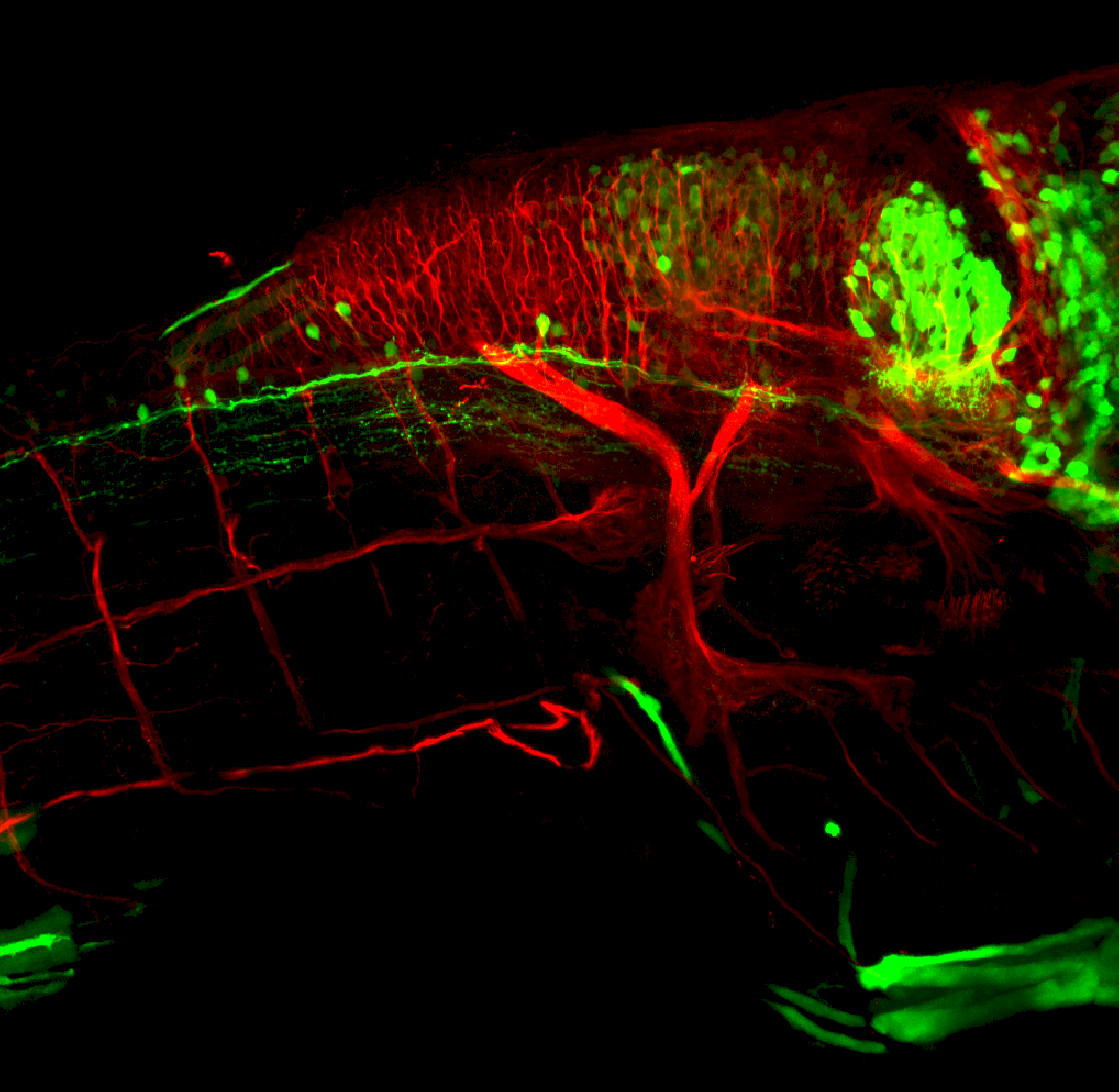
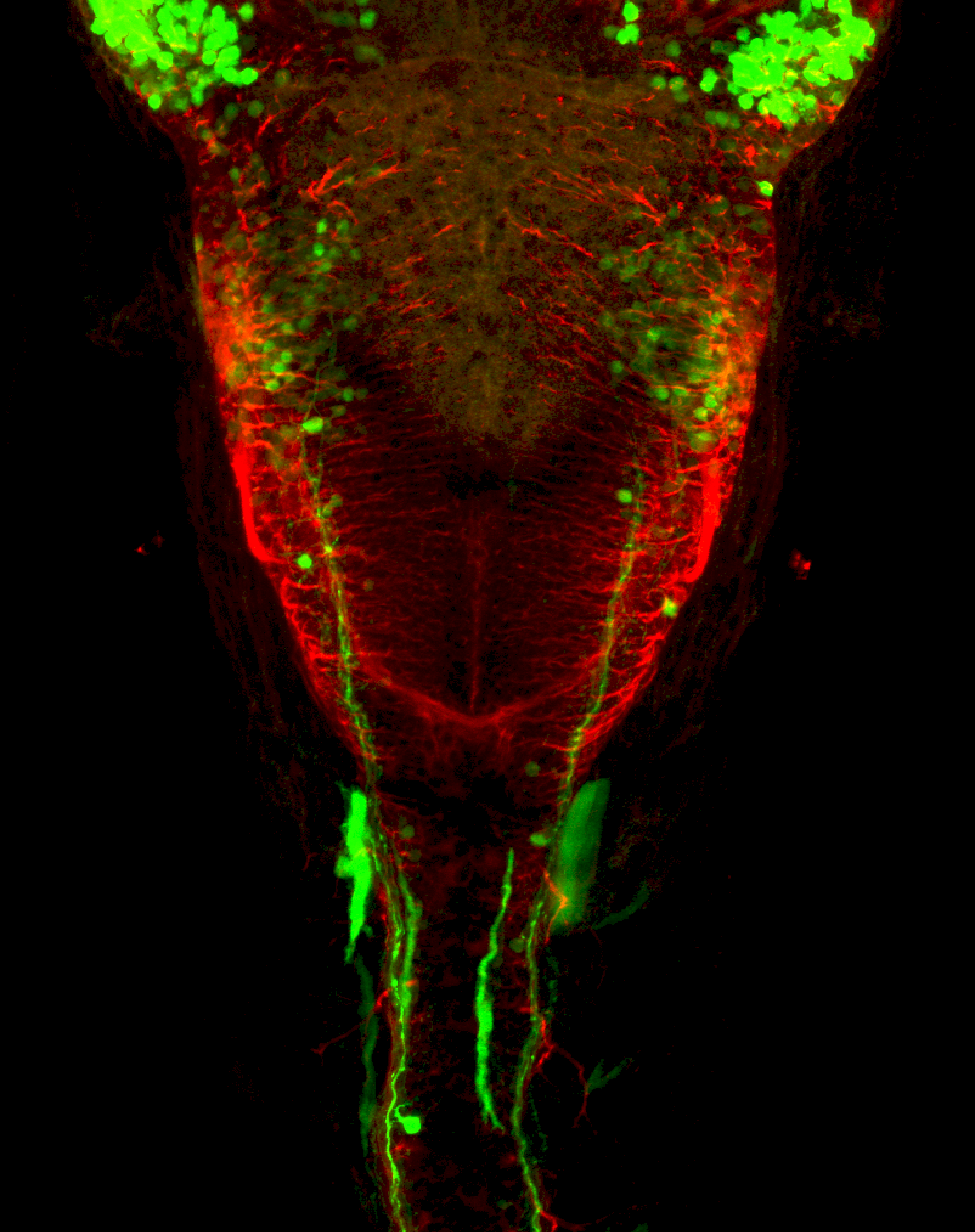
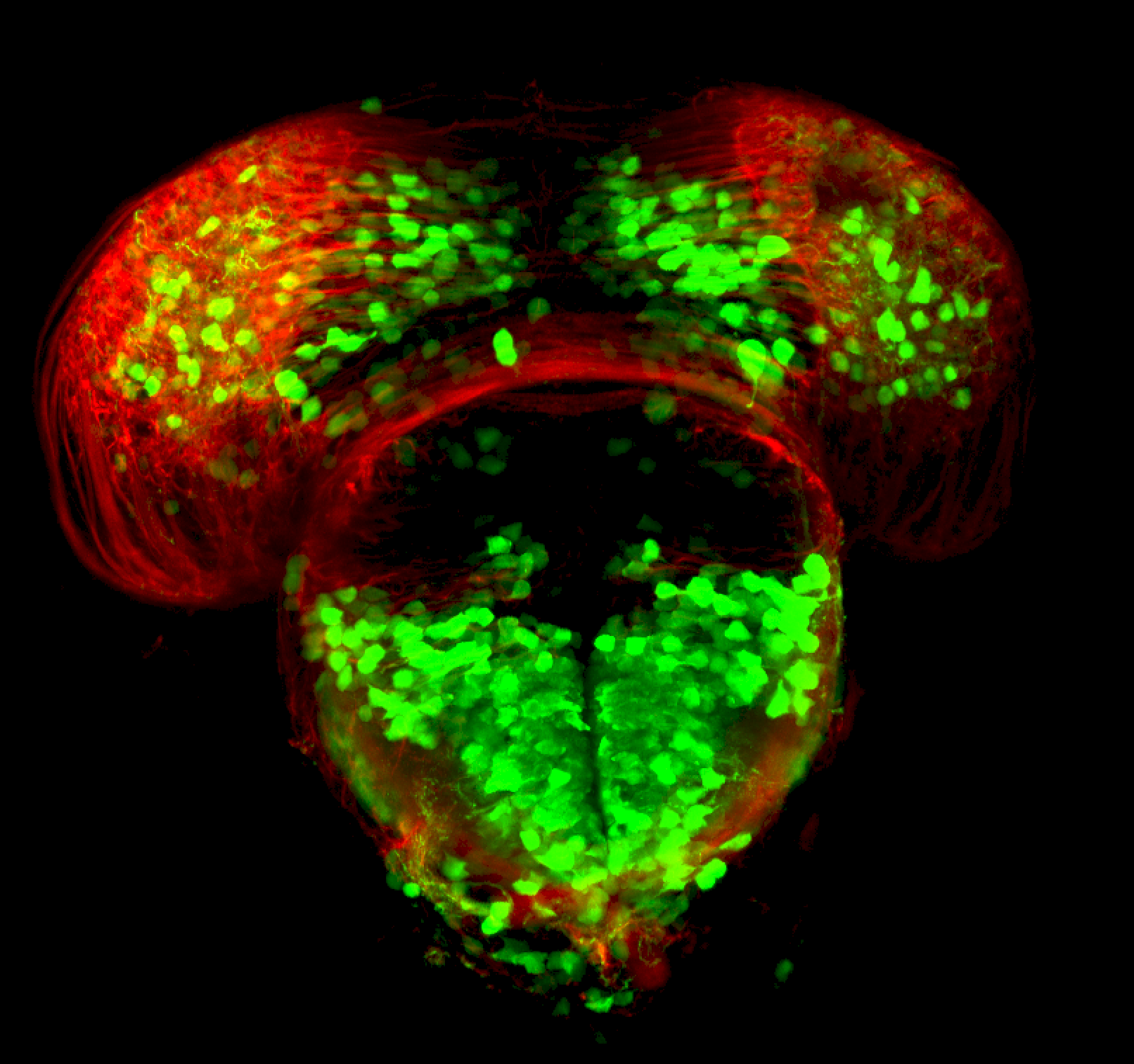
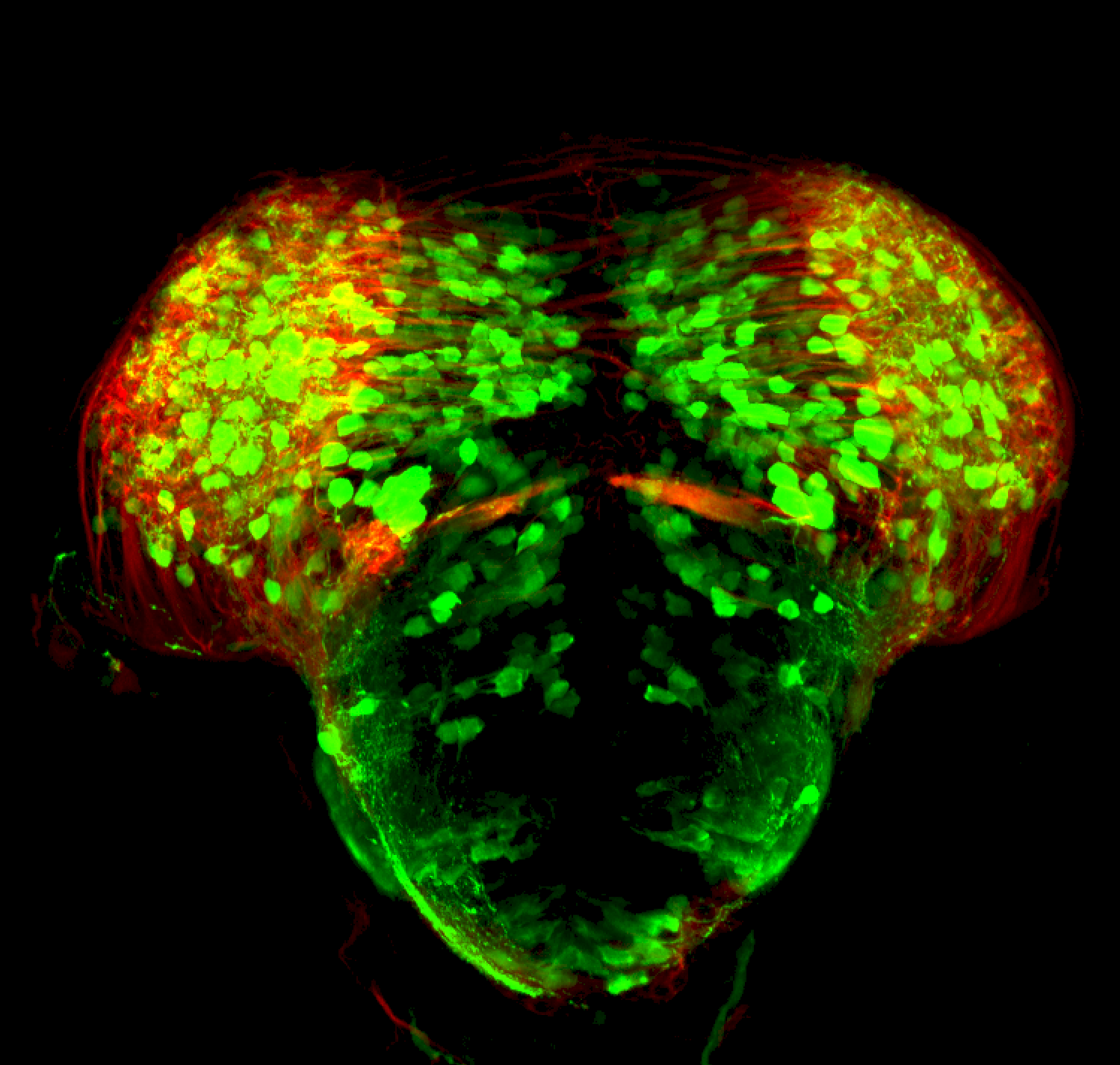
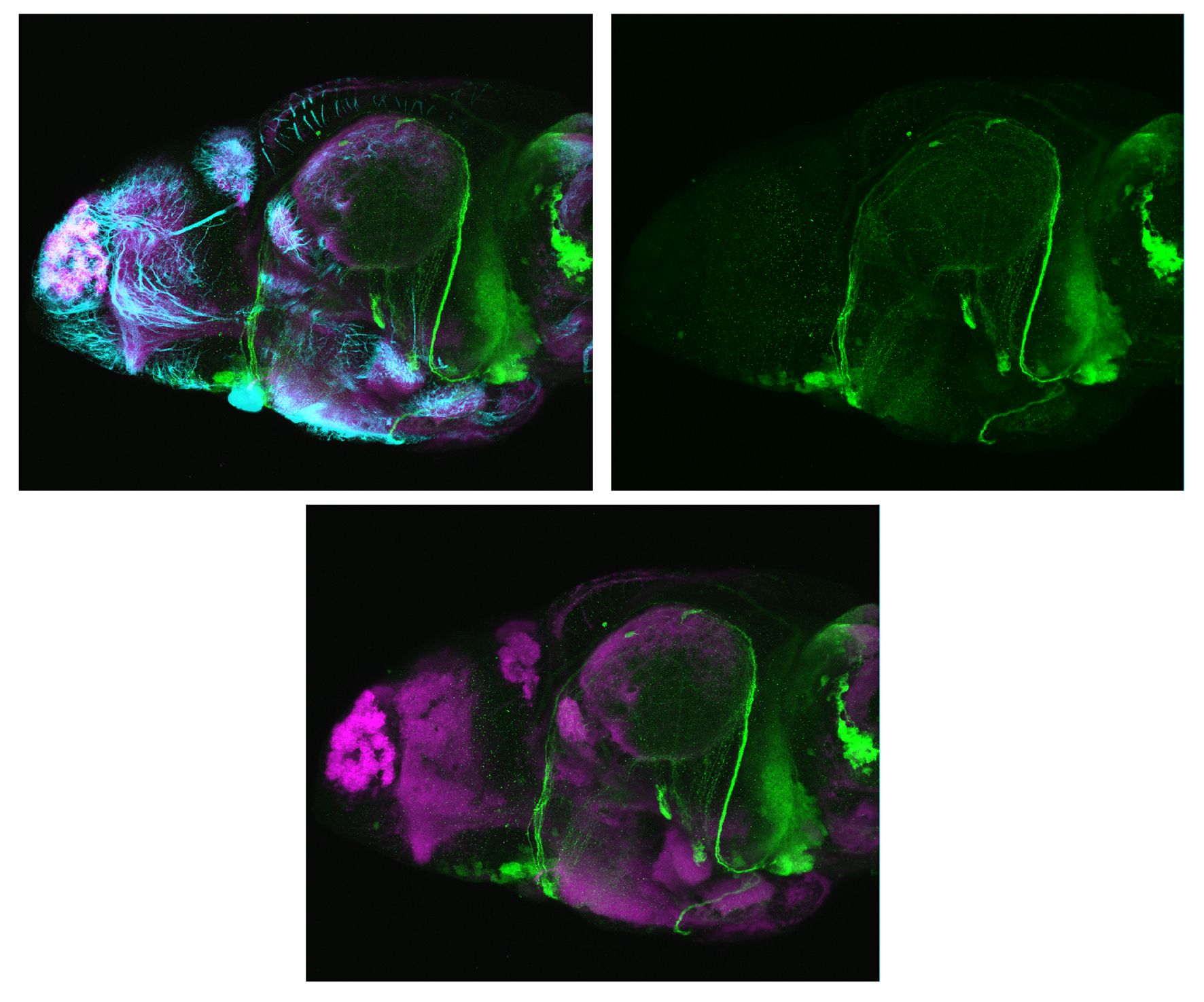
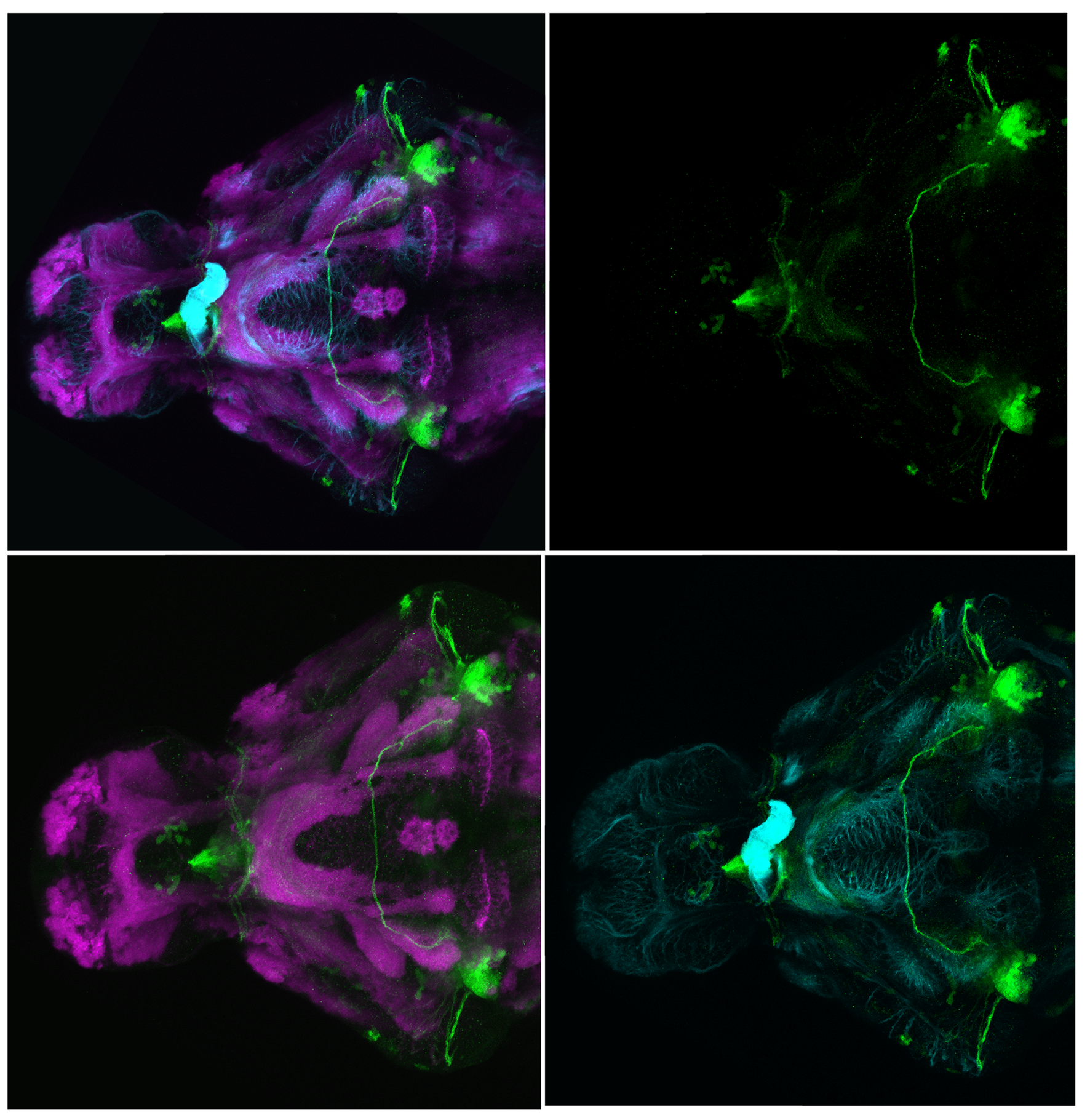
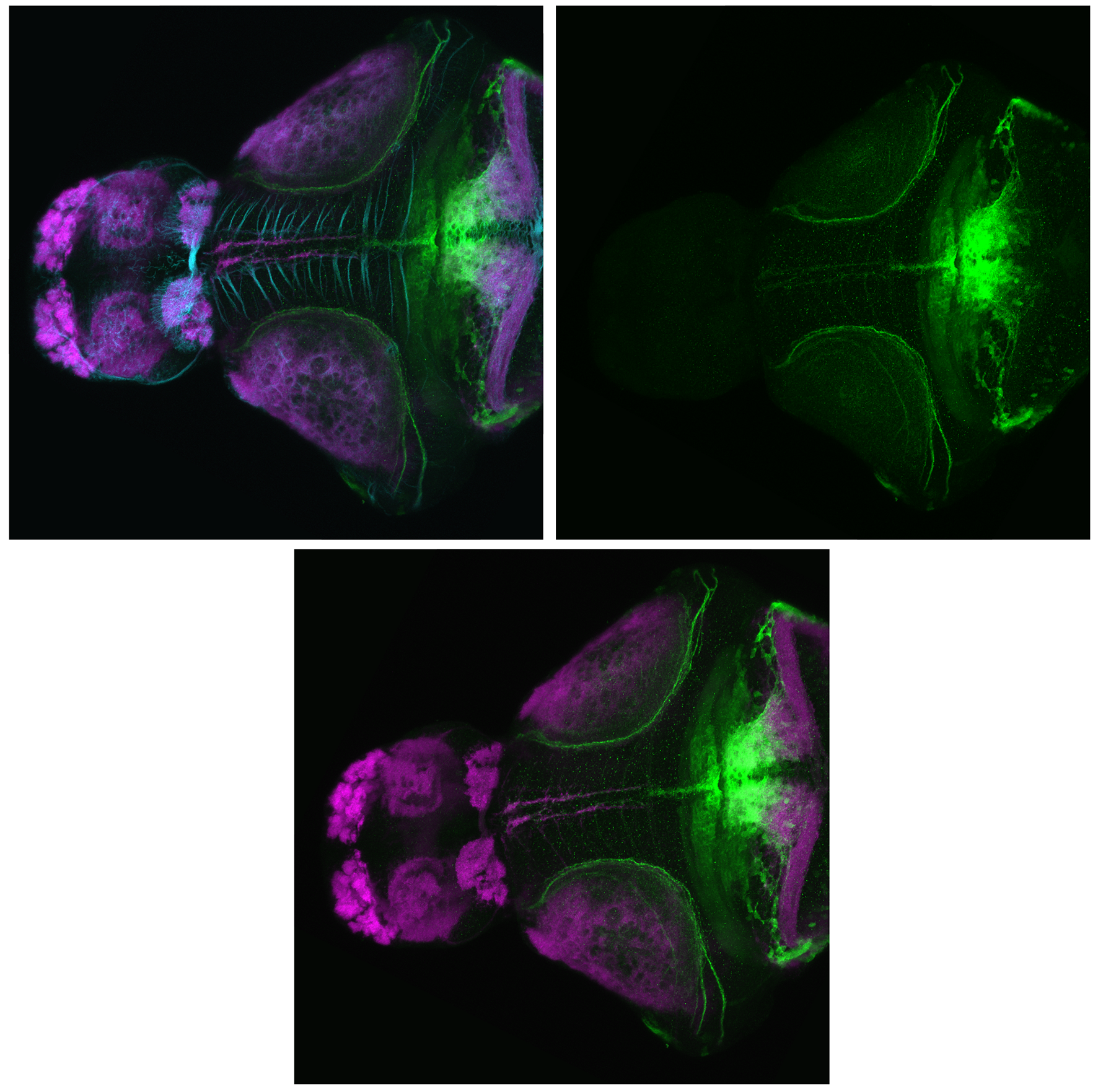
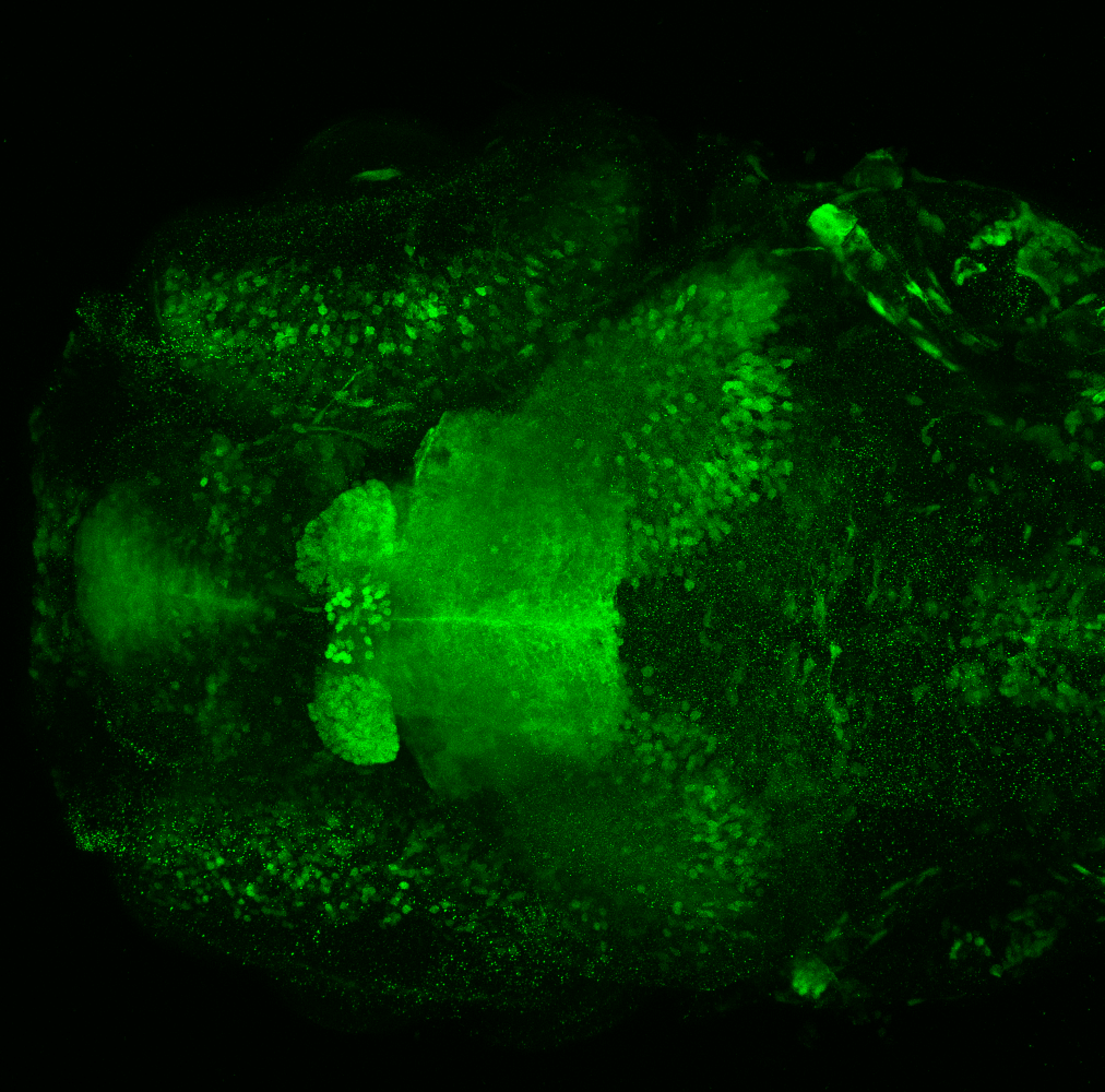
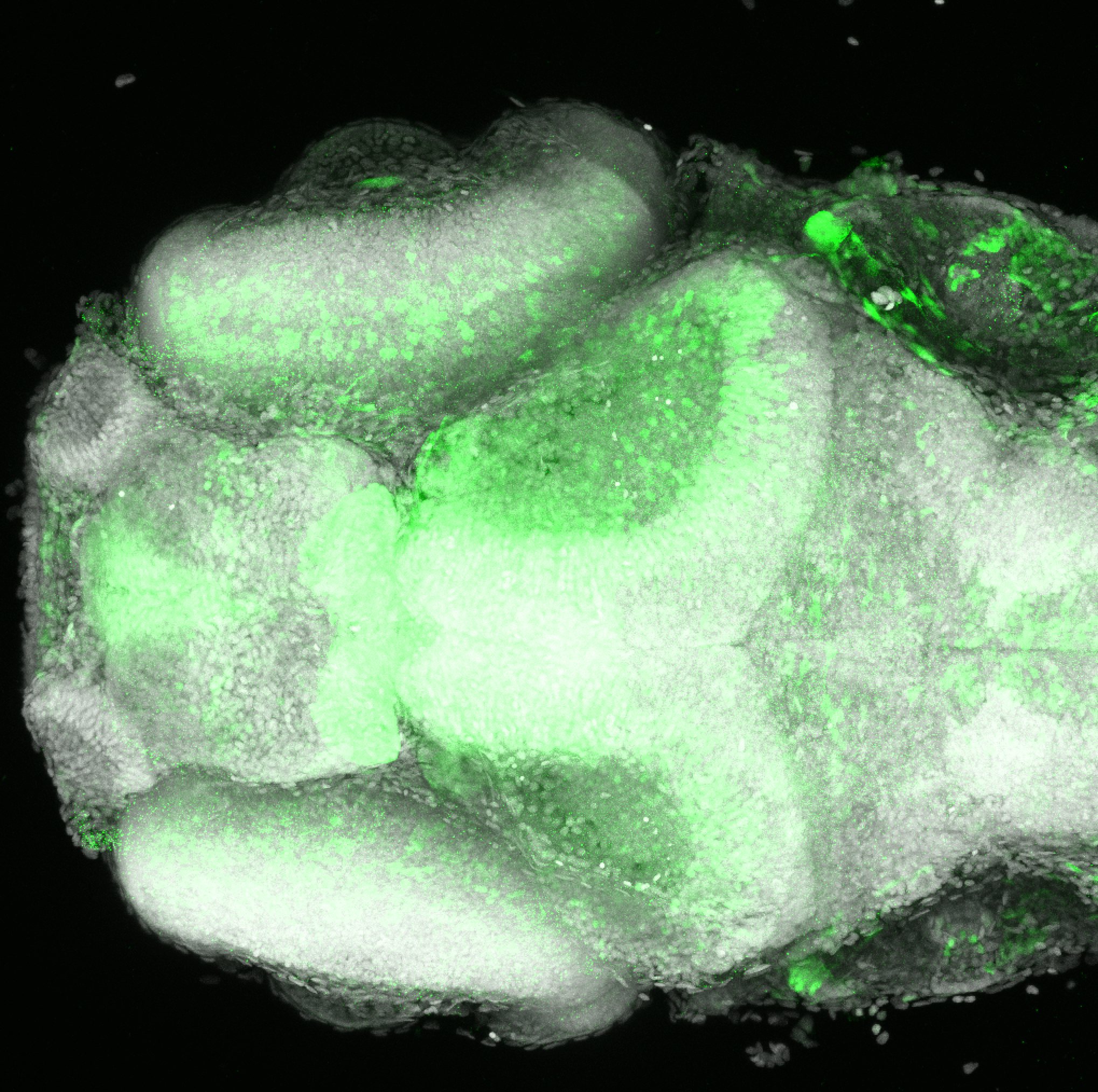
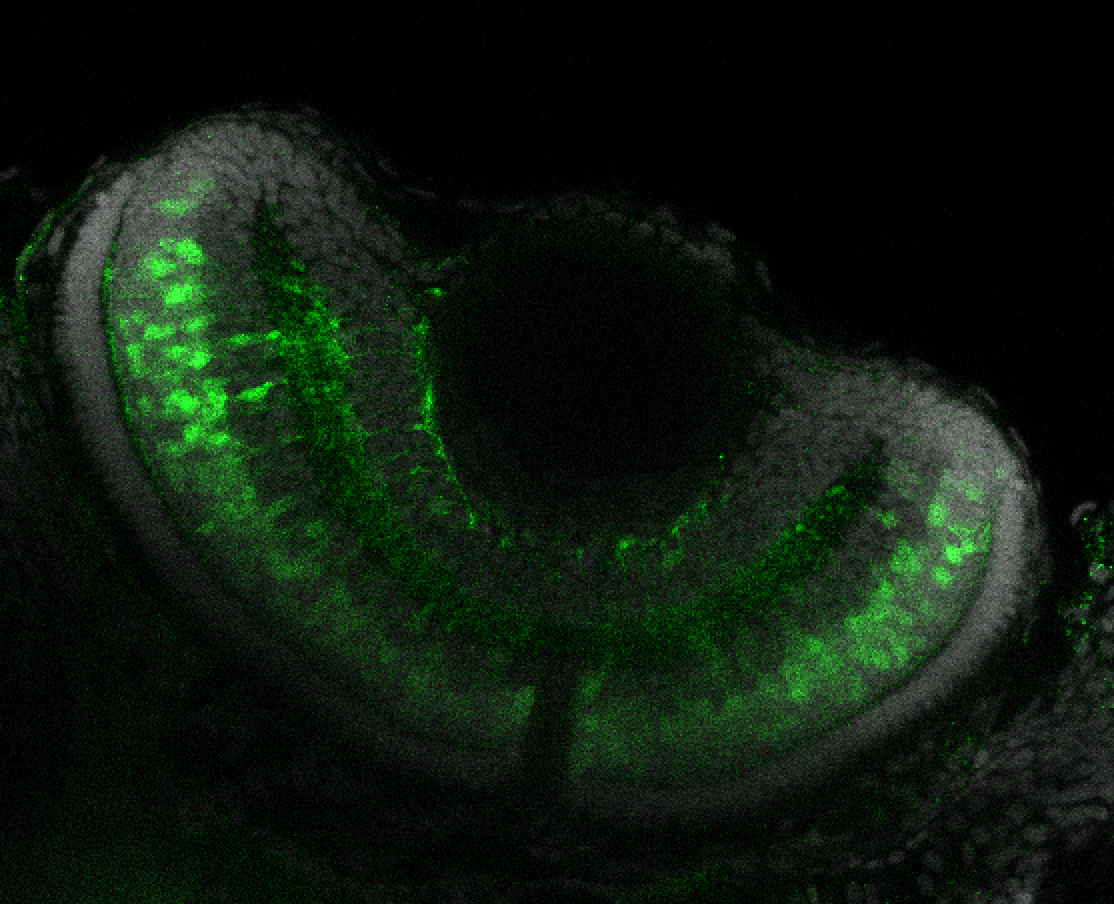
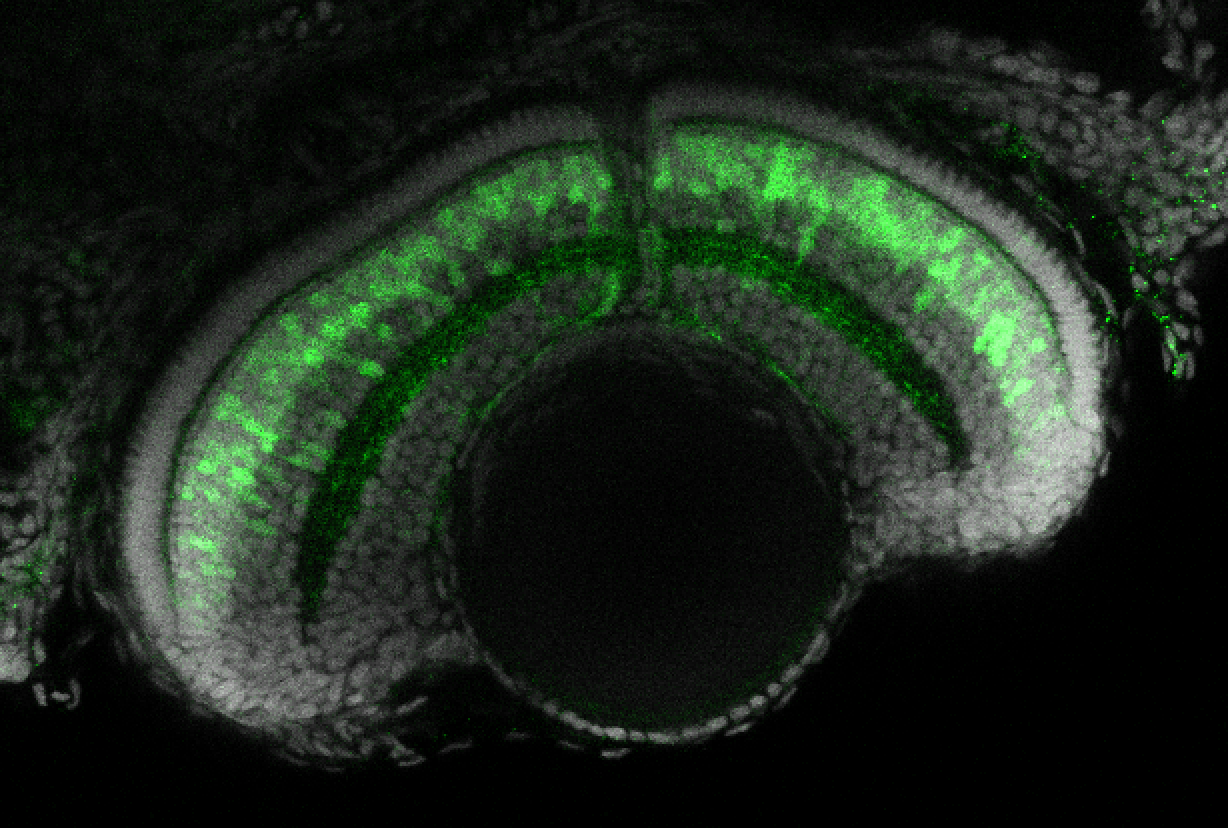
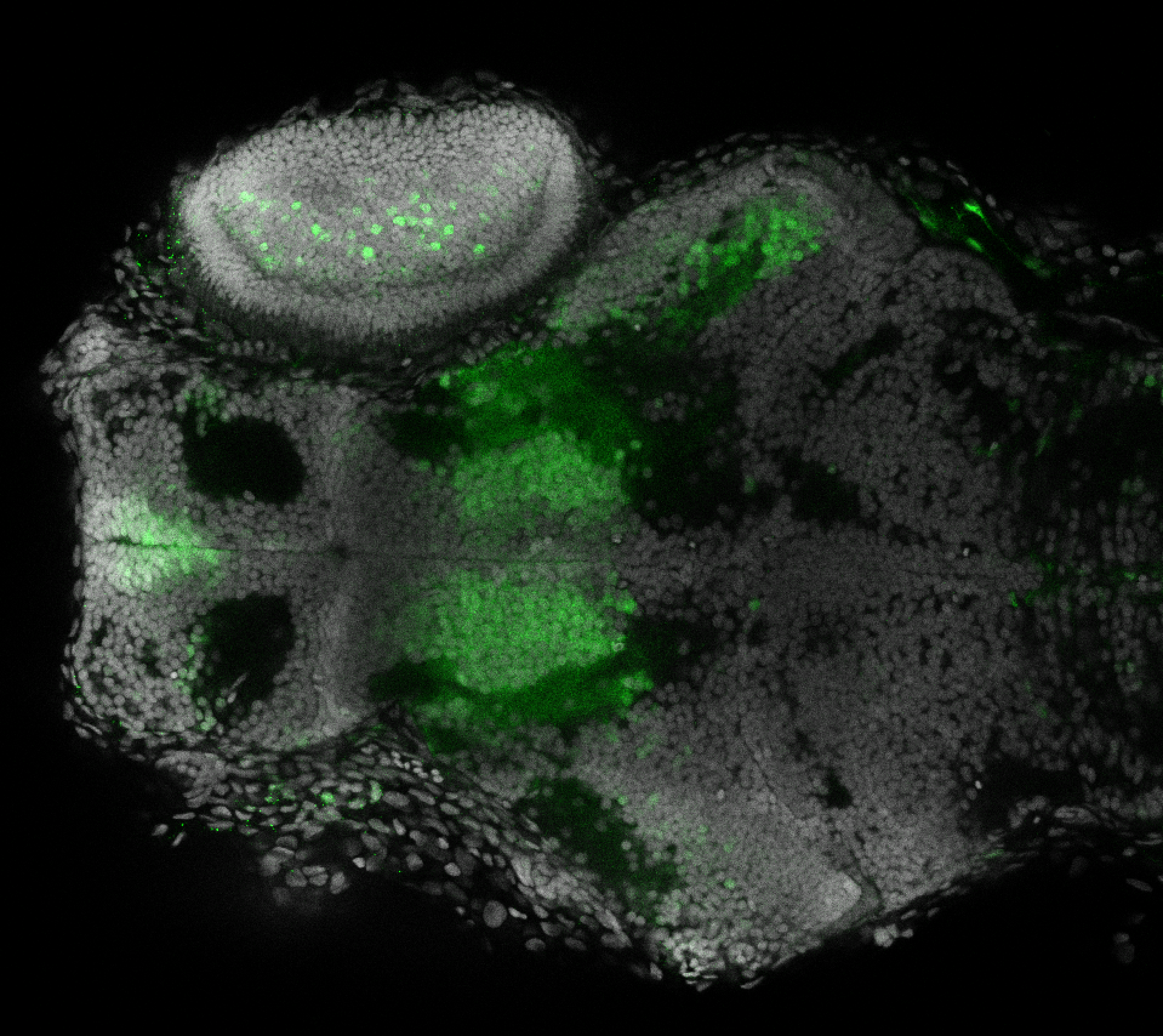
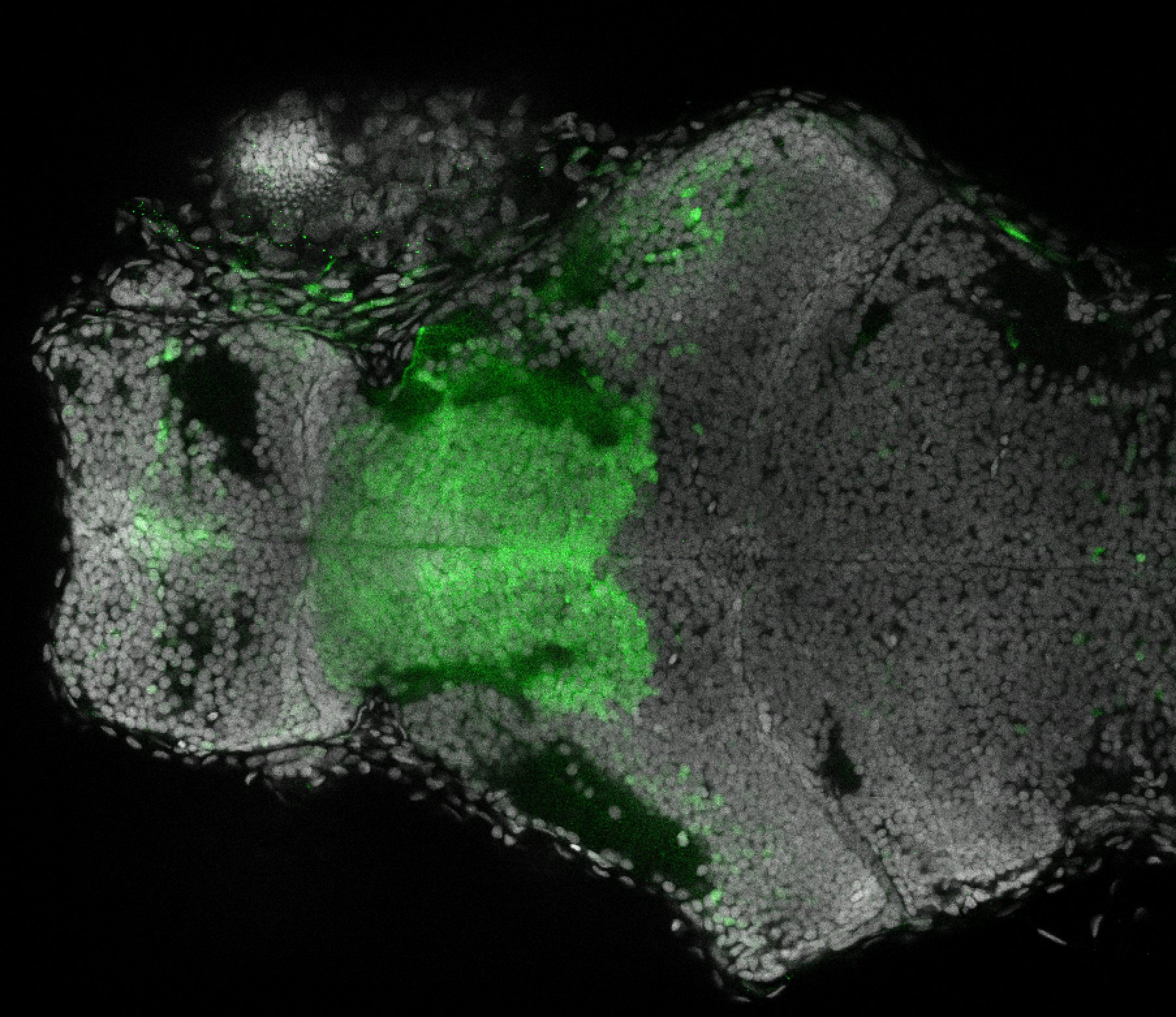
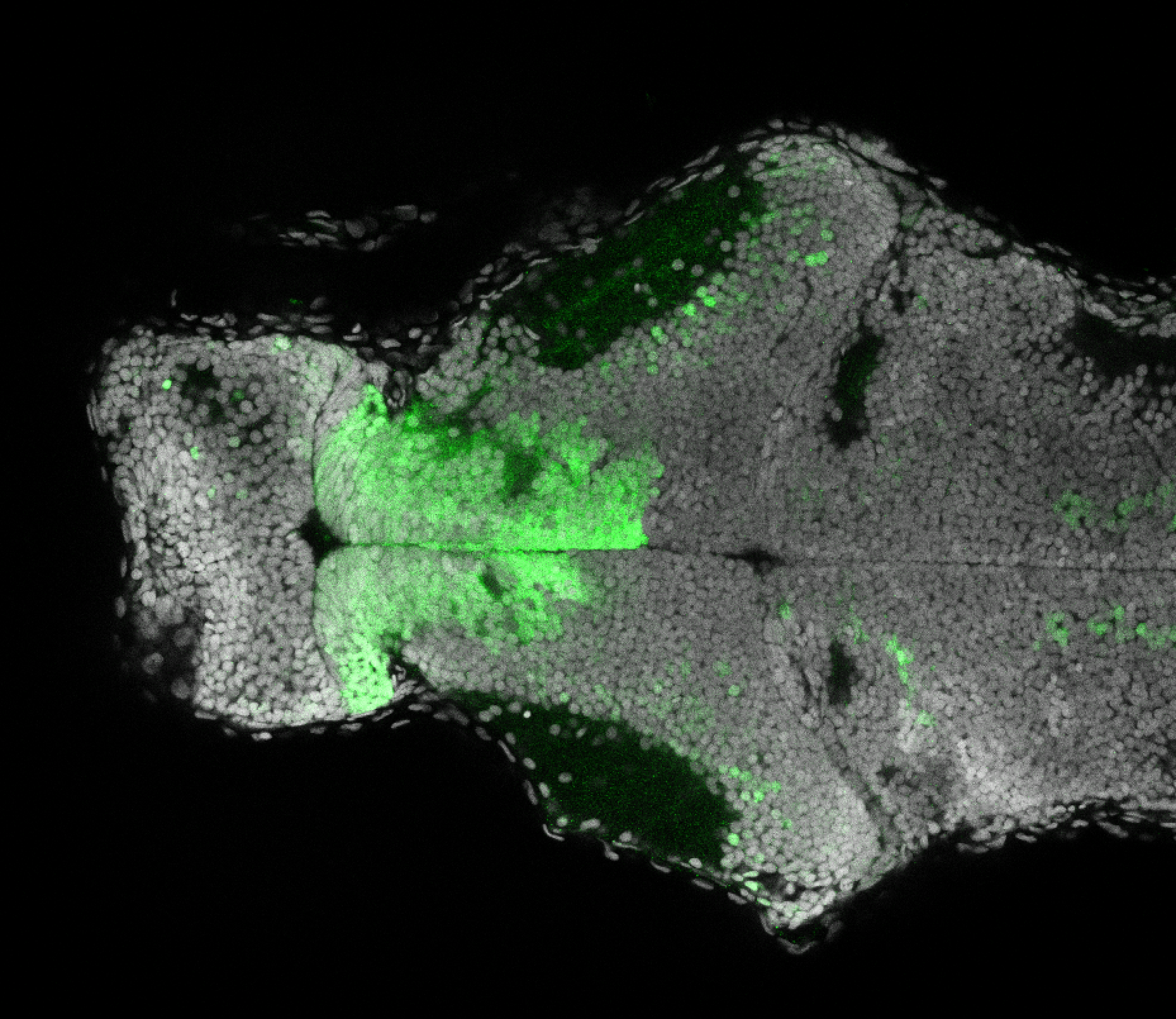
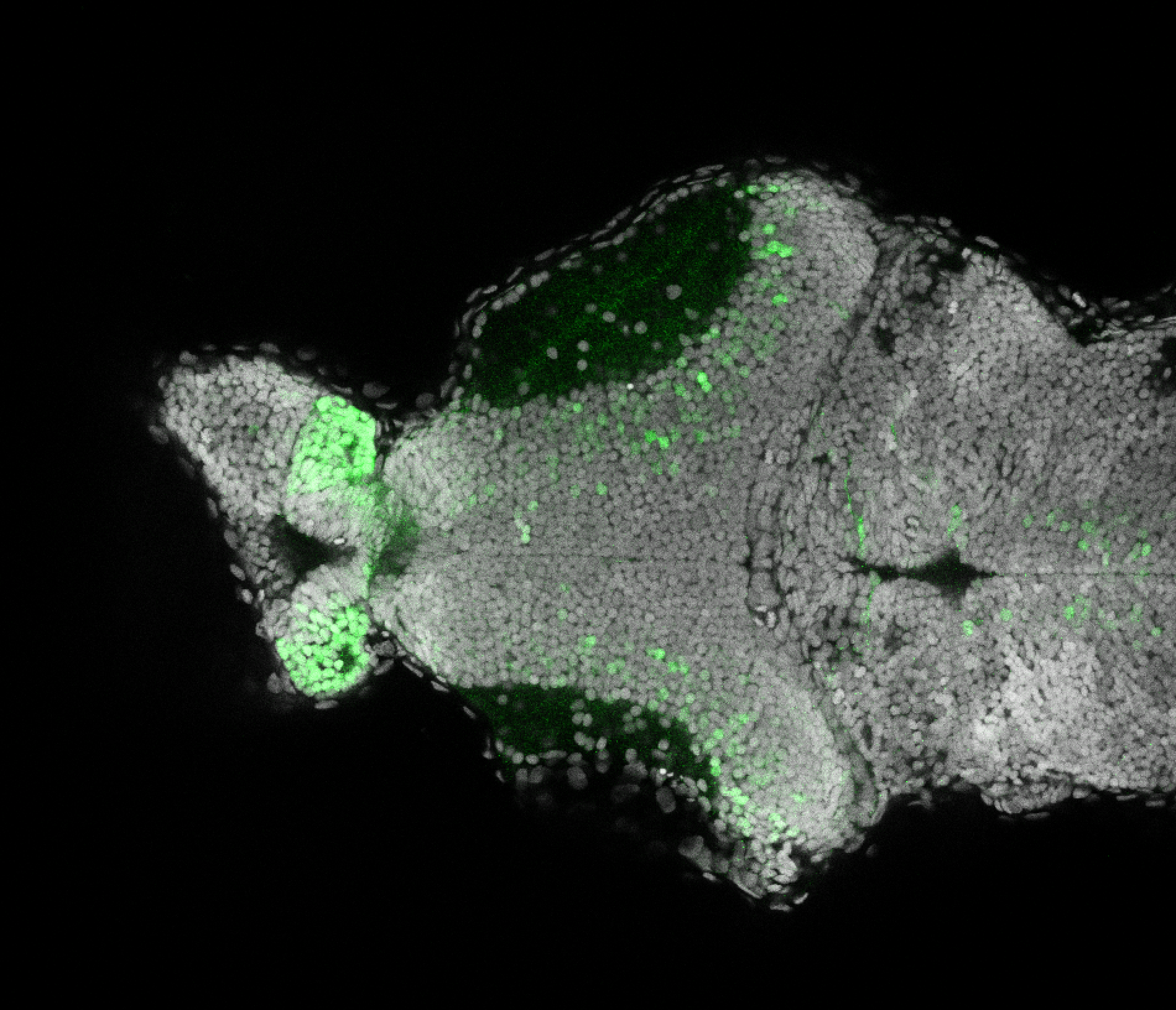
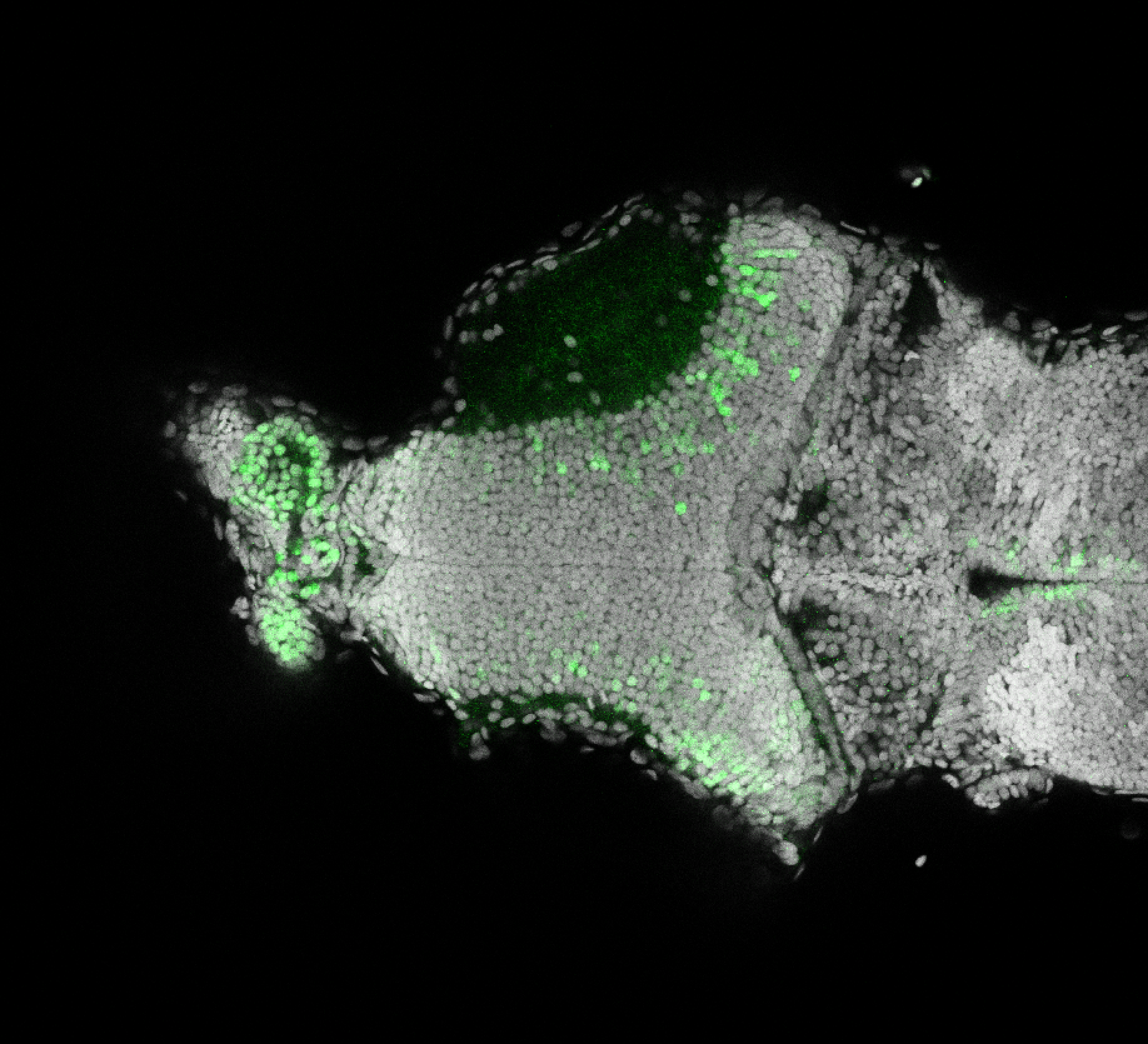
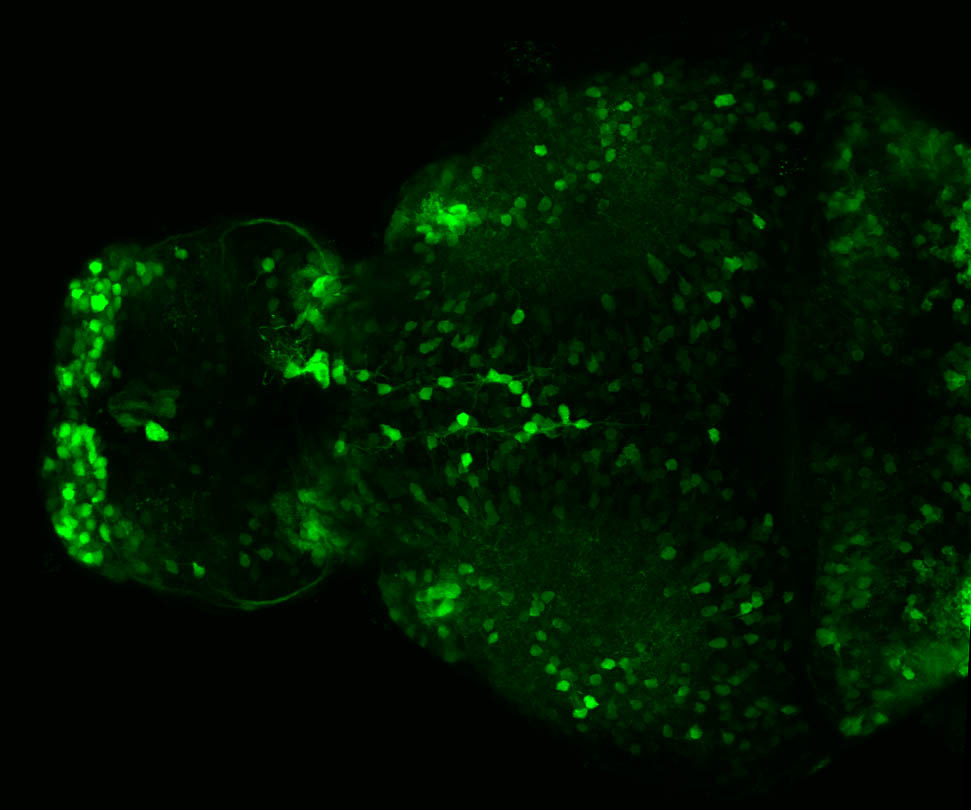
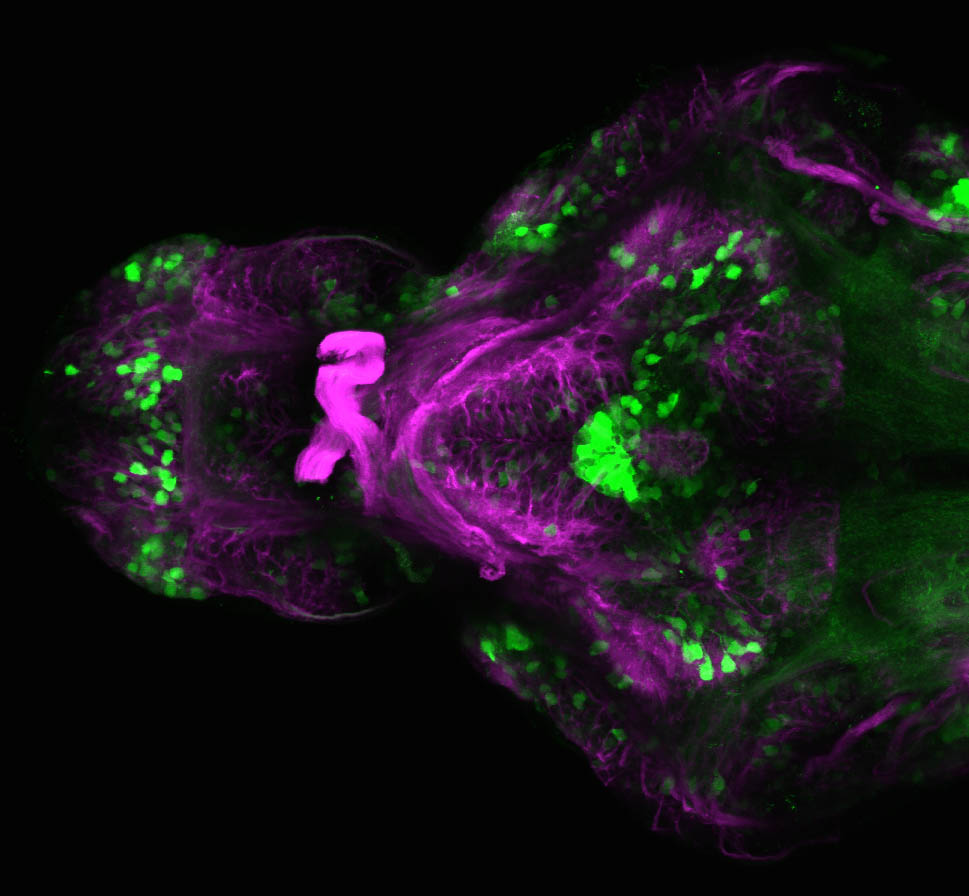
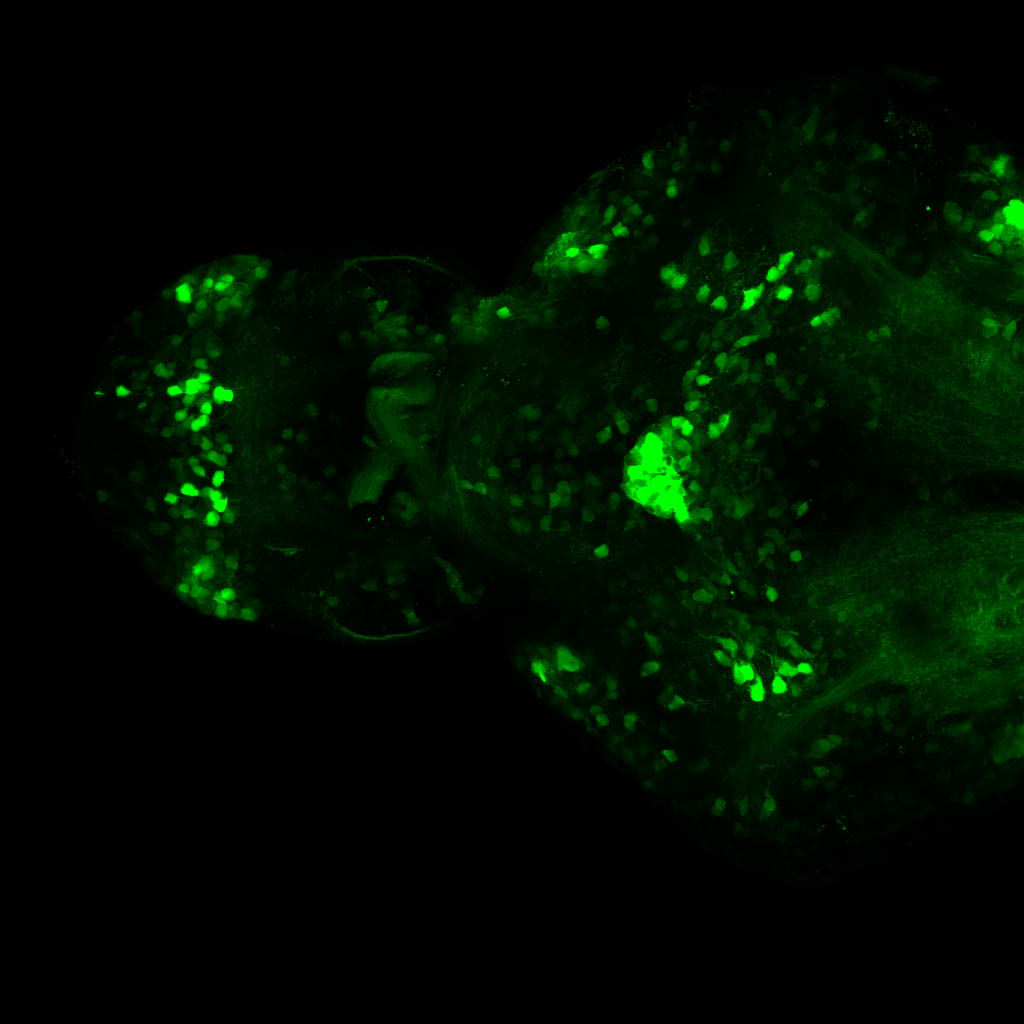
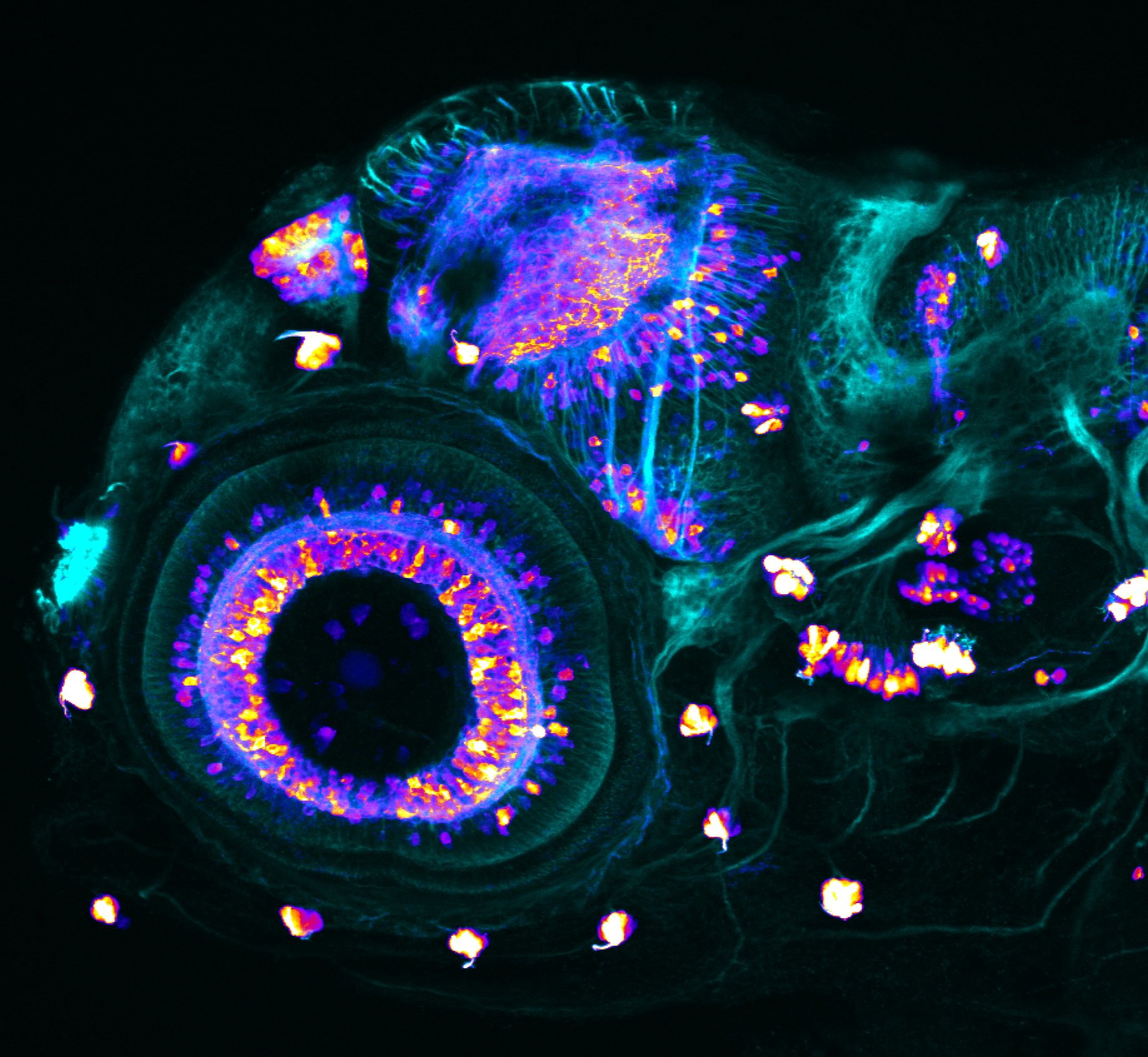
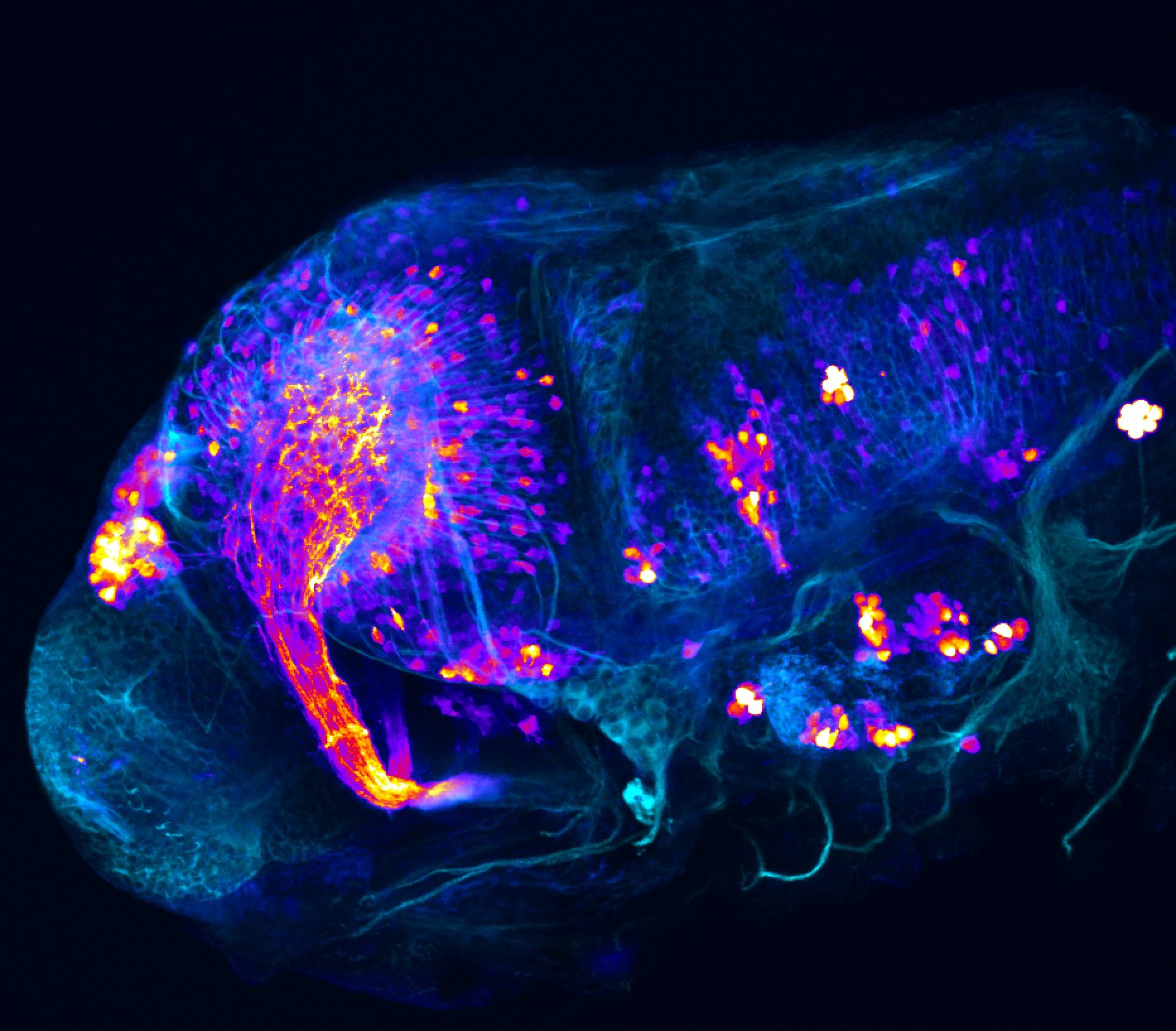
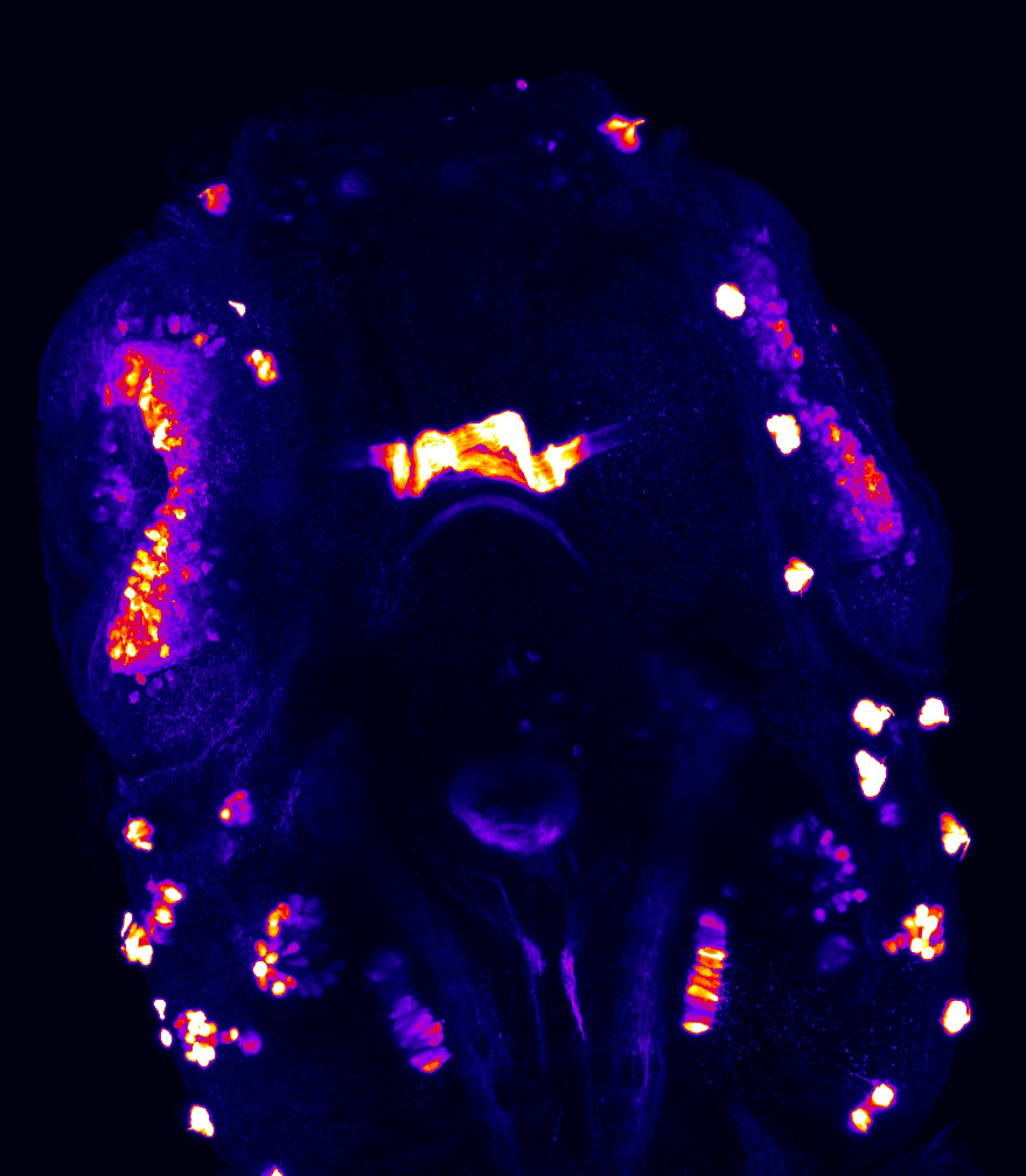
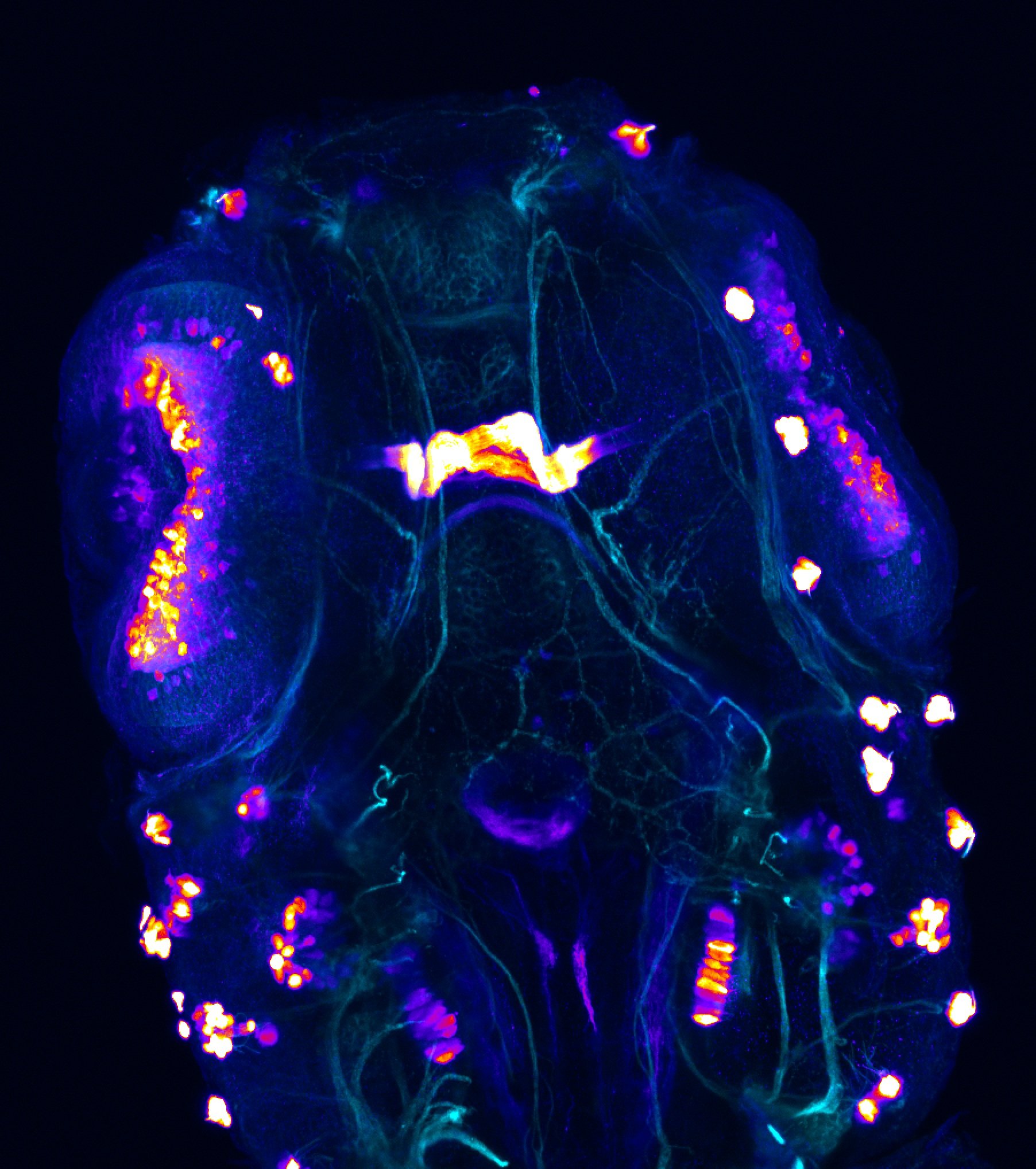
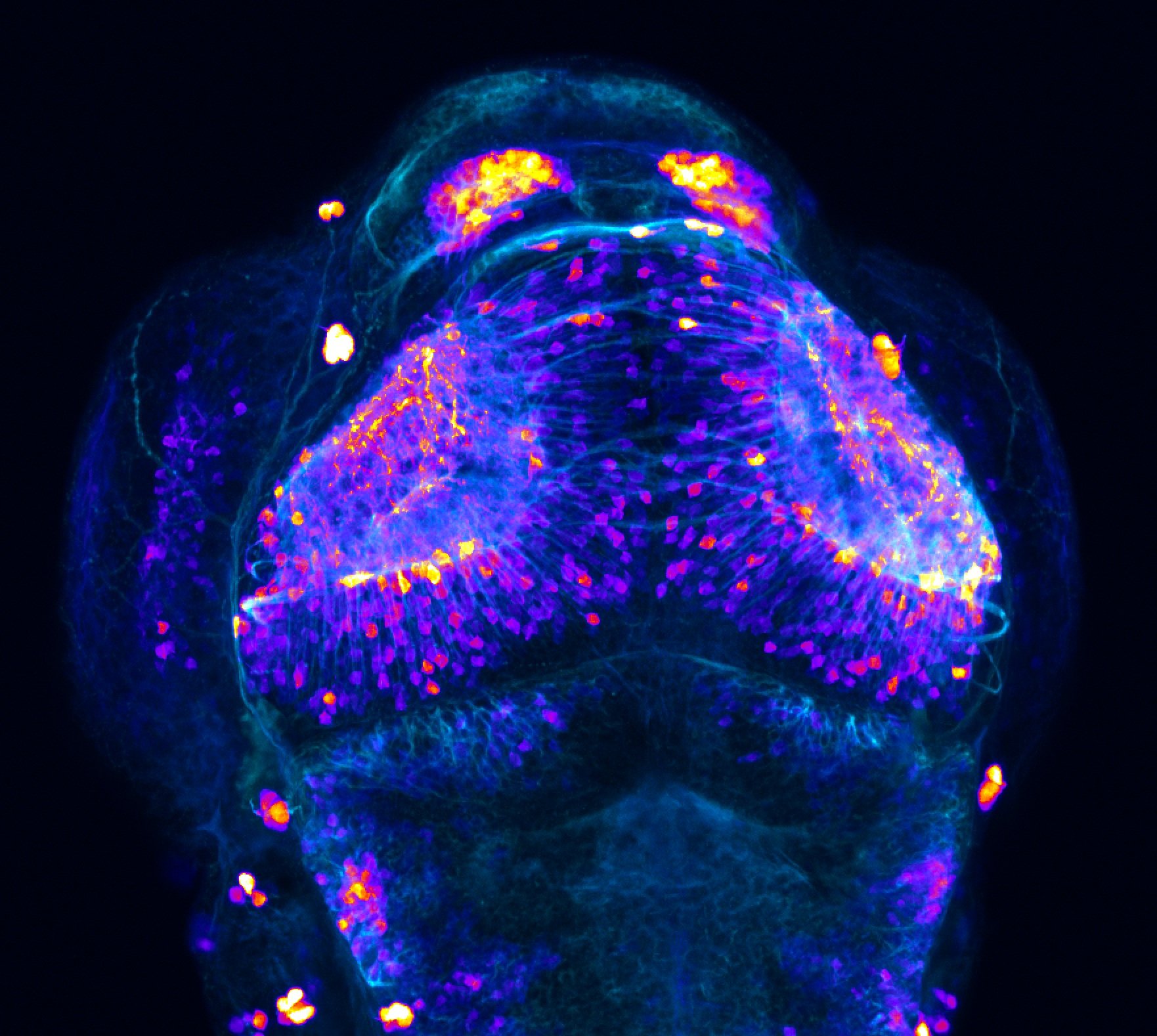
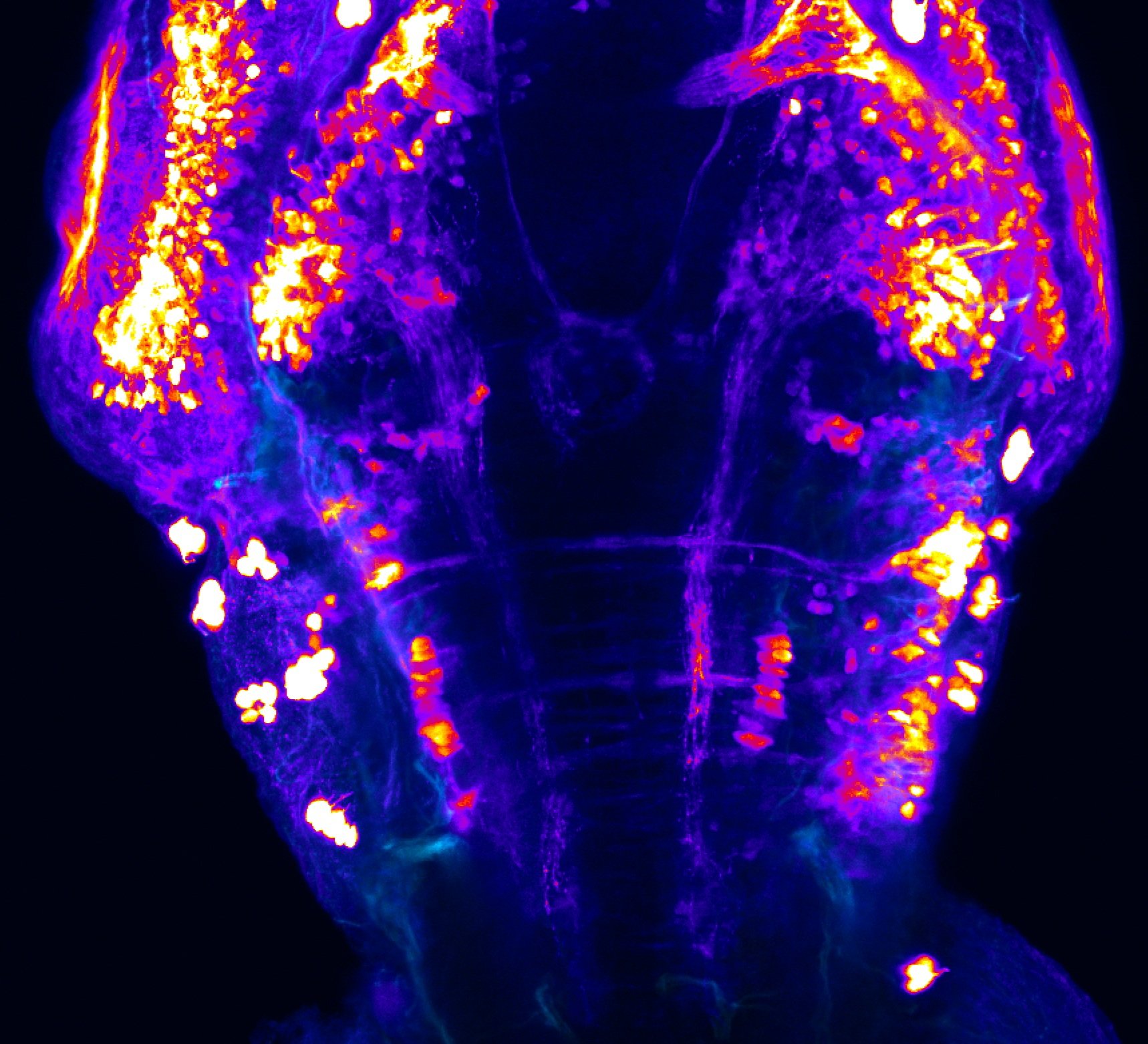
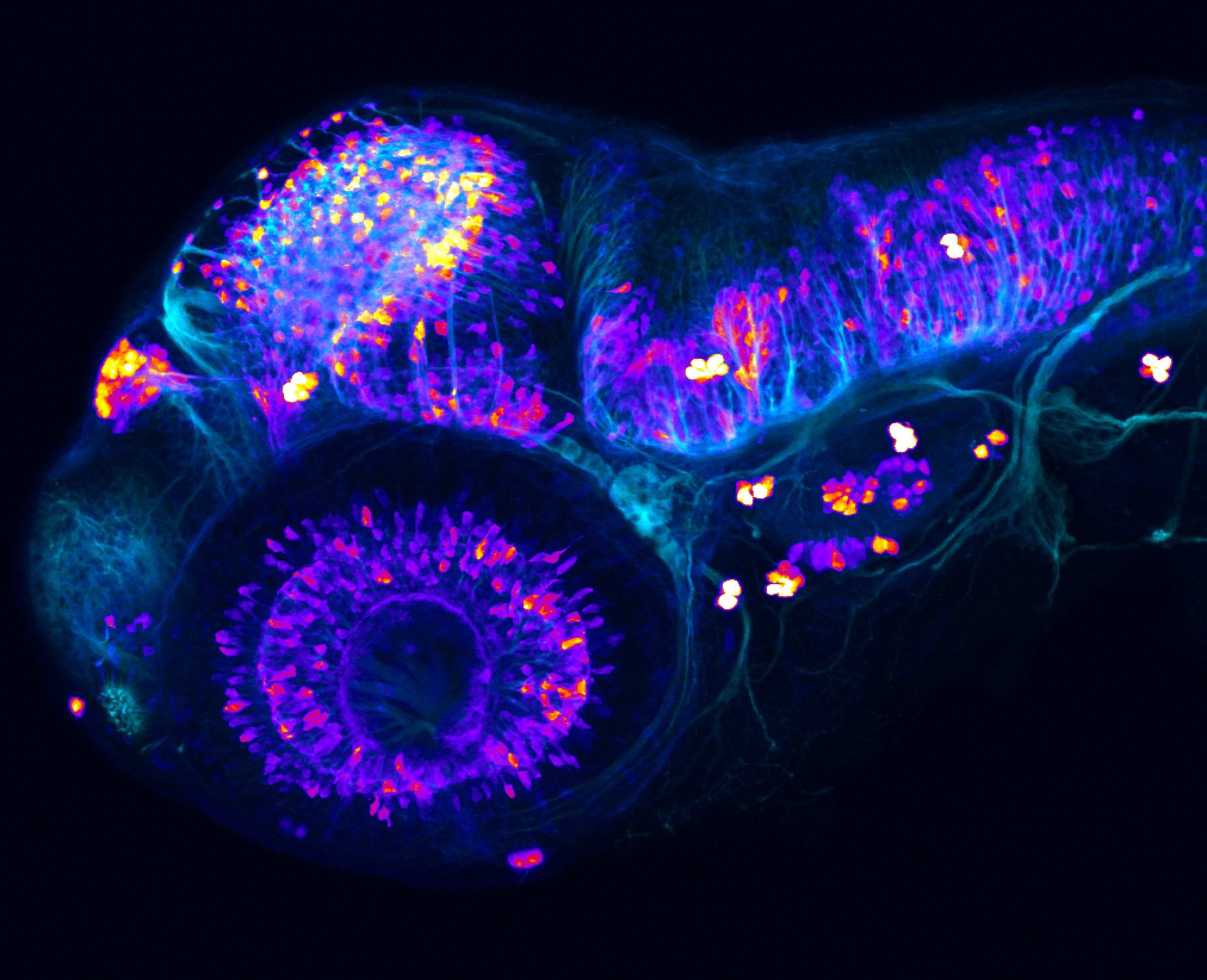
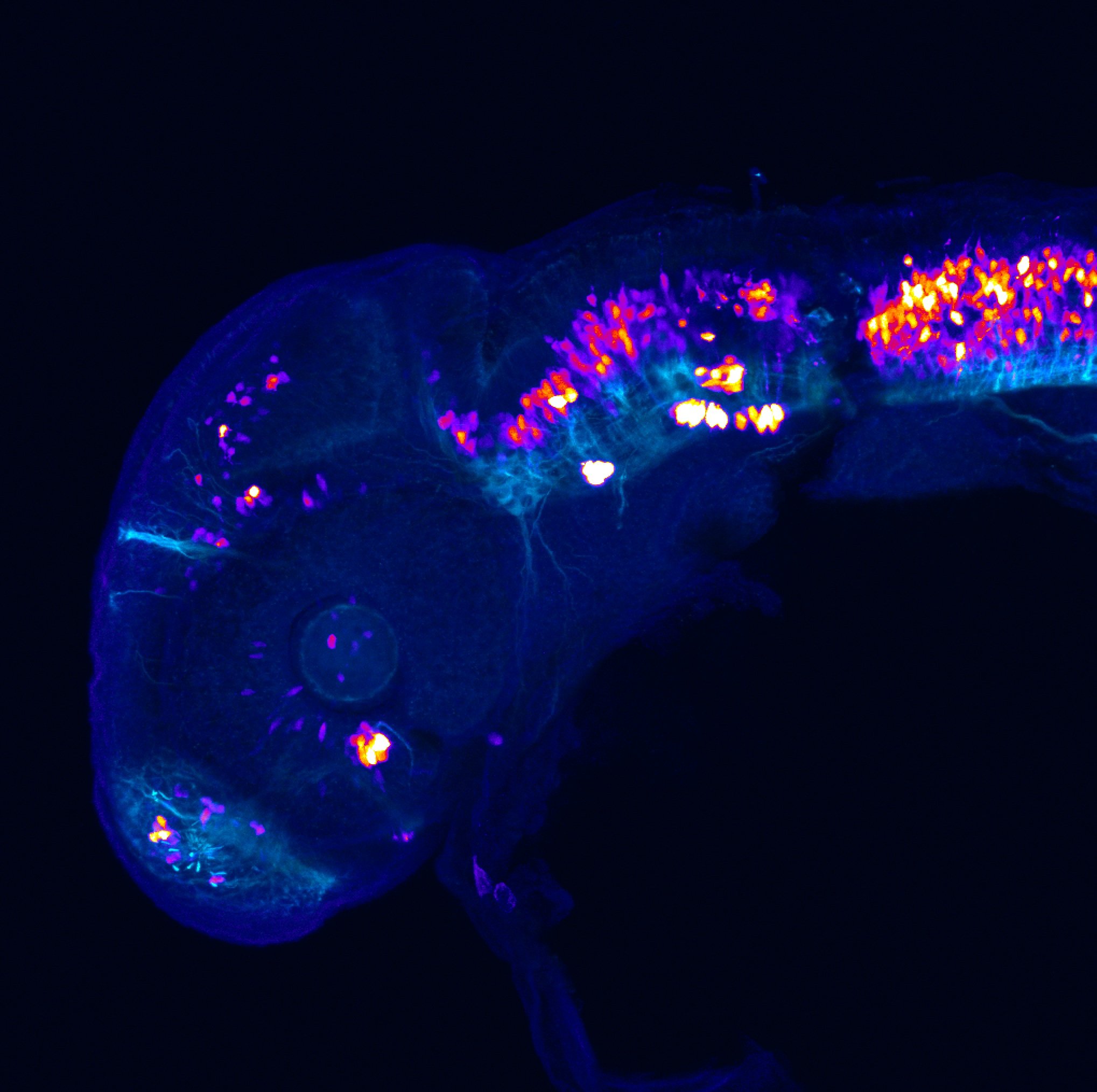
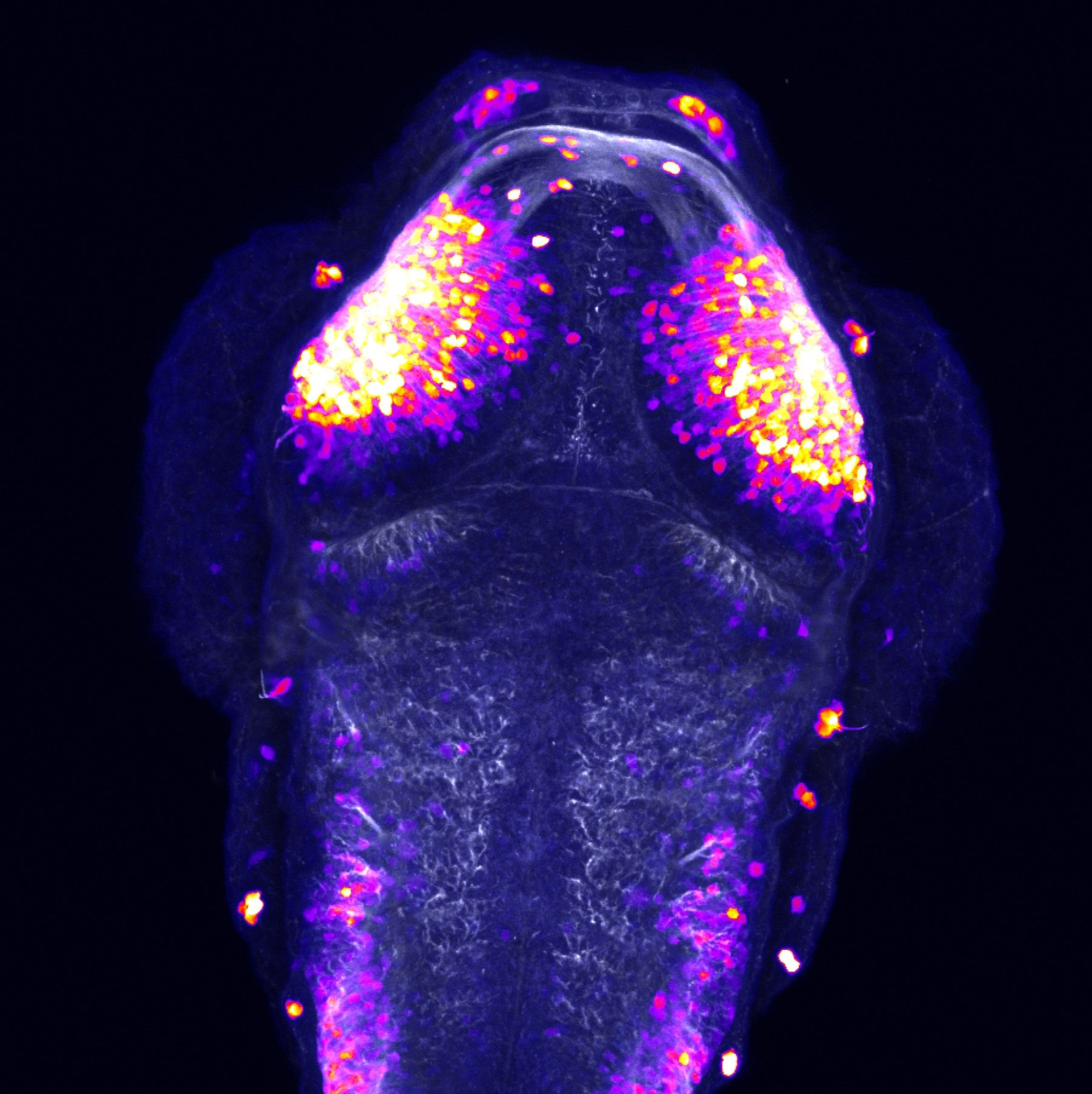
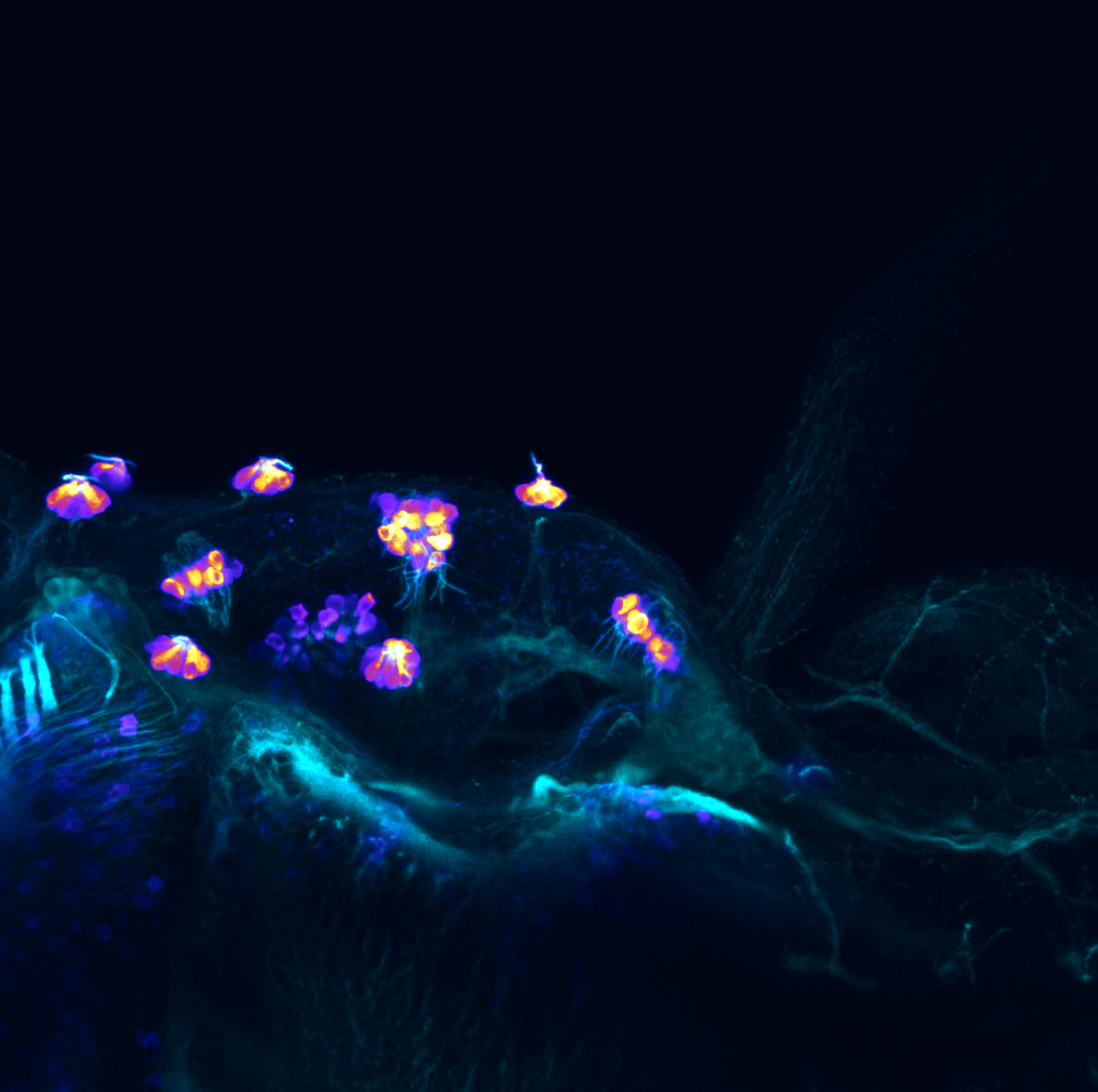
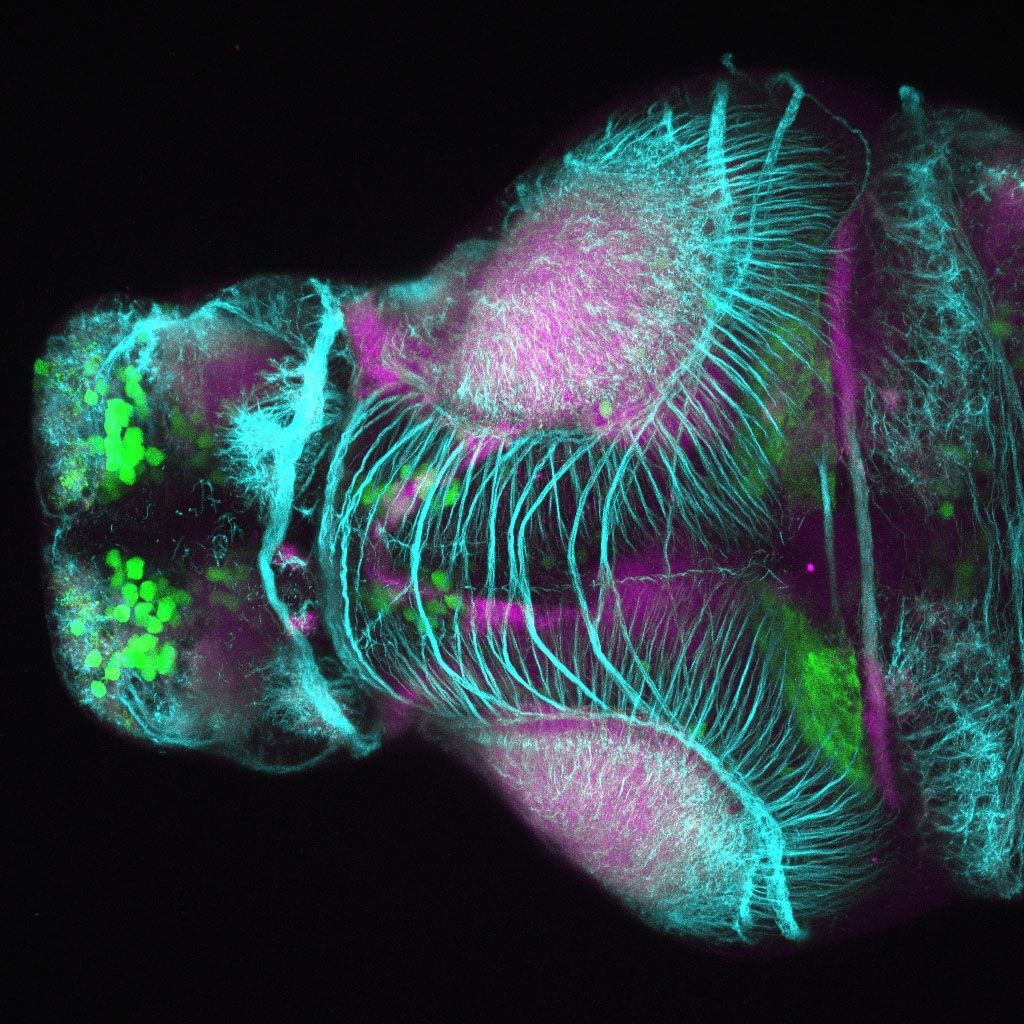
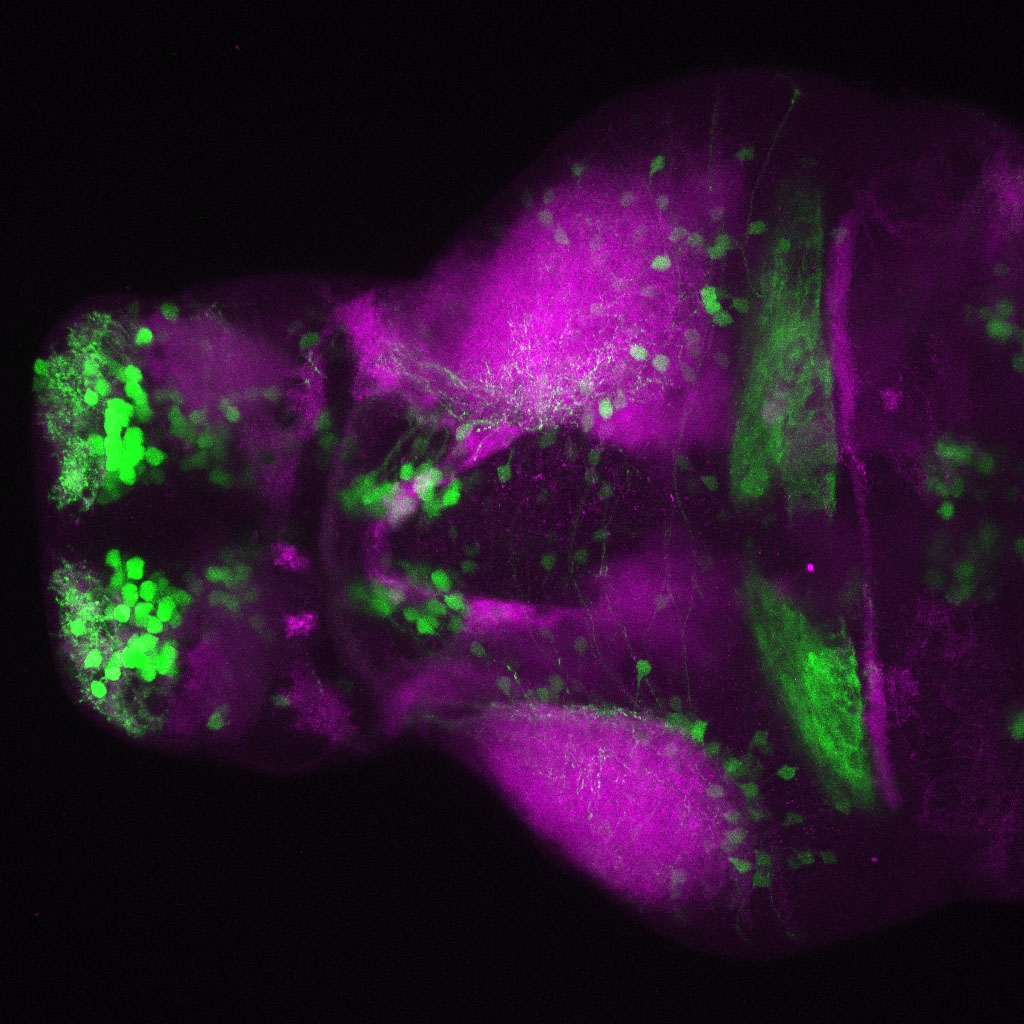
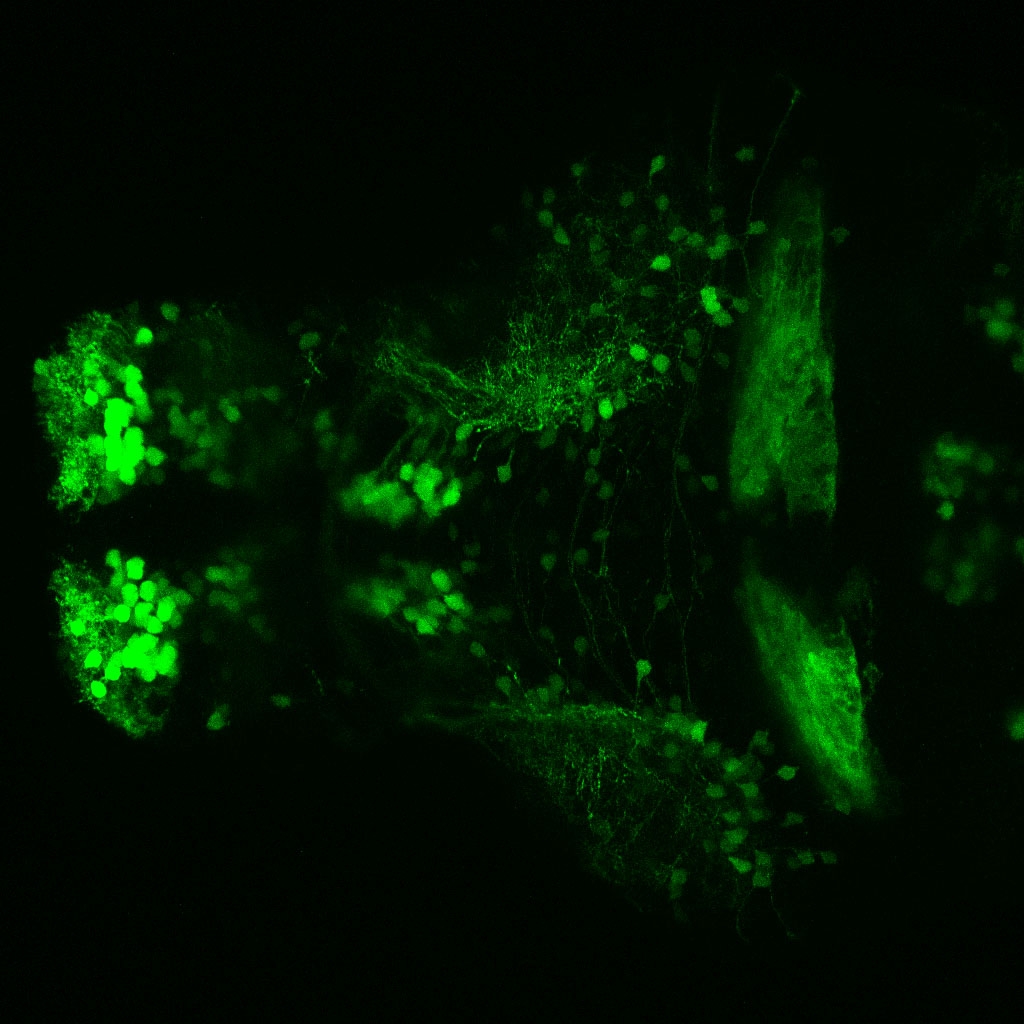
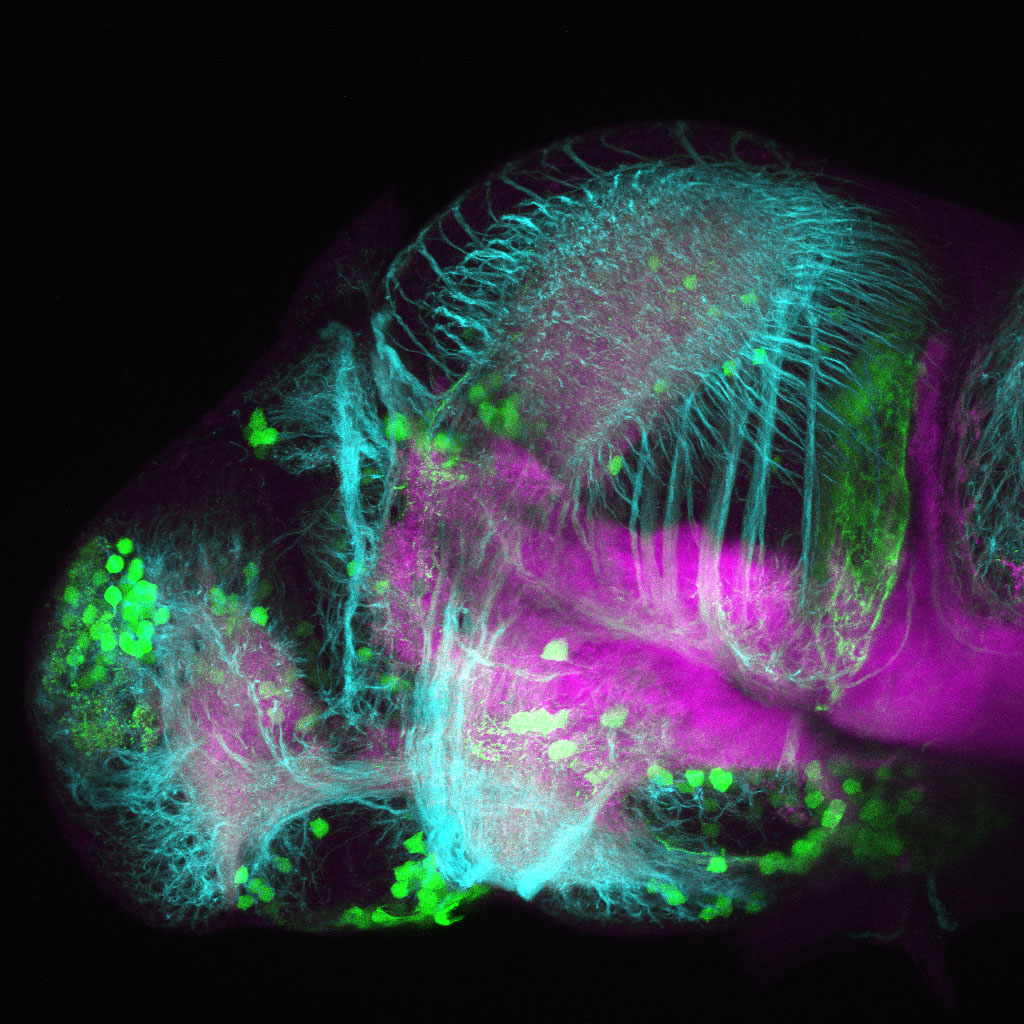
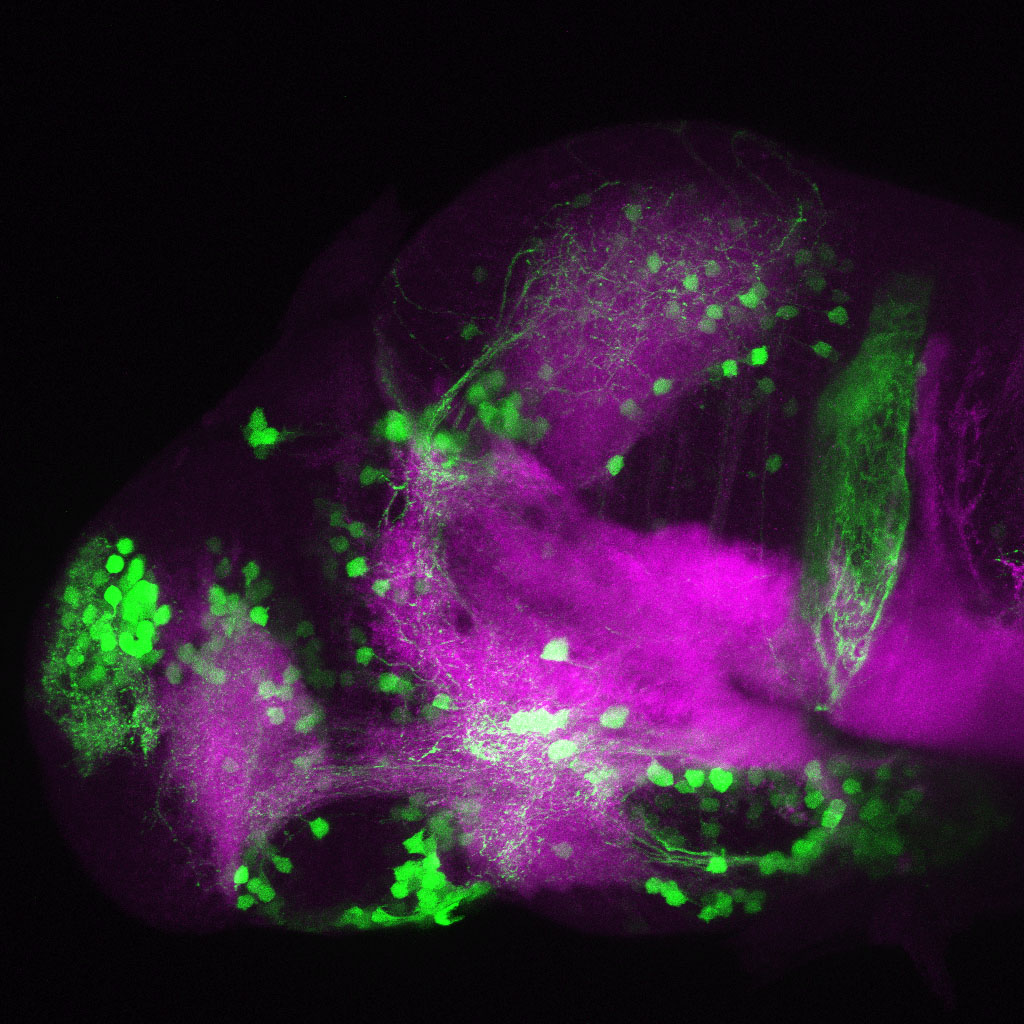
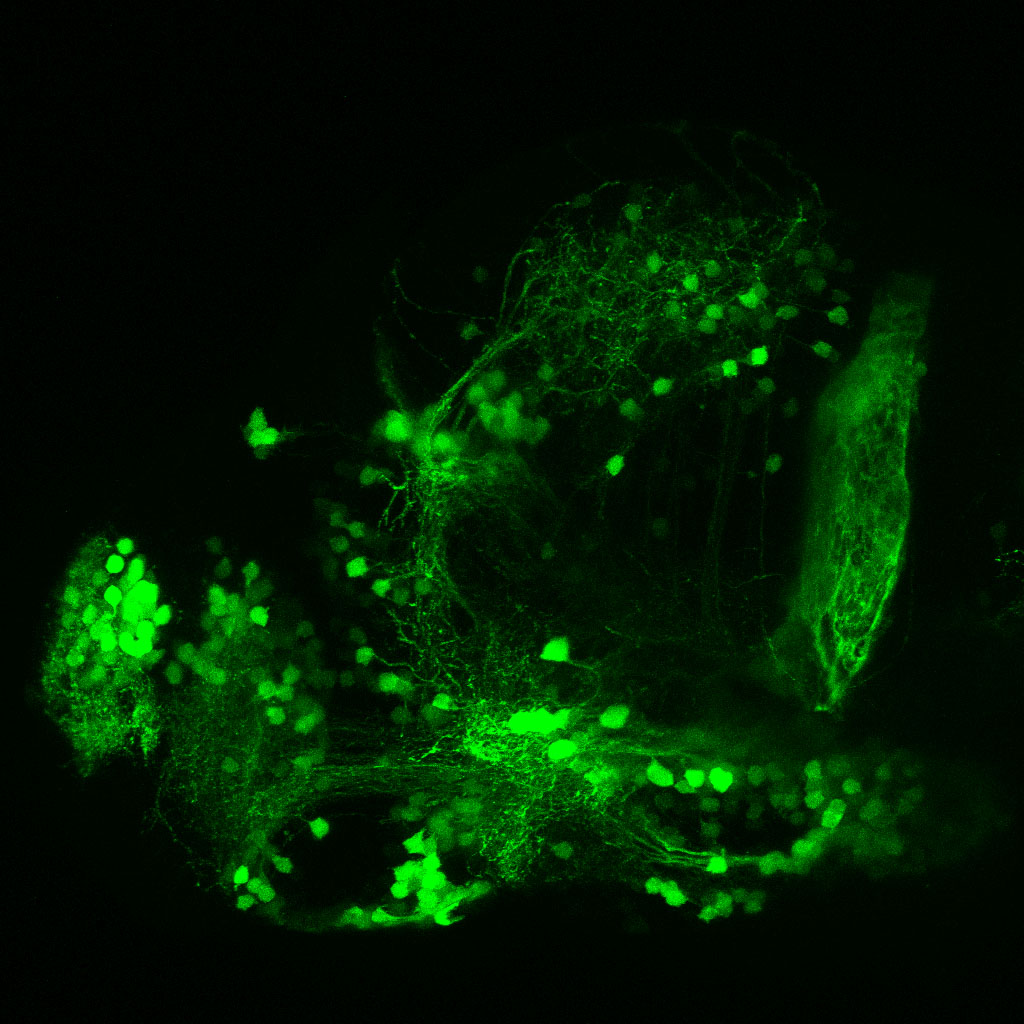
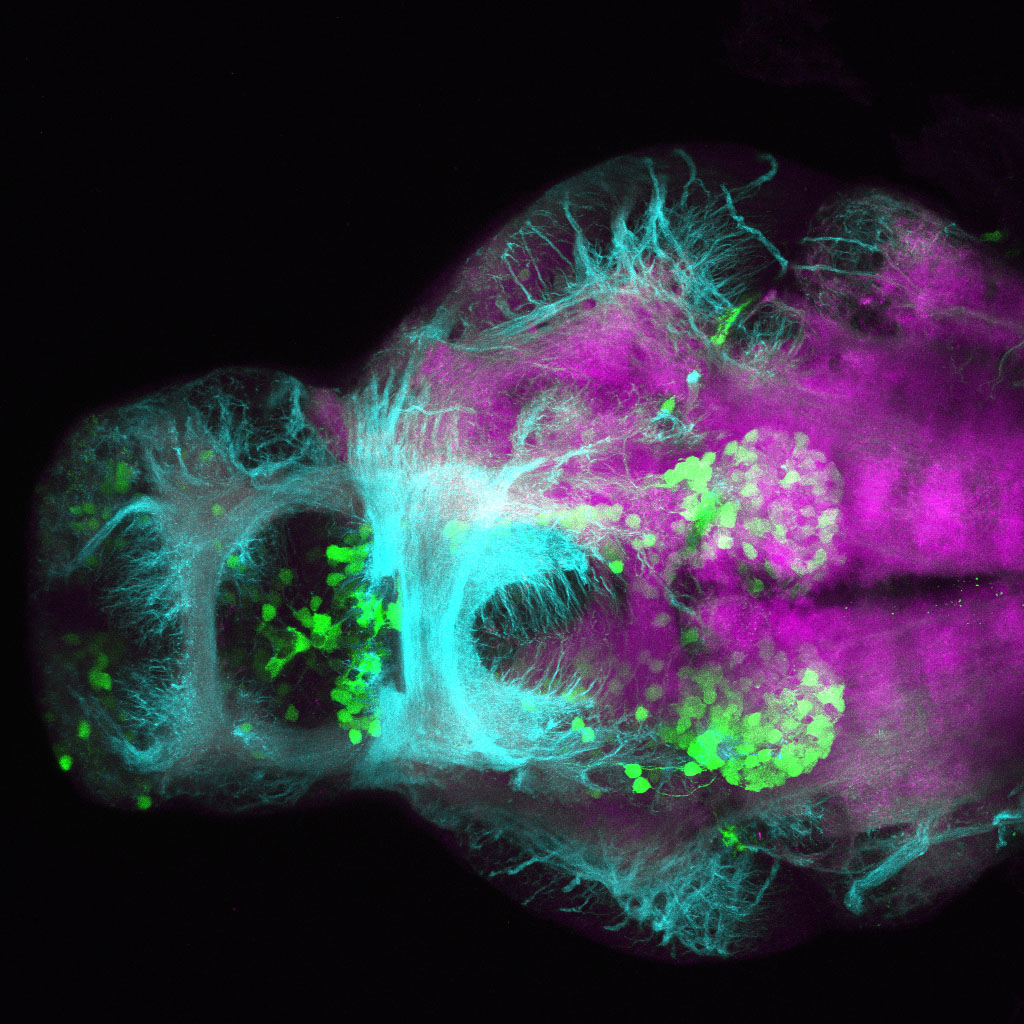
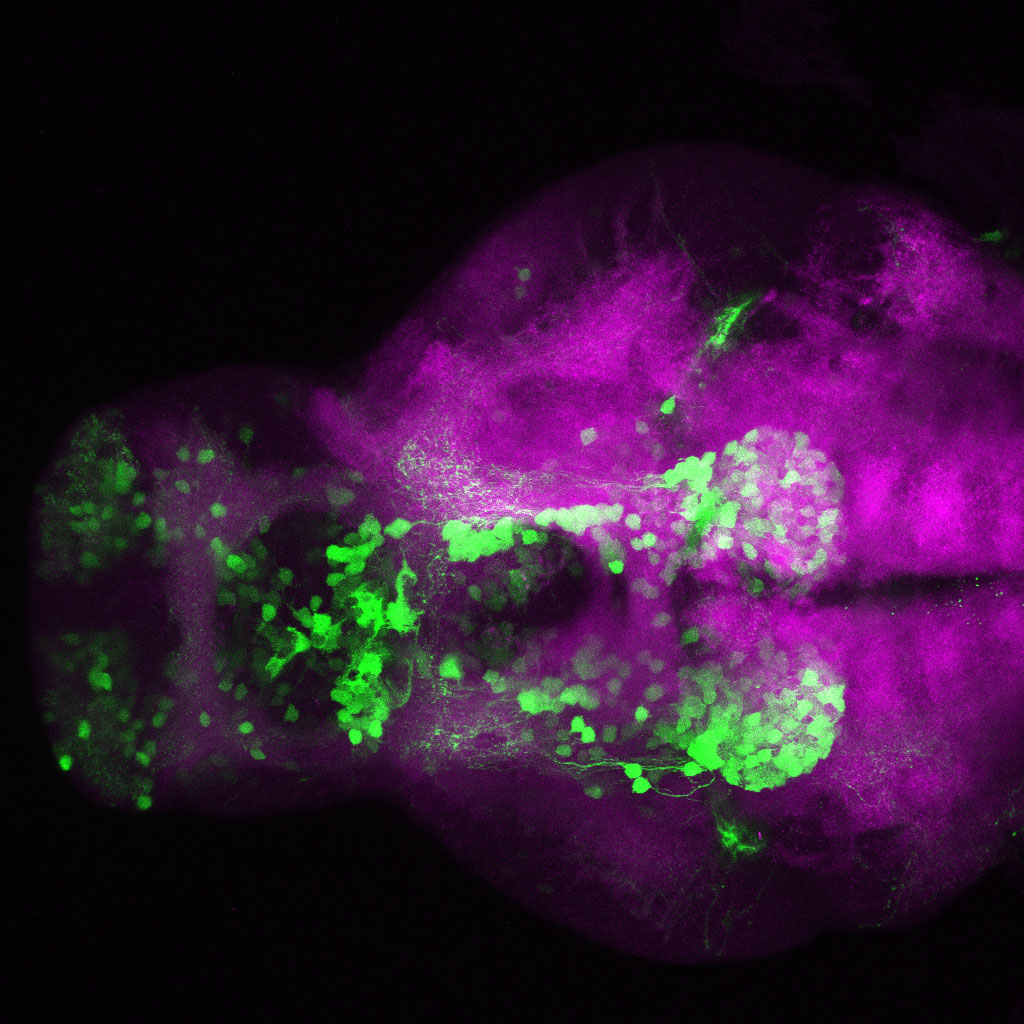
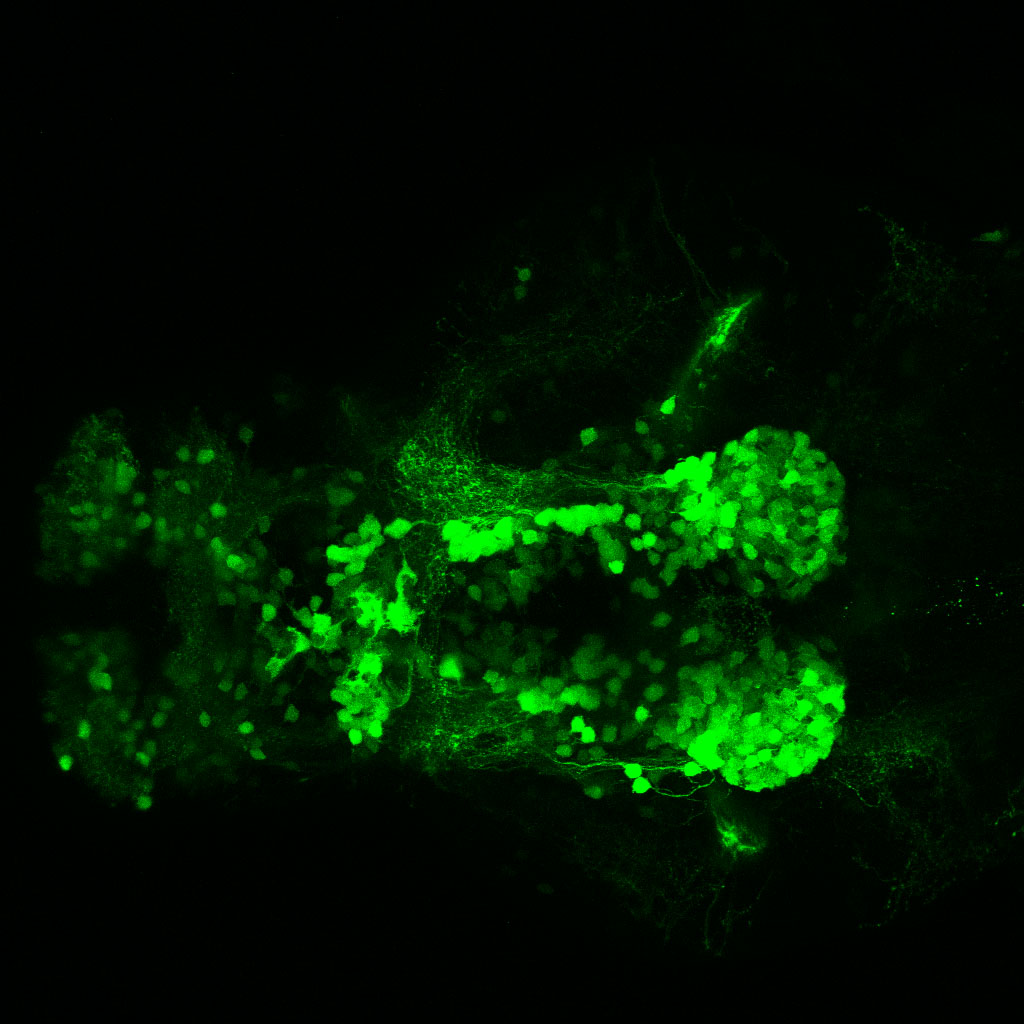
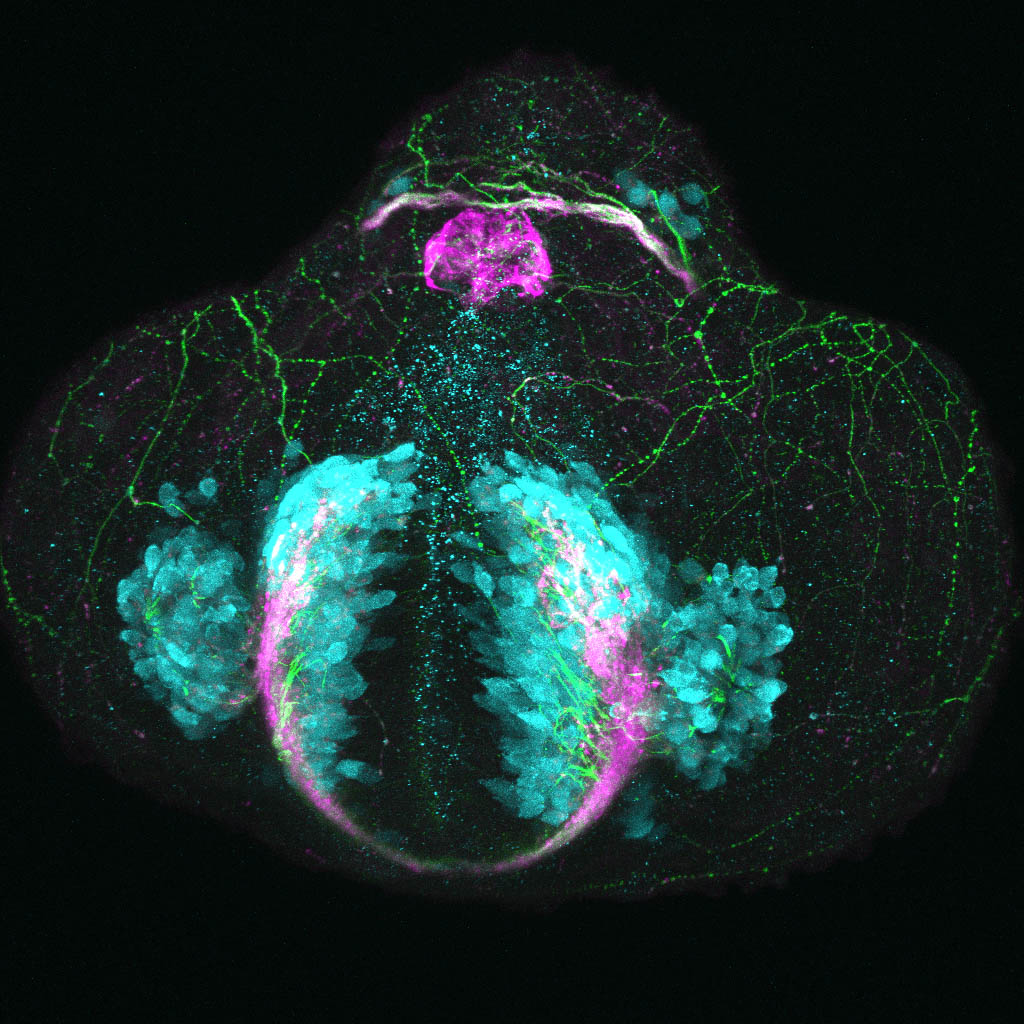
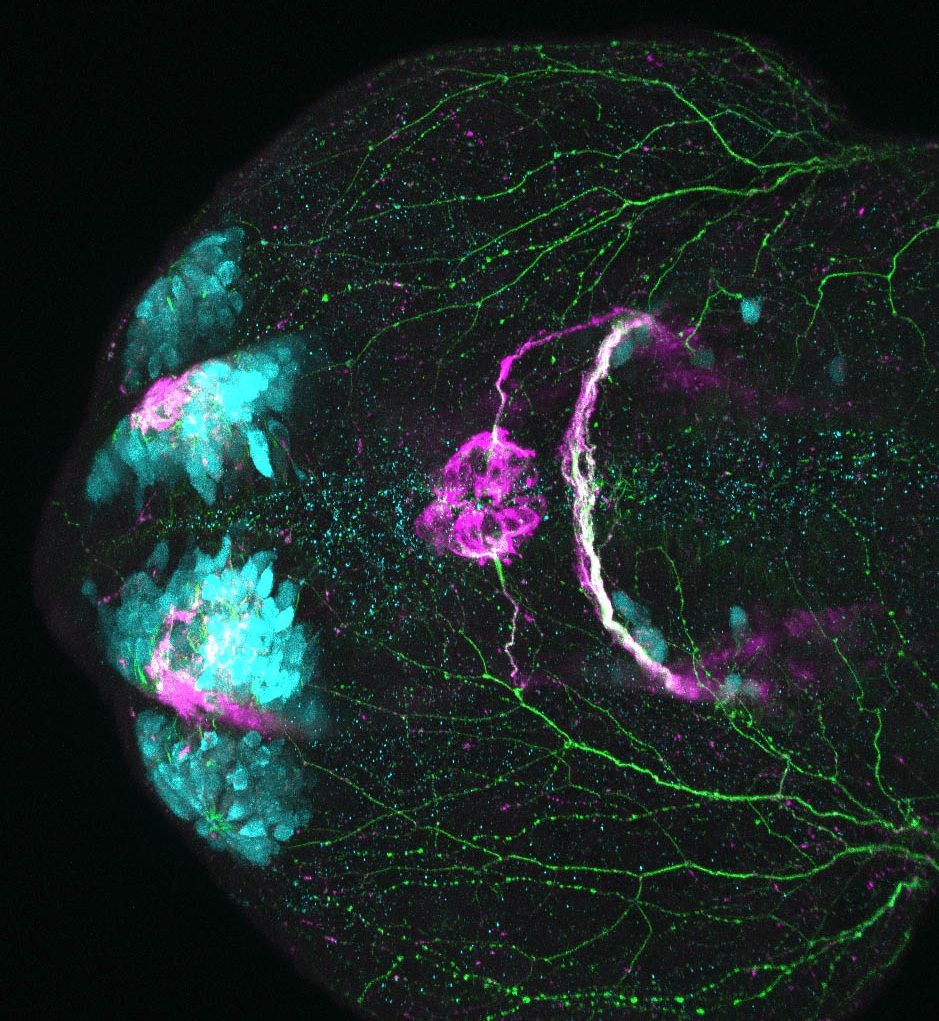
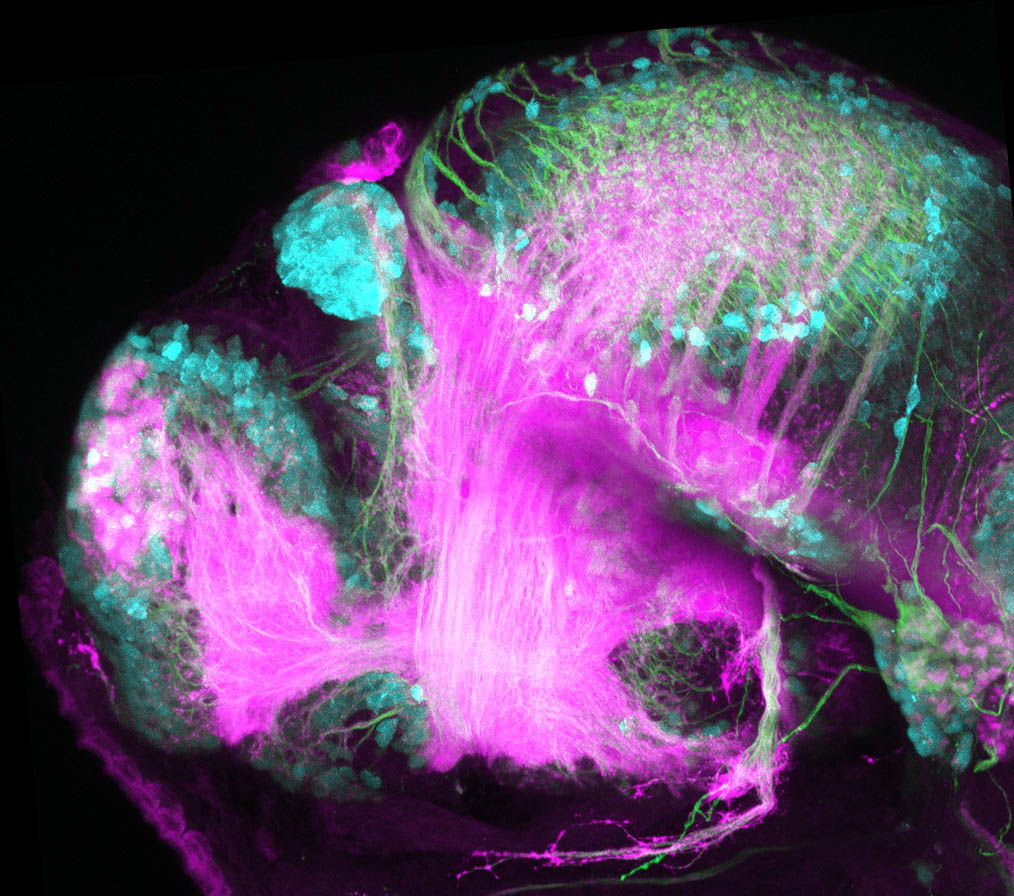
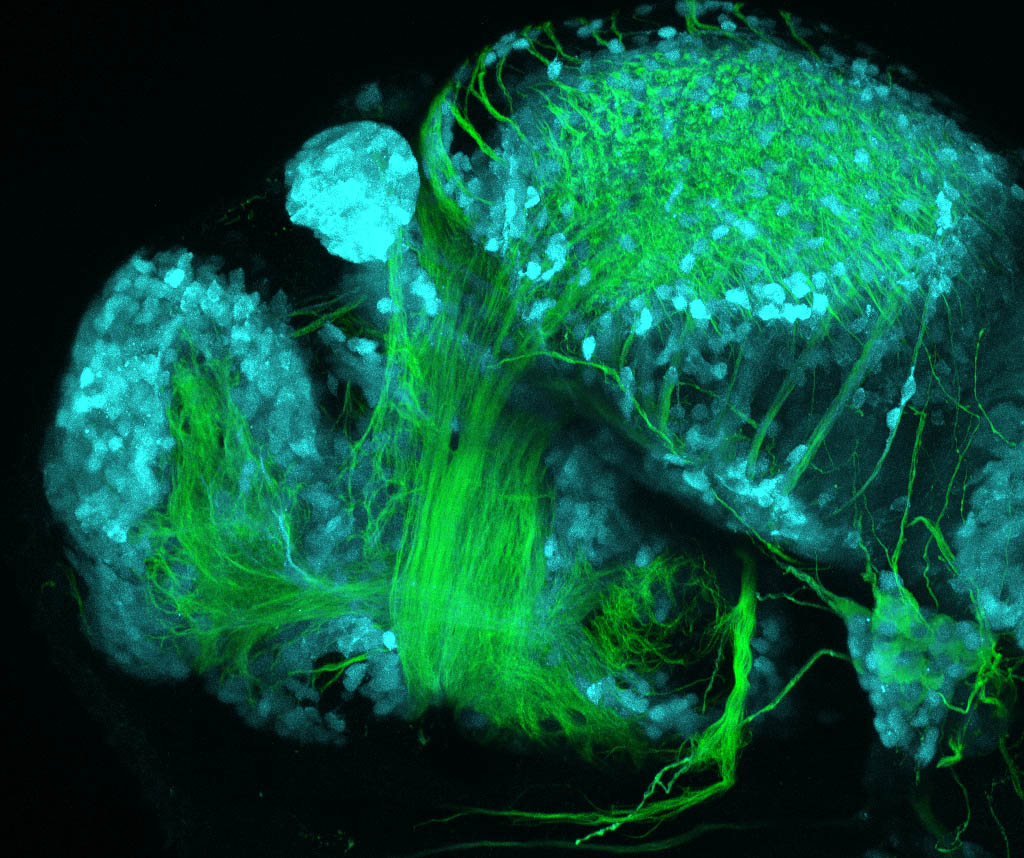
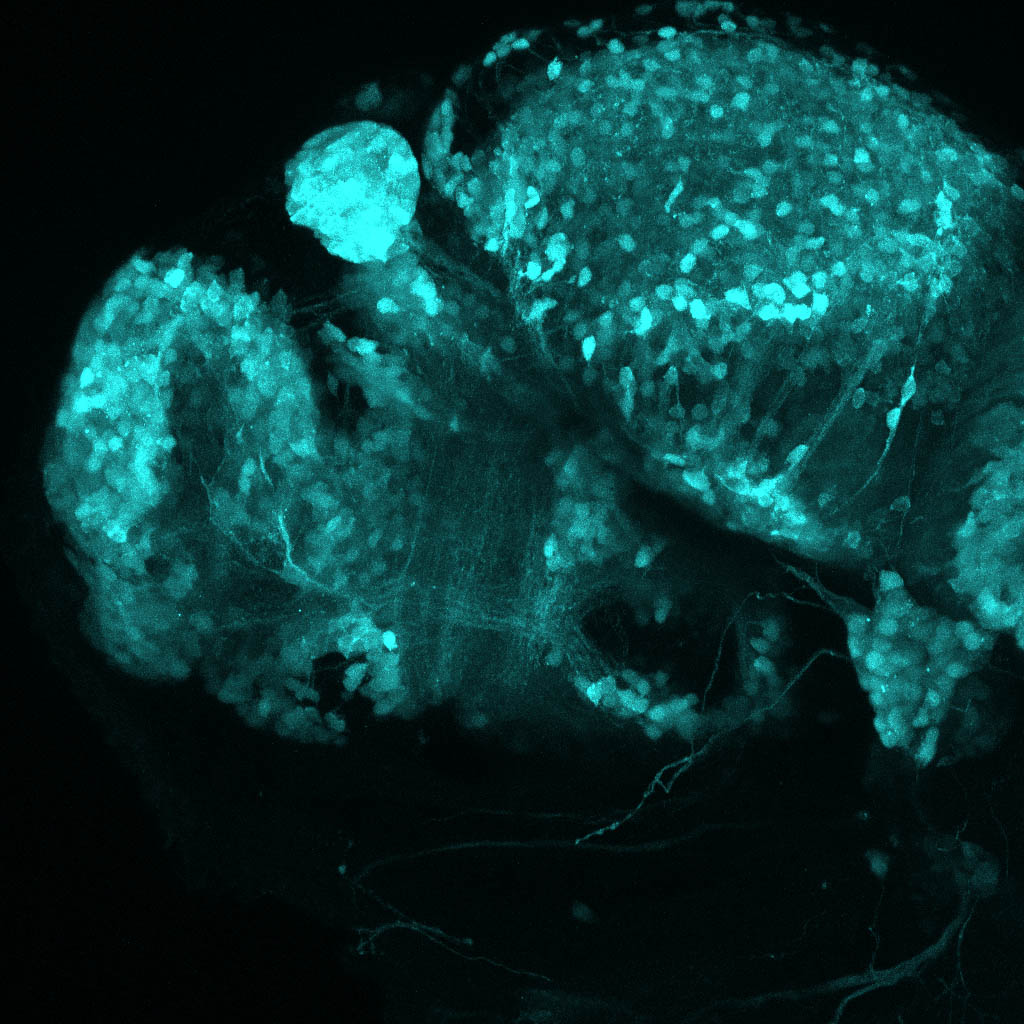
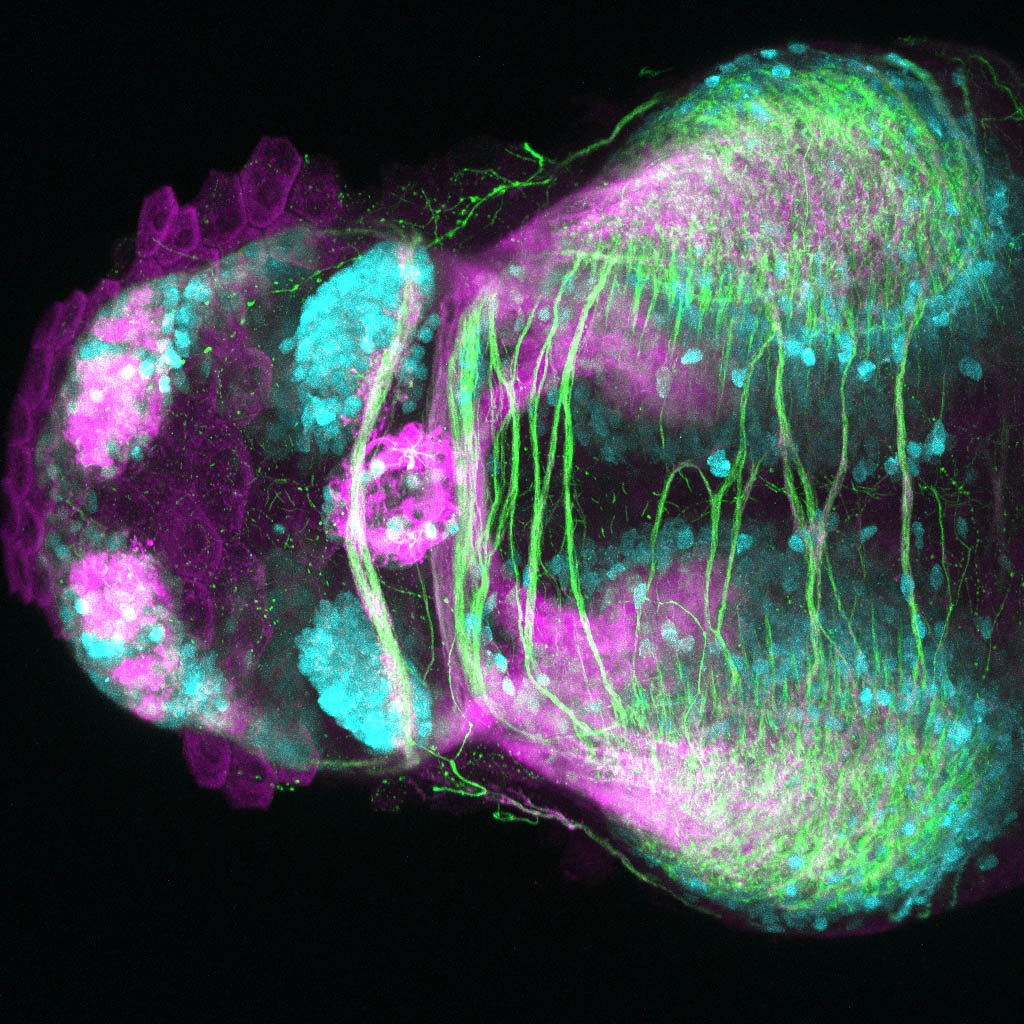
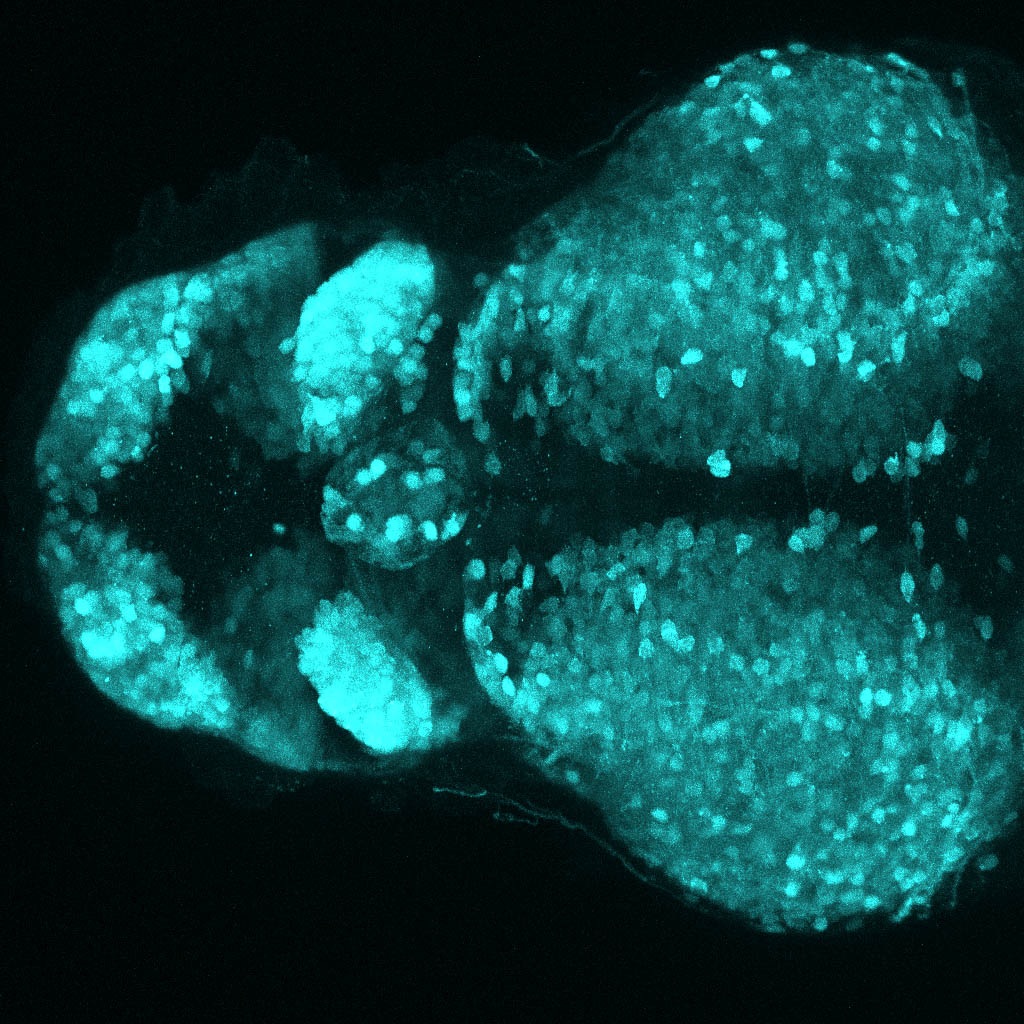
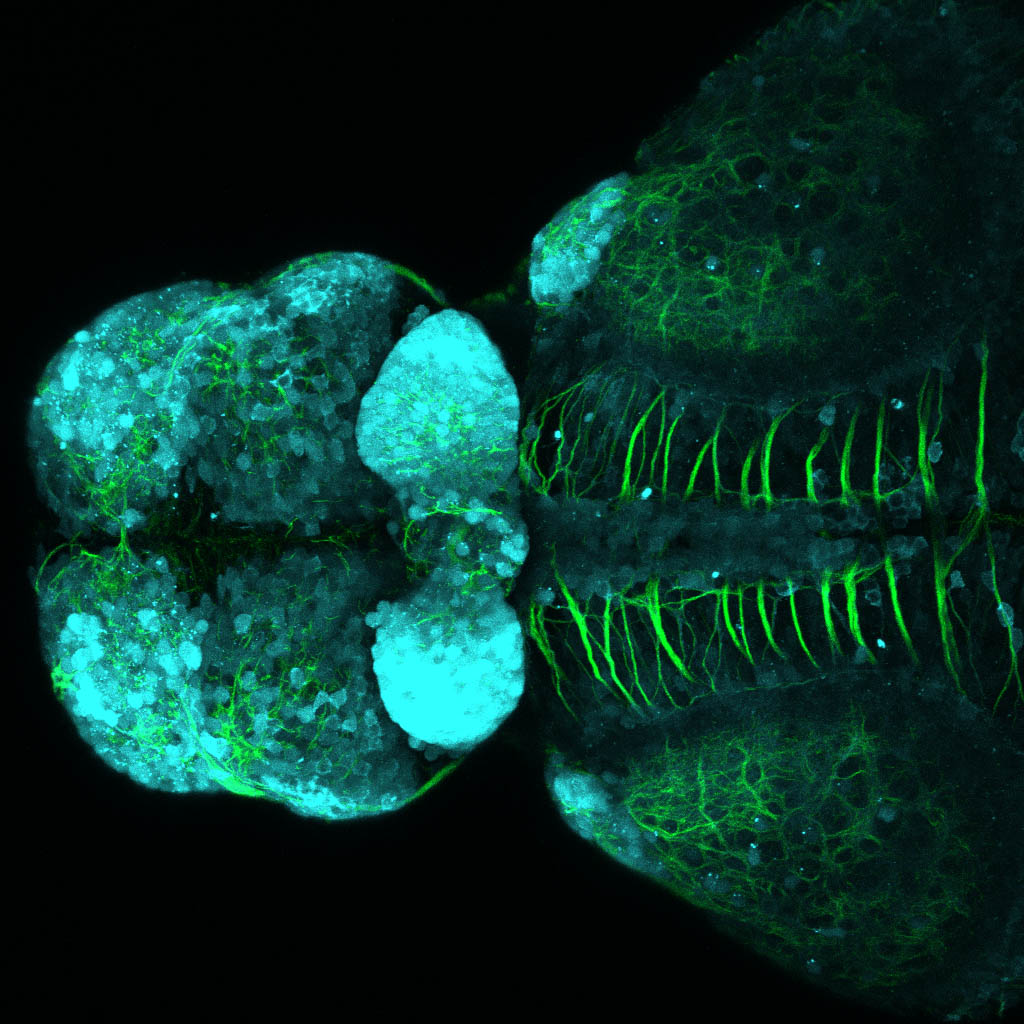
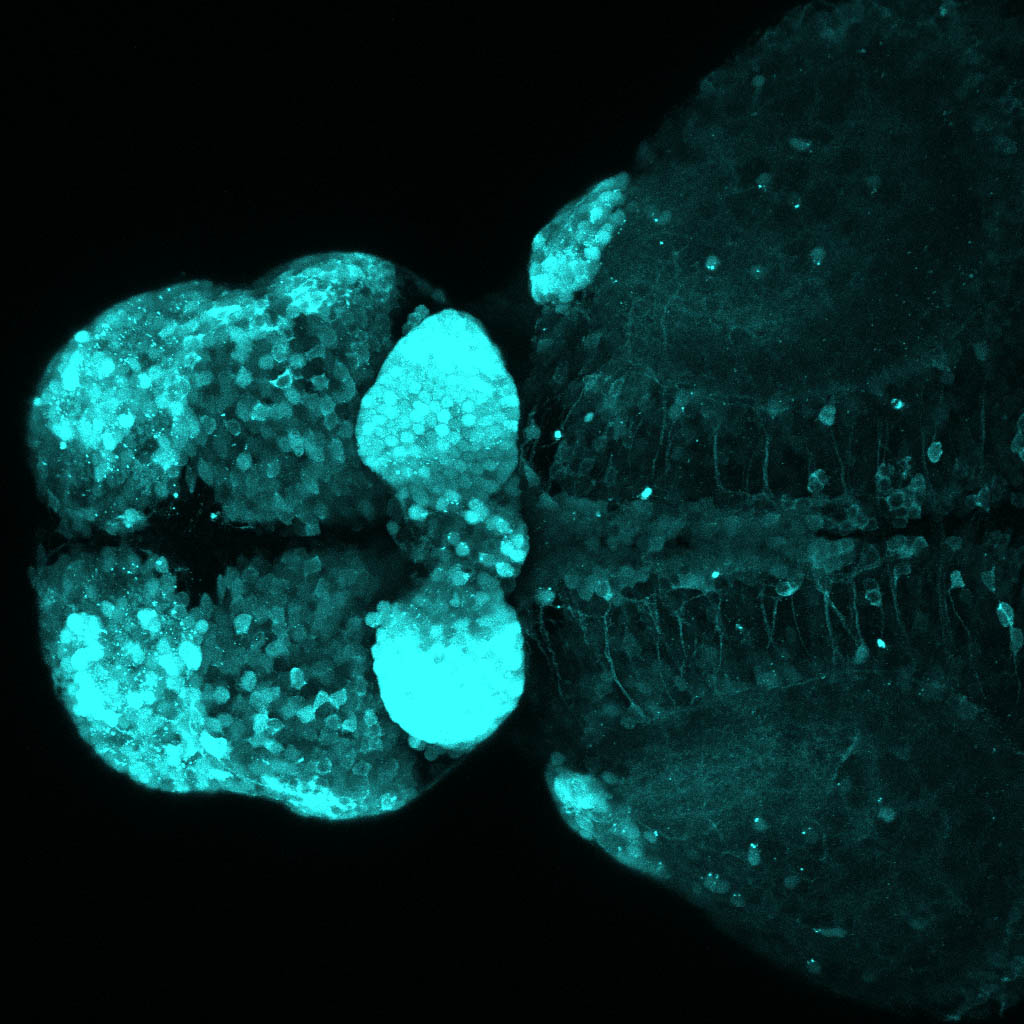
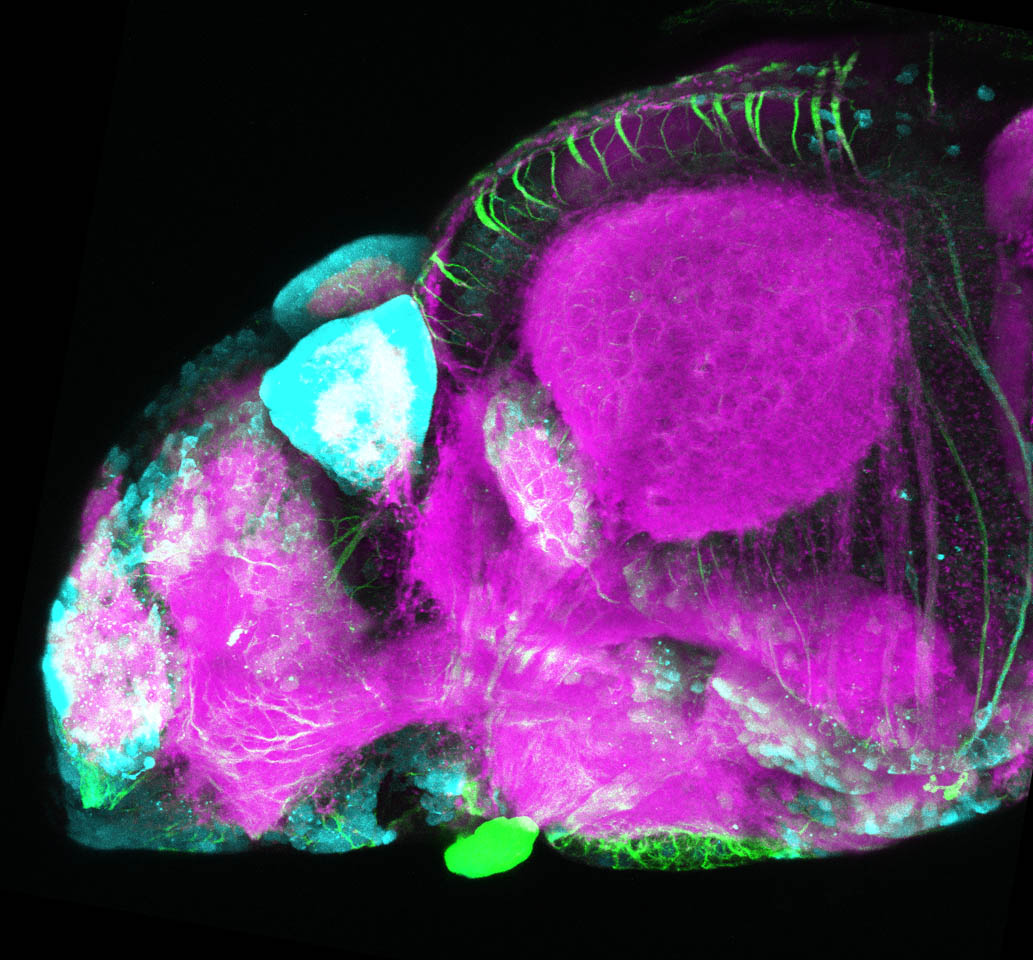
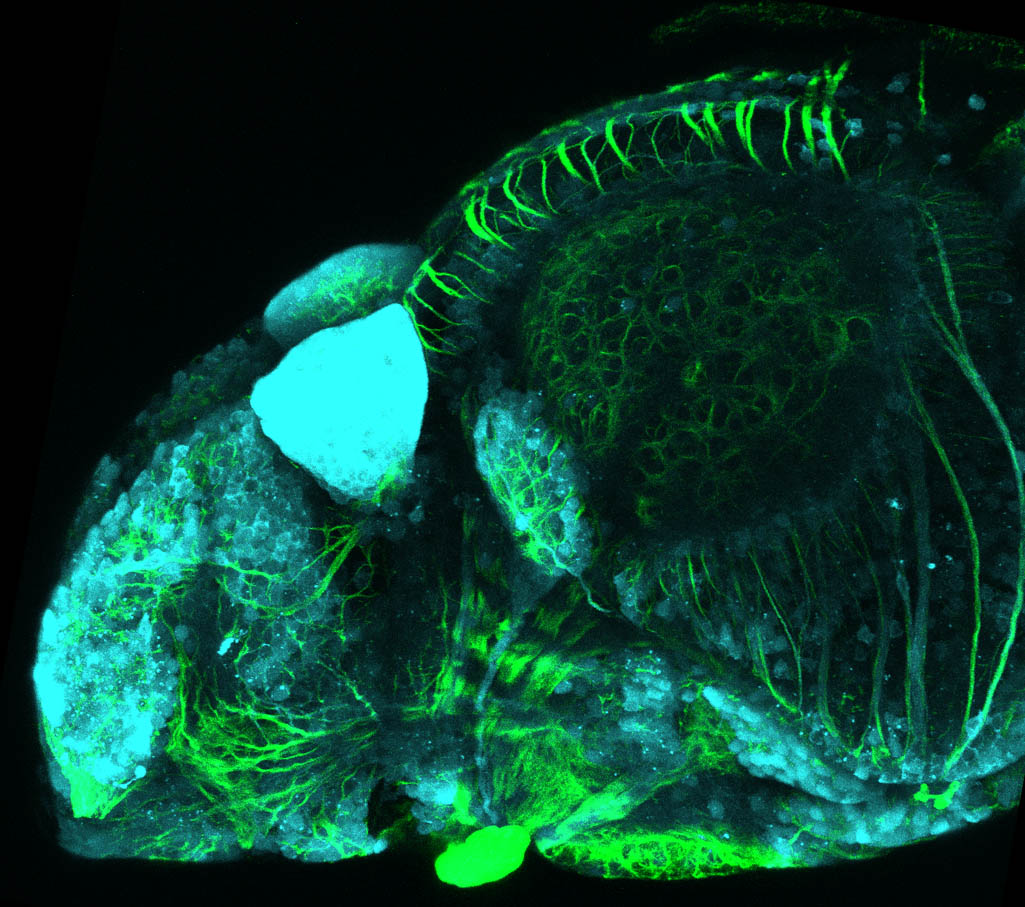
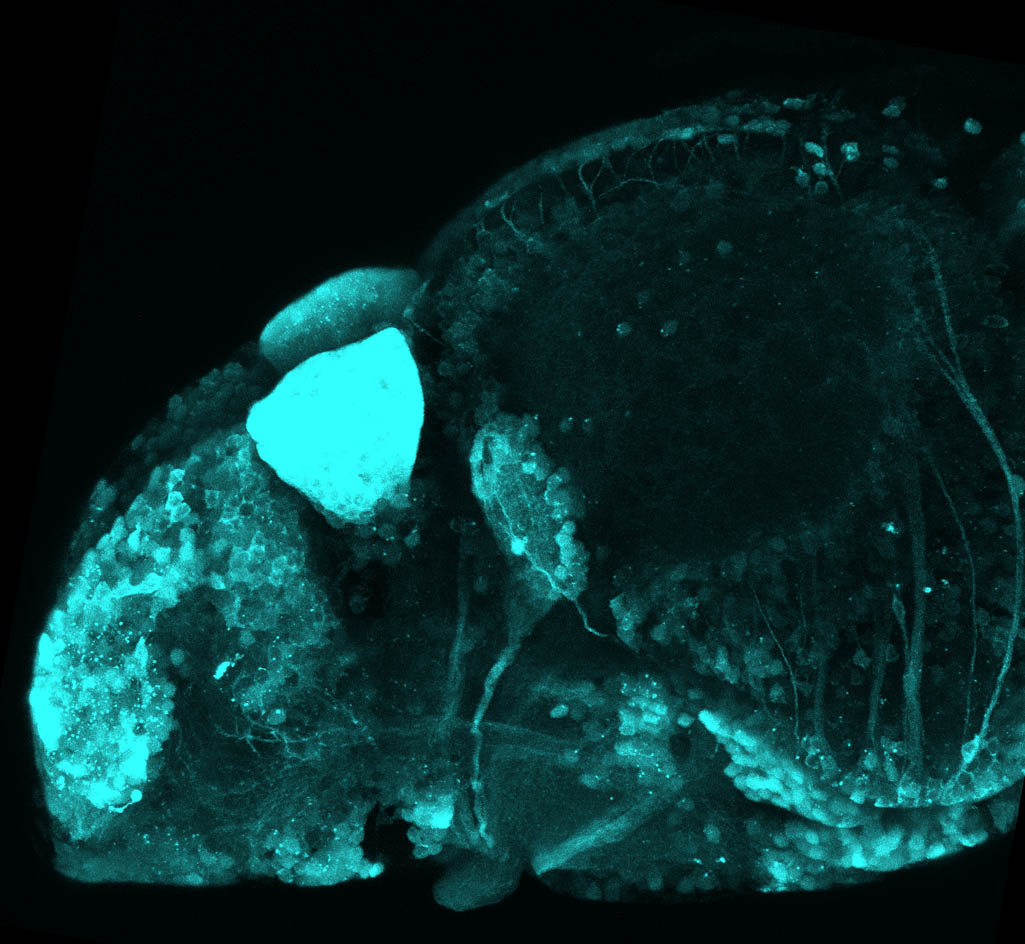
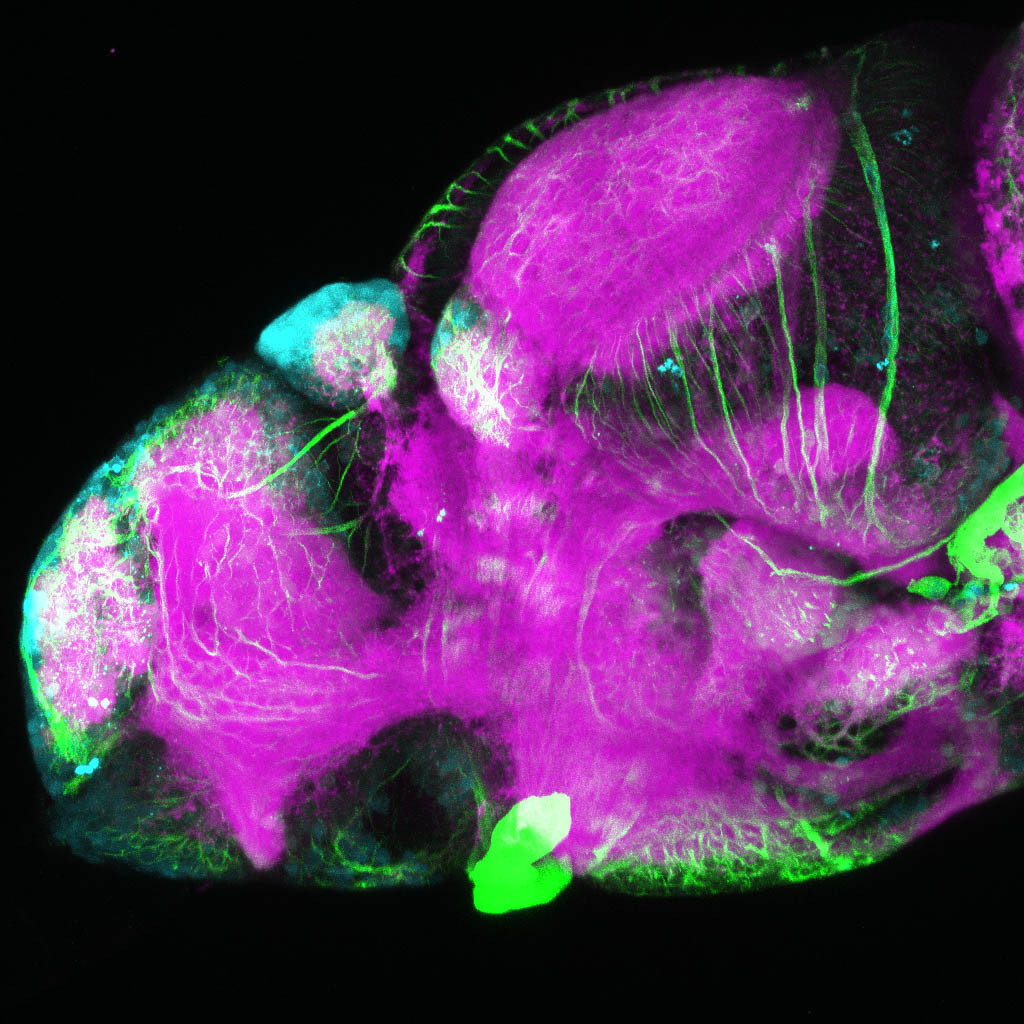
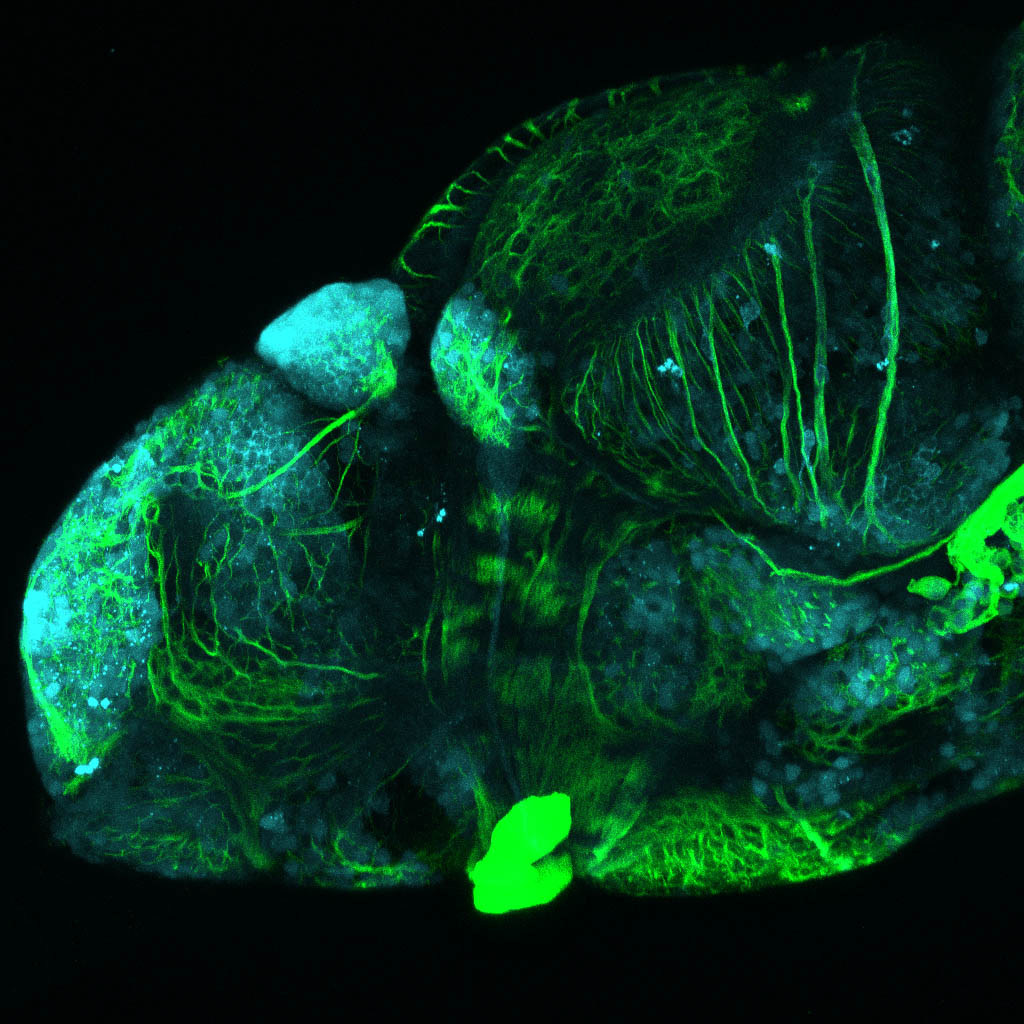
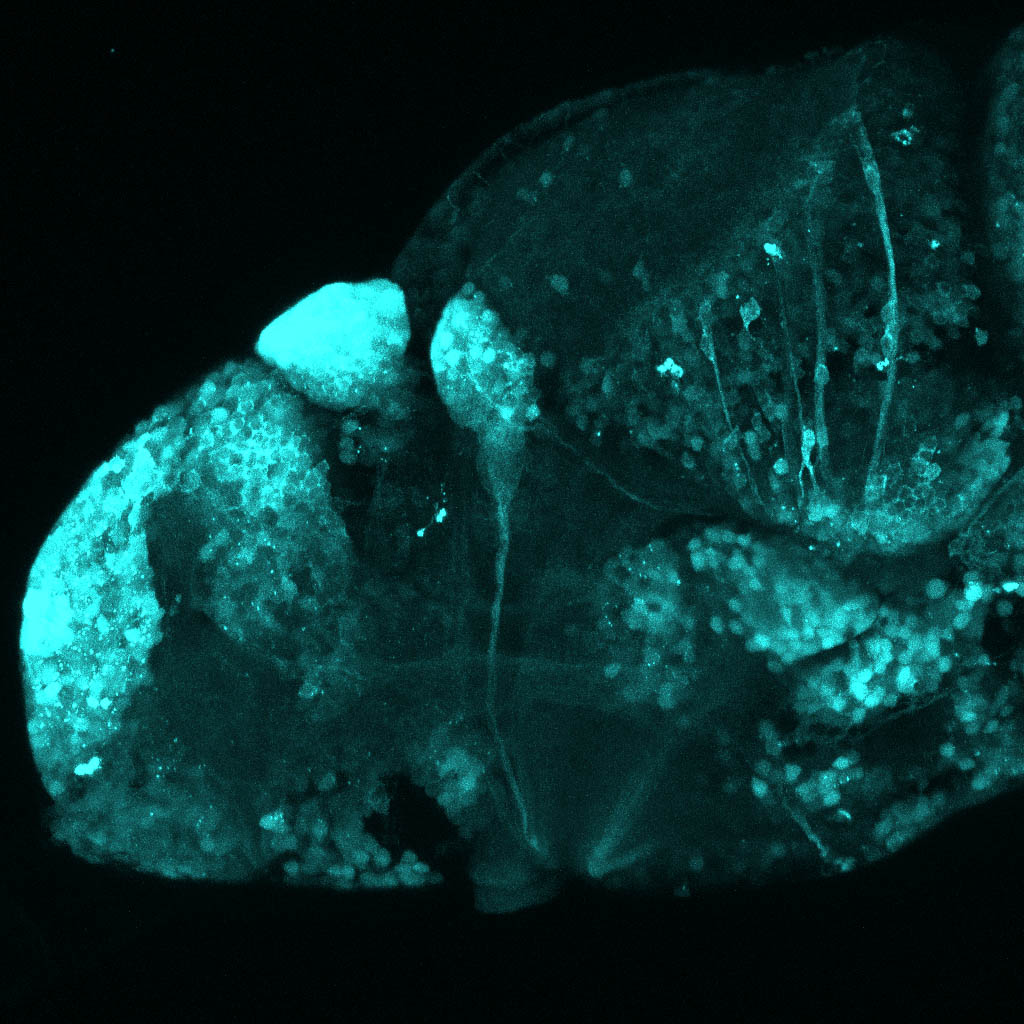
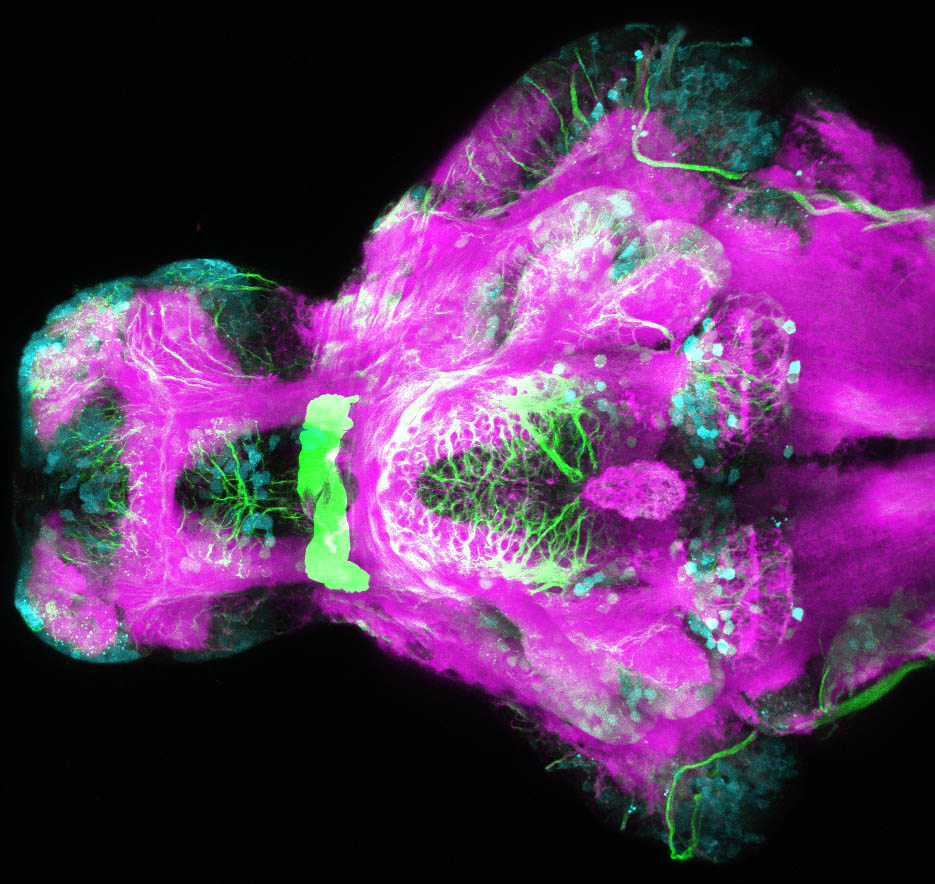
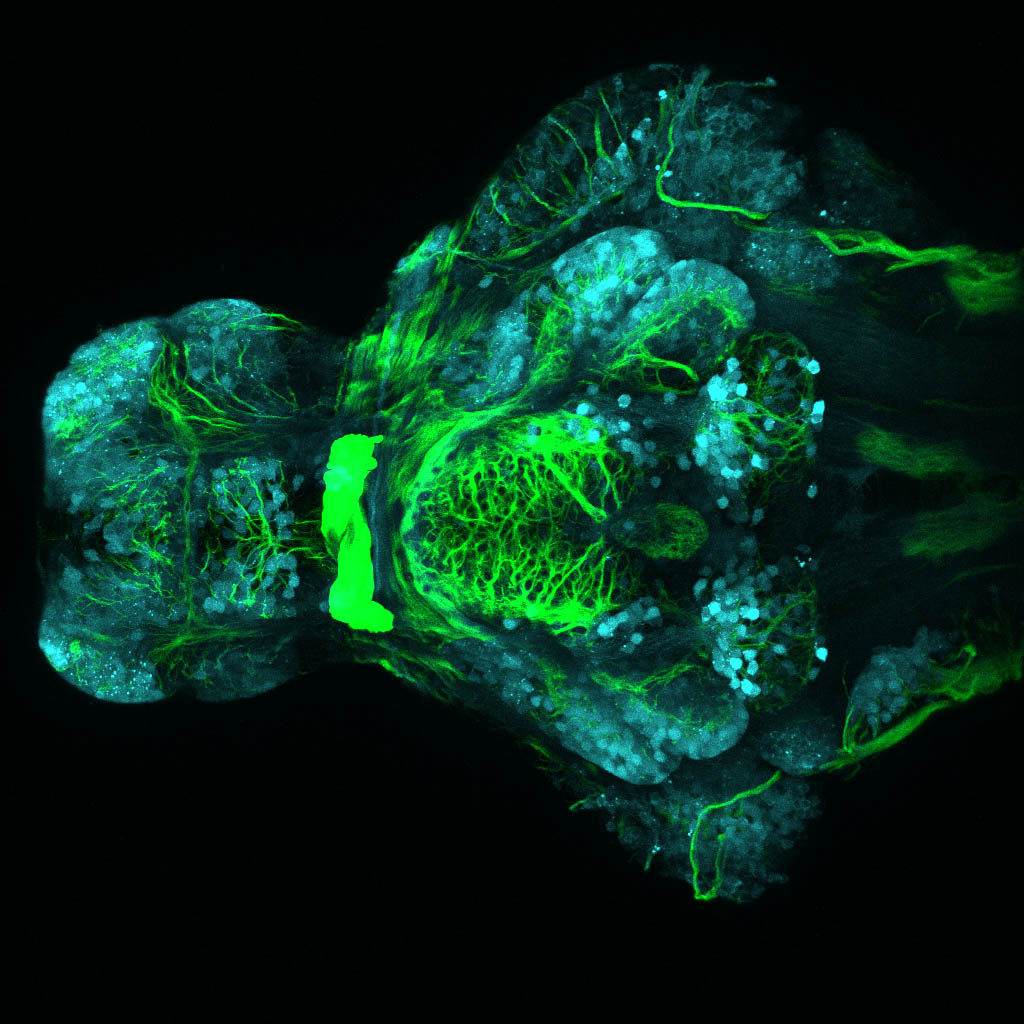
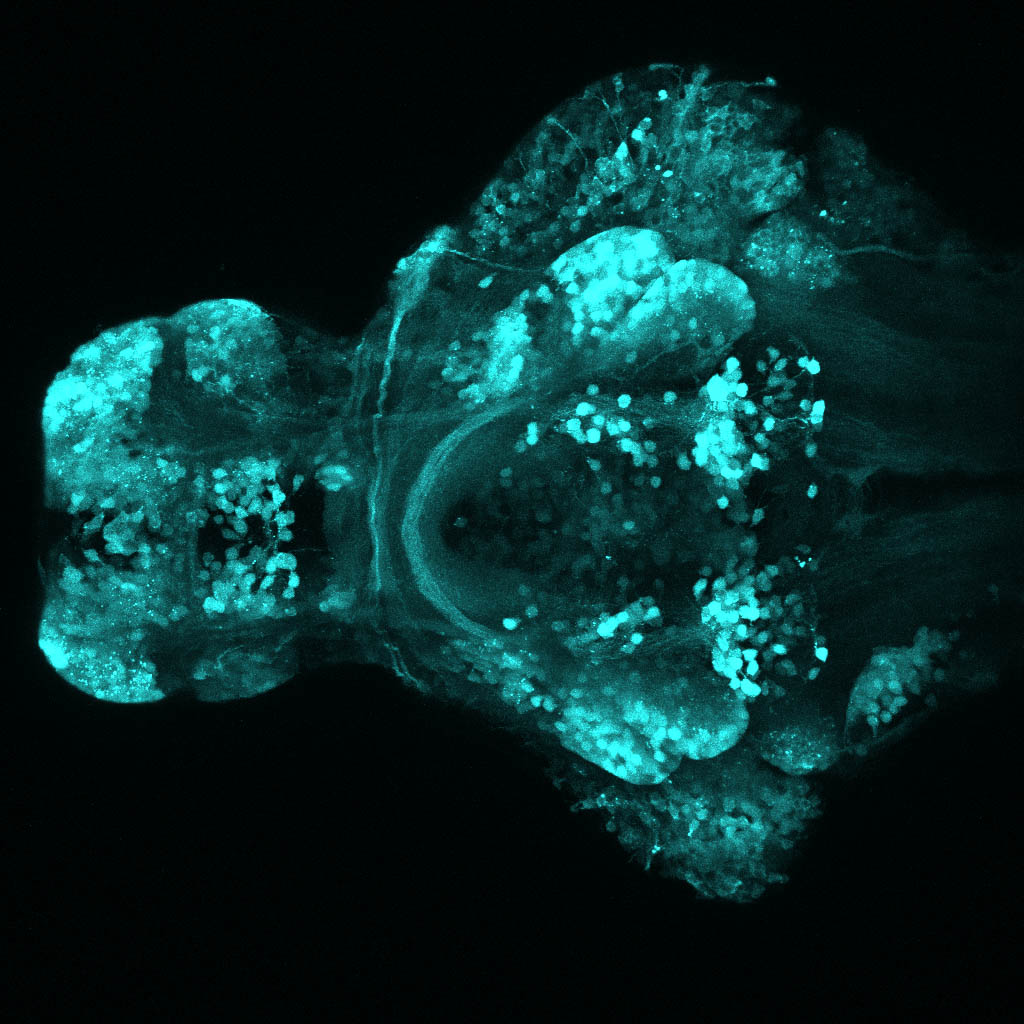
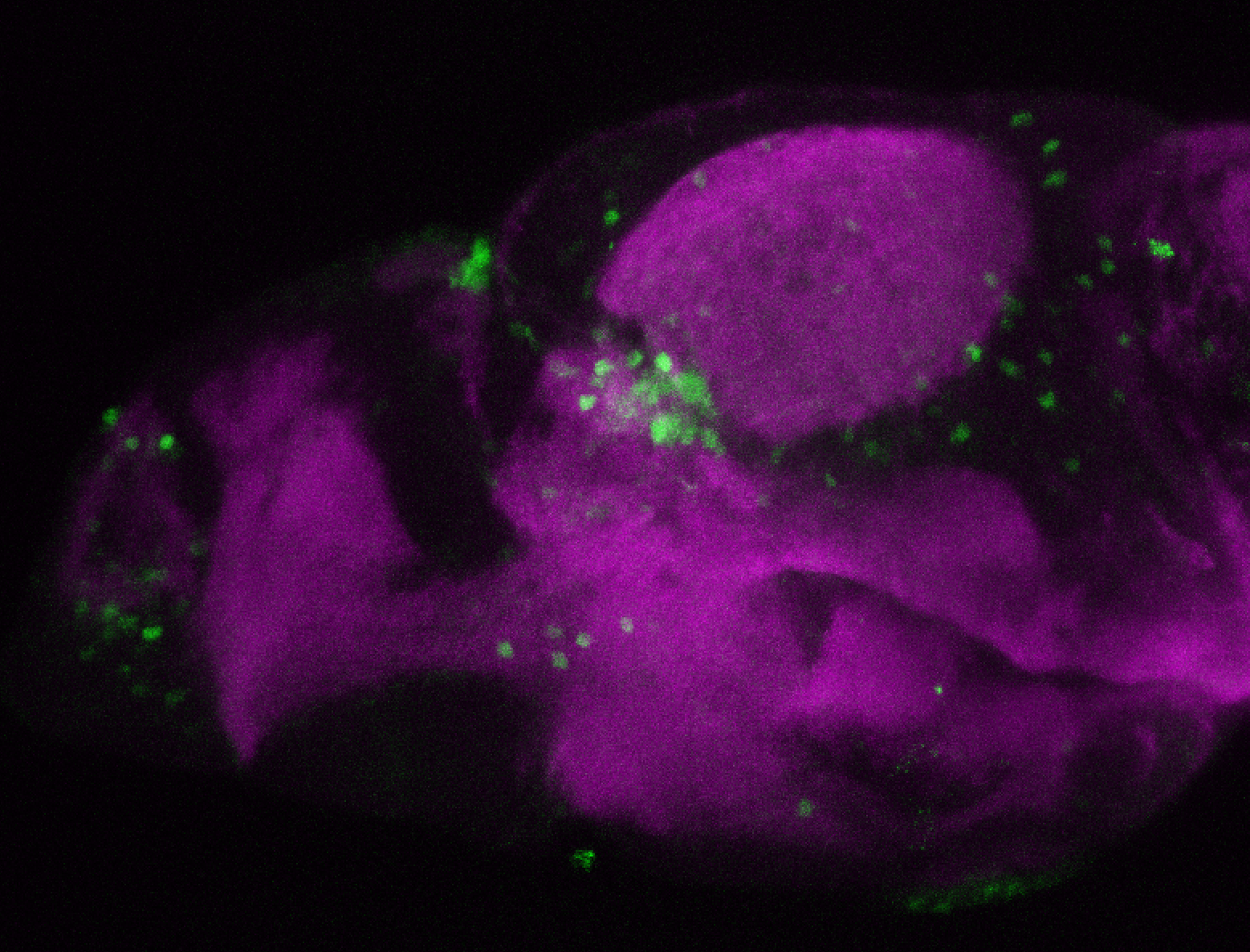
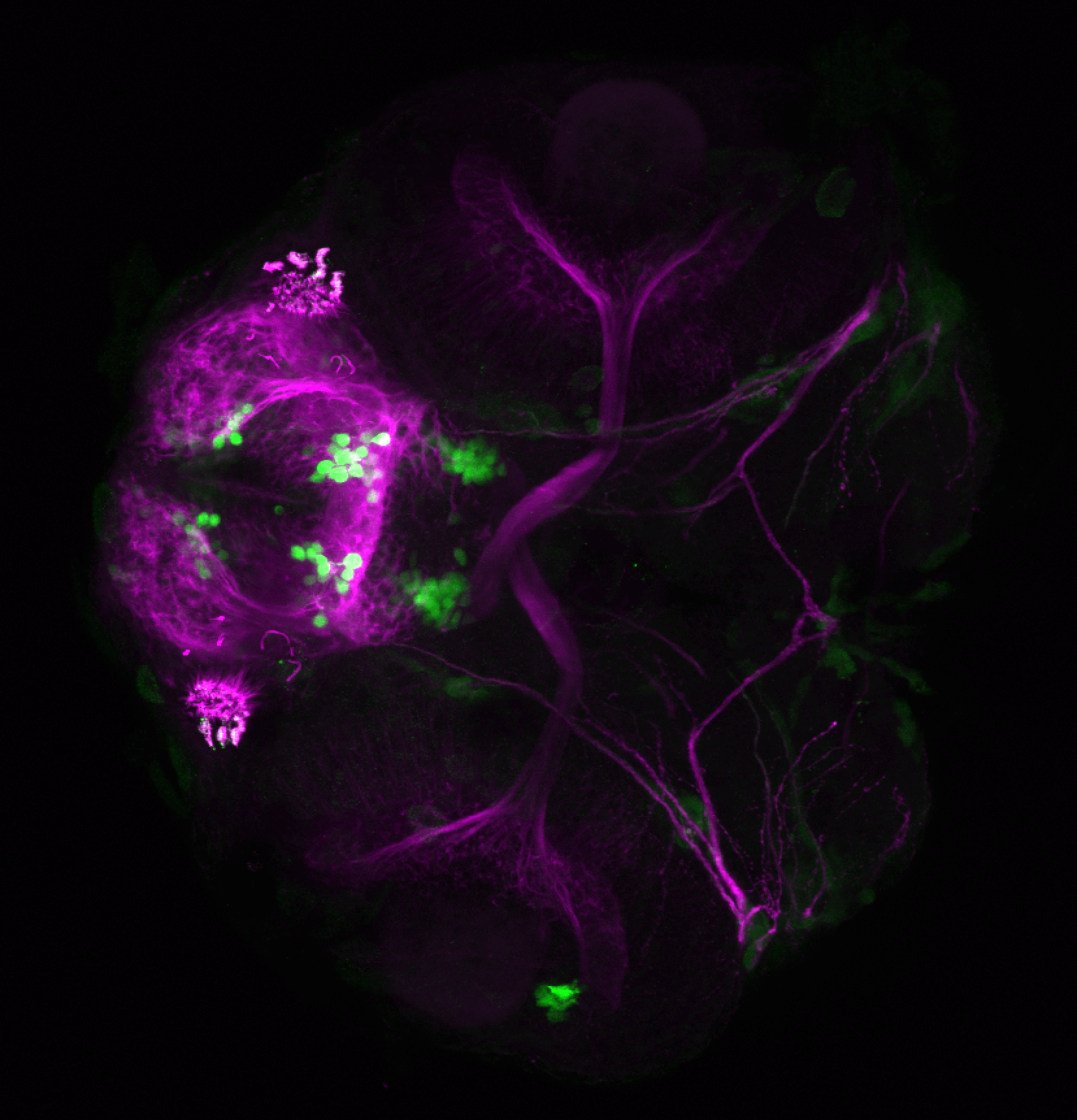
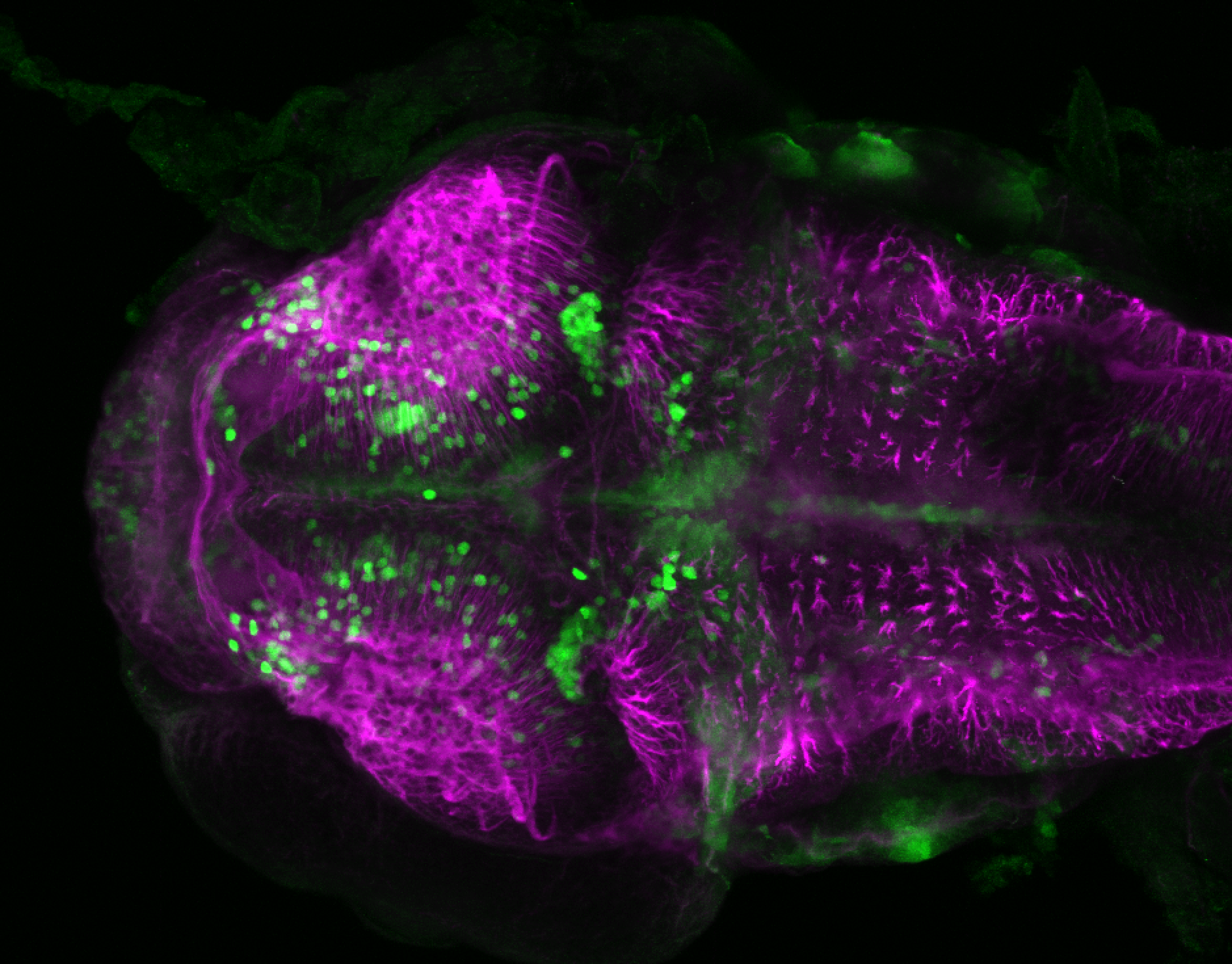
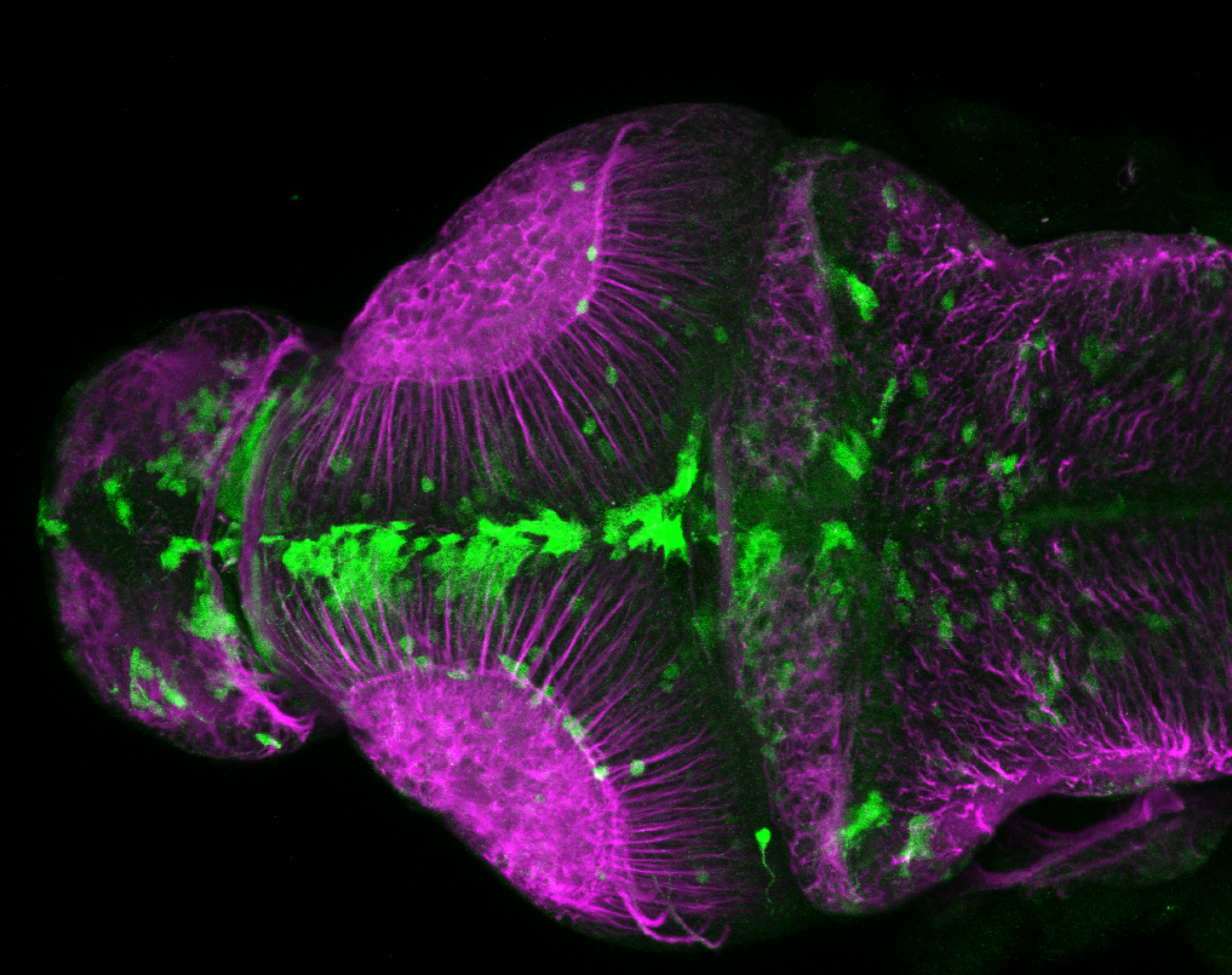
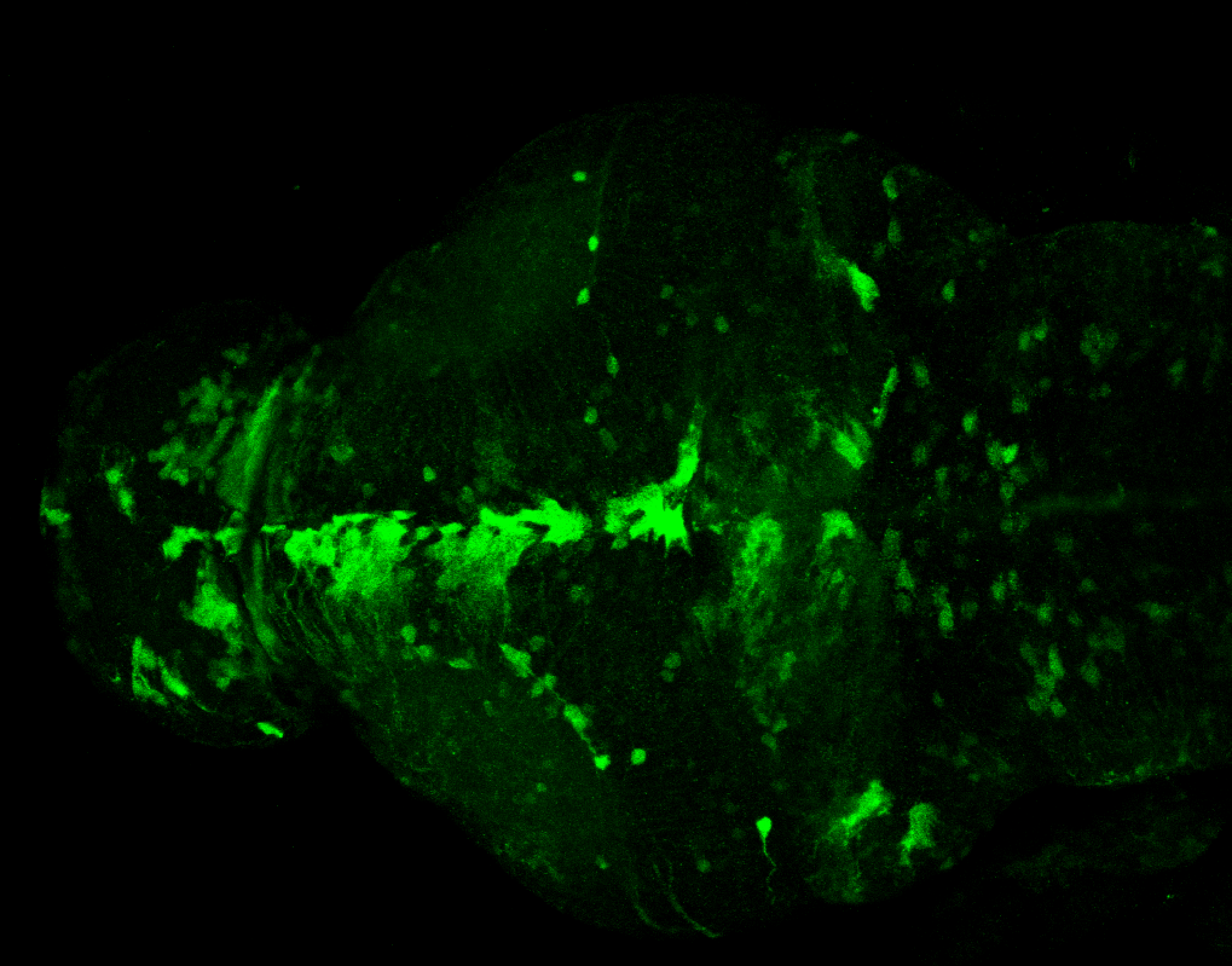
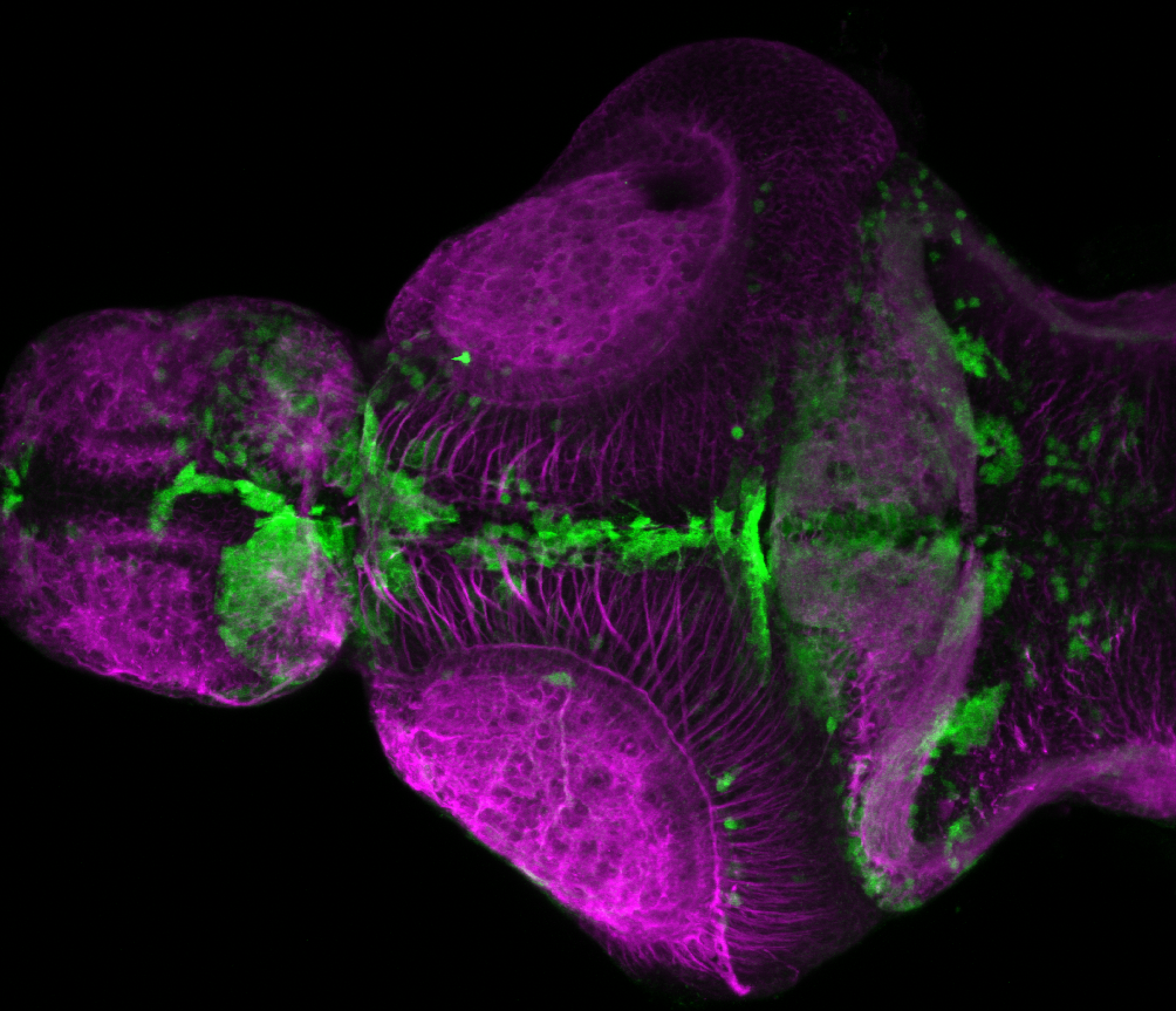
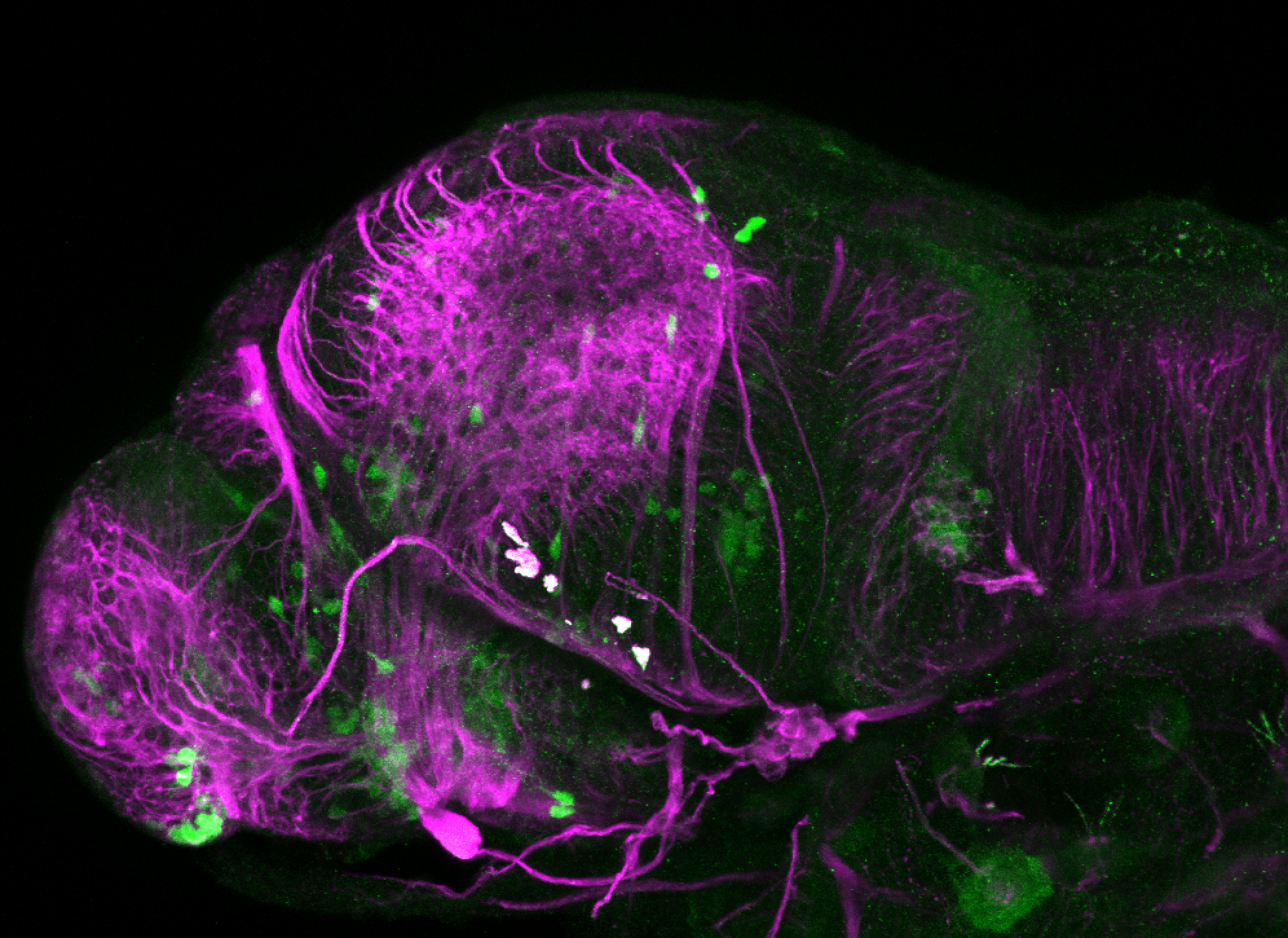
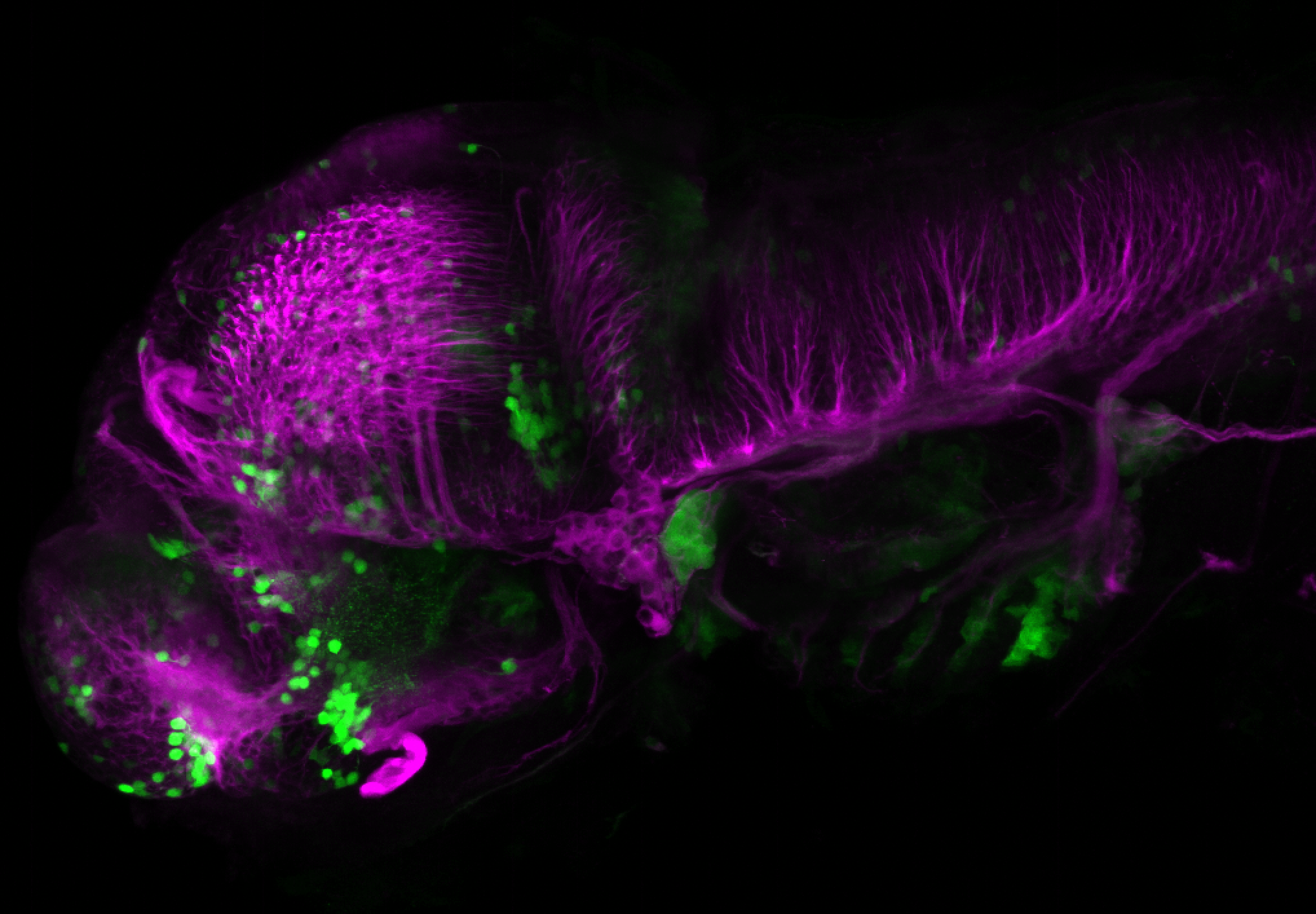
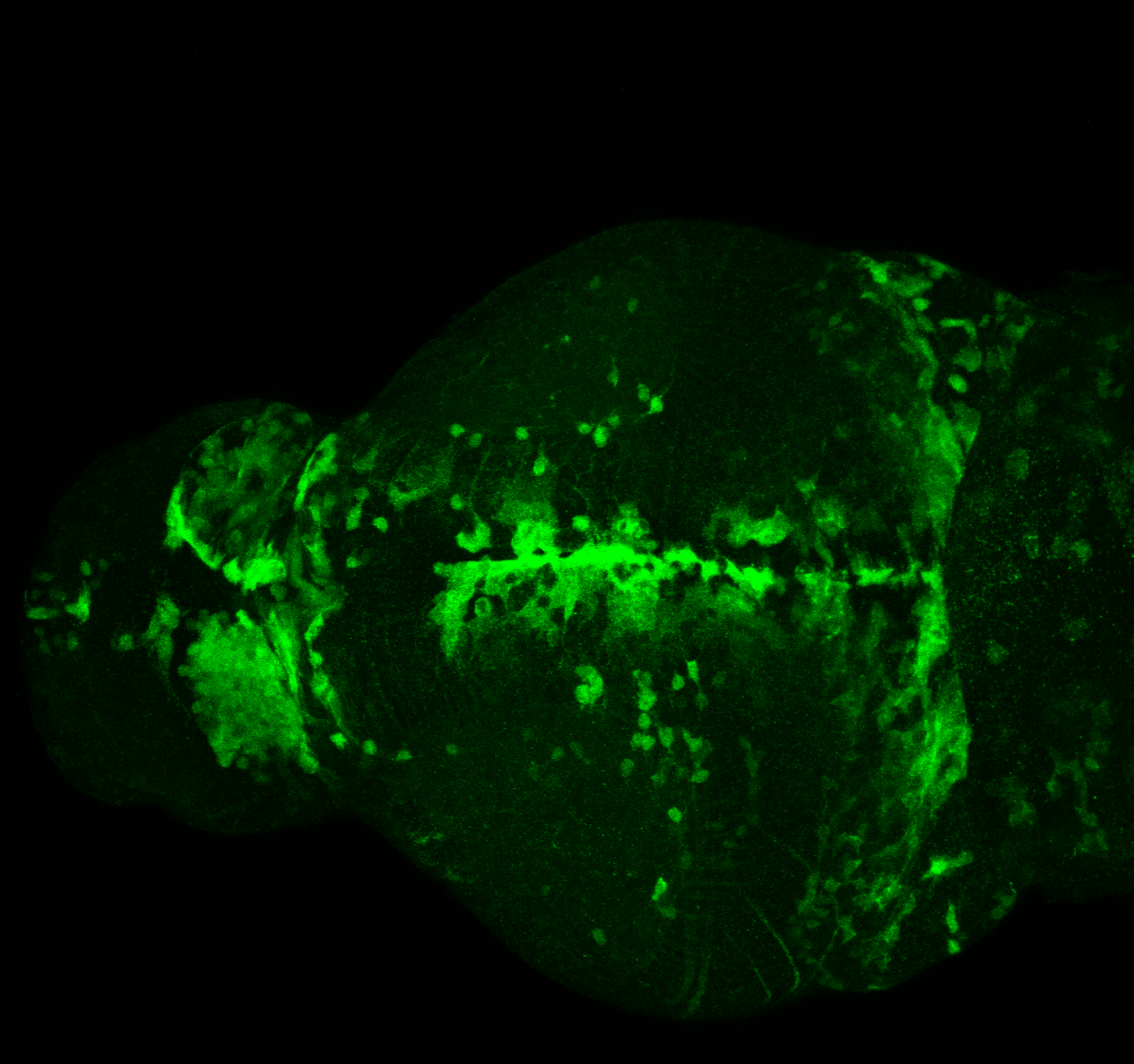
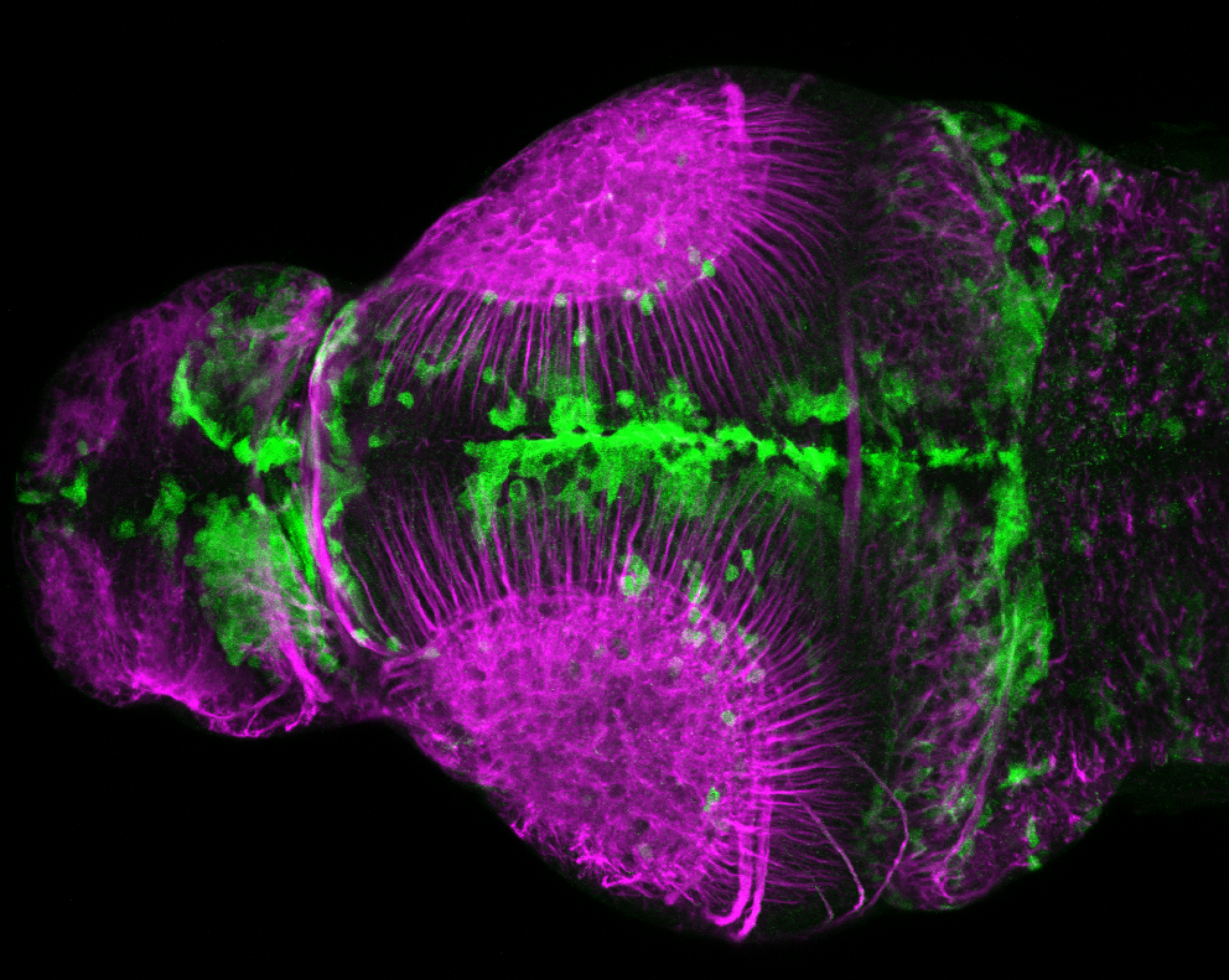
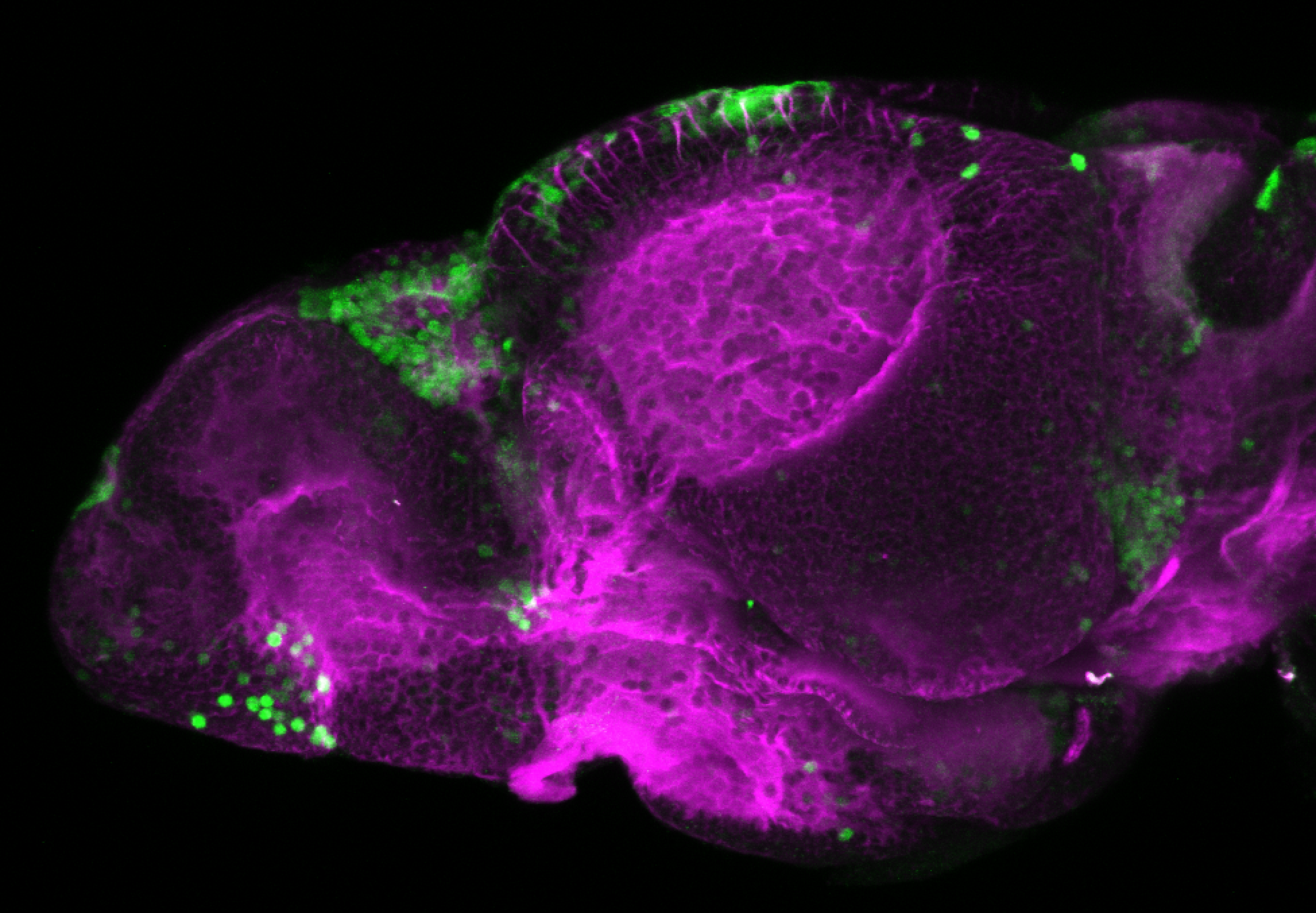
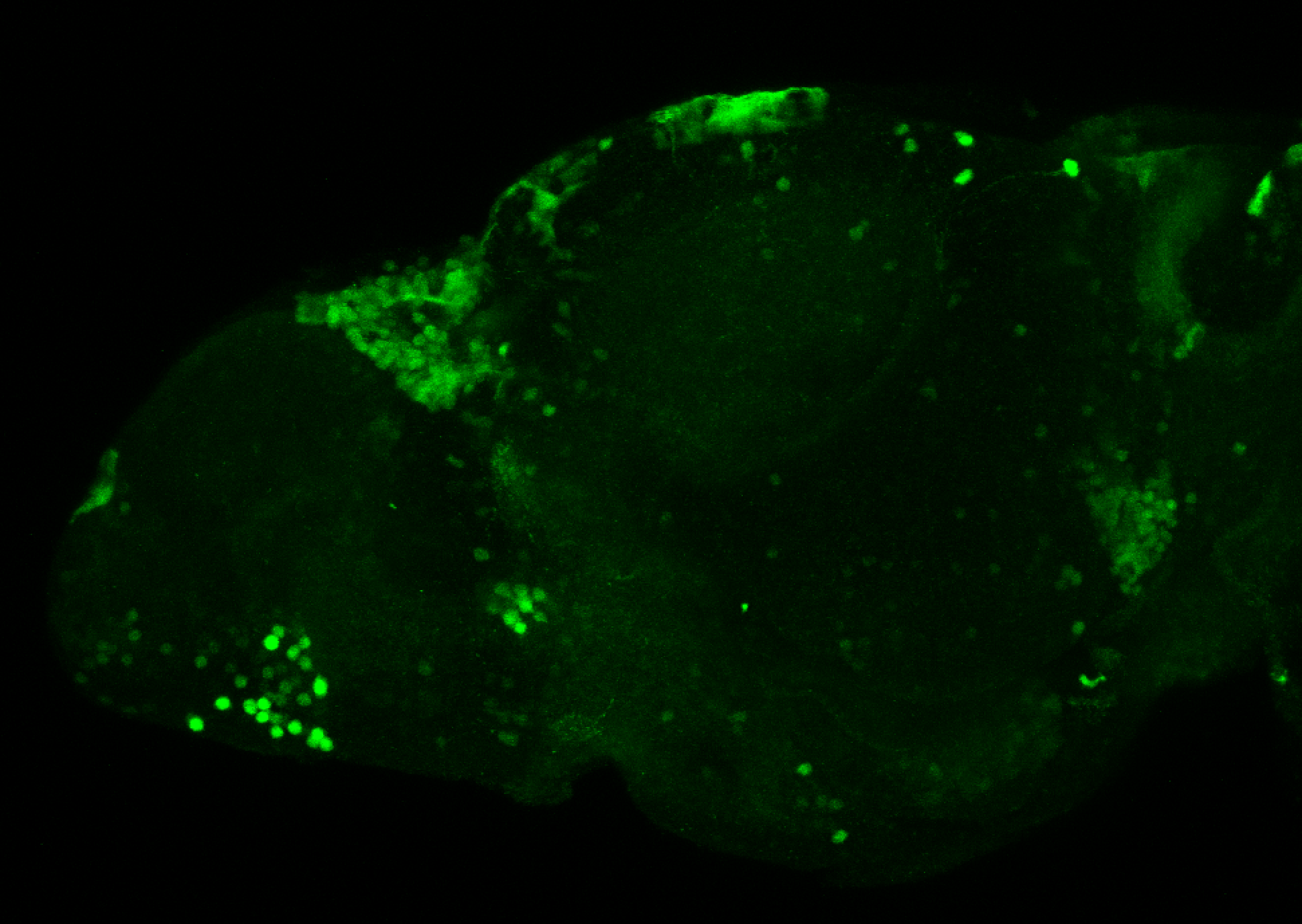
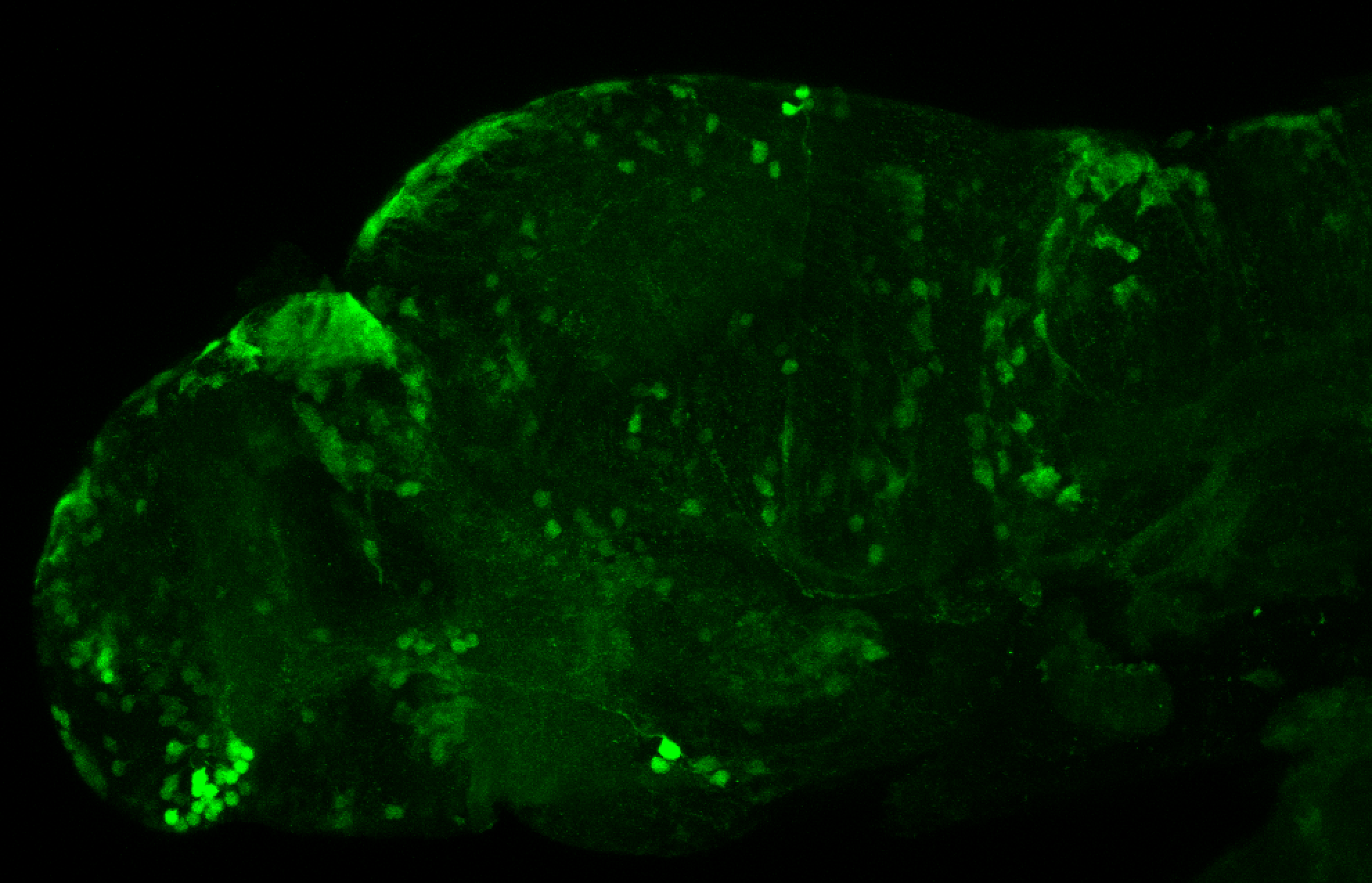
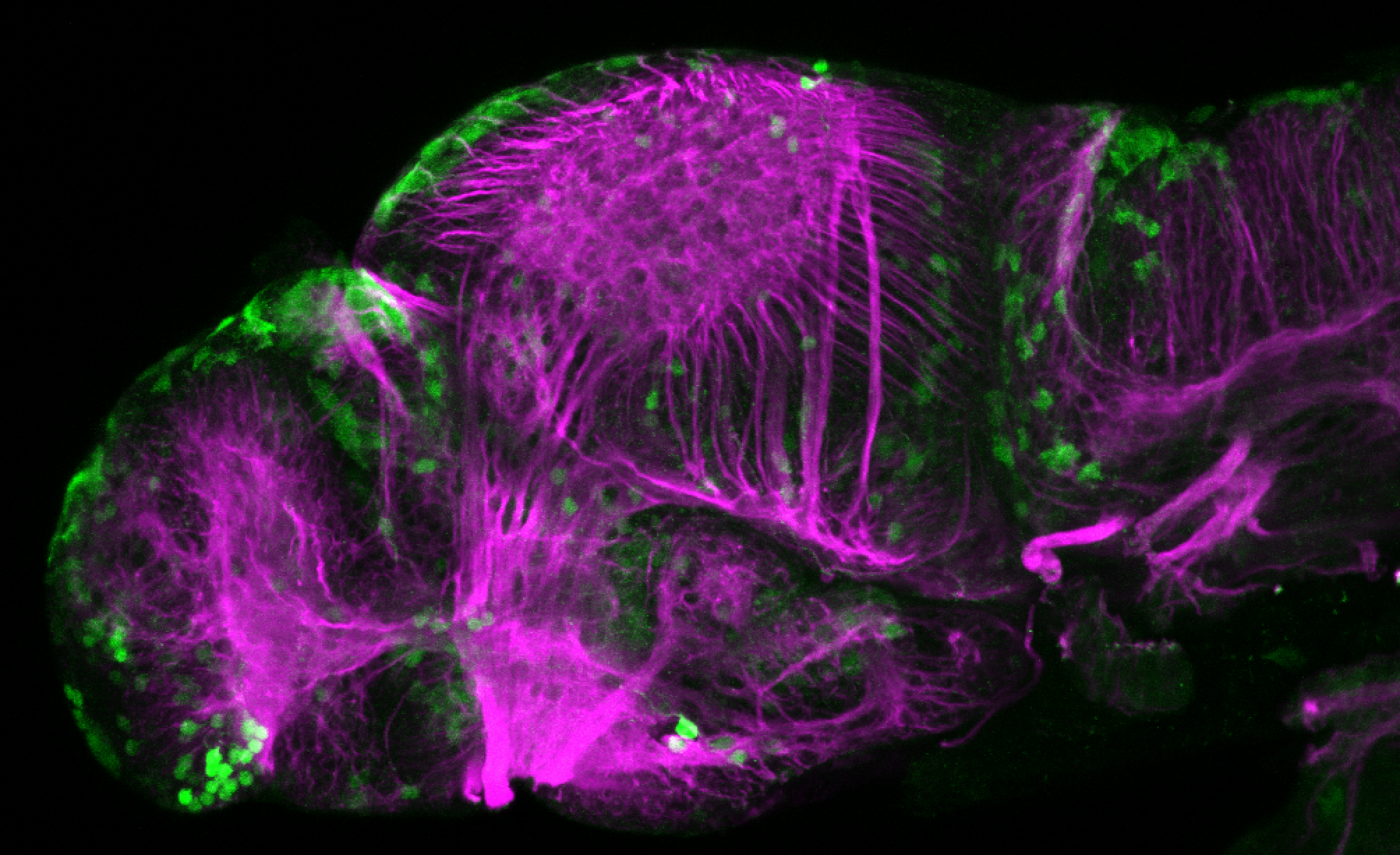
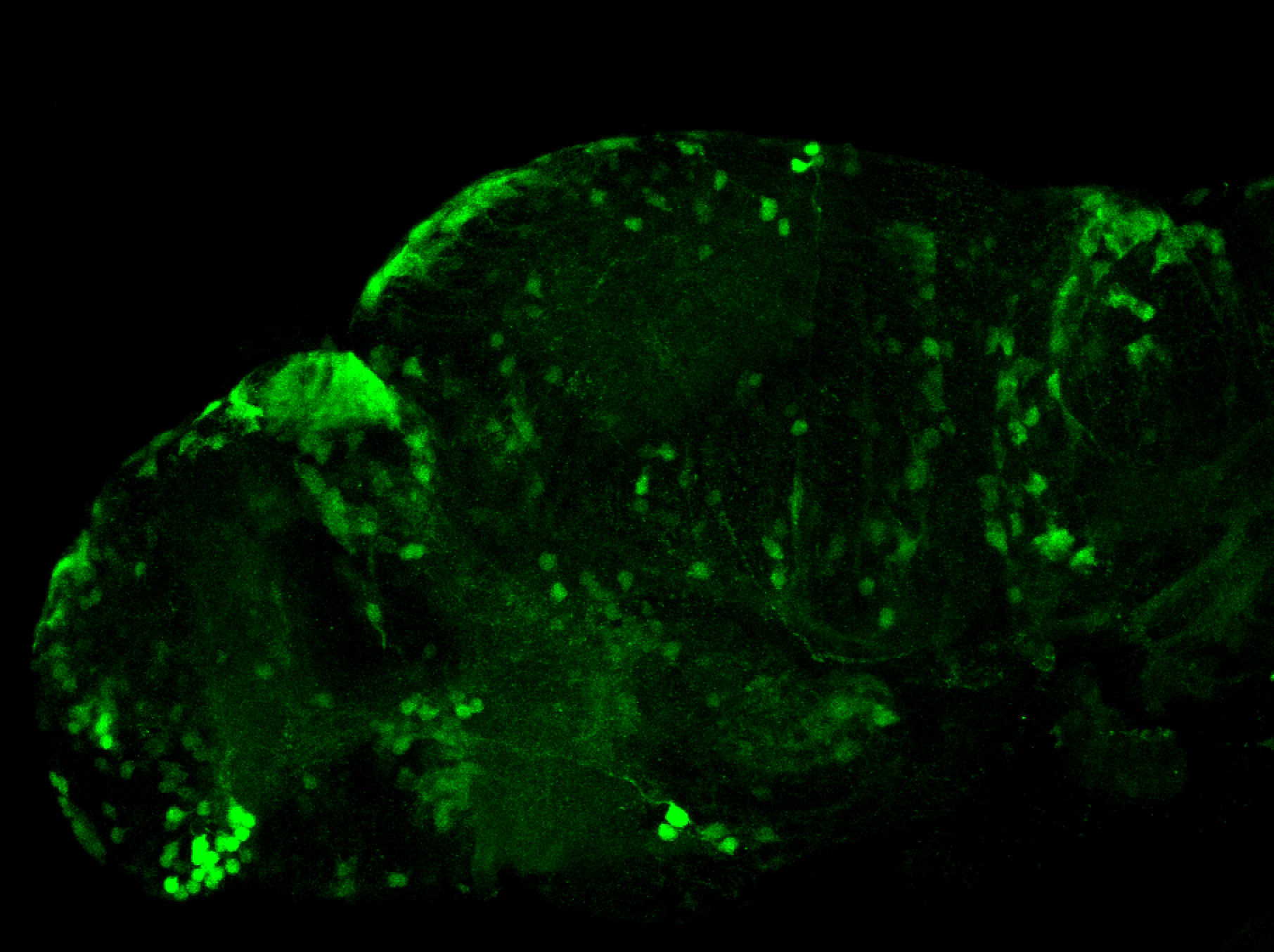
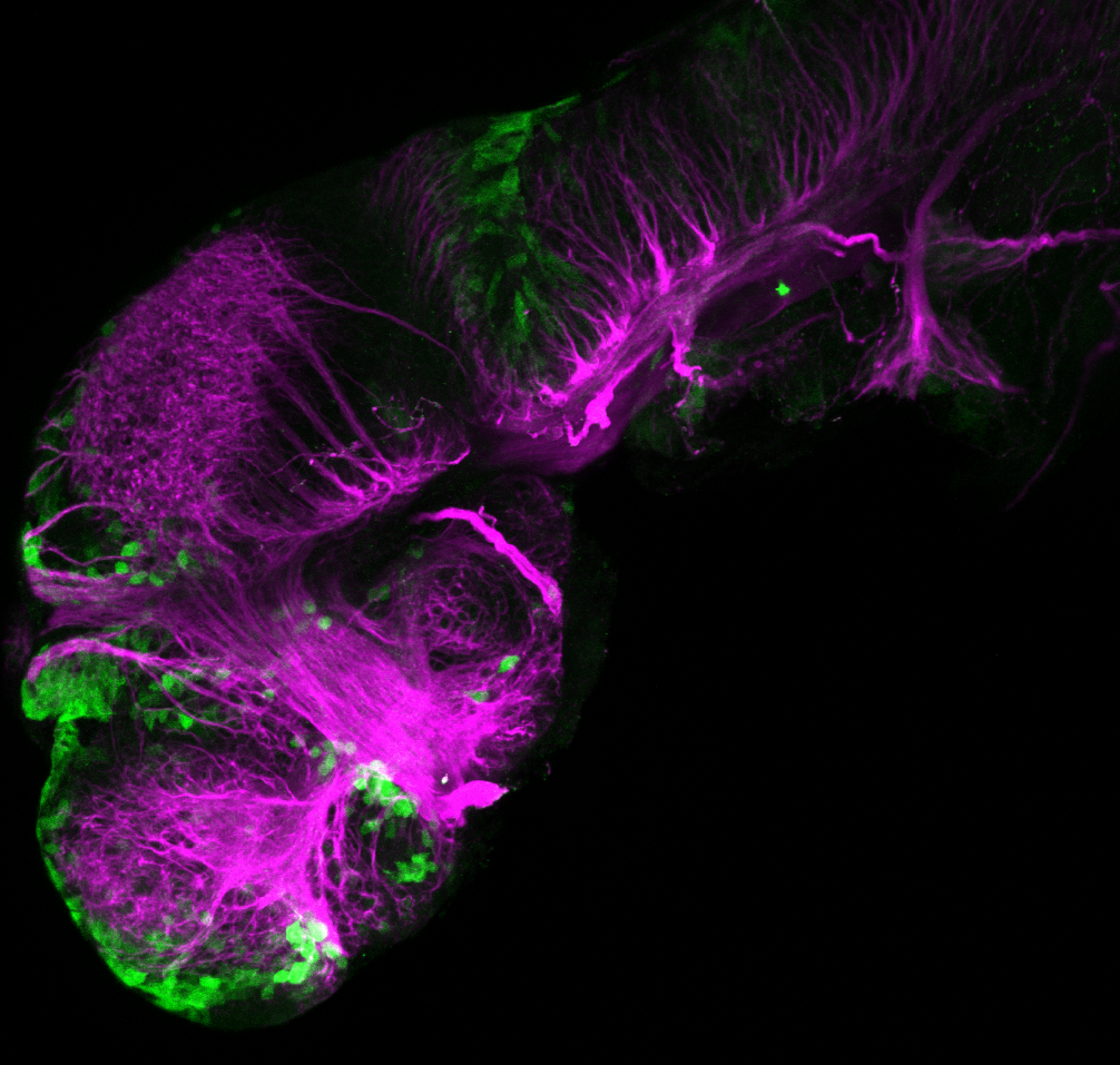
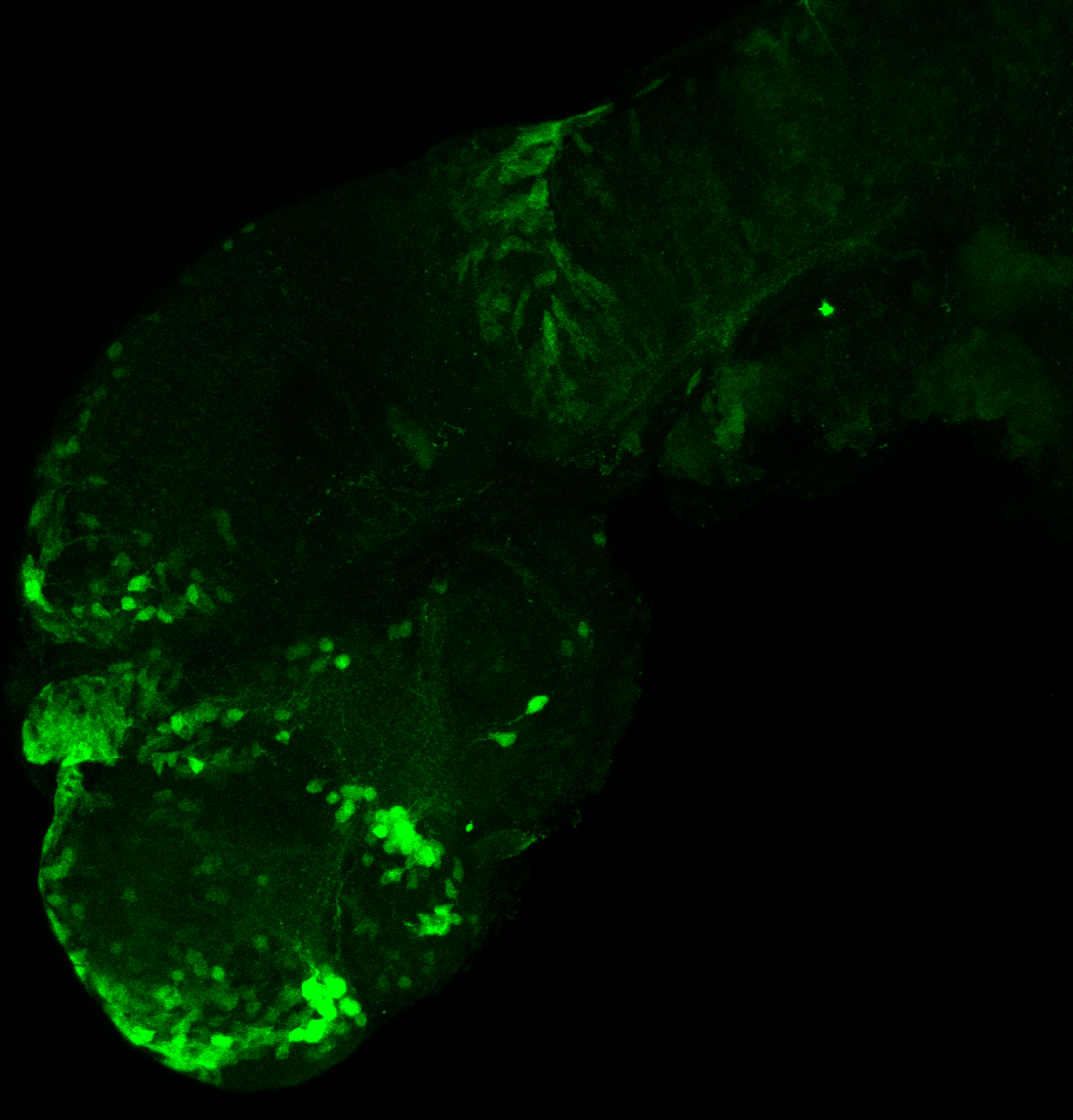
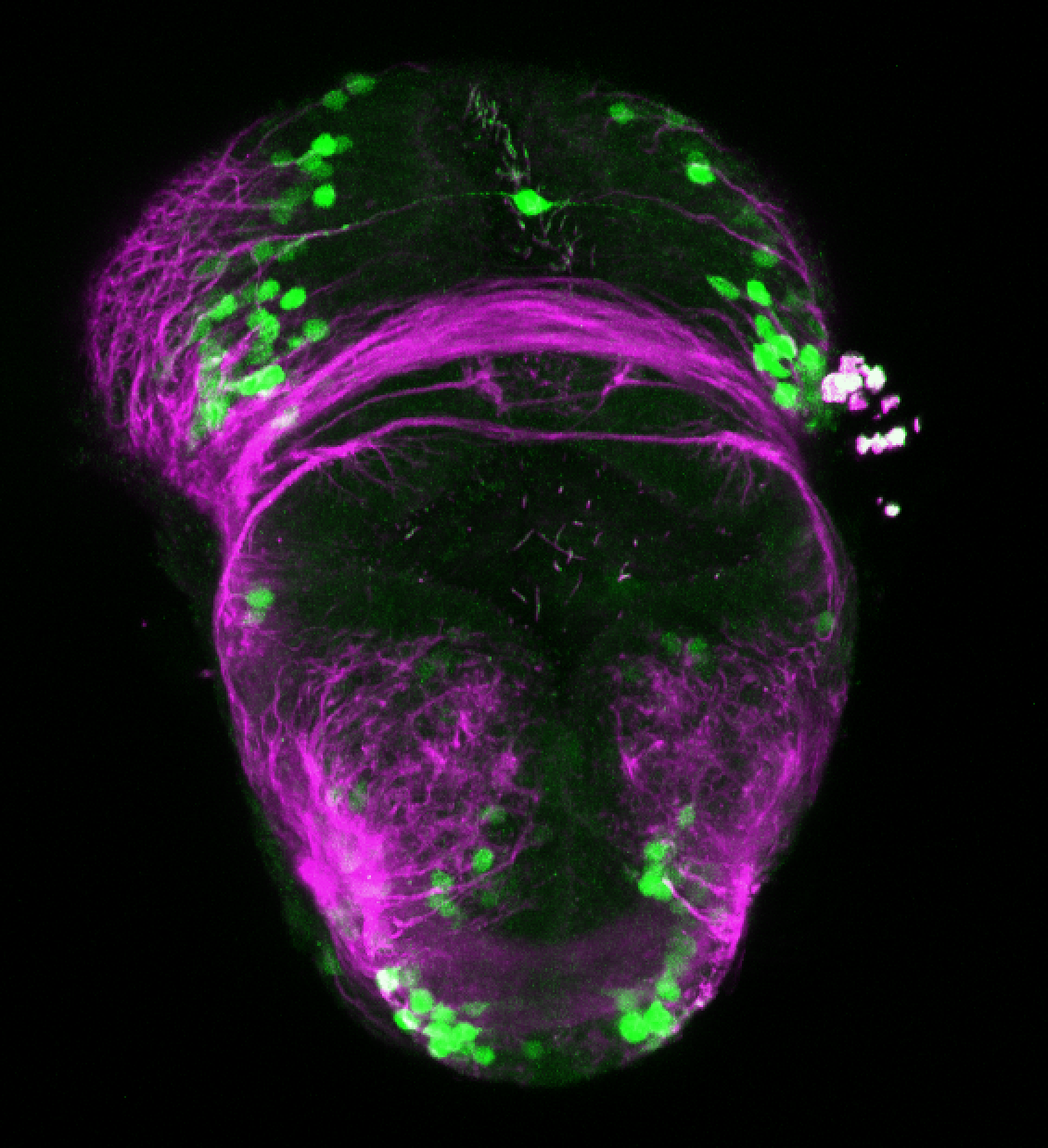
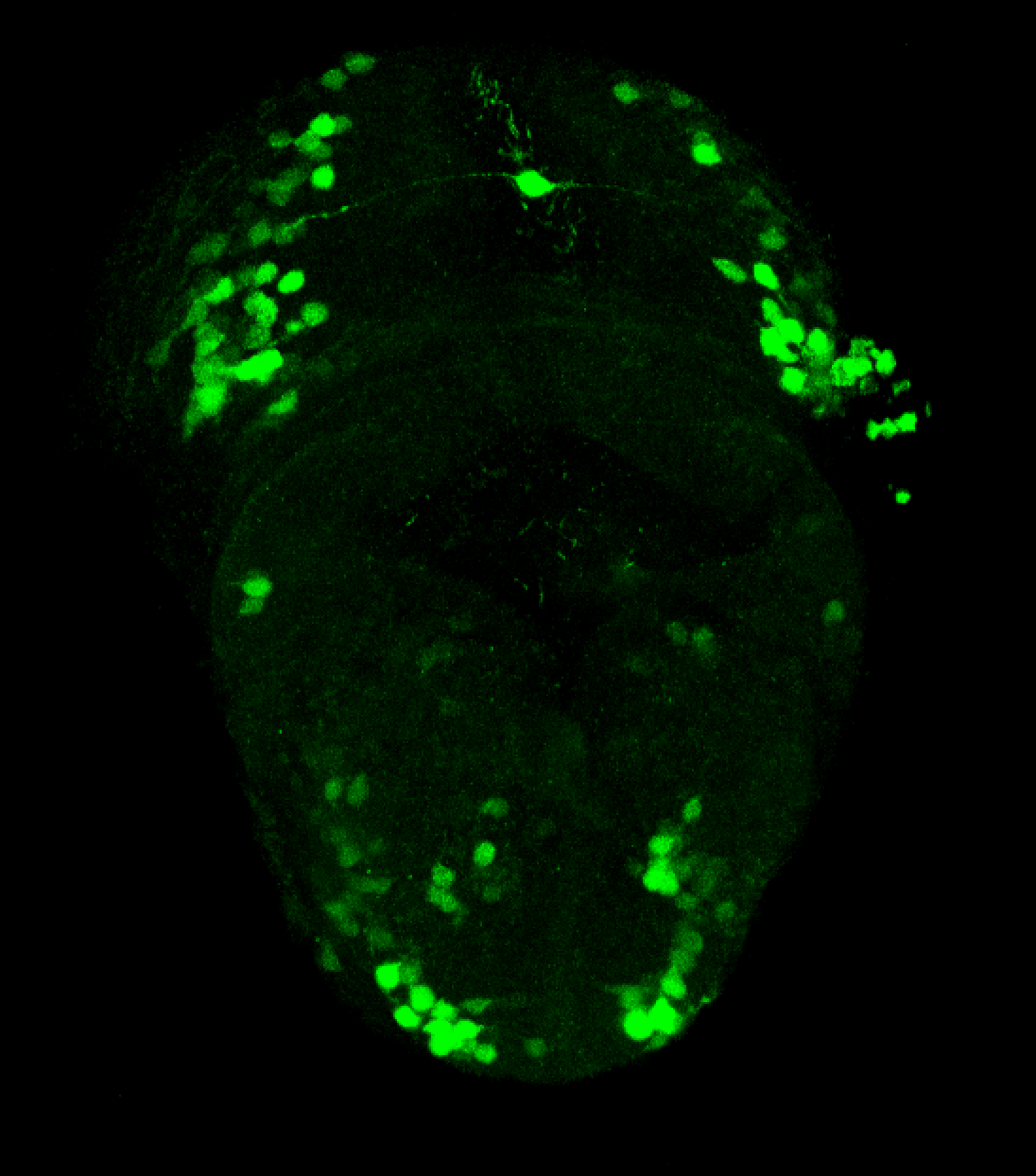
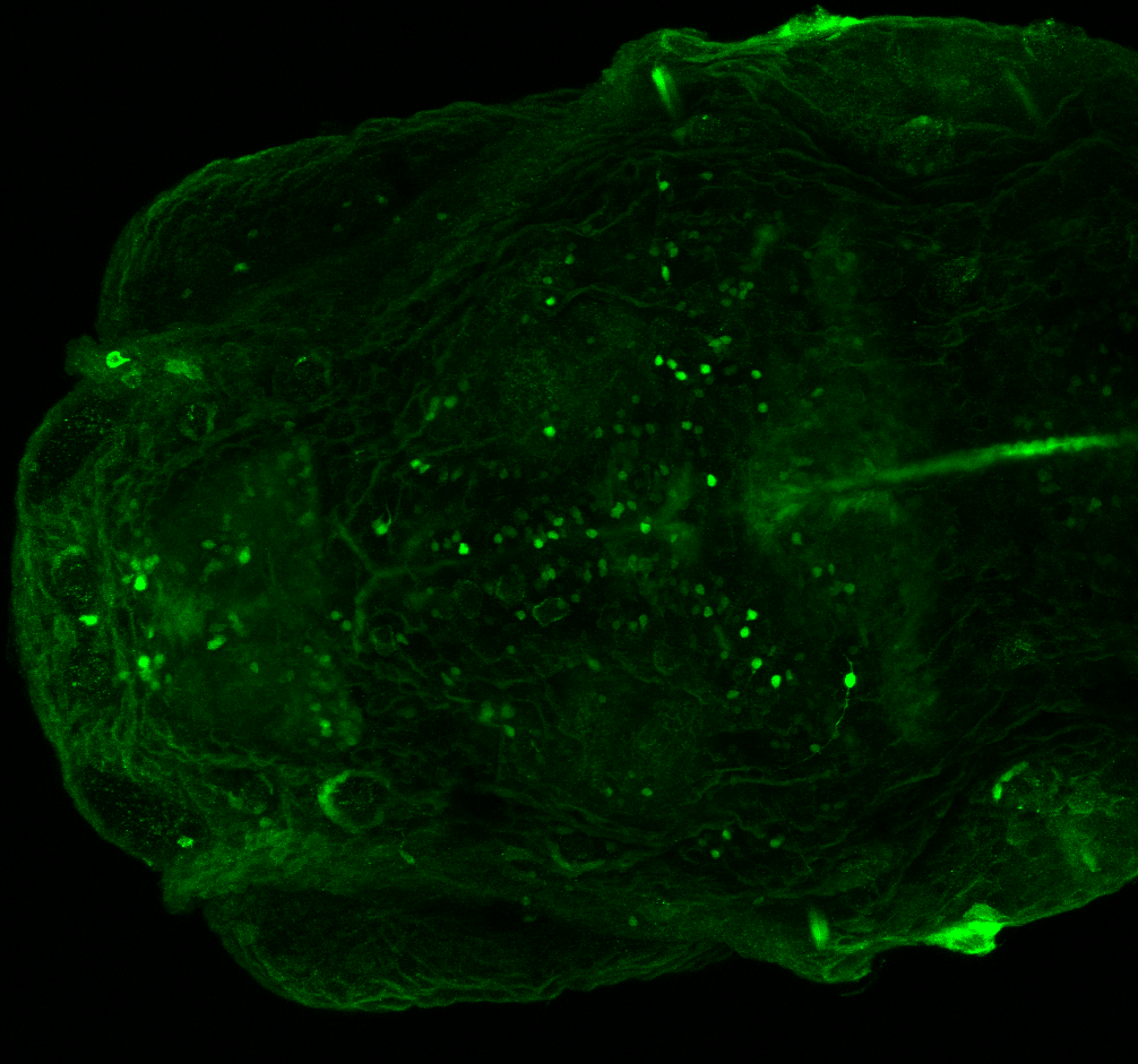
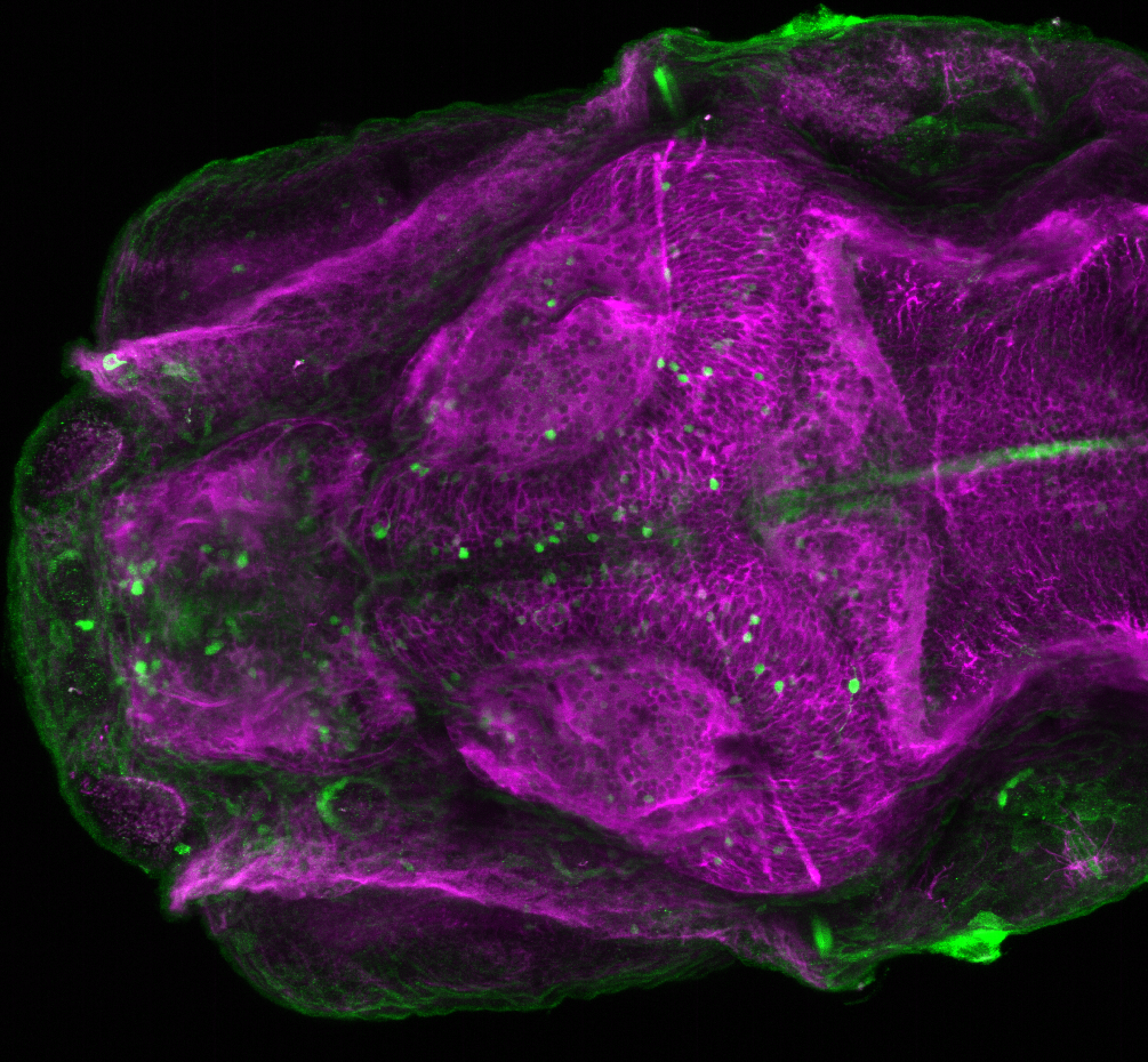
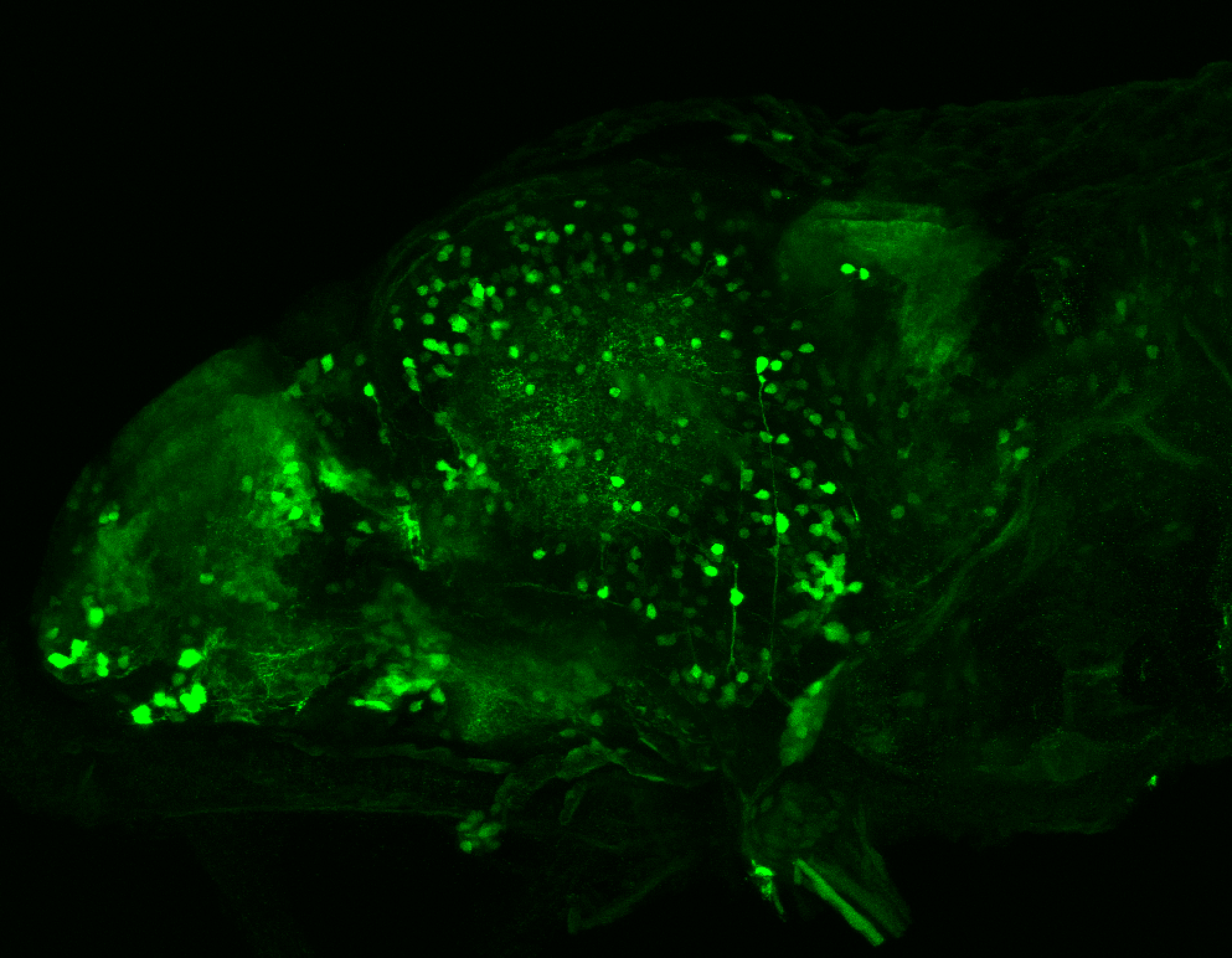
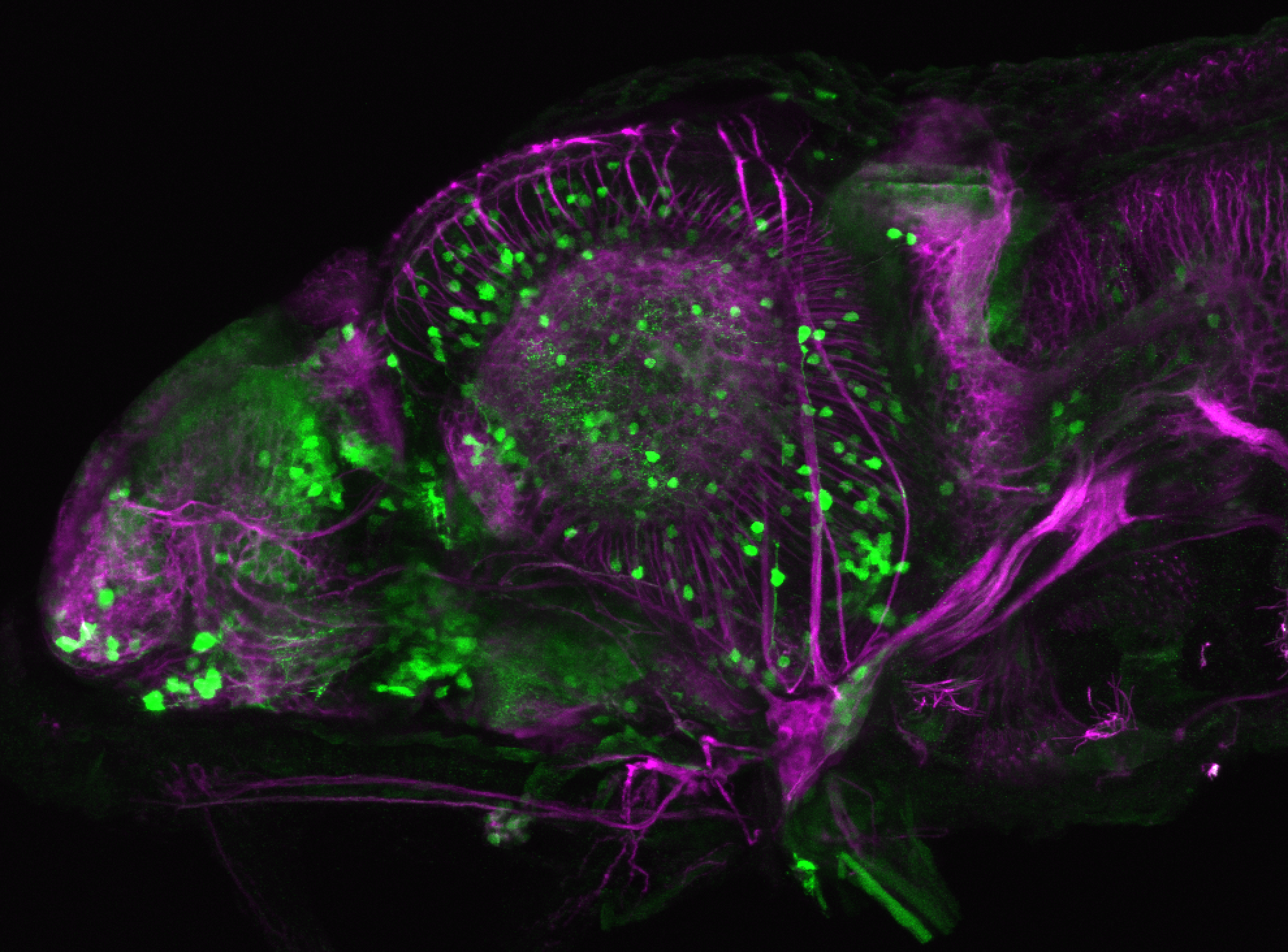
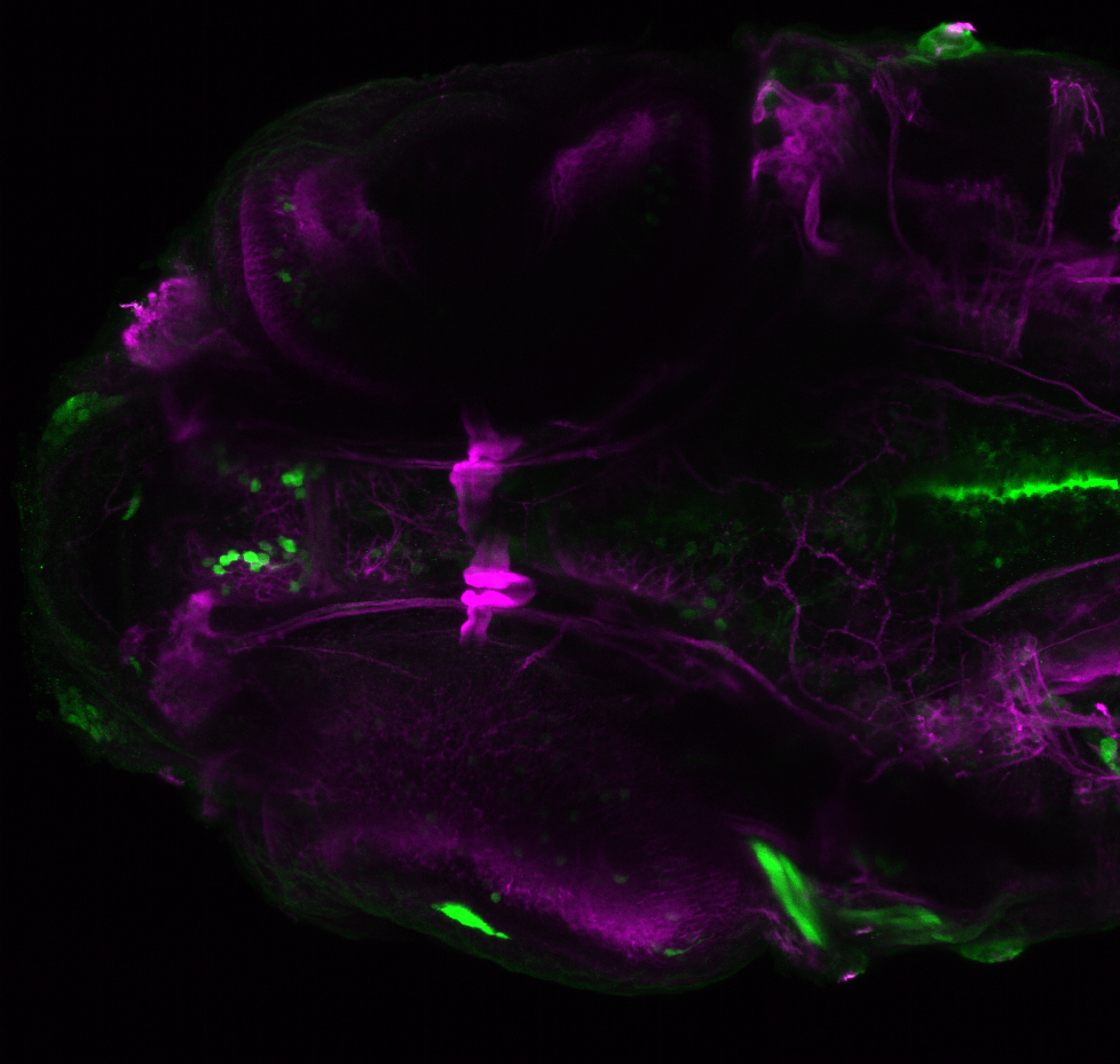
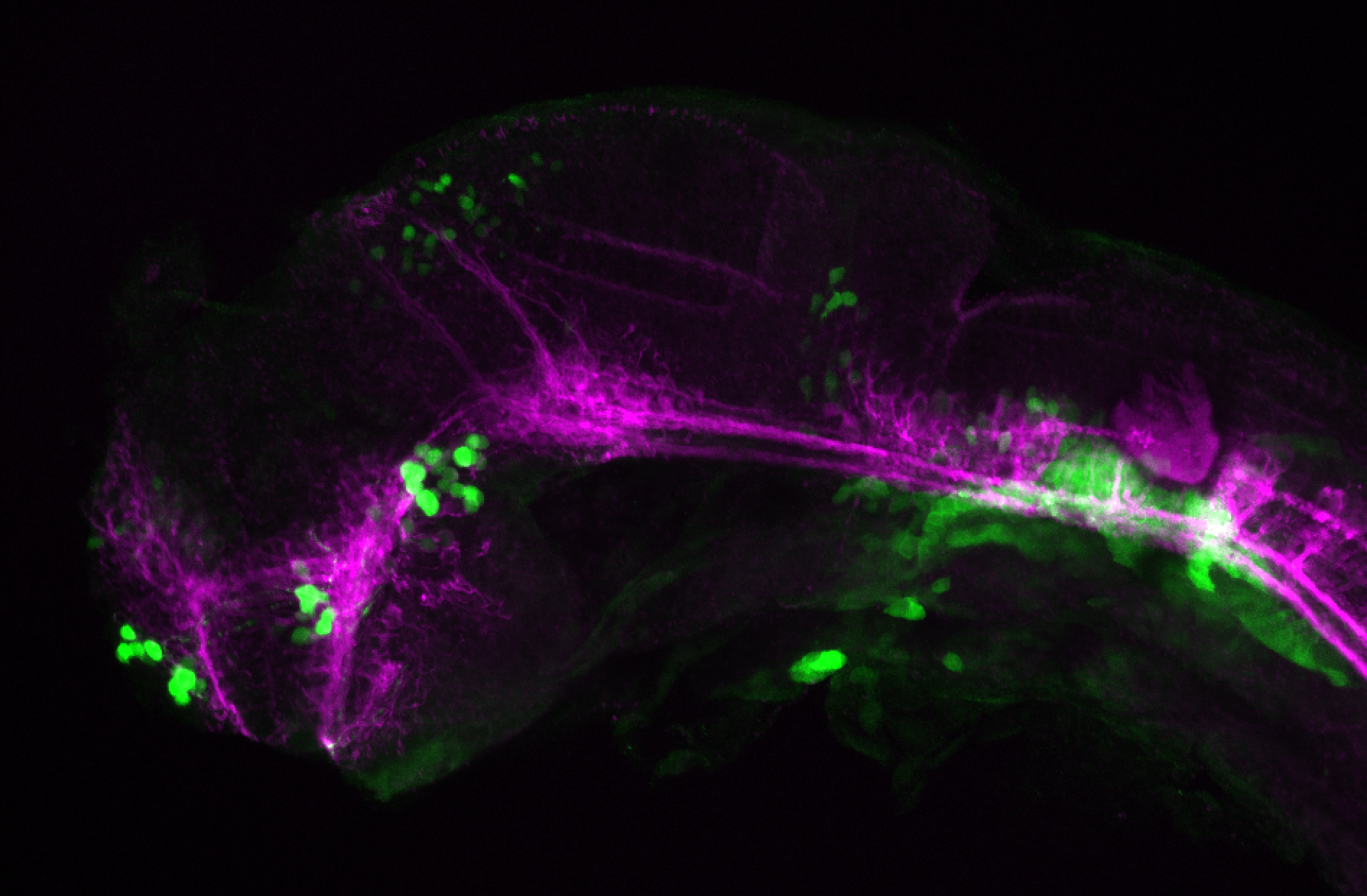
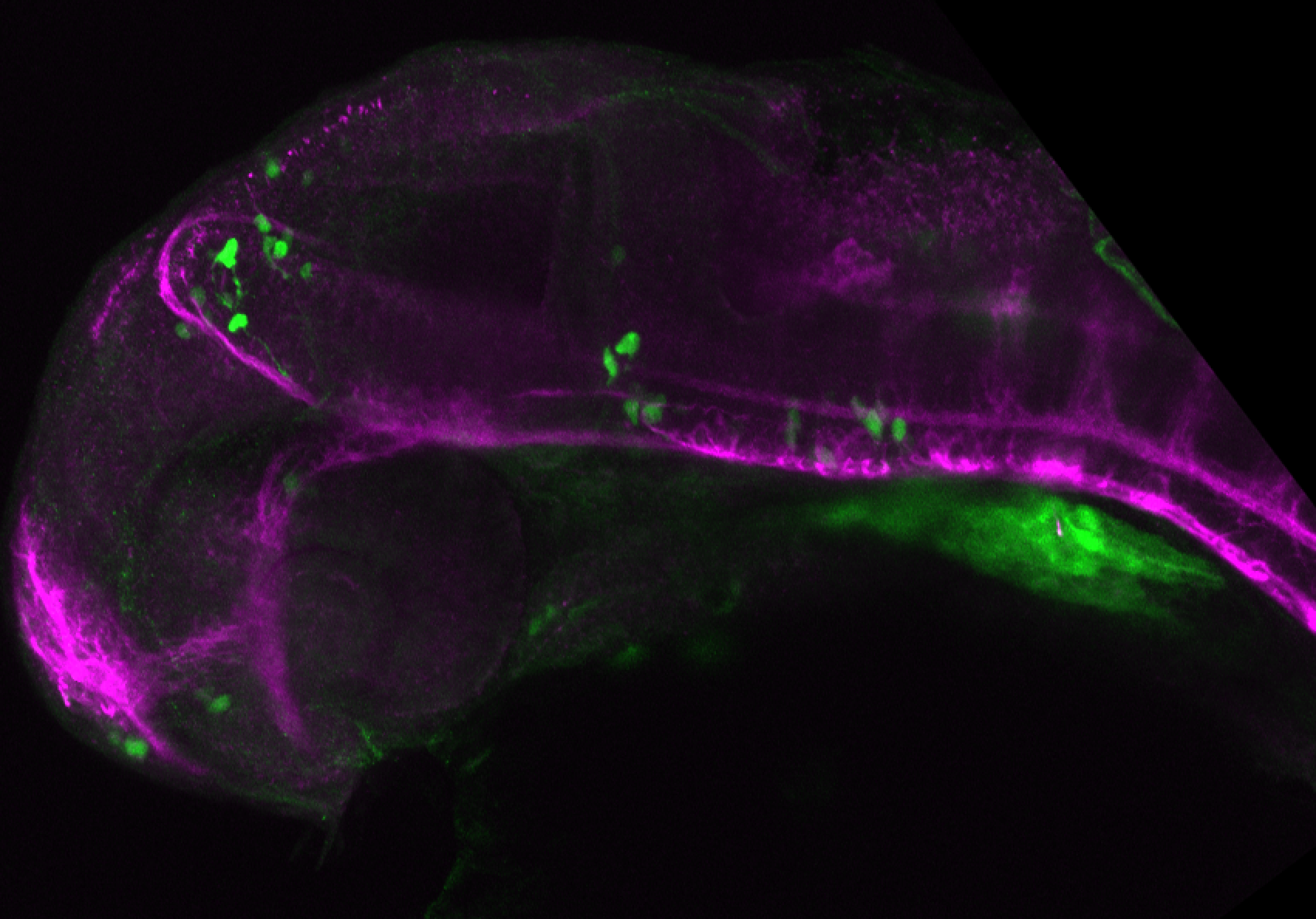
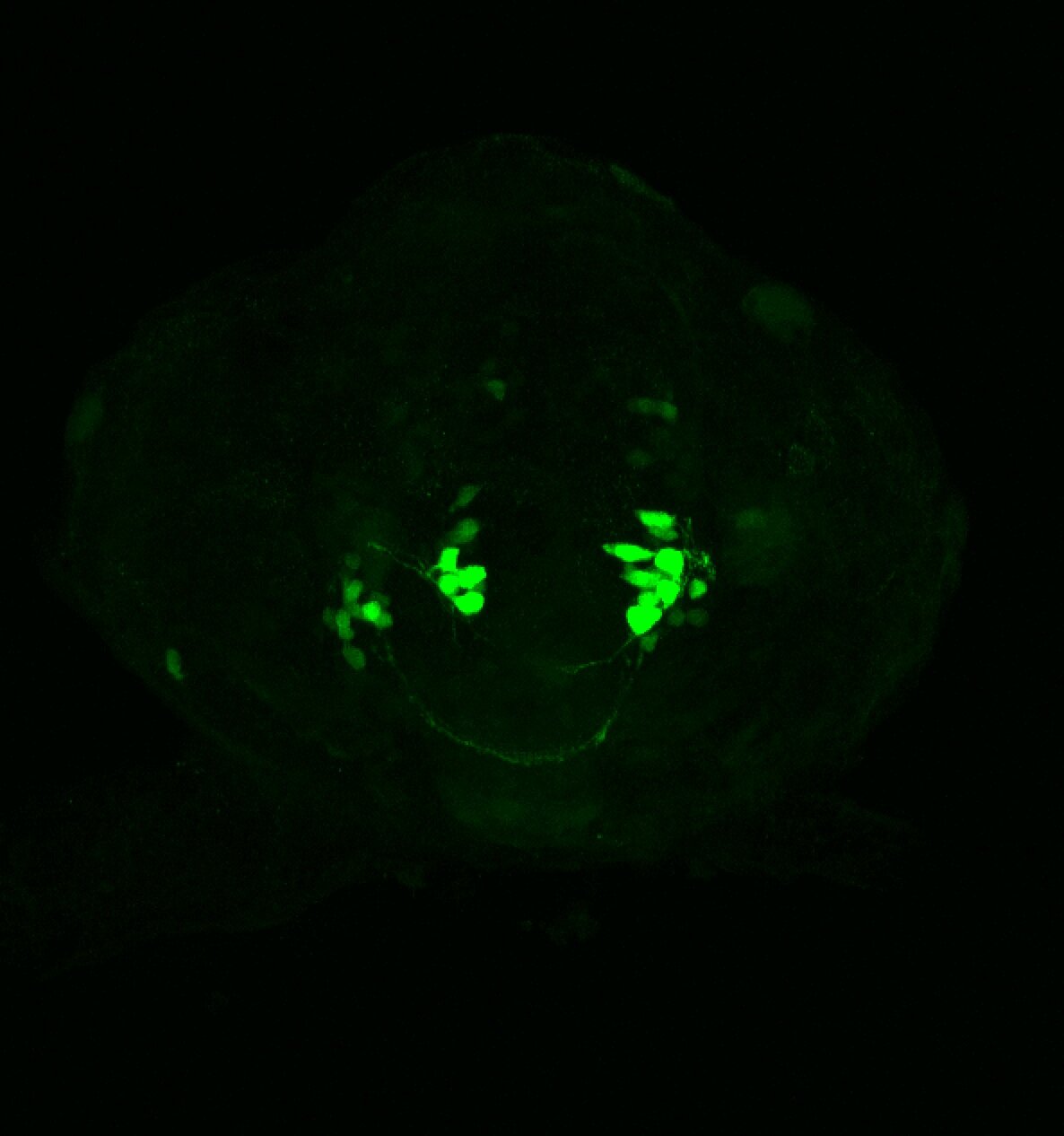
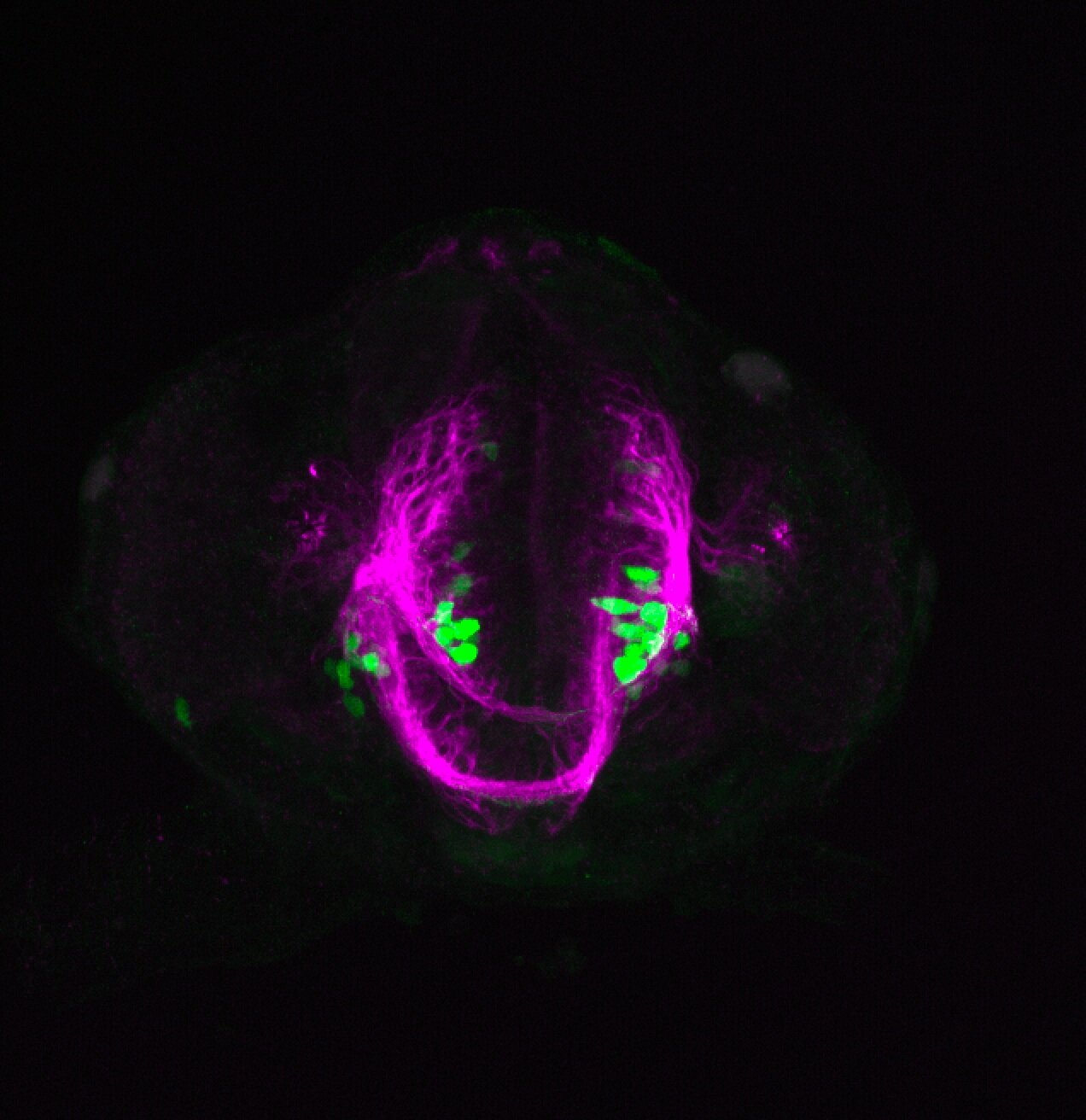
Construct contains the highly conserved noncoding sequence C99 from the human IRXB cluster, containing the genes IRX3, IRX5, and IRX6.
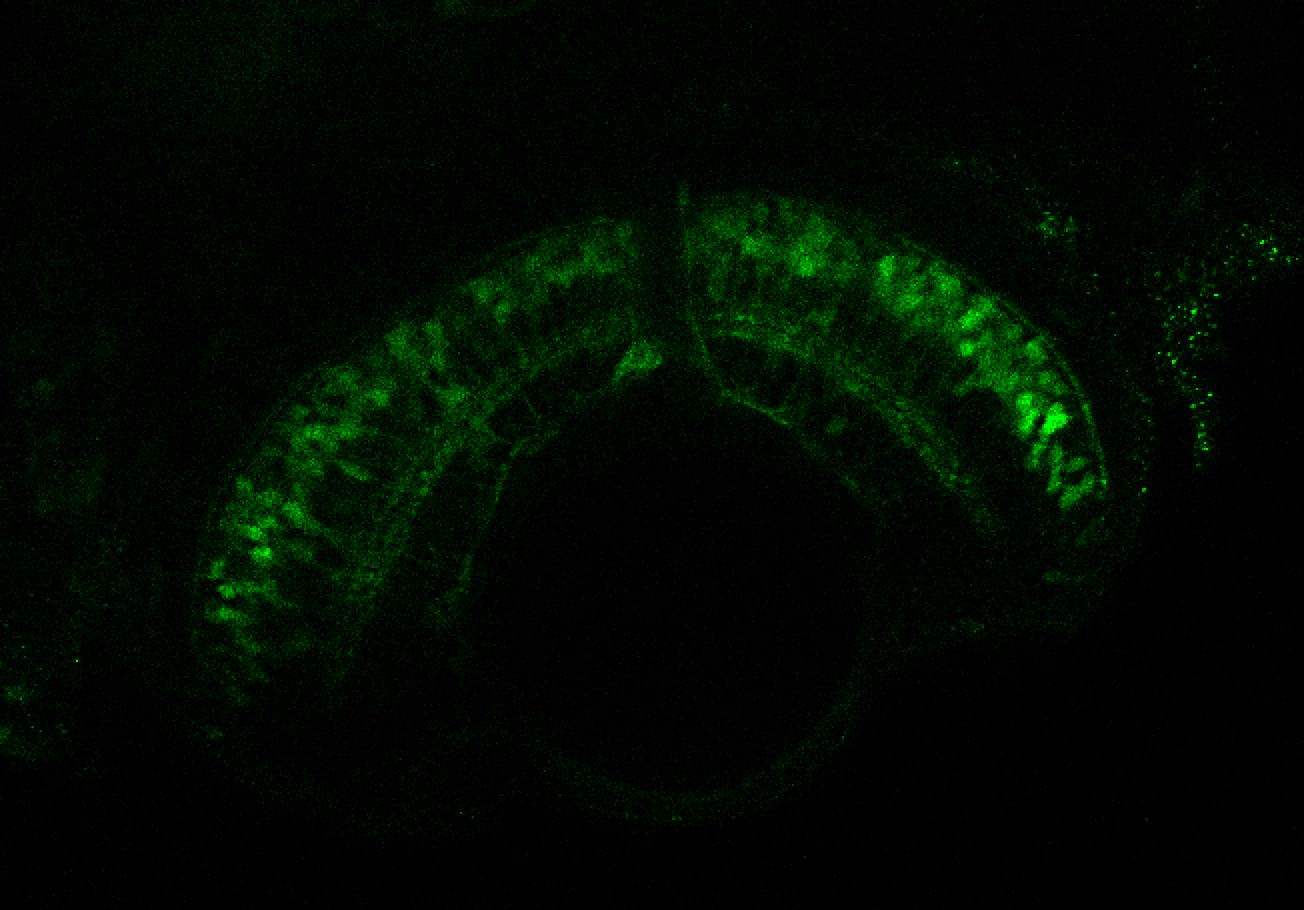
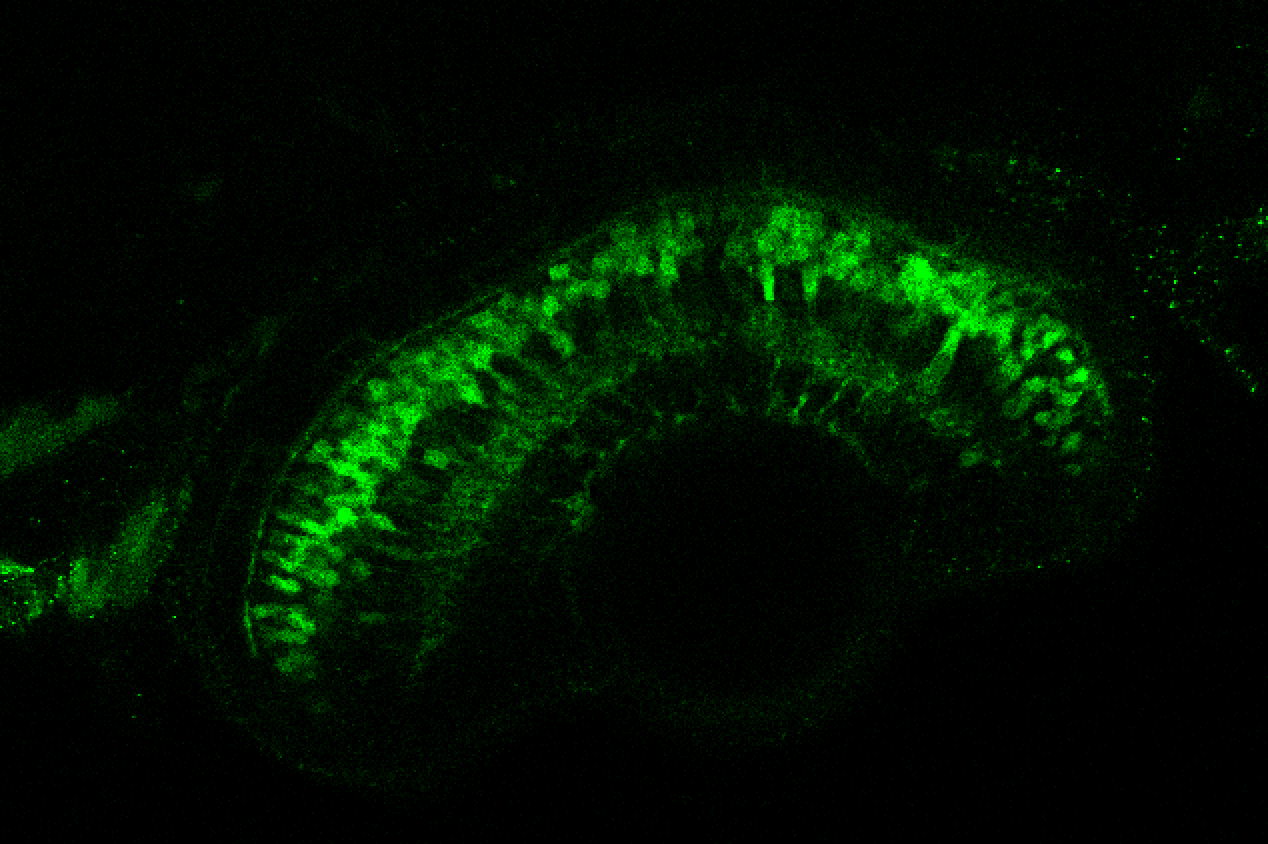
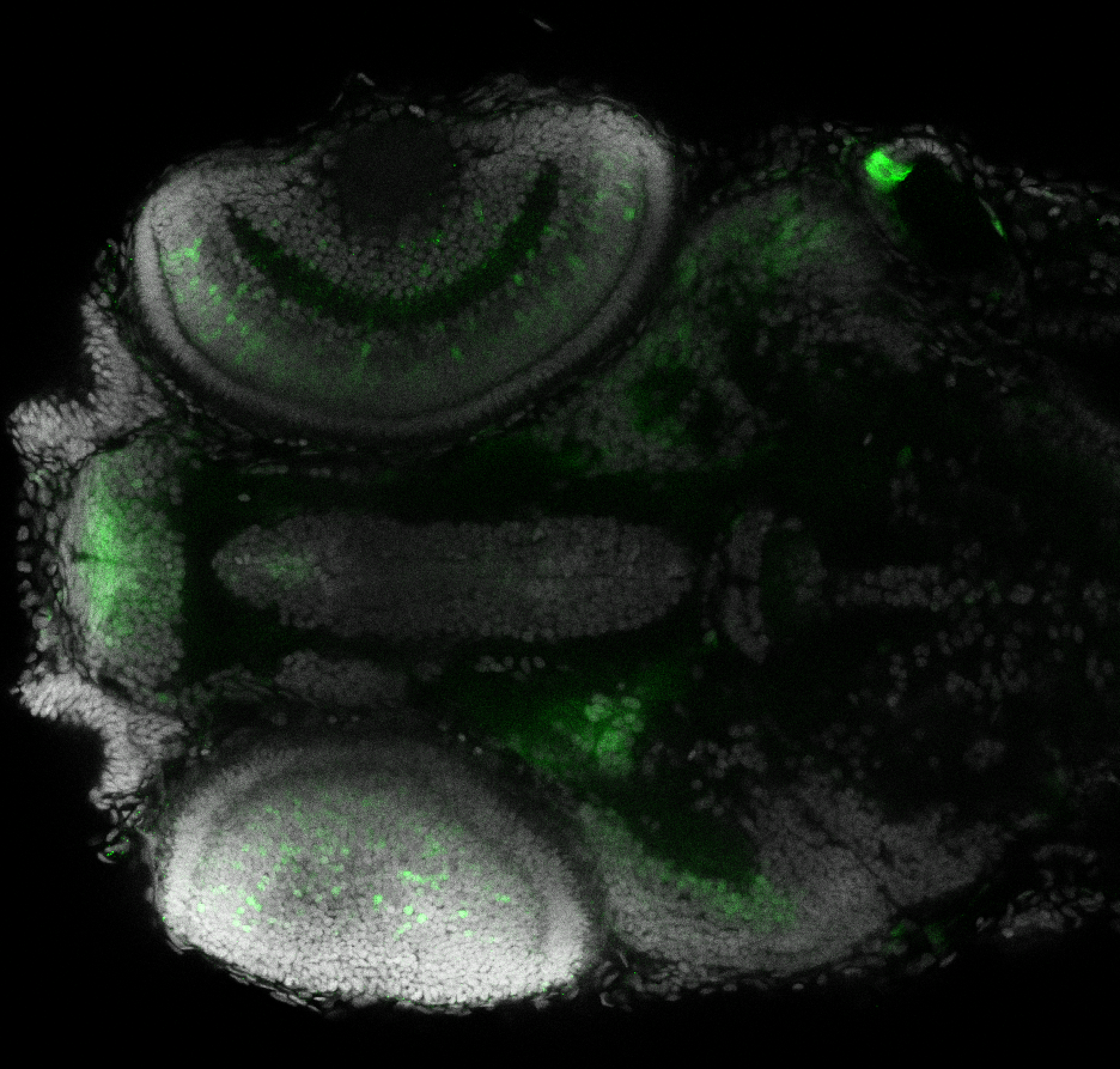
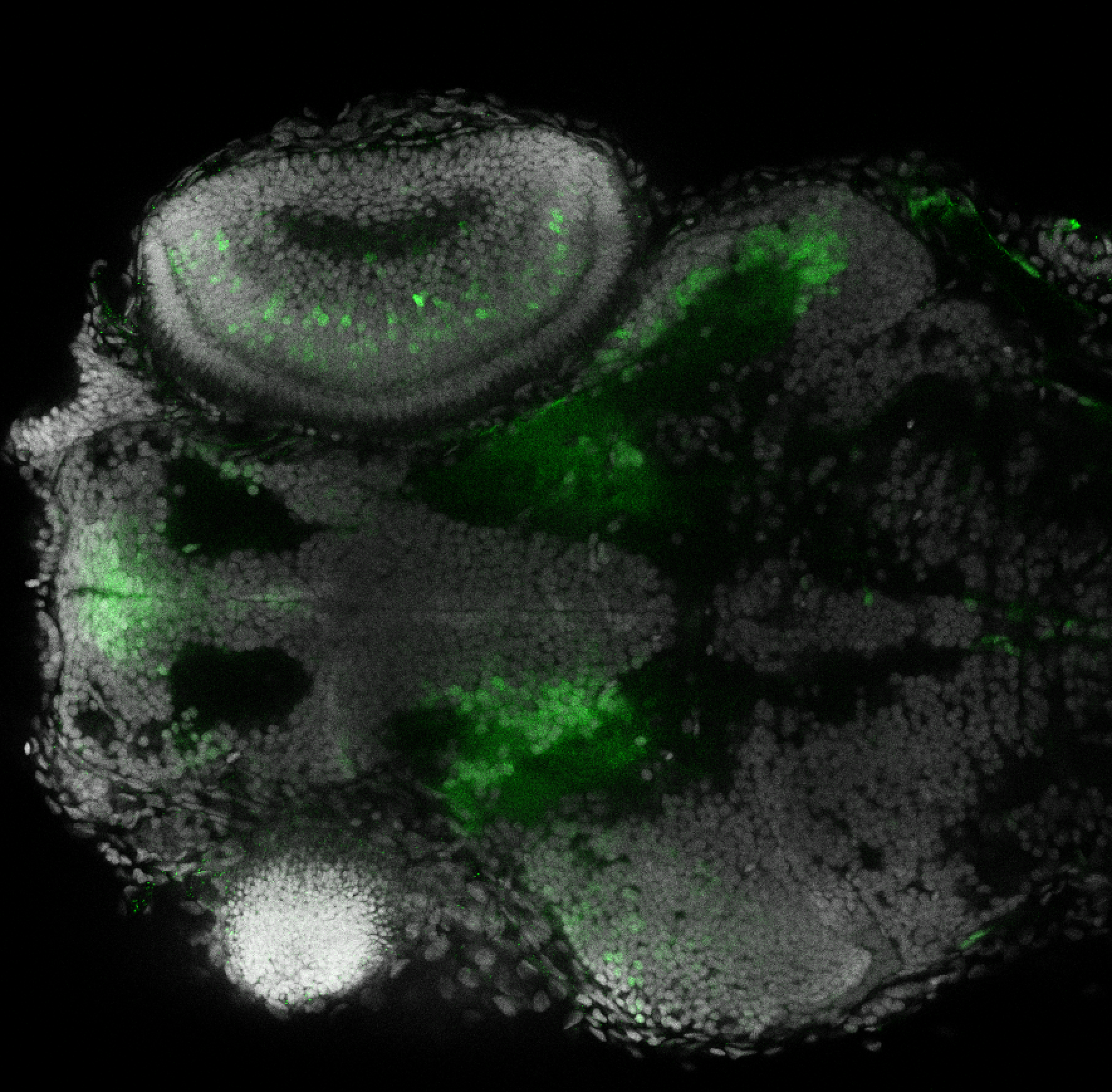
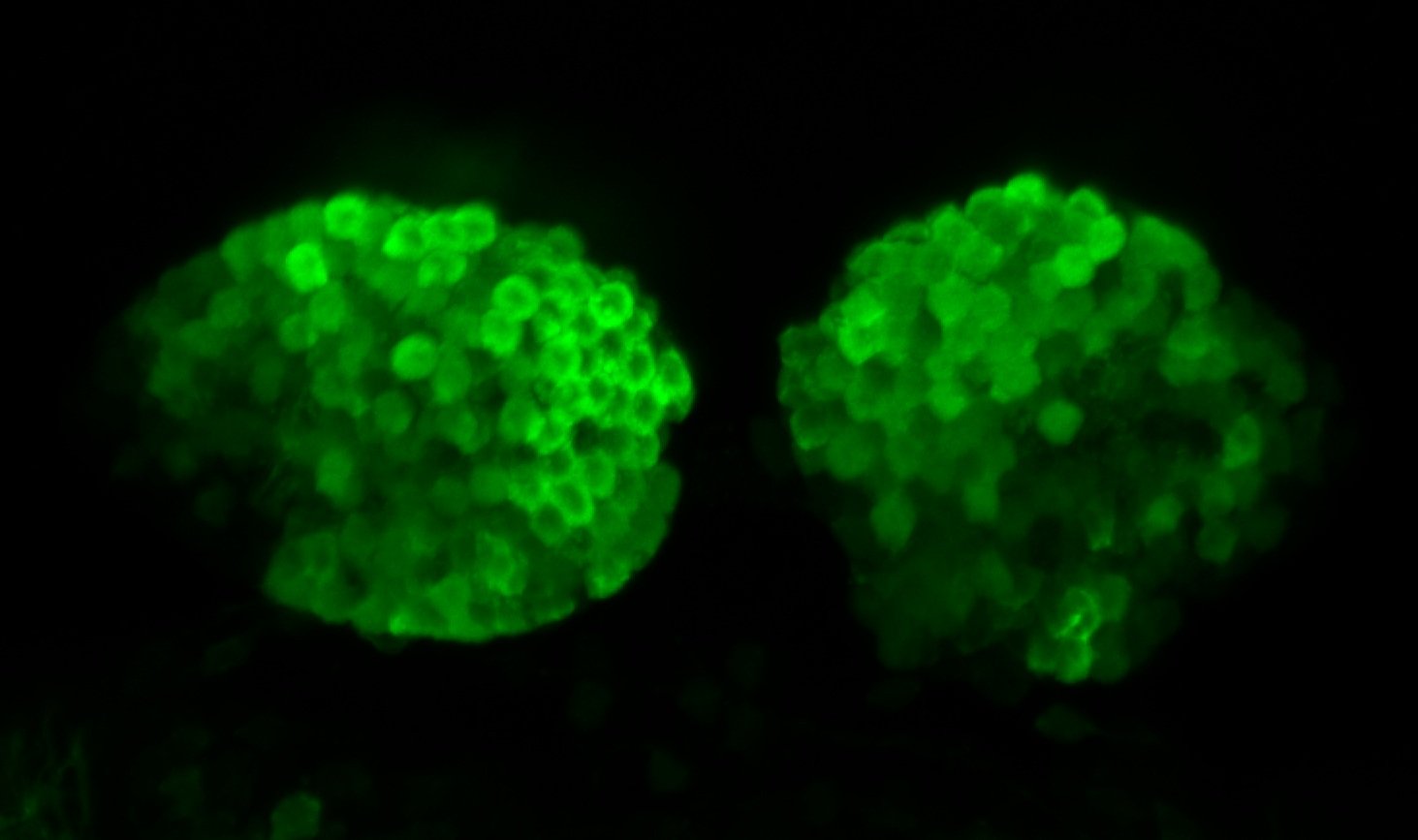
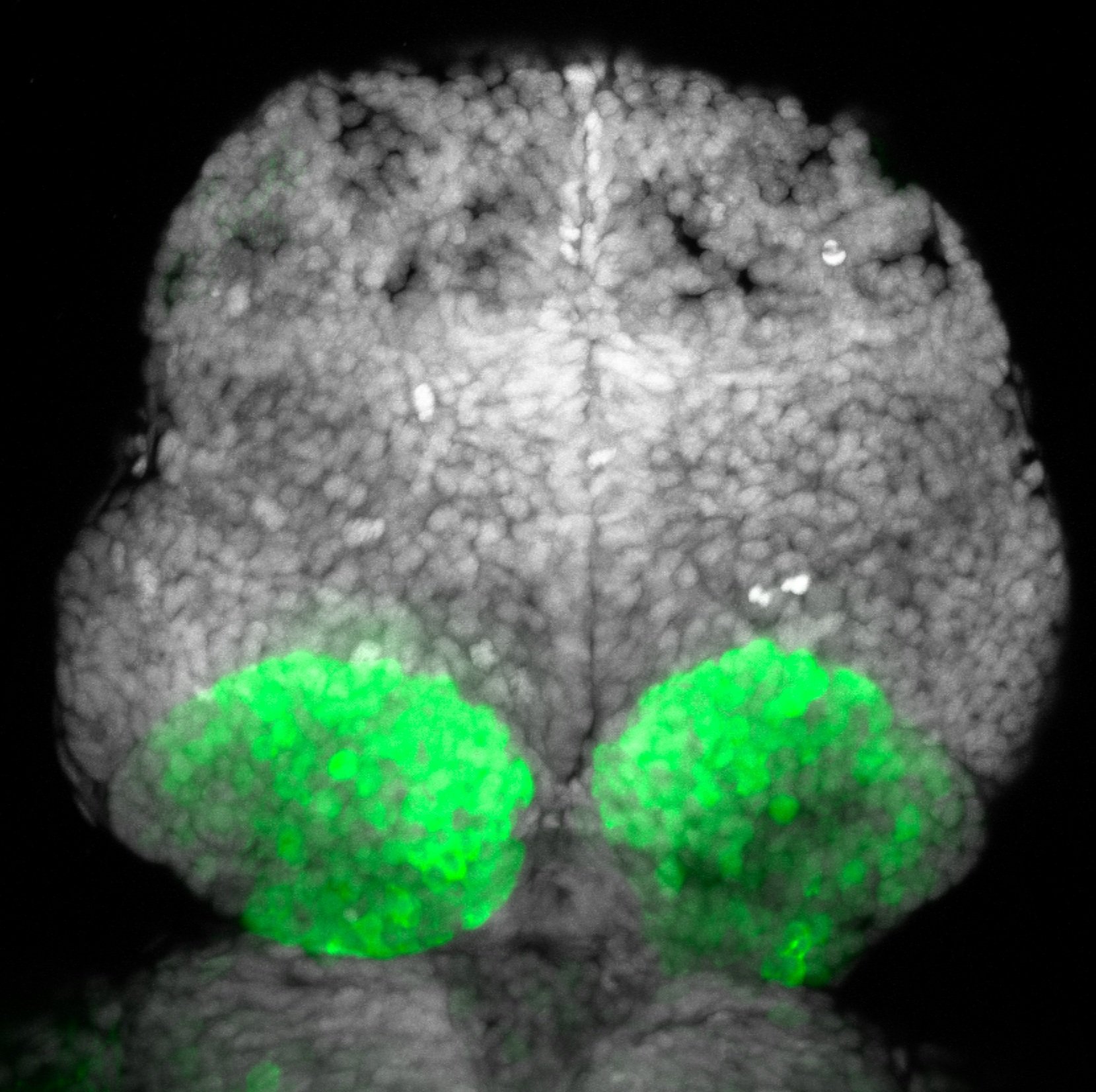
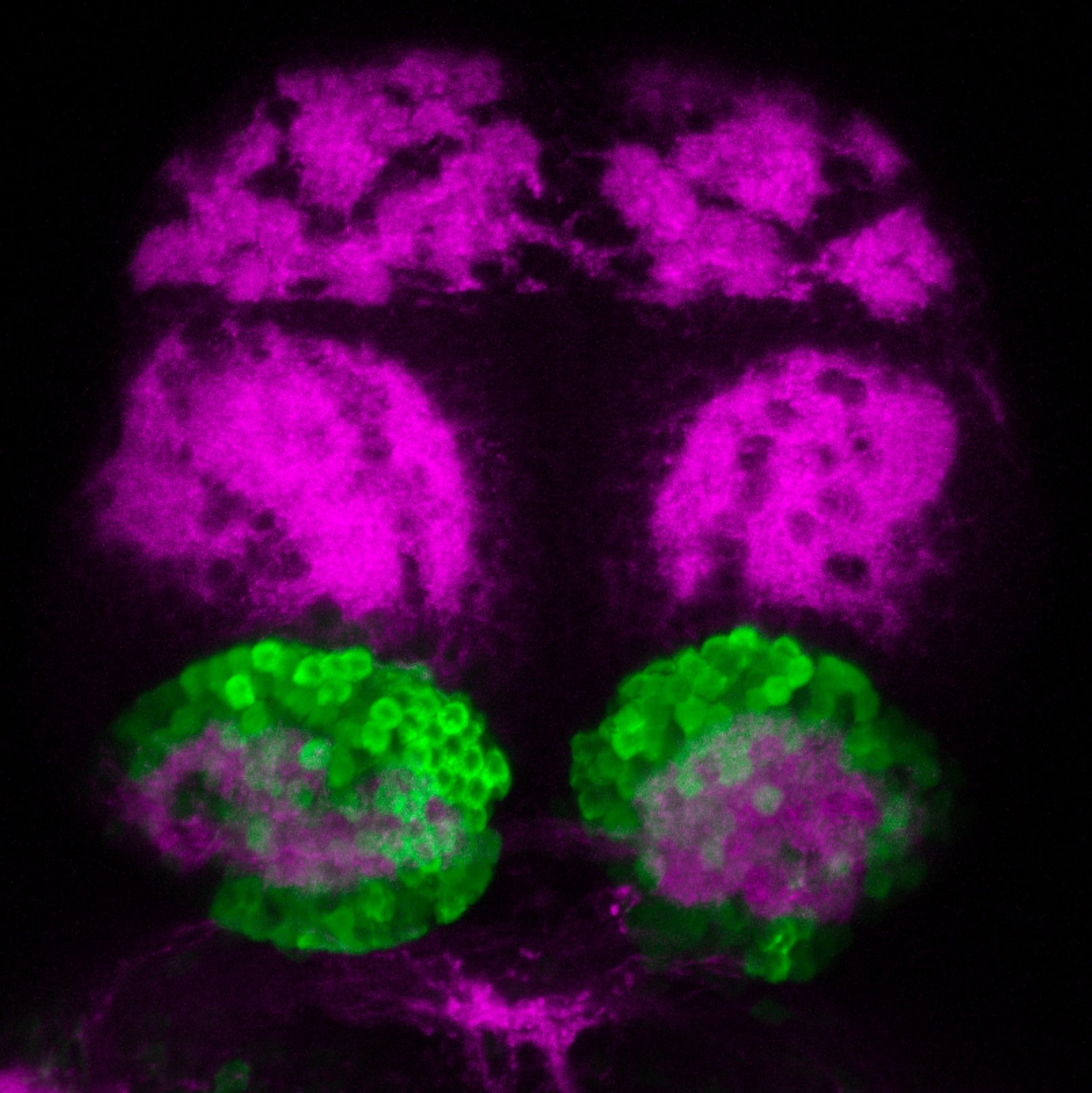
TG44 is an enhancer trap line from the Skarmeta Lab. Generated as part of a study looking at the transcriptional regulatory properties of highly-conserved noncoding elements on chromosome 16.
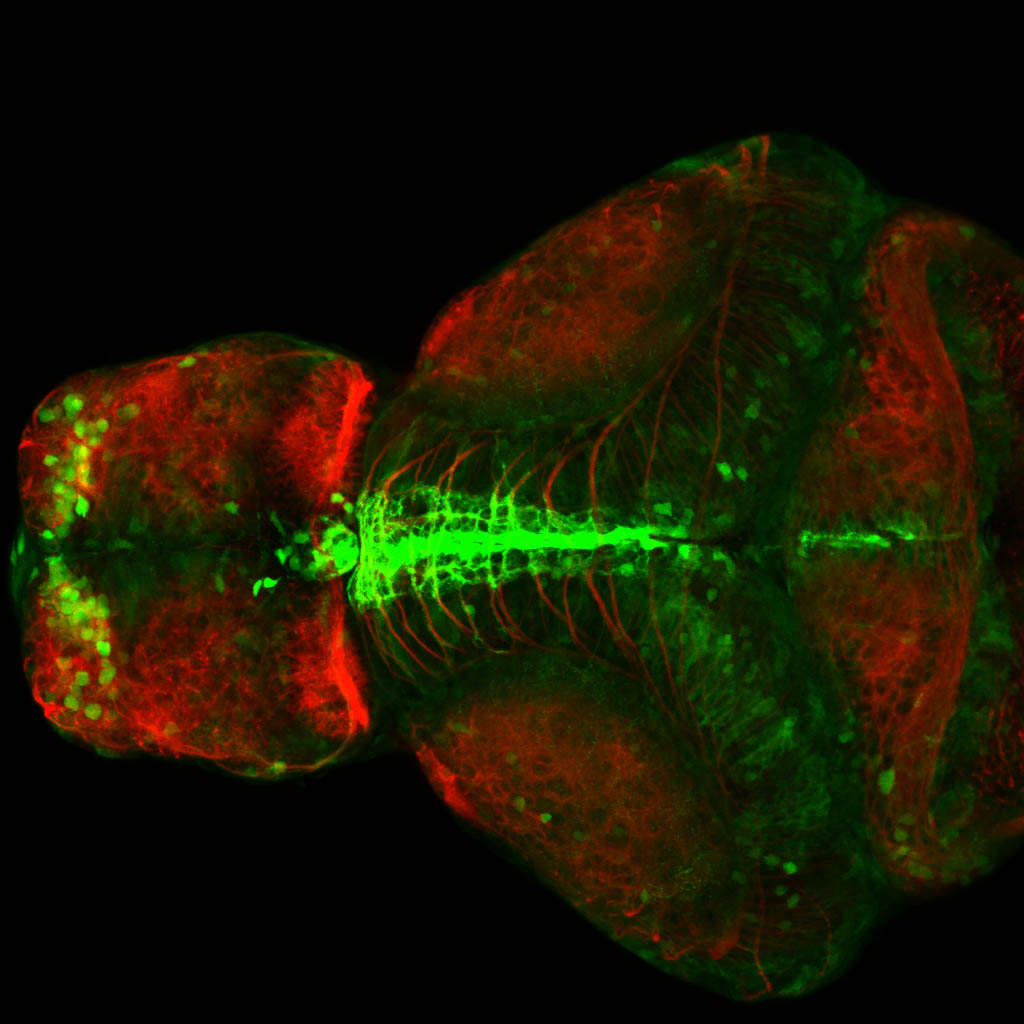
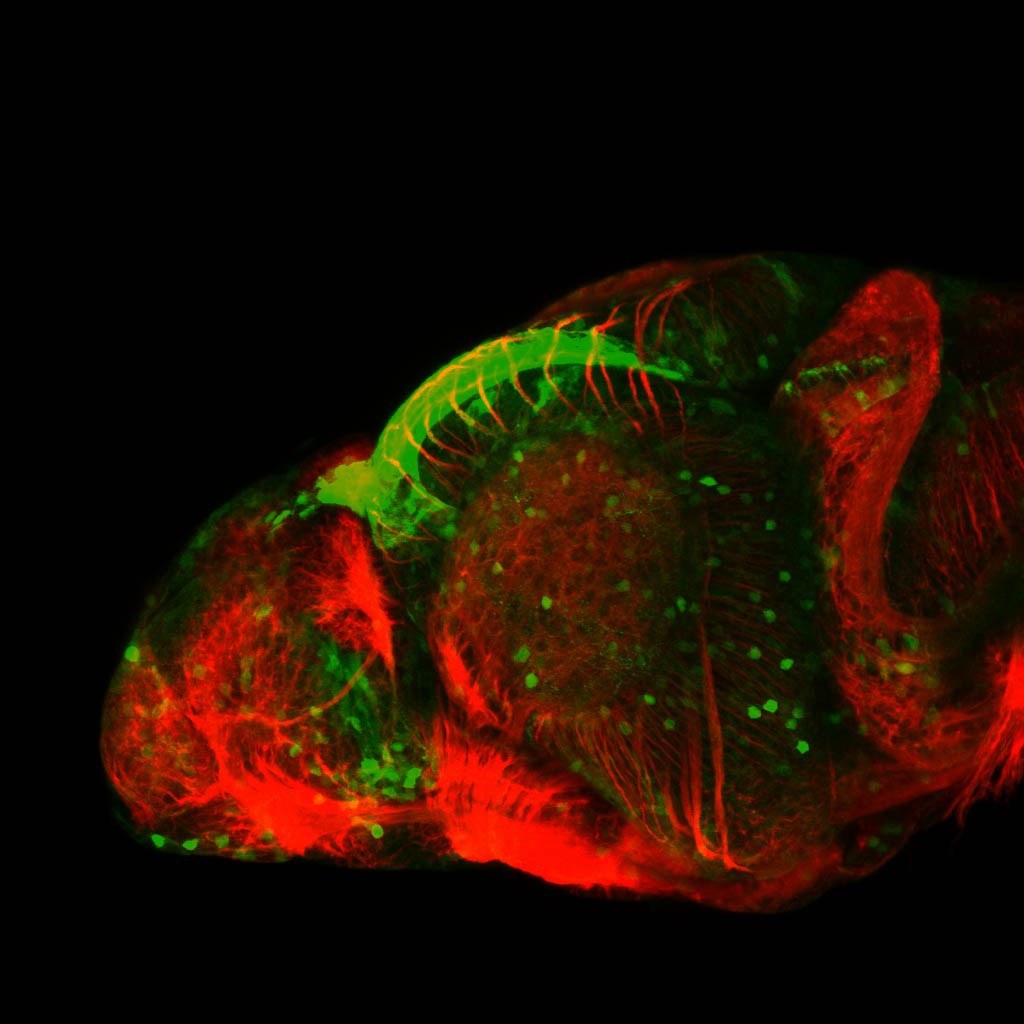
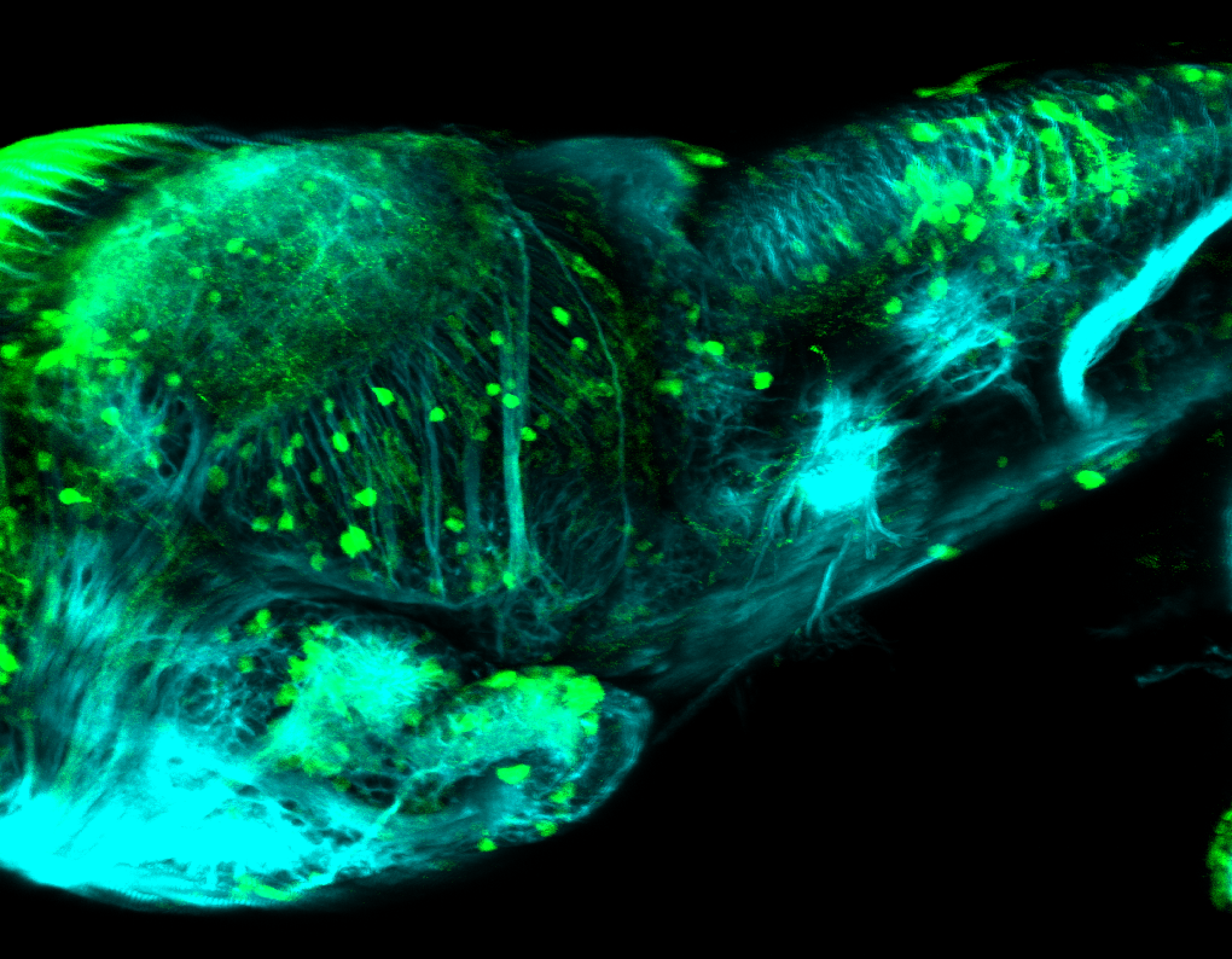
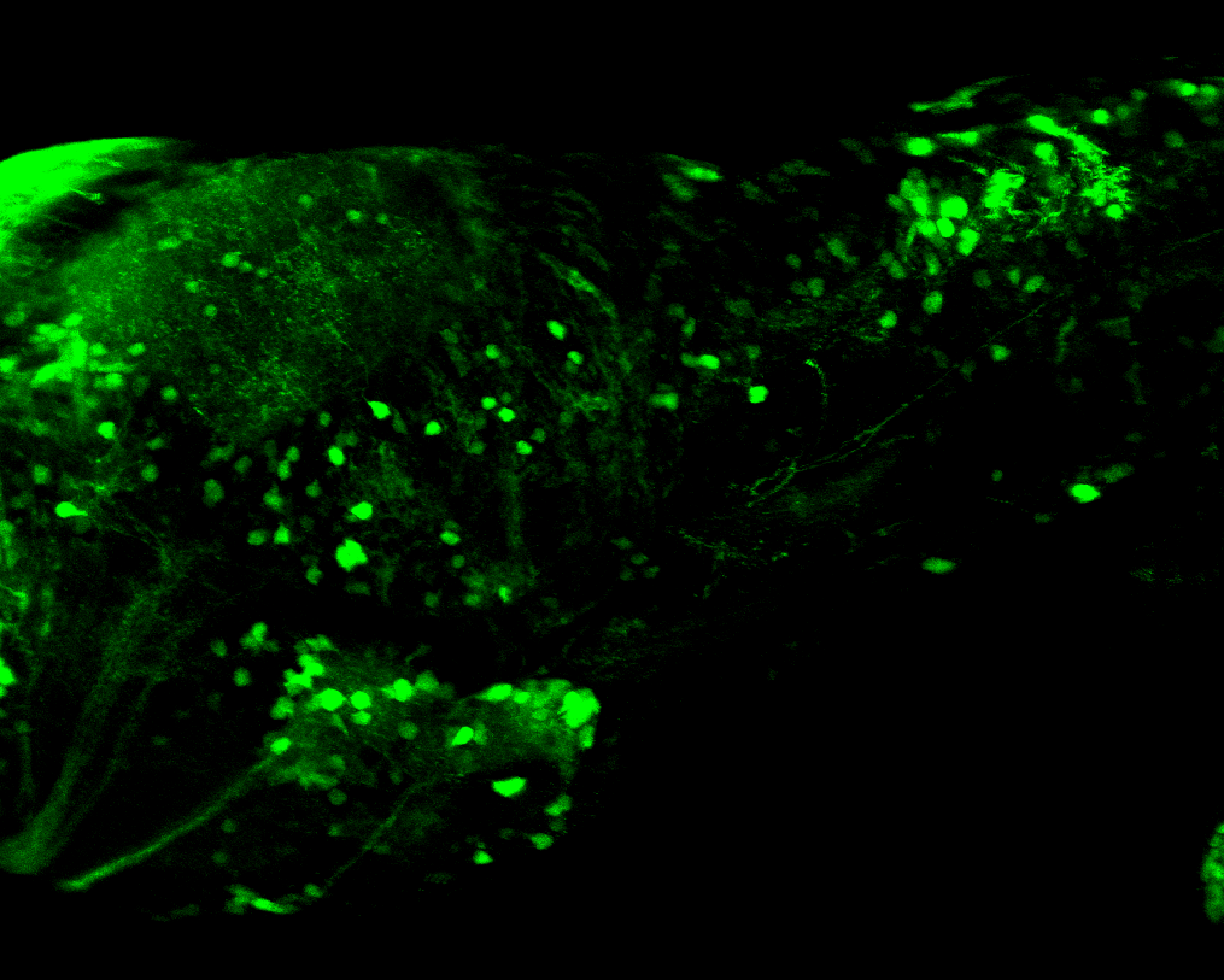
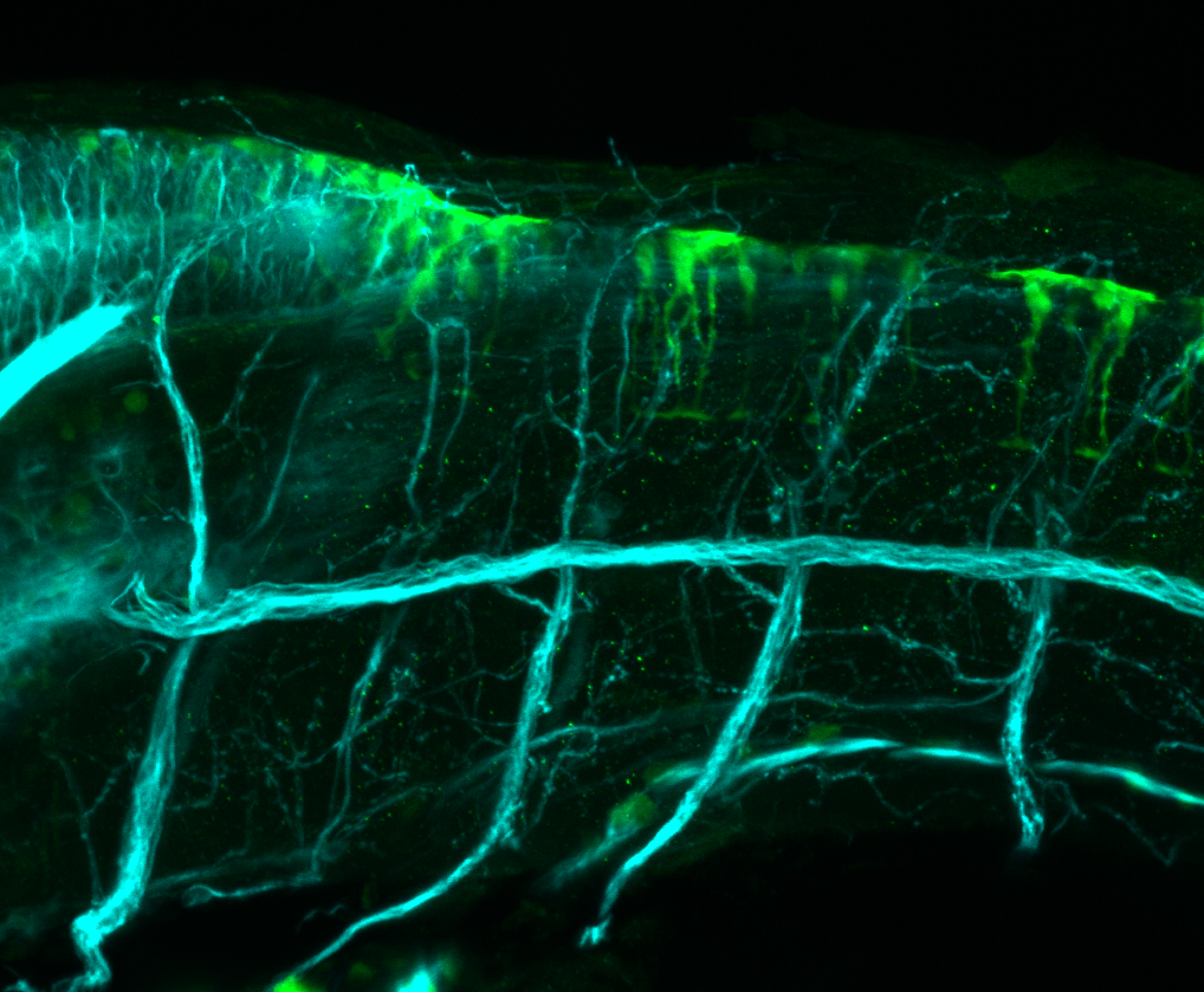
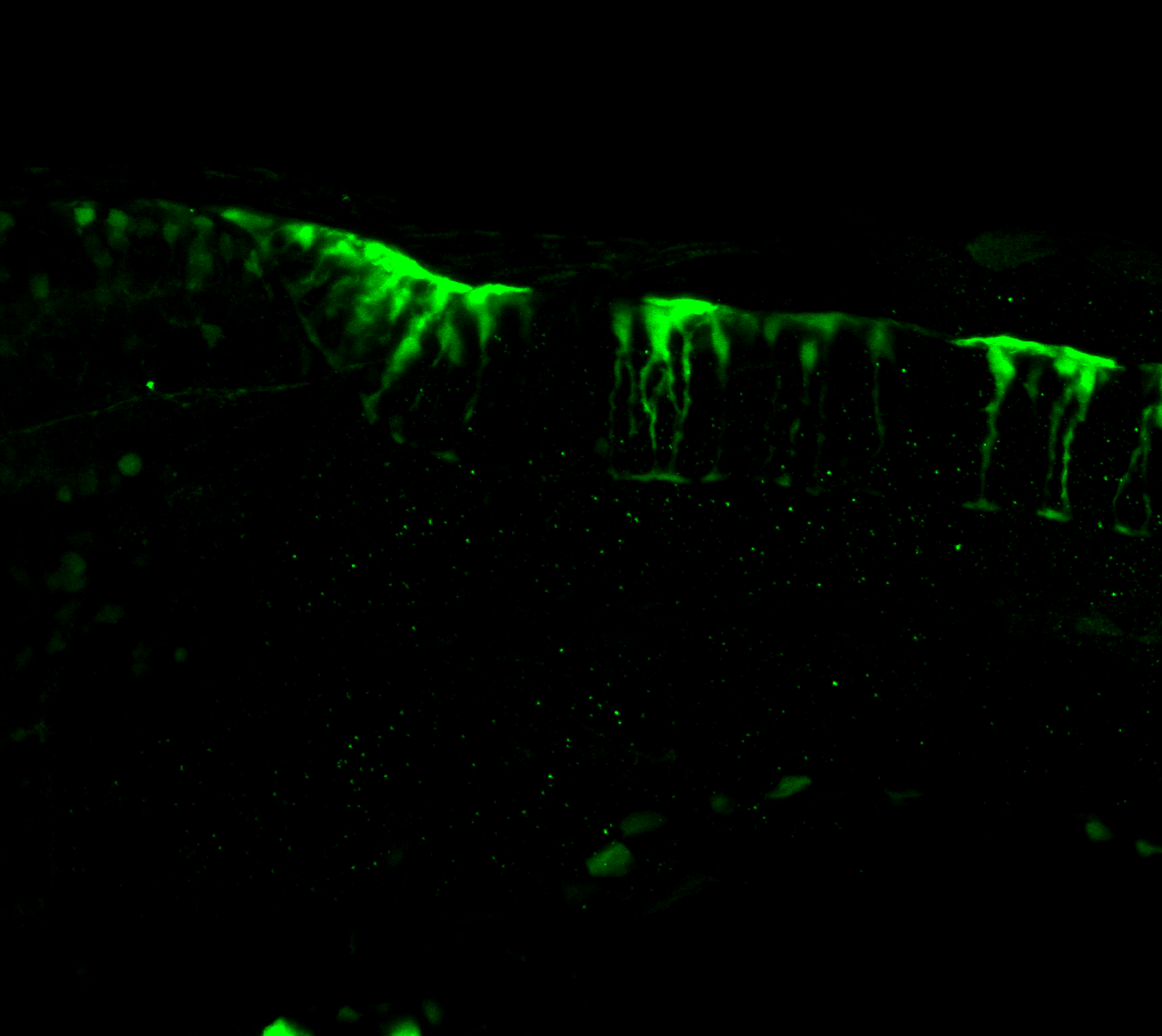
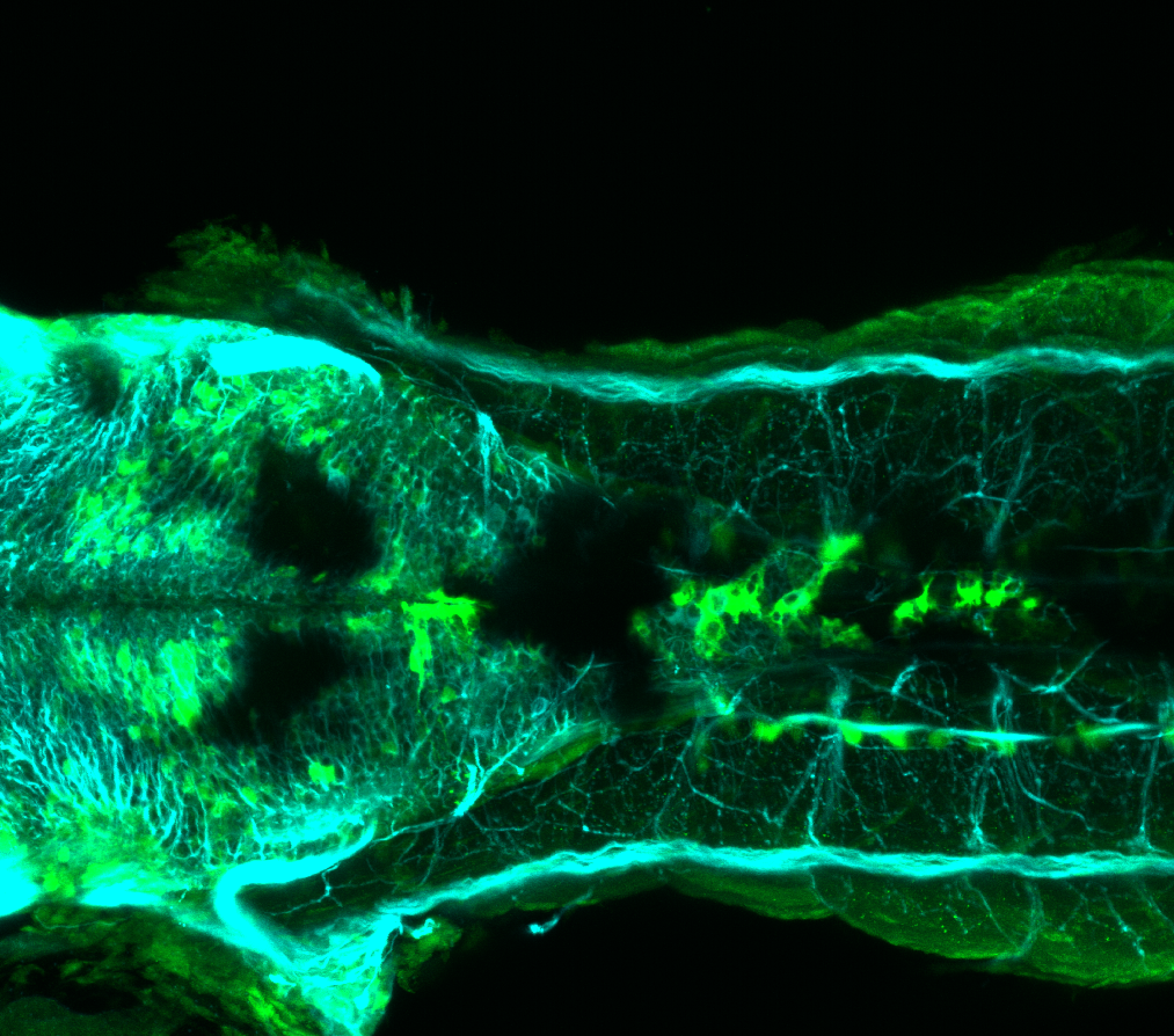
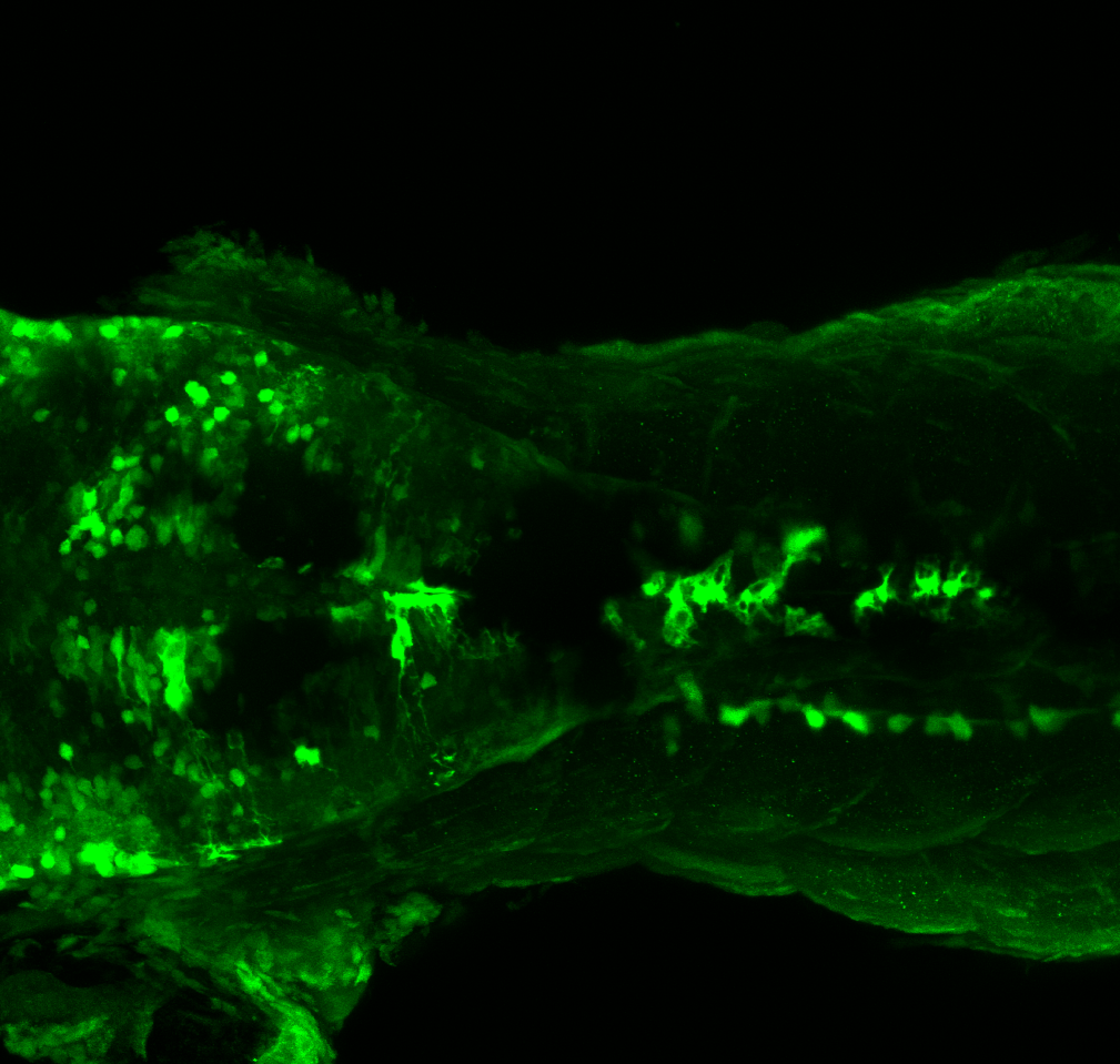
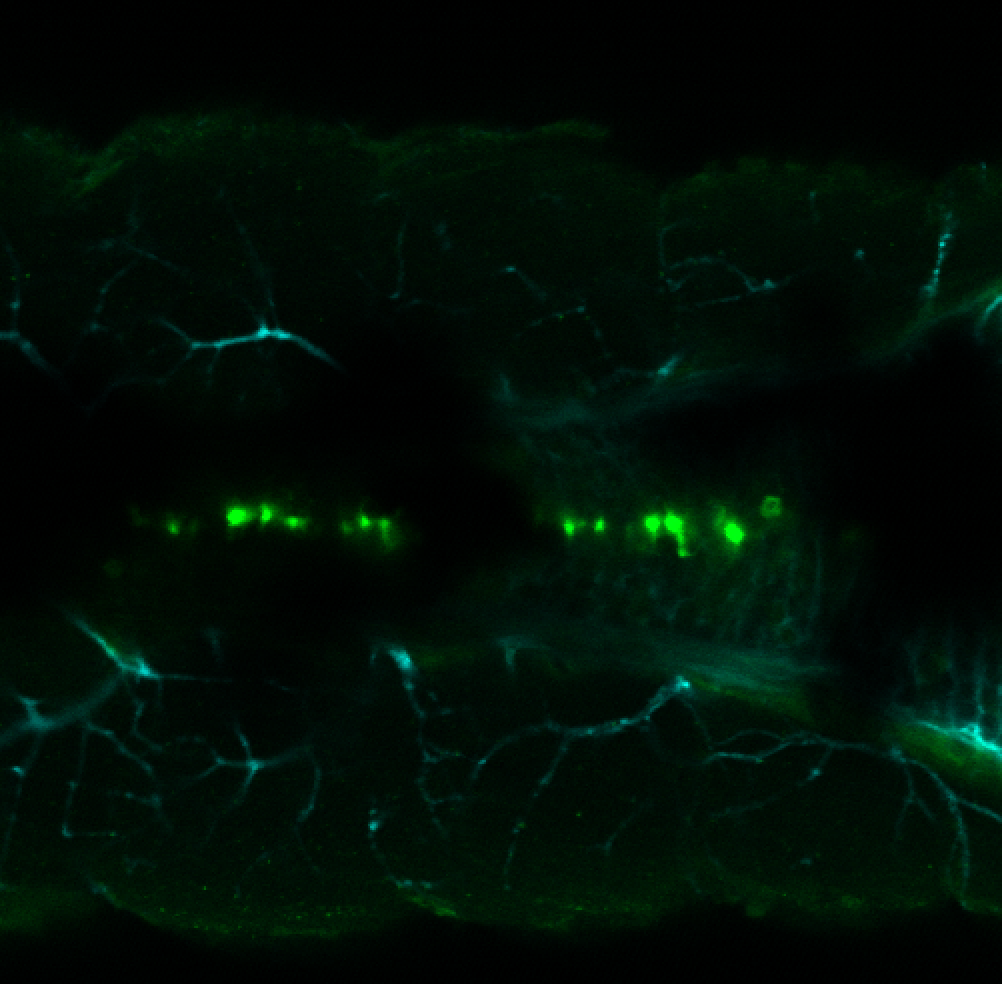
Expressed in:
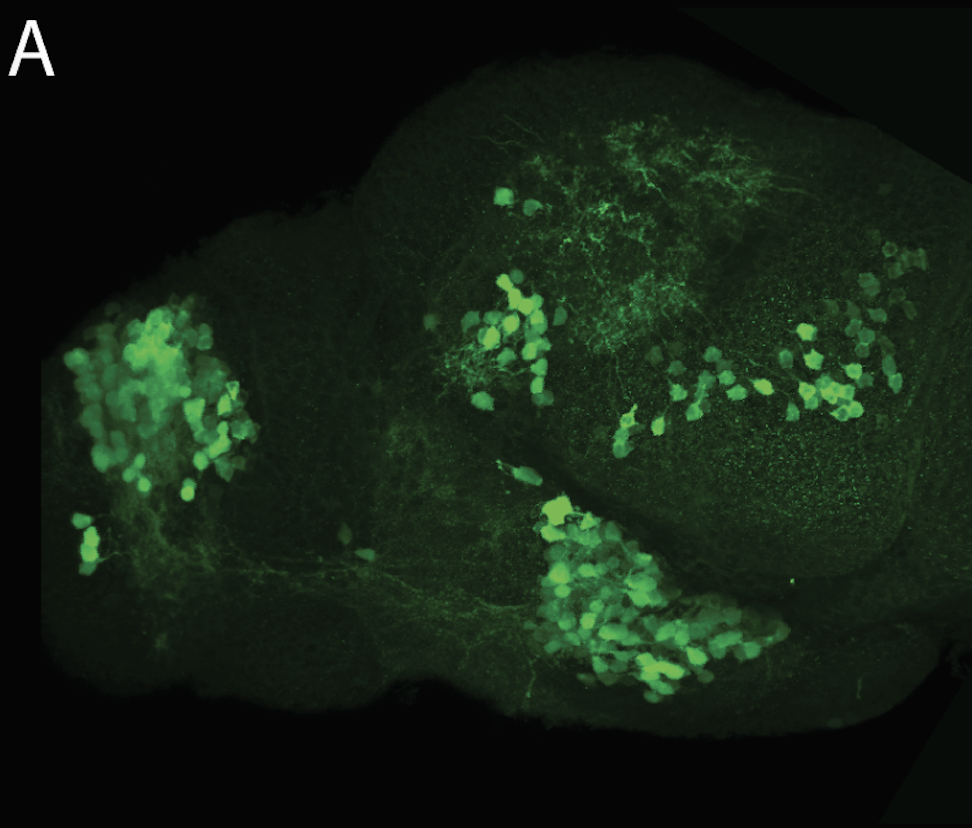
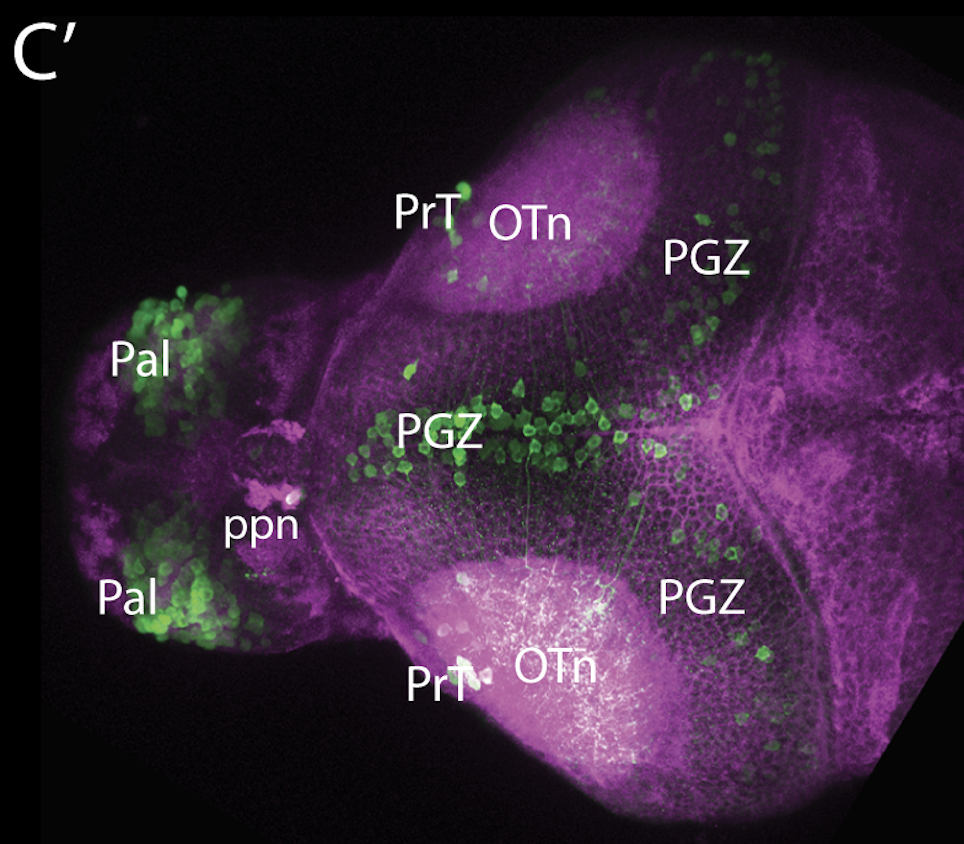
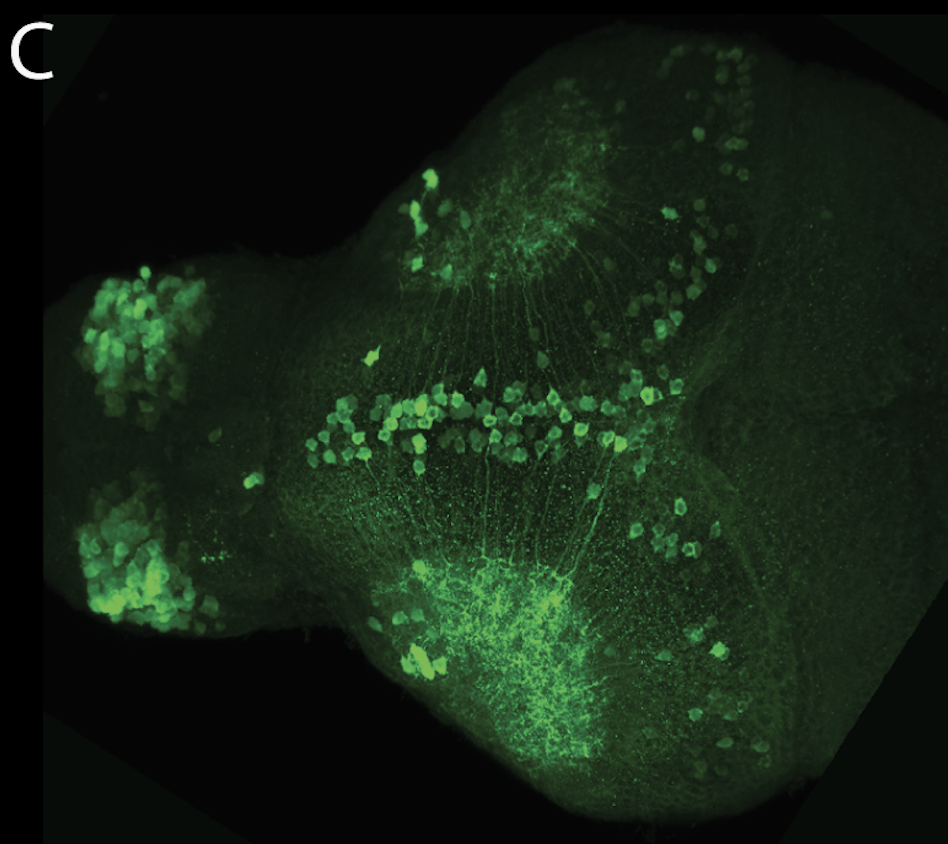
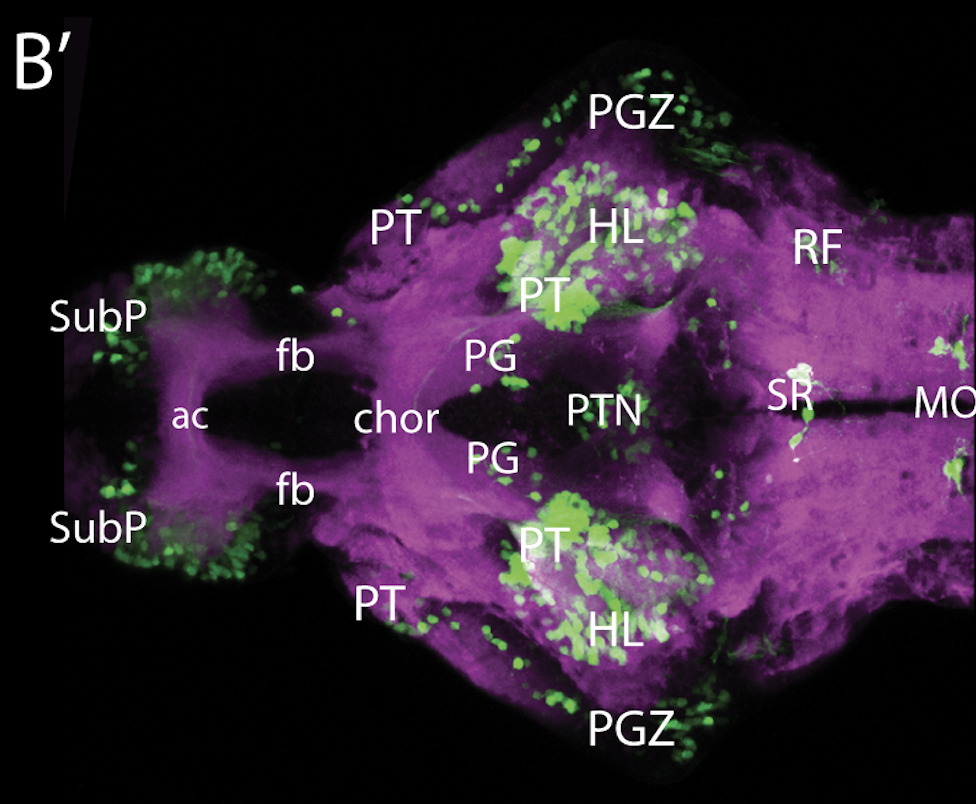
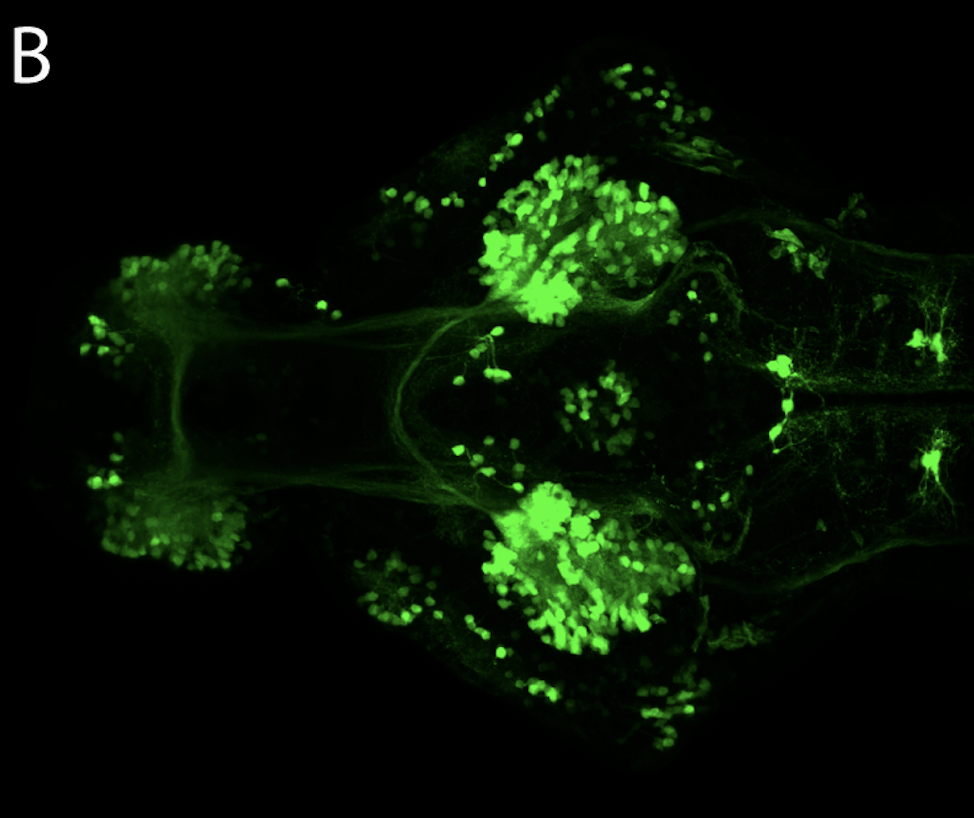
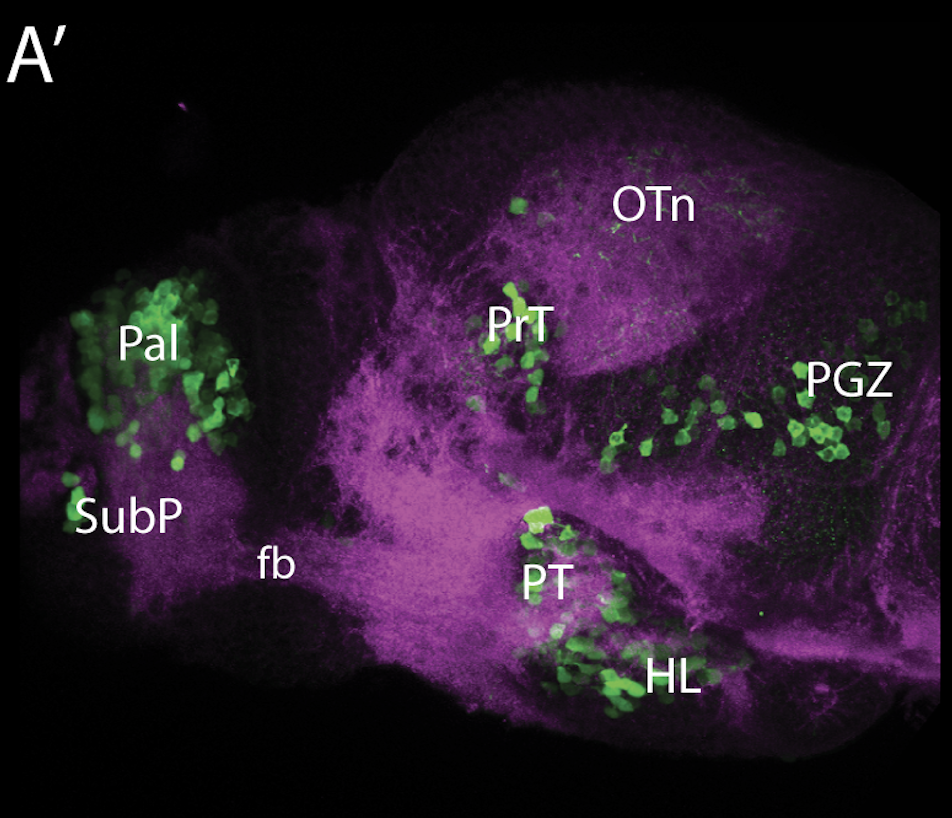
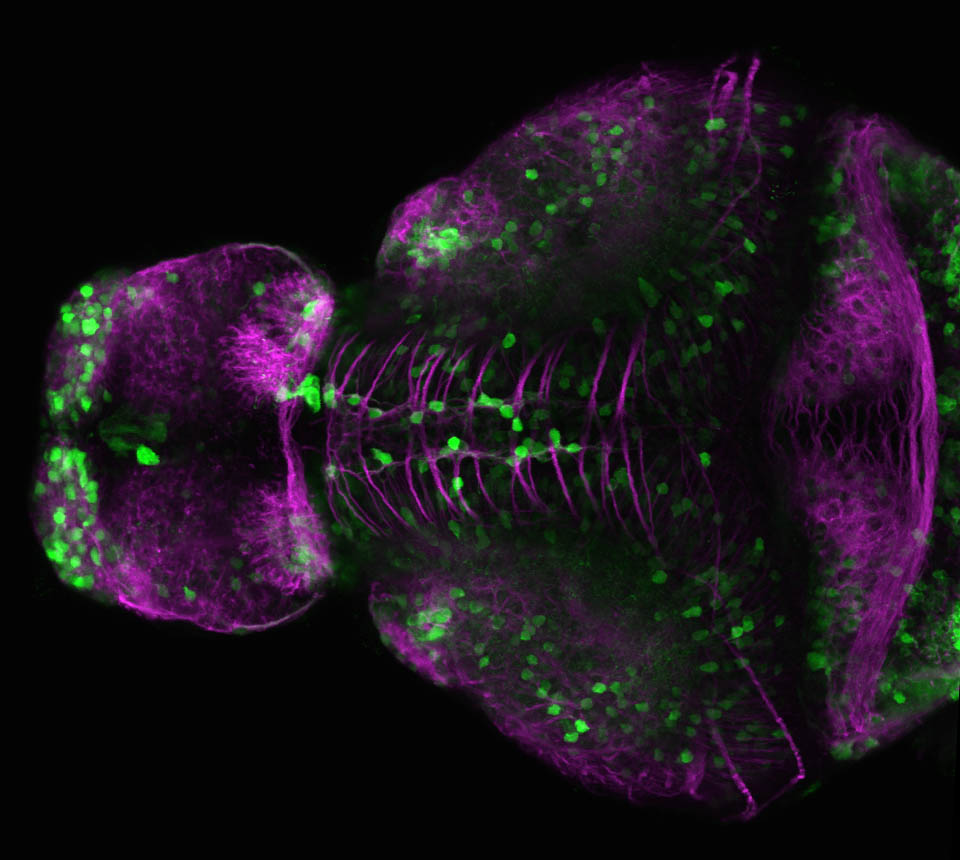
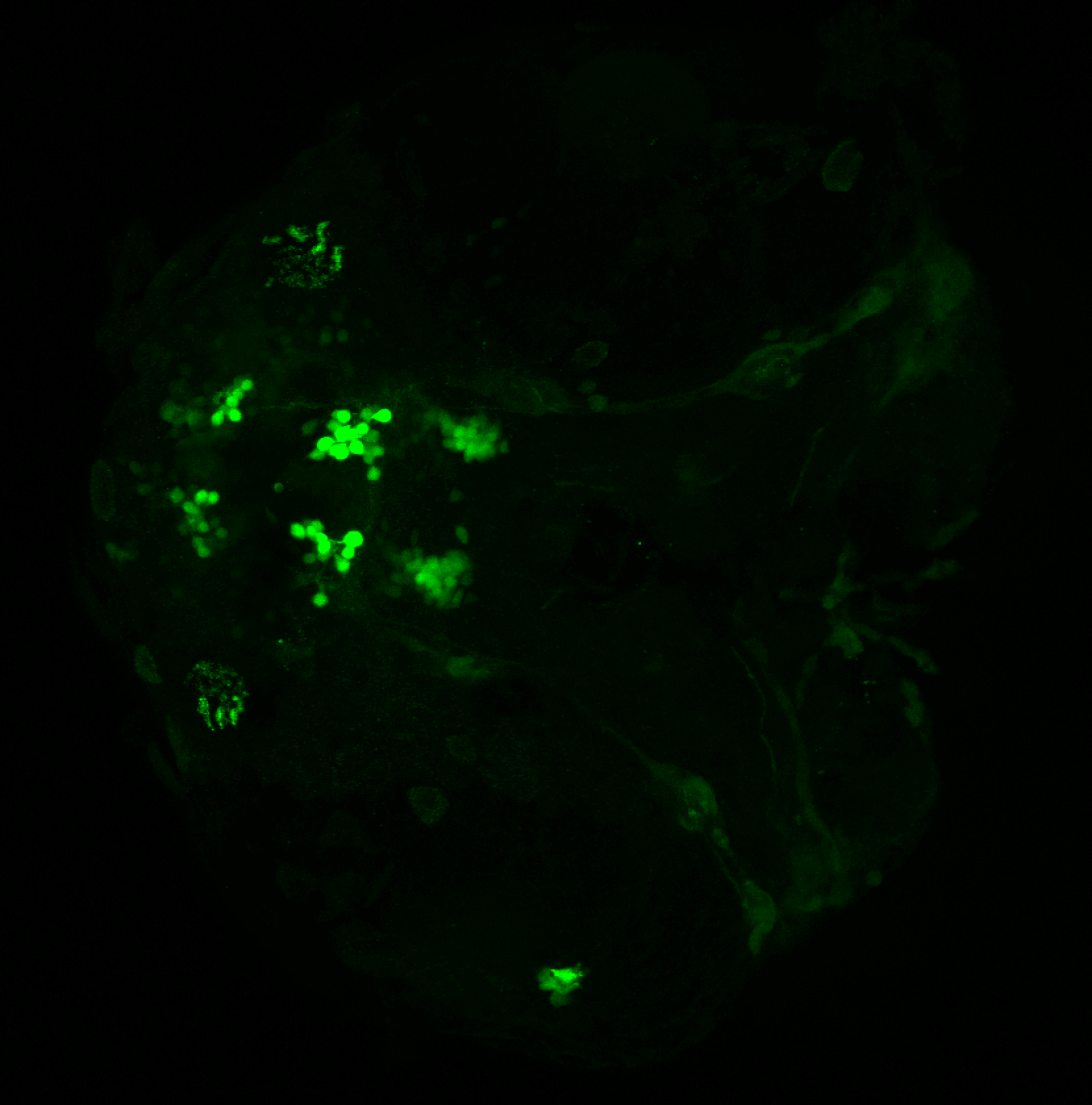
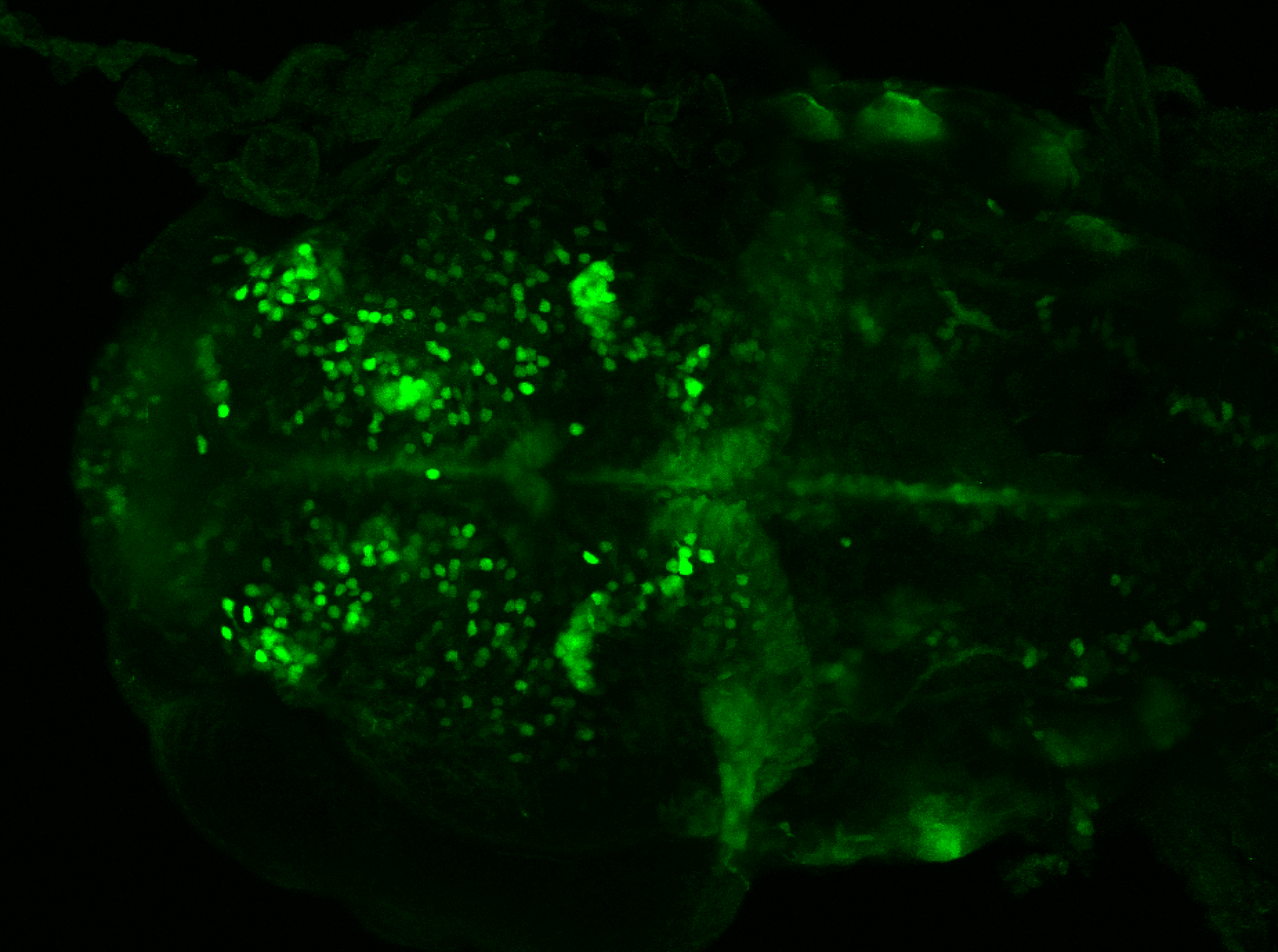
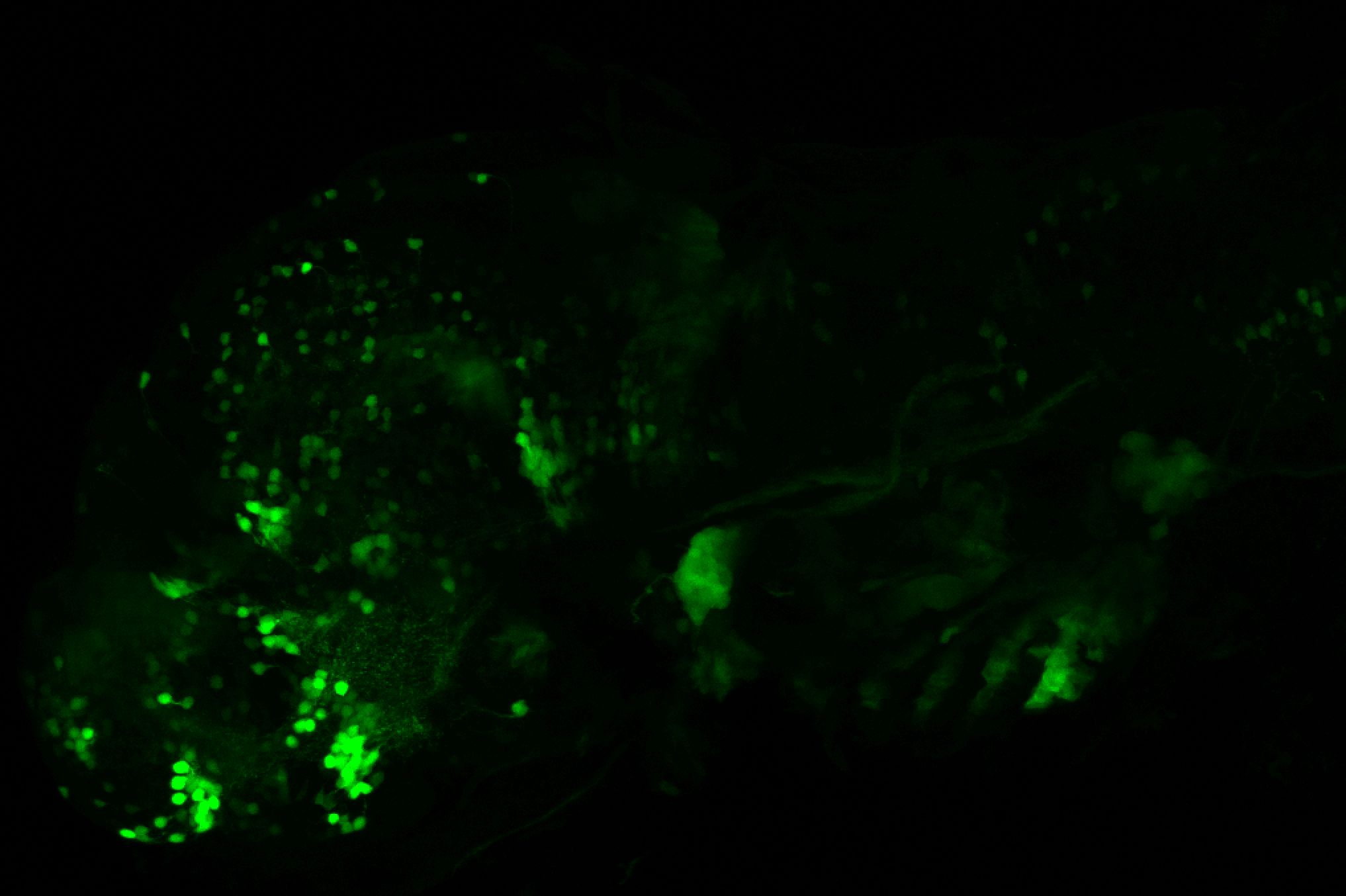
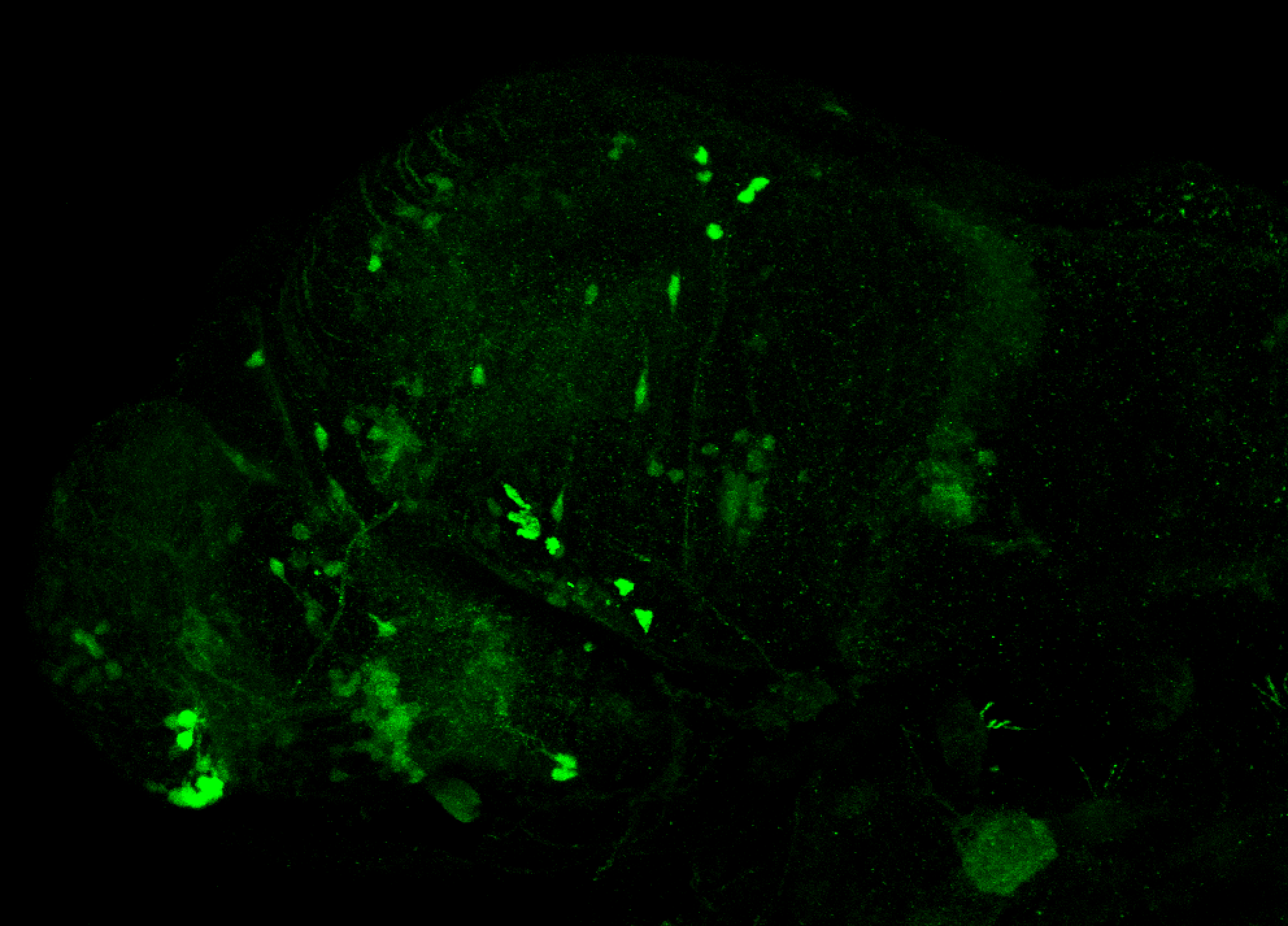
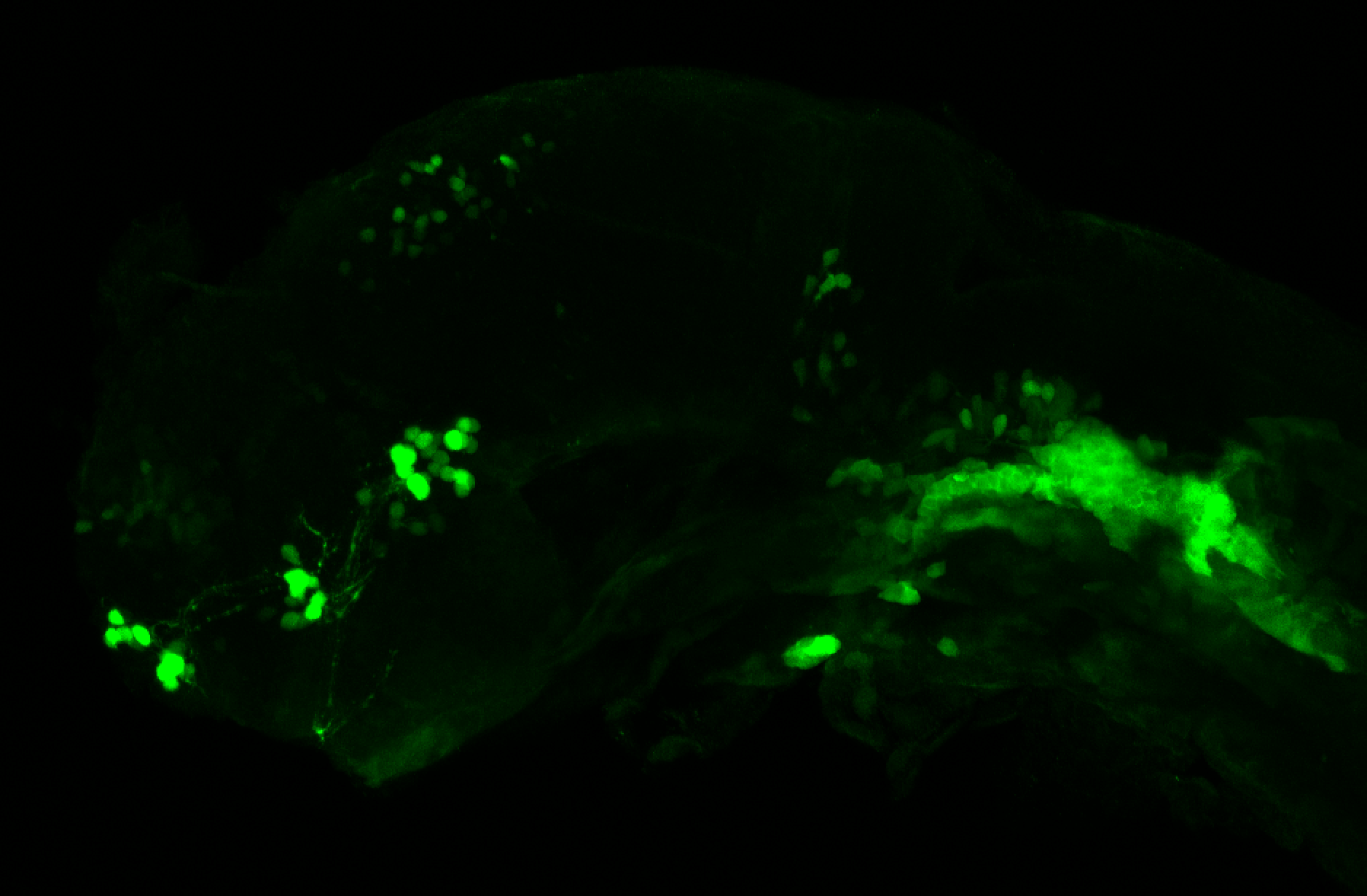
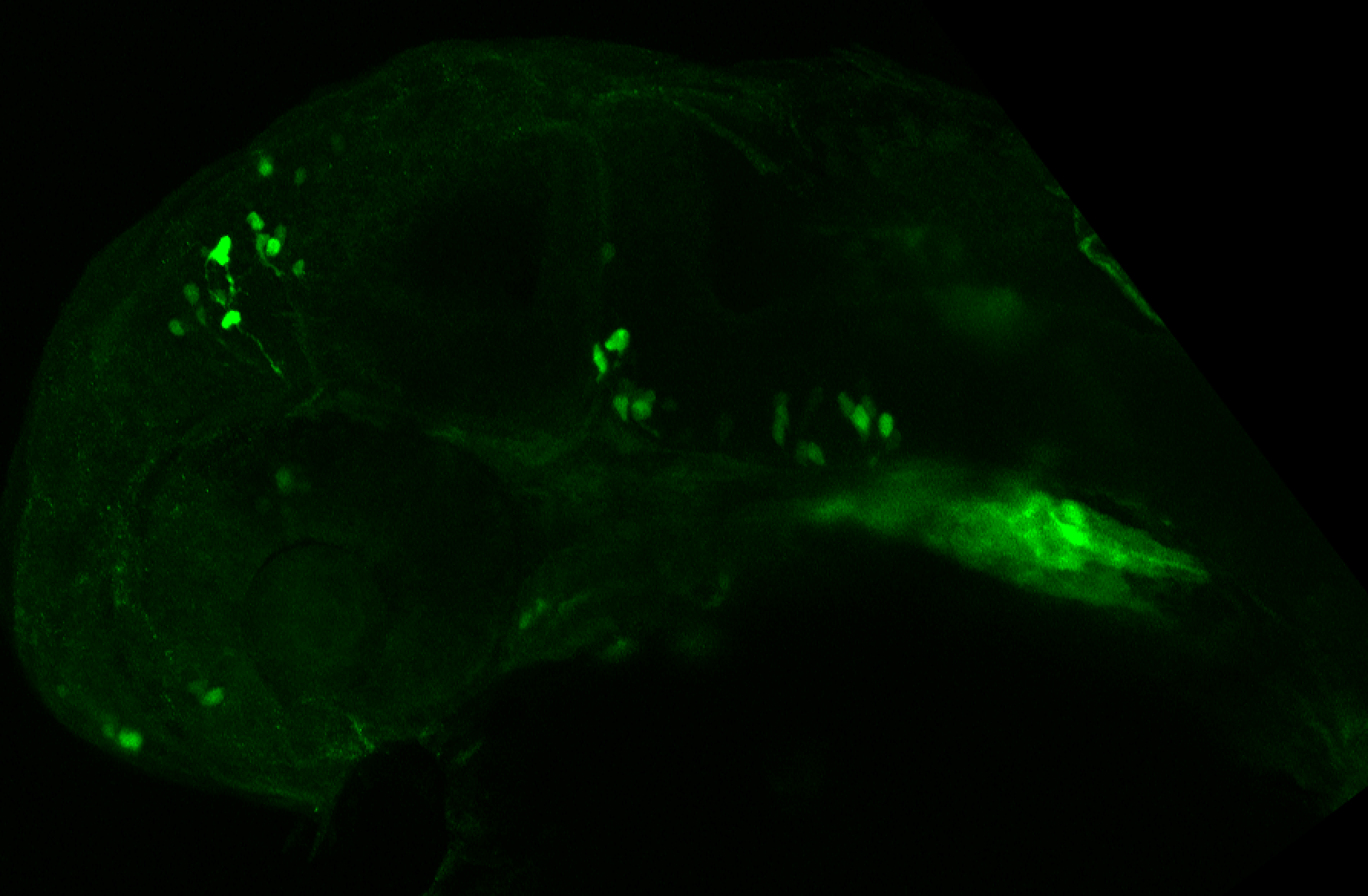
olfactory bulb, pineal, torus longitudinalis, optic tectum, hypothalamus, hindbrain, cerebellum
Key Publications
Royo JL, Hidalgo C, Roncero Y, Seda MA, Akalin A, Lenhard B, et al. (2011) Dissecting the Transcriptional Regulatory Properties of Human Chromosome 16 Highly Conserved Non-Coding Regions. PLoS ONE 6(9): e24824. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0024824