4C4
ABOUT THIS ANTIBODY
Anti-4C4 labels microglia
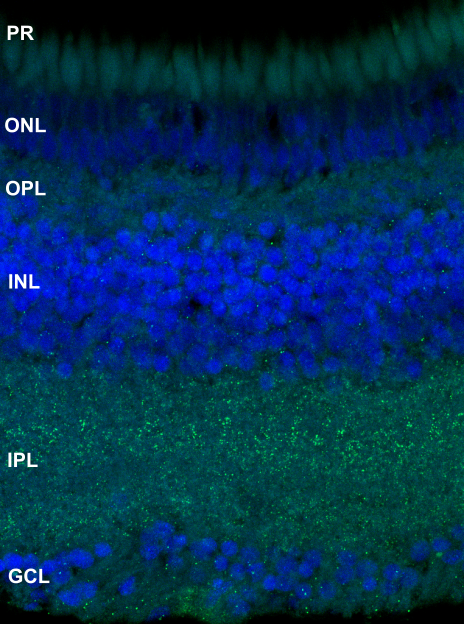
4C4 antibody has been found to bind to microglia in the zebrafish retina (Raymond et al., 2006). In the killifish 4C4 labelled Müller glia in the ganglion cell layer, particularly the endfeet. Further, staining was found in the photoreceptors.
Mouse Monoclonal anti-4C4 (Merck, Cat#92092321, dilution 1:150)
image
by Eva-Maria Breitenbach
Section of 4 mpf male killifish sodium citrate antigen retrieval anti-4C4 in magenta and DAPI in blue
PS = photoreceptors, ONL = outer nuclear layer, OPL = outer plexiform layer, INL = inner nuclear layer, IPL = inner plexiform layer, GCL = ganglion cell layer
labels these retinal cell types
Microglia
key publications
Raymond PA, Barthel LK, Bernardos RL and Perkowski JJ. 2006. Molecular characterization of retinal stem cells and their niches in adult zebrafish. BMC Developmental Biology. 6:1-17.